The new generation of TIG torches includes a modular system and a huge number of configuration options. The choice is almost endless. From burner bodies, including all different types of gas nozzles, to a wide range of handles. But what exactly are the differences between TIG torches and which torch body is right for each application?
The main thing is to get to the point: this is the most important task. Because even the most comfortable and largest TIG torch in the world is worth nothing if you can't get to the place where you need to weld. That's why welding torch bodies and caps come in a variety of lengths, angles, and even flexible torch necks that can be bent to shape.
Two contrasting examples are a fillet weld on a workbench and a ceiling pipe that must be welded from the inside. Work on the welding table can be done using virtually any torch body. However, welding pipes requires a particularly compact torch - ideally small and flexible, with a short cap.
Features of argon welding
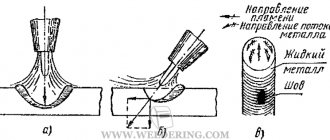
The general principle of argon arc welding is easier to describe using the connection diagram of welding equipment shown in the figure.
The main working tool is an argon torch connected to the welding machine. The required current is supplied to the electrode, and the welding zone itself is protected by a cloud of inert argon gas from interaction with atmospheric oxygen, which prevents the possibility of metal oxidation.
The operating principle is the same for burners from different manufacturers. The design is presented below.
When sold, the kit includes a cable: a hose for supplying argon and a power cable.
In rare cases, the burner is sold without a cable - you need to pay attention to this when ordering.
Modular TIG torch design for maximum flexibility
Since the optimal torch design depends on the welding task in question, a modular TIG torch system is of great importance. In modular systems, a handle is selected, to which various controls and burner bodies can be added if necessary. The ability to quickly and easily replace the burner body is provided by the Multilock system. With this system, pushing and turning the torch body releases it from the handle and hose package, while the new torch body is simply locked into place by inserting and turning. The system is available for both gas and water hose packages. The Multilock system allows you to configure the torch in accordance with the specific welding task and the personal preferences of the welder.
Types of argon torches for manual welding
Welding can be done manually, semi-automatically or automatically. Accordingly, the design will be different. The more automated the process, the more complex the device.
Let's look at devices exclusively for manual welding (TIG): what they are, what to look for when choosing a particular model.
The main functions of the torch are to hold the welding electrode, which creates the arc, and to supply gas to the welding zone. Even the simplest burners can handle this. For a high-quality result, in addition to the experience of the welder, it is required that it be convenient to work and one cannot expect a catch in the form of, for example, a falling electrode or other unpleasant “trifles.”
Argon burners can be classified according to the type of cooling: air or liquid. Most TIG torch models are air cooled. A water heat sink requires additional equipment.
According to the method of gas supply, burners are distinguished, equipped with a valve or a button. Some models come with both.
It is difficult to classify torches based on the type of connector connected to the welding machine due to their diversity.
Typically, the manufacturer installs connectors for certain types of inverters. The connector must match the socket of the welding machine. This is where problems may arise when purchasing a burner online, since only a few manufacturers indicate the type of connector in the name. For example, in the FUBAG FB TIG 26 5P torch there is a 5pin control connector, in the TORCH 24 WATER 4m M12x1 there is an M12x1 connector. As a last resort, the connector is soldered.
But the length of the train must be indicated. Its most common size is 4 meters, less often - 8 meters, and even less often - intermediate values.
What can the labeling tell you?
On most burners or in the product name on websites, sellers still indicate a “defining” numerical value. For example, TIG 26 after the manufacturer's name.
When choosing a torch, a novice welder should have an idea of the differences between torches hidden under the numbers.
By and large, argon burners can be divided into two groups by size: small and large. The small ones include 9 (air-cooled) and 20 (water-cooled). Consumables and components for them are interchangeable. For large (suitable for household welding) torches with numbers 18 (water cooling), 17 and 26 (air) the same applies to replacement.
In the designation of inexpensive domestic burners, a designation like WP 17 is often found (the manufacturer’s name is indicated somewhere, but you will have to look for it). In principle, the minimum information was obtained: a large air-cooled argon burner under pure tungsten electrodes.
Electrodes for argon welding
When argon welding, electrodes made of refractory tungsten are used, sometimes pure, sometimes with additives. The presence of additives makes it easier to work with a number of metals and alloys.
In addition to letter markings, different types of tungsten electrodes are marked by the color of the shank.
For convenience, the information is presented in the table.
| Letter designation. | Color | Current (DC or AC) | Metals to be welded | Note |
| W.P. | green | A.C. | Magnesium, aluminum, alloys | |
| WZ | white | A.C. | Bronze, aluminum, nickel, alloys | |
| W.T. | red | DC | Stainless steel, tantalum, molybdenum | Special safety measures: mandatory ventilation in the room. |
| W.Y. | blue | DC | Carbon, low alloy, stainless steels, titanium | |
| W.L. | golden | DC,AC | Any steels and alloys | |
| W.C. | grey | DC,AC | Any steels and alloys |
The diameter of the electrode is selected depending on the operating current: up to 50 A - diameter 1 mm, up to 100 A - 1.6 mm, up to 200 A - from 2 mm to 2.4 mm, over 200 A - 3.2 mm, over 300 A – 4 mm.
In addition to the current strength, the thickness of the metal being welded is taken into account. It would be more correct to say that the choice of electrode and current depends on the thickness and composition of the metal. Non-consumable tungsten electrodes require sharpening before use. The general principle for choosing the sharpness of an angle is that the wider the planned seam, the thinner the point.
The tip itself is cleaned.
What else does a welder need before work?
Concern for safety precautions when performing welding work falls on the shoulders of the welder himself. A mask (with a shield is less convenient), overalls or a jacket with pants, mittens made of specially treated fabric are mandatory equipment. Exposed skin areas are not allowed.
It is necessary to check the workplace for the correct connection of the torch to the welding machine and cylinder, the integrity of the cable and hose, the presence of a fire extinguisher, and the absence of flammable and combustible objects nearby.
Constructive
In addition, a wide range of gas nozzles are used with different burner bodies, which vary in length, hole diameter, material and type of fastening.
Long or short
Like the torch body, the shape of the part and the accessibility to the seam are critical in determining the length of the gas nozzle required. For example, the smaller the pipe diameter, the shorter the selected nozzle. Larger gas nozzle diameter means wider gas shielding spot: The diameter of the gas nozzle or its opening determines the size of the area around the weld that will be covered with shielding gas. A wide zone of gas protection is especially important for sensitive materials such as titanium, since the cooling weld, heated after welding, must be protected from atmospheric oxygen for much longer to avoid the formation of oxides and discolorations.
Champagne gas nozzle type - with widened outlet
A feature of the so-called “champagne” gas nozzle is the increased diameter of the outlet hole - larger than the diameter of the landing part. This provides a wide area of gas coverage, making it particularly useful for active metals such as titanium or zirconium. The nozzle itself can be made of ceramic or glass, with clear glass providing an ideal view of the burning arc and weld pool.
Mounting method
TIG gas nozzles can have a threaded fit or be placed on the body of the welding torch, pressed with a sealing lip. The choice depends on the design of the welding torch, although the welder's preference will usually be a key factor. Systems where the nozzle is inserted into the housing allow for faster replacement - even immediately after welding while the welding torch and nozzle are still hot. On the other hand, a screw connection provides a stronger and more rigid fastening.
Gas lens
Similar to a filter mesh - it provides a laminar, uniform gas flow without turbulence or turbulence. This is especially useful when working with high alloy steels and active metals, especially when welding with long stick extensions or in open air or drafts. All gas nozzles, large or small, long or short, are available with or without a gas lens.
Tack welding and spot welding
For these purposes, there are special point gas nozzles. To produce tack welds or spot welds without the use of filler material, these shaped nozzles are applied directly to the workpiece. Pressing the nozzle against the workpiece ensures that the distance between the electrode and the metal being welded is always ideal and constant. Spot nozzles are available for a variety of workpiece configurations—for example, for tack welding internal fillet welds, external fillet welds or for butt joints. The big advantage is that in this case the use of a welding helmet is not necessary, since this special nozzle hides the arc from view. In addition, the use of such a nozzle for spot welding or tack welding does not require high qualifications and is accessible even to beginners.
Ideal handle for TIG torch
Various types of welding torch handles have also been developed. Considering that most welders prefer small handles, especially for fine welding, along with the standard handle size there is also a compact version. Compact handles allow you to comfortably hold the torch like a pencil, which is ideal for delicate work. Essentially, it all comes down to which handle the welder finds most comfortable. The size of the handle also determines its weight and range of functions. A small handle, of course, has the advantage of being lighter, but larger ones usually have more functionality, such as an LED light that can be used to illuminate the seam before welding begins, and can include different types of controls. In addition, large welding torches are better suited for high current welding because they have a more advanced heat dissipation system and can withstand higher temperatures.
Argon welding process
Main components of the workplace:
- welding machine;
- argon cylinder;
- burner;
- electrodes;
- filler rod.
The general procedure of work has some differences from conventional arc welding, they are worth paying attention to.
When the required welding current is selected and set on the machine, and the ground is connected to the part being welded, the process can begin.
In one hand there is a torch, in the other there is a filler rod. Welding, unlike conventional arc welding, cannot begin with the electrode touching the workpiece. First, gas is applied to the workpiece for 15-20 seconds, then the nozzle is smoothly brought to the metal (the distance between the workpiece and the electrode should be approximately 2 mm and remain so during operation). The resulting arc is smoothly guided along the seam, preventing transverse movements. The filler wire is positioned in front of the nozzle and feeds smoothly. An experienced welder can handle this easily, but a beginner will have to “feel the process.” As a rule, 3-5 attempts are enough.
The supply of argon should not be stopped immediately, but 5-7 seconds after completion of the seam.
TIG torch control
Various controls can be built into the torch handle, allowing the welder to easily control the amperage using a potentiometer or up-down switch. A welding torch equipped with a Job Master control unit allows you to adjust several parameters or select preset mode parameters for the corresponding weld section, stored in the Job cells of the welding source, and activate them using the welding torch, even directly during welding. This function is especially useful when the power source is installed at some distance from the welding site, for example, during repair and installation work.
Popular models of argon burners
Despite the general operating principle of argon burners, each manufacturer brings something different. Some use especially durable or especially flexible materials, others modify the basic design for convenient operation, others set the goal of durability or some other parameter.
When looking at offers based on pictures on sellers’ websites, it is difficult to obtain comprehensive information, especially when prices range from 2.5 to 20 (sometimes higher) thousand rubles, and this is the cost without delivery.
Brief overview of manufacturers
The brand, of course, makes adjustments to the cost of the argon burner, but the name of the device means nothing for operation. Let's consider the products of the most popular manufacturers today.
- AURORA TIG 9V 110A is a torch of a domestic manufacturer, adapted to work with welding machines of the SVAROG brand. It's easy to find and purchase consumables. Devices from this manufacturer, depending on the modification, cost from 2.5 to 4.5 thousand rubles.
- Svarog TS 26V (M12×1) 4m – maximum operating current – 180 A (DC) and 130 A (AC). The electrodes used are from 0.5 to 4 mm, air cooling. Price - from 4 to 6 thousand rubles.
- Bars TIG-17V – current (direct) – 140 A, air cooling, connector type not specified. The train, as in previous samples, is 4 meters long. The cost is about 3.5 thousand rubles.
- TORCH burners are distinguished by their low price (up to three thousand rubles). The advantage is that it works on direct and alternating current. The connector is the same for the entire range of models - M12x1.
The next price segment is represented by argon burners FUBAG (from 5 thousand rubles), AGNI 03 (from 9 thousand rubles), BlueWeld (number 9 costs from 9 thousand, number 26 - from 15 thousand rubles).
According to reviews from experienced welders, BlueWeld argon torches are distinguished by their exceptional quality of work and are reliable in AGNI operation. SVAROG burners are not ideal, but they are quite suitable considering their price. Useful video on this topic
Recommended selection criteria
- If you purchased a welding machine recently, you should try to equip it with an argon torch from the same manufacturer.
- To avoid problems with welding aluminum, you should pay attention to whether the design is designed to work with alternating current.
- It is necessary to carefully study the package. If a set of spare parts is missing, but you really like the price, it’s worth remembering that you’ll then have to spend about a thousand rubles on consumables.
- It’s better to choose not by the picture, but by hand: examine it, figure out whether it fits comfortably in your hand, make sure that the connector is the same type as on the inverter, and that the cable is flexible enough.
When the lowest price is a priority, the buyer must be prepared for the fact that in the process of working with such equipment, unforeseen moments may arise, not critical, but unpleasant: for example, something is not securely connected, it is inconvenient to hold, the cable is too hard, etc.
But a beginner can afford to purchase an inexpensive torch for training, mastering the welding process in an argon environment, and then, having gained experience, look for a more convenient model based on his own experience.