This article contains the most necessary information about semi-automatic welding.
Everything is presented in an accessible form and divided into sequential blocks for better assimilation of the material. To make it easier to find the information you need, use the article navigation: Theoretical part:
- Construction of a semi-automatic welding machine
- Choosing gas for semi-automatic welding
- Wire for semi-automatic welding
- Semi-automatic welding without gas (with flux-cored wire)
Practical part:
- Preparing the device for operation - ASSEMBLY | How to thread wire into a semi-automatic machine
- Setting up a semi-automatic welding machine using a live example
- Preparatory stage and process of welding with a machine
- Direction and speed of movement for a perfect weld seam
- Conclusion + VIDEO
Despite the opportunity to jump straight to practical advice, we recommend that you read the material in its entirety. You will probably find something new for yourself or refresh your previously acquired knowledge.
Semi-automatic welding machine - briefly about the device
Semi-automatic welding requires a basic understanding of the design of the welding machine. The inverter provides space for installing a coil of wire, which serves as an analogue of a consumable electrode, and also has an automatic feed mechanism. The device allows you to independently set the current strength and wire feed speed depending on production needs.
Semi-automatic devices vary in functionality depending on their purpose. For novice welders, the best choice would be reliable and easy-to-operate devices without excesses (for example, IRMIG 160) or options with synergetic control, which will greatly facilitate setup (for example, INMIG 200 SYN). For experienced professionals, powerful three-phase semi-automatic machines, such as the INMIG 500 DW SYN, are suitable for continuous production.
Regardless of the type of device, the operating equipment remains standard:
- Welding machine
- Semi-automatic welding torch
- Gas cylinder and reducer
- Gas hose
- Cable with ground clamp
Of course, the work will require specialized wire, as well as standard protective equipment that is absolutely necessary for the safety of the welder.
The choice of gas depending on the metal being welded
The main function of shielding gas is to isolate the weld pool, electrode and arc from the influence of ambient air. In order to select the appropriate gas, it is necessary to take into account the type of material and its thickness. Depending on this, inert, active gases or mixtures thereof are selected. The most commonly used are CO2 and argon. The latter reduces metal spatter and contributes to better weld quality.
Pay attention to the table:
| Material | Gas |
| Structural steel | CO2 |
| Structural steel | CO2 + Ar |
| Stainless steel | CO2 + Ar |
| Alloy steels (low carbon) | CO2 + Ar |
| Aluminum and its alloys | Ar |
HELPFUL ADVICE.
When searching for gas, you can come across cylinders of various sizes. The larger the volume, the cheaper a liter of gas will be. For rare use of a semiautomatic welding machine, mobile packaging of 5-10 liters is suitable. In this case, it is best to take an additional supply of gas to insure against a sudden shortage.
Relationship between metal thickness and wire diameter
There are many wire options for semi-automatic welding on the welding materials market. It is important to remember the rule - the composition of the wire must match the composition of the material being welded. The welding wire SV08G2S, which is used for carbon and low-carbon steels, is most often in demand.
The table will help you choose the diameter:
| Metal thickness, mm | The diameter of the wire |
| 1 — 3 | 0,8 |
| 4 — 5 | 1,0 |
| 6 — 8 | 1,2 |
The usual packaging for wire is 200 or 300 mm.
IMPORTANT!
The wire diameter is indicated when setting up the semi-automatic machine, which we will talk about in the practical part of this article.
How to weld semi-automatically without gas
Shielding gas is essential to the welding process. It ensures quality welding work while creating a protected environment. However, if you use the device quite rarely, then it is simply not profitable to spend too much money and buy a cylinder. To avoid unnecessary costs, you can always use a special welding wire - flux-cored or flux-cored. It consists of a steel tube containing flux inside. During welding, it burns, forming a cloud of shielding gas in the welding zone.
It is worth remembering that work with flux-cored wire must be carried out with a current of straight polarity (plus is supplied to the product) - this is due to the need for more power to melt the flux-cored wire. It is worth paying attention to the fact that in addition to the obvious advantages of use, there are also disadvantages: when welding with flux-cored wire, a cloud of smoke is usually formed, which complicates visual control of the process. It cannot be used for ceiling seams.
Blueweld 4.165 wire feed regulator burned out - Community "Electronic Crafts" on DRIVE2
Help me figure it out, I can’t fix a burnt-out regulator on a semi-automatic device! A new one from Italy must be ordered, they promise to deliver 90 days(((.
The power input and the output to the welding wire feed regulator motor were mixed up, and the regulator stopped working.
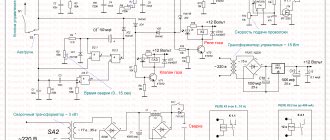
Here's the diagram I found:
Wire feed regulator diagram
As I understand it, the HEF 4069 UB chip contains an adjustable frequency generator that opens the mosfet at different frequencies. The plus input and output of the regulator are connected and are regulated by ground. This circuit works as a PWM generator. The mosfet opens and powers the motor.
The peculiarity of the circuit is a fairly high supply voltage - from 42 to 55 volts. Measured it on a welder.
It was visually clear that the resistors below the mosfet, circled in red, were damaged. I decided to replace them, and since I couldn’t find an SMD, I installed the regular ones at 1 ohm. I also replaced the mosfet.
I rang the diodes and they were all alive. I checked the transitions of the transistor - the transitions are ringing. Here is a diagram of the welder.
Diagram of semi-automatic welding machine Blueweld Combi 4.165
I supply power: the current is not regulated. The mosfet is completely open. The voltage at the output of the regulator is equal to the voltage at the input. The zener diode has 12 volts.
I changed the microcircuit. Nothing has changed.
Where to dig? Today I’ll use an oscilloscope to measure the frequency at the input to the mosfet, from the frequency generator, but I think if it’s open there’s a unit hanging there...
view from the parts
view from the board side.
UPD: 1. Apparently the frequency generator started working after replacing the microcircuit. But the output voltage still does not change - the mosfet is open all the time! I connected an oscilloscope. pulses with an amplitude of 11 volts arrive at the Gate mosfet leg.
The oscillogram shows how the pulse width changes depending on the position of the resistor slider.
Regulator position - minimum feed
Middle position.
Maximum feed.
For some reason the mosfet is not working.
www.drive2.ru
Feed rollers for cored wire
Article: 005.020.107 Feed roller 30x10x10 K 1.0–1.2
Feed roller for cored wire with a diameter of 1.0–1.2 mm. K-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 30x10x10. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines of the PTK MASTER MIG S, MASTER MIG F, MASTER MIG SYNERGY D and PTK RILON MIG GDM series.
Price: 673 RUR
Article: 005.040.124 Feed roller 30x22x10 K 0.8–0.9
Feed roller for cored wire with a diameter of 0.8–0.9 mm. K-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 30x22x10. Suitable for PROFI semi-automatic welding machines MIG 300, MIG 350-1, MIG 350, MIG 500 from the HISTER factory and RILON MIG 250 GS, MIG 250 GDM, MIG 300 GDL, MIG 200 GW.
Price: 598 RUR
Article: 005.040.131 Feed roller 40x32x10 K 0.8–0.9
Feed roller for cored wire with a diameter of 0.8–0.9 mm. K-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 40x32x10. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines PTC RILON MIG 350 GF, MIG 500 GF, MIG 500 I, MIG 500 F, MIG 500 FW.
Price: 797 RUR
Article: 005.040.118 Feed roller 30x10x12 K 0.8–0.9
Feed roller for cored wire with a diameter of 0.8–0.9 mm. K-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 30x10x12. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines PROFI MIG 350, MIG 500 and PTK RILON MIG 250 P GDM, MIG 300 P GDL, MIG 300 GN, MIG 300 GD.
Price: 598 RUR
Article: 005.020.105 Feed roller 30x10x10 K 0.8–0.9
Feed roller for cored wire with a diameter of 0.8–0.9 mm. K-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 30x10x10. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines of the PTK MASTER MIG S, MASTER MIG F, MASTER MIG SYNERGY D and PTK RILON MIG GDM series.
Price: 673 RUR
prow
ROTATION SPEED REGULATOR FOR SEMI-AUTOMATIC WELDING ENGINE FEEDING WIRE.
ROTATION SPEED REGULATOR FOR SEMI-AUTOMATIC WELDING ENGINE FEEDING WIRE. Everyone who is involved in the repair of semi-automatic welding machines designed for welding in a carbon dioxide environment during car body work knows that this is the most unreliable component of the welding unit, including industrial machines. A control circuit for the motor of feeding wire into the welding environment using an integrated stabilizer 142EN8B is proposed. The unit must provide a wire feed delay of 1-2 seconds after turning on the gas valve and the fastest possible braking after releasing the welding voltage switch button, which is what this device does.
I would like to draw attention to the cheapest and very effective principle of engine braking by closing the motor armature winding with relay contacts. The disadvantage of this circuit is the rather large power dissipated by the VT1 transistor. The 10X10cm needle radiator heats up to 70 degrees during operation. But in general the circuit turned out to be very reliable.
18.06.09
www.pictele.narod.ru
Feed rollers for steel wire
Article: 005.040.120 Feed roller 30x22x10 V 0.6–0.8
Feed roller for steel wire with a diameter of 0.6–0.8 mm. V-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 30x22x10. Suitable for PROFI semi-automatic welding machines MIG 200, MIG 250, MIG 300, MIG 350-1, MIG 350, MIG 500 from the HISTER factory and RILON PTK MIG 250 GS, MIG 250 GDM, MIG 300 Y, MIG 200 GW, MIG 300 GW , MIG 300 GDL.
Price: 598 RUR
Article: 005.040.127 Feed roller 40x32x10 V 1.0–1.2
Feed roller for steel wire with a diameter of 1.0–1.2 mm. V-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 40x32x10. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines PTC RILON MIG 350 GF, MIG 500 GF, MIG 500 I, MIG 500 F, MIG 500 FW.
Price: 723 RUR
Article: 005.040.109 Feed roller 40x32x10 V 1.2–1.6
Feed roller for steel wire with a diameter of 1.2–1.6 mm. V-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 40x32x10. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines PTC RILON MIG 350 GF, MIG 500 GF, MIG 500 I, MIG 500 F, MIG 500 FW.
Price: 723 RUR
Article: 005.040.108 Feeding roller 40x32x10 V 0.8-1.0
Feed roller for steel wire with a diameter of 0.8–1.0 mm. V-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 40x32x10. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines PTC RILON MIG 350 GF, MIG 500 GF, MIG 500 I, MIG 500 F, MIG 500 FW.
Price: 723 RUR
Article: 005.040.107 Feed roller 30x22x10 V 1.2–1.6
Feed roller for steel wire with a diameter of 1.2–1.6 mm. V-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 30x22x10. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines PROFI MIG 350-1, MIG 350, MIG 500 from the HISTER factory.
Price: 598 RUR
Article: 005.040.105 Feed roller 30x22x10 V 1.0–1.2
Feed roller for steel wire with a diameter of 1.0–1.2 mm. V-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 30x22x10. Suitable for PROFI semi-automatic welding machines MIG 200, MIG 250, MIG 300, MIG 350-1, MIG 350, MIG 500 from the HISTER factory and RILON PTK MIG 250 GDM, MIG 300 Y, MIG 250 GW, MIG 300 GW, MIG 300 GDL .
Price: 598 RUR
Article: 005.040.106 Feed roller 30x22x10 V 0.8–1.0
Feed roller for steel wire with a diameter of 0.8–1.0 mm. V-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 30x22x10. Suitable for PROFI semi-automatic welding machines MIG 200, MIG 250, MIG 300, MIG 350-1, MIG 350, MIG 500 from the HISTER factory and RILON PTK MIG 250 GS, MIG 250 GDM, MIG 300 Y, MIG 200 GW, MIG 250 GW , MIG 300 GW, MIG 300 GDL.
Price: 598 RUR
Article: 005.040.101 Feed roller 30x10x12 V 0.8–1.0
Feed roller for steel wire with a diameter of 0.8–1.0 mm. V-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 30x10x12. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines PROFI MIG 350, MIG 500 and PTK RILON MIG 250 P GDM, MIG 300 P GDL, MIG 300 GN, MIG 300 GD.
Price: 598 RUR
Article: 005.040.102 Feed roller 30x10x12 V 1.0–1.2
Feed roller for steel wire with a diameter of 1.0–1.2 mm. V-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 30x10x12. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines PROFI MIG 350, MIG 500 and PTK RILON MIG 250 P GDM, MIG 300 P GDL, MIG 300 GN, MIG 300 GD.
Price: 598 RUR
Article: 005.040.103 Feed roller 30x10x12 V 1.2–1.6
Feed roller for steel wire with a diameter of 1.2–1.6 mm. V-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 30x10x12. Suitable for PROFI semi-automatic welding machines MIG 350, MIG 500.
Price: 598 RUR
Article: 005.040.113 Feed roller 35x25x8 V 1.0–1.2
Feed roller for steel wire with a diameter of 1.0–1.2 mm. V-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 35x25x8. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines PROFI MIG 200, MIG 250.
Price: 626 RUR
Article: 005.040.112 Feed roller 35x25x8 V 0.8–1.0
Feed roller for steel wire with a diameter of 0.8–1.0 mm. V-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 35x25x8. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines PROFI MIG 200, MIG 250.
Price: 626 RUR
Article: 005.020.102 Feed roller 30x10x10 V 0.6–0.8
Feed roller for steel wire with a diameter of 0.6–0.8 mm. V-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 30x10x10. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines of the PTK MASTER MIG S, MASTER MIG F, MASTER MIG SYNERGY D and PTK RILON MIG GDM series.
Price: 673 RUR
Article: 005.020.103 Feed roller 30x10x10 V 0.8–1.0
Feed roller for steel wire with a diameter of 0.8–1.0 mm. V-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 30x10x10. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines of the PTK MASTER MIG S, MASTER MIG F, MASTER MIG SYNERGY D and PTK RILON MIG GDM series.
Price: 673 RUR
How to set up a semi-automatic welding machine correctly?
- Date: 06/12/2015
- Rating: 54
Many types of welding equipment are expensive. The most convenient is a semi-automatic welding machine (SPA), which is multifunctional. The operating principle of a semi-automatic welding machine depends on its correct settings. Semi-automatic welding machines are universal and practical. Their use in the domestic economy is widespread.
Scheme of an inverter semi-automatic welding machine.
In everyday life and industry, SPA is used to produce effective welding. Performing welding work using semi-automatic machines is based on high-quality welding of non-ferrous and ferrous metals without the use of additional elements. The welding process uses carbon dioxide or argon, which are protected by the use of a melting type of solid wire.
What are the requirements for the preliminary welding stage?
Basic semi-automatic welding modes.
Powerful welding equipment should be used while observing safety precautions. The spa is dangerous because it can cause electric shock. Incorrect use of the equipment may result in fire.
Incorrect configuration of a semi-automatic machine can lead to damage to some parts of its design. All of these preliminary steps must precede mechanized welding using this device. The idle mode of operation of the spa should not be associated with the delivery of voltage to the tip of the hose.
Before starting work, the grounded terminal is connected to the SPA. Then you should adjust the power parameters, as well as the welding wire feed speed. Setting options are provided according to the thickness and type of metal. There are tables indicating all welding parameters using SPA. They can be found in specialized literature describing the welding process.
List of possible malfunctions of the welding inverter.
Setting up the SPA involves mandatory monitoring of the voltage on the welding wire, that is, the electrode. The control process of a semi-automatic device assumes appropriate logic based on the following circuit for removing and supplying voltage to the SPA:
- Removal from microswitch.
- Engine supply.
- It flows to the reverse winding of the motor.
- Receiving it with a sleeve and gas cutoff.
Having studied all the safety requirements and special instructions in books, they proceed to working with a semi-automatic device. First, you should connect it to the electrical network and press the power button. The trigger of the device should be pressed when the face is protected by a special mask.
First you need to cut off the excess wire, leaving about 3 mm, counting from the end of the burner. After the arc appears, you should slowly move the torch to the future connection. When lumps form on the end of the wire, it is necessary to increase the wire feed speed into the apparatus.
How to set up a semi-automatic machine for high-quality gas supply?
Inverter front panel diagram
You can adjust the dosage of the amount of inert or carbon dioxide coming from a gas cylinder or reducer automatically or manually. With the correct settings of the semi-automatic welding machine, the electric arc will burn perfectly evenly. This allows the welding process to be carried out virtually without splashes.
It is necessary to ensure that the metal of the connection does not boil. This is achieved by correctly setting up the semi-automatic welding machine by ear. The gas hisses quietly during welding, producing a uniform noise.
An experienced welder ensures that the gas is blown and not blown. In this case, the arc should not break, so you need to move the wire forward. If intermittent hissing sounds occur and the wire melts rapidly, which occurs faster than the burner moves, it is necessary to reduce the feed speed.
Sometimes it is necessary to adjust all the settings for high-quality welding for several days until an even, stable arc is obtained.
It has a stable sound and a characteristic crackling sound. The type and amount of gas supplied plays an important role in the process of regulating the welding machine. For example, a porous and weak weld will result from insufficient gas flow.
What semi-automatic devices allow you to make adjustments?
Image 1. Schematic diagram of the SPA.
The operation of any spa is associated with the presence of a welding transformer in its design. The susceptibility of welding current switches to wear requires the constant participation of a master regulating the welding process. For this purpose, you can use a contactless relay, which is the switching board of the transformer device. This is due to the presence of a significant resource in terms of switching.
The adjustment process is based on the use of an electrical signal transmitted through a circuit (IMAGE 1). The semi-automatic control system has an action logic that allows blocking the switching of each stage of the transformer device during a welding load. However, this can be a common reason associated with broken switches.
The simplest device that allows you to customize the SPA circuit is a throttle. It has several stages, which can be switched when the inductance level decreases or increases. Another possible device for adjusting the device is an active throttle.
Power supply circuit for a semi-automatic welding machine.
When using this device, you will not need to use mechanical switching, which will ensure smooth adjustment of inductance parameters. This adjustment mechanism allows you to correctly configure the process associated with the transfer of materials.
Manual arc welding, which allows connections to be made using a welding inverter, is also typical for semi-automatic machines. Therefore, an important PV parameter is provided for it. It is a percentage designation showing the permissible operating time of the semi-automatic device. This indicator will allow you to maintain the level of wear resistance of the equipment for a long time, ensuring its operation at a high-quality level.
Before using the semi-automatic device, the current value must be adjusted so that the metal does not become burnt. However, determining the exact current value is difficult. This point requires, before starting welding, to carry out training using a metal plate into which the wire is inserted. You can change the welding current using a rheostat. This is the most effective means of adjusting the welding arc for different metal thicknesses.
Recommendations for correctly setting up a semi-automatic welding machine
Semi-automatic welding process.
The welding current indicator should be set in the settings depending on the thickness of the metal being welded and the diameter of the wire used as an electrode. This dependence is relatively standard, so the value of the indicator does not fluctuate much.
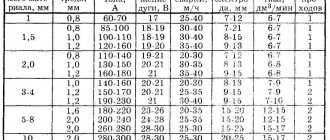
Typically, the device body or its instructions should contain information about the possible values of the welding current indicator. In certain cases, the table with indicators may be missing for some reason. Then experts recommend using the following current indicators for welding metal, taking into account its thickness, indicated in brackets:
- 20 - 50 A (1-1.5 mm).
- 25 - 100 A (2-3 mm).
- 70 - 140 A (4-5 mm).
- 100 - 190 A (6-8 mm).
- 140-230 A (9-10 mm).
- 170 - 280 A (11-15 mm).
Torch for semi-automatic welding with a consumable electrode: 1 - mouthpiece, 2 - replaceable tip, 3 - electrode wire, 4 - nozzle.
This list is associated with a fairly large range of indicators that are united by a common trend. Its principle boils down to the fact that to weld the thickest material, a greater welding current is required. This indicator is determined by the diameter of the wire used.
If you use thin wire during the welding process, it allows you to configure the semi-automatic machine to operate using less current. If you use thicker welding wire, more current will be required. Due to the inertia of mechanics, the movement of the welding wire occurs slowly, gradually accelerating.
You can regulate the motor current using a special switch. The welding current must be sufficient to ensure complete braking of the wire. The current is adjusted in the semi-automatic welding machine using a trimming rheostat. Subsequent braking of the wire occurs after a certain time.
What results can you get from setting up a spa?
Submerged arc welding diagram.
As a result of the adjustments made, the welding wire should not spread or melt. This occurs when a very small current value is selected. You will need to increase the voltage to check the result. If the wire has spread well, then a “drop” should appear on the back of the metal. This will mean that everything is normal.
If, after using the welding wire, a slight depression is formed, then the “drop” will hang on the other side. This is due to the choice of the welding current value above the norm. You should take another piece of metal to conduct the experiment at a lower voltage level.
If a hole appears instead of a wire, then this is due to the choice of too high a current value. You should use another workpiece to carry out semi-automatic welding at a lower voltage level. For training welding, workpieces coated with zinc cannot be used, since it evaporates and releases harmful substances. They can harm the human body.
https://moyasvarka.ru/youtu.be/gsBDcZWozYE
After preliminary training, you should finally make sure that the current settings are correct. In this case, the metal workpiece must be clamped with sufficient force. Only after this can you proceed to the main welding, not forgetting about safety precautions. Before welding, you should be dressed in a welder’s suit and protect your face with a special mask.
moyasvarka.ru
Feed rollers for aluminum wire
Article: 005.040.116 Feed roller 30x10x12 U 1.0–1.2
Feed roller for aluminum wire with a diameter of 1.0–1.2 mm. U-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 30x10x12. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines PTC RILON MIG 250 P GDM, MIG 300 P GDL.
Price: 598 RUR
Article: 005.040.111 Feed roller 40x32x10 U 1.0–1.2
Feed roller for aluminum wire with a diameter of 1.0–1.2 mm. U-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 40x32x10. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines PTC RILON MIG 350 GF, MIG 500 GF, MIG 500 I, MIG 500 F, MIG 500 FW.
Price: 723 RUR
Article: 005.040.130 Feed roller 40x32x10 U 1.2–1.6
Feed roller for aluminum wire with a diameter of 1.2–1.6 mm. U-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 40x32x10. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines PTC RILON MIG 350 GF, MIG 500 GF, MIG 500 I, MIG 500 F, MIG 500 FW.
Price: 723 RUR
Article: 005.040.123 Feed roller 30x22x10 U 1.0–1.2
Feed roller for aluminum wire with a diameter of 1.0–1.2 mm. U-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 30x22x10. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines PTC RILON MIG 250 GDM, MIG 300 GDL.
Price: 598 RUR
Article: 005.040.121 Feed roller 30x22x10 U 0.6–0.8
Feed roller for aluminum wire with a diameter of 0.6–0.8 mm. U-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 30x22x10.
Article: 005.040.115 Feed roller 30x10x12 U 0.8–1.0
Feed roller for aluminum wire with a diameter of 0.8–1.0 mm. U-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 30x10x12. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines PTK RILON MIG 300 GD.
Price: 598 RUR
Article: 005.020.101 Feed roller 30x10x10 U 0.8–1.0
Feed roller for aluminum wire with a diameter of 0.8–1.0 mm. U-shaped groove. The dimensions of the roller are 30x10x10. Suitable for semi-automatic welding machines of the PTK MASTER MIG S and PTK RILON MIG GDM series.
Price: 673 RUR