01/03/2022 Author: VT-METALL
From this material you will learn:
- History of the creation of a quick cutter
- Characteristics of high-speed steels
- Brands and varieties of high-speed steel
- Production of high-speed steels and their processing
- Application area of high speed steel
- Scope of application of various grades of high-speed steels
There are a huge number of all kinds of metals with different characteristics and properties on the market. High-speed steel is a tool type, as it is used in the production of cutting tools. It makes it possible to cut metal at very high speeds and under high temperatures.
The properties and special characteristics of quick cutters allow them to be used for the manufacture of tools of increased strength for a wide variety of uses. Other features of this alloy are described below.
History of the creation of a quick cutter
The purpose of high-speed steel was determined through a historical process. Before quick cutters appeared, craftsmen used ordinary steel cutters. They were not so well suited for processing wood parts and non-ferrous metal products. The main problem associated with turning with such a tool is the slowness of the process. Also, the cutting part quickly becomes unusable and reaches high temperatures.
VT-metall offers services:
High-speed steel has become a real discovery for craftsmen. It appeared in 1858, when an alloy of tungsten and manganese was discovered. Chemical elements were ideal as alloying elements. Throughout the 21st century, scientists have been looking for options with improved characteristics. Particular successes have been achieved in the strength of the material.
As a result, the processing speed of parts has become many times greater, as has the productivity of metal-cutting machines.
In the 20th century, self-hardening compounds successfully replaced tungsten compounds. Nowadays, tungsten-free compounds are considered the most effective.
Characteristics of high-speed steels
As a result, the question arises: which high-speed steel? Of all its diversity, only alloys that contain many alloyed additives can be considered as such. Different chemical elements can significantly change the properties of a metal.
If we talk about the main qualities of steel, this is primarily an increase in the hardness of the alloy. This property is determined by the purpose of the material - to create conditions under which the metal can work at a higher speed. Steel must retain its qualities even with strong friction that appears during the cutting process. Otherwise, the material will be unsuitable for production.
Other properties of high speed steel:
- Maintains a high level of resistance even at high temperatures.
Stability is explained by the ability of a tool to operate without changing characteristics. Any transformations may lead to a deterioration in the quality of the result, so it is important to maintain the original balance. For example, changes associated with the crystal lattice result in excessive friction and heating of the metal. Then the hardness of the material decreases, and the plasticity, on the contrary, becomes higher. Wear of such a tool will occur much faster than under correct operation conditions. - Strength.
The hardness of high speed steel is related to its application. The material is often used for cutting workpieces or processing parts. Research results indicate that high-quality steel retains its characteristics at temperatures up to +6,000 °C. If the quality of the steel is ordinary, then the hardness will be less than that of any other carbon metal. - Increased stability, due to which the steel tool is difficult to destroy.
Fragility and flexibility are unacceptable for such a metal, since it operates at a fairly high speed. Due to its resistance, the steel can also be used with high feed rates. This will result in a greater depth of cut.
Application area of high speed steel
High speed steel cutters can be used for a variety of tools. Basically, these are small drills and cutters. These tools are used to process materials from which structures, machine parts and some structures are created. The scope of application can be expanded by impurities.
For example, with tungsten, steel becomes suitable for toothing or threading. Tools with the addition of vanadium are used to create devices capable of finishing the material. Cobalt can be used to process metal with anti-corrosion and heat-resistant properties.
Both cutters and high-speed steel drills must be resistant to different temperatures and wear. But there are a number of additional requirements that can improve the quality of steel. First of all, this is the ability to resist corrosion, as well as maintain its original dimensions and shape even at high speeds.
Equally important is resistance to dynamic loads. High-speed tool steel grades are characterized by resistance to high temperatures from +600 °C to +6,400 °C. These parameters allow them to be used to create cutters, taps, broaches, cutters, saws and countersinks.
Recommended articles
- Types of welds: we understand the classification and features
- Production of metal products: technologies, advantages, step-by-step control
- Fusion welding: where it is used and how it is produced
APPENDIX 1 Recommended
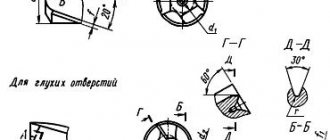
The maximum deviations of the width of the working part of keyway slotting cutters must correspond to those indicated in the table.
| Keyway width | Maximum deviation for tolerance ranges for the width of the keyway | |
| From 3 to 6 | +0,015 | +0,055 |
| +0,005 | +0,045 | |
| St. 6 to 10 | +0,020 | +0,065 |
| +0,010 | +0,055 | |
| St. 10 to 20 | +0,025 | +0,075 |
| +0,015 | +0,065 | |
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 5).
Scope of application of various grades of high-speed steels
| High speed steel grade | Scope of application and main characteristics of the brand |
| P9 | Most often used with tools of simple shape, which do not require lengthy grinding. Also suitable for construction materials. Steel has a reduced grinding performance, but at the same time higher ductility compared to other grades. The characteristic makes it suitable for the application of the plastic deformation method. |
| P18 | This type of steel has high manufacturability. Due to its performance properties, the scope of application is quite wide. Almost all types of conventional construction materials can be processed. High level of sandability |
| P12 | The scope of application is almost the same as in the case of P18 high-speed steel. However, grinding performance is lower than that of P18 |
| 10Р6М5 | Suitable for processing cutting tools and those working with shock loads. The range of quenching temperatures is smaller than in the case of P18. Increased likelihood of decarbonization |
| R6M5 | The characteristics are similar to the 10Р6М5 brand. The difference is less hardness, but greater strength |
| R6M5F3 | Sandability is low. Used in processing reamers, shaped cutters, structural steels (subject to medium cutting conditions), broaches, semi-finishing and finishing tools |
| R12F3 | At medium cutting speeds it is possible to process semi-finishing and finishing tools, as well as abrasive materials. A good alternative for grades R14F4 and R6F5, since grindability is higher and other characteristics are almost the same |
| R9F5, R14F4 | Sandability is low. Used with tools of simple shape that do not require time-consuming grinding. Excellent in processing abrasive materials and finishing tools with small cut sections |
| R9M4K8, R6M5K5 | The brands can withstand high temperatures, so they are suitable for heat-resistant materials. Sandability is slightly reduced |
The set of types of metal products includes such shapes as strip, sheet metal, circle and square. In practice, the circle is most often used. The square is designed for creating knives, electric planers and turning tools. Each component of the assortment has its own specifics, so for reliability you should consult with a specialist.
Thus, it was possible to find out what high-speed steel and hard alloy mean, what characteristics and features the steel has, as well as how to decipher its markings. The scope of application of the brands was also given, and more detailed information can be obtained from specialized companies. They will select material with qualities that will be most optimal for your situation. The necessary conditions for the production and heat treatment of high-speed steel, which will ensure its high quality, will also be presented.
II. TEST METHODS
2.1. Appearance control is carried out visually using a magnifying glass of 4 magnification in accordance with GOST 25706.
2.2. Control of cutter parameters is carried out using control means that have measurement errors of no more than:
when monitoring linear dimensions - the values specified in GOST 8.051;
when checking angular dimensions - 35% tolerance for the angle being checked;
when controlling the shape and location of surfaces - 25% tolerance on the parameter being tested.
2.3. Control of cutter surface roughness parameters is carried out by comparison with roughness samples in accordance with GOST 9378 or control samples having values of surface roughness parameters not exceeding those specified in clause 6.
2.4. Hardness control (clause 3) is carried out in accordance with GOST 9013 using TR devices in accordance with GOST 23677.
2.5. Tests of cutters for performance, average and established periods of durability must be carried out on lathes, planers and slotting machines that meet the standards of accuracy and rigidity established for them.
2.6. Tests of cutters are carried out on workpieces made of steel grade 45 according to GOST 1050 with a hardness of 187-207 HB, cooled with a 5% emulsol solution in water with a flow rate of at least 5 l/min.
2.6.1. The tops of the cutters are installed along the line of the centers of the machine with permissible deviations of no more than, mm:
| 14 | for turning external surfaces; | ||
| +1,0 -0,5 | for turning internal surfaces; | ||
| -1,0 | for cutting and slitting. | ||
2.6.2. The projection of the cutting part of the cutters from the tool holder should not exceed:
| (1.2-1.3)N | for turning external surfaces; | ||
| length of the drawn part of the cutter | for turning internal surfaces; | ||
| length of the narrow part of the cutter | for slotting and cutting; | ||
| N | for planing and chiselling with straight cutters; | ||
| 2H | for planing with curved cutters. | ||
2.7. The surfaces of the workpiece for testing must be pre-treated to a roughness parameter of 12.5 μm, radial runout tolerance of 0.1 mm.
2.8. Tests of cutters for performance, average and established periods of durability are carried out in the modes established in Tables 3-5.
Table 3
| Cutter type | Cutter section НхВ, mm | Cutting mode | ||
| , mm | , mm/rev | , m/min | ||
| Passing and scoring | 4x4 | 1 | 0,2 | 45 |
| 6x6 | ||||
| 8x8 | ||||
| 10x10 | ||||
| 12x12 | ||||
| 16x10 | ||||
| 16x16 | 2,5 | 0,3 | 32 | |
| 20x12 | ||||
| 20x20 | ||||
| 25x16 | 0,4 | 28 | ||
| 32x20 | ||||
| 40x25 | 5 | 0,5 | 22 | |
| Boring | 12x12 | 1,0 | 0,15 | 38 |
| 16x16 | ||||
| 20x20 | 1,5 | 0,2 | 32 | |
| 25x25 | 2,0 | 0,3 | 28 | |
| Cut-off and slotted | 4x4 | — | 0,06 | 40 |
| 6x6 | ||||
| 8x8 | ||||
| 10x10 | 0,08 | 36 | ||
| 12x12 | ||||
| 16x10 | ||||
| 16x16 | 0,1 | 30 | ||
| 20x12 | ||||
| 25x16 | 0,15 | 27 | ||
| 32x20 | ||||
Table 4
| Cutter type | Cutter section НхВ, mm | Cutting mode | ||
| , mm | , mm/d. move | , m/min | ||
| Planing, passing and scoring | 20x12 | 1,0 | 0,6 | 30 |
| 25x16 | ||||
| 32x20 | ||||
| 40x25 | 1,0 | 27 | ||
| 50x32 | ||||
| 63x40 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 21 | |
| Wide finishing passage | 20x12 | 0,9 | 1,7 | 15 |
| 25x16 | ||||
| 32x20 | ||||
| 40x25 | 1,0 | 4,7 | 11 | |
| 50x32 | ||||
| 63x40 | ||||
| Cutting and slotting | 20x12 | — | 0,15 | 20 |
| 25x16 | 0,18 | 16 | ||
| 32x20 | ||||
| 40x25 | 0,30 | 12 | ||
| 50x32 | ||||
| Slotting pass | 20x12 | 1,6 | 0,5 | 30 |
| 25x16 | ||||
| 32x20 | 2,8 | 0,8 | 20 | |
| 40x25 | ||||
| 50x32 | ||||
| Slotted for keyways | 16x10 | — | 0,12 | 11 |
| 20x12 | ||||
| 20x20 | 0,15 | 10 | ||
| 25x16 | ||||
| 25x25 | ||||
| 32x20 | 0,18 | 8,0 | ||
| 32x32 | ||||
| 40x25 | 0,23 | 7,0 | ||
| 40x40 | ||||
| 50x32 | ||||
| 63x40 | ||||
Table 5
| Cutter type | Thread pitch, mm | Number of passes | Cutting speed, m/min | |
| drafts | finishing | |||
| Threaded for external metric thread | Until 3 | 5 | 3 | 33 |
| St. 3 to 6 | 6 | 20 | ||
| For internal metric thread | Until 3 | 8 | 4 | 29 |
| St. 3 to 6 | 20 | |||
| For external trapezoidal thread | Until 6 | 12 | 9 | 24 |
| St. 6 to 12 | 33 | 8 | 21 | |
| St. 12 to 24 | 39 | 10 | 15 | |
| For internal trapezoidal thread | Until 6 | 14 | 22 | |
| St. 6 to 12 | 41 | 20 | ||
| St. 12 to 16 | 45 | 11 | 16 | |
2.9. After performance tests, the cutting edges of the cutters should not show chipped areas, traces of deformation of the rod and weld, and they should be suitable for further work.
2.10. Acceptance values for the average and established durability periods must be at least 35 minutes and 16 minutes.
Sec. II. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 5).