Semi-automatic welding is one of the most popular types of welding. Using a semi-automatic machine, you can even weld dissimilar metals, not to mention working with complex alloys such as aluminum or copper. For this reason, production facilities of any scale always need welders who will have semi-automatic welding skills.
However, in addition to technology, the master must also know how to calculate the optimal welding mode, in particular its speed. In this article we will briefly describe how to calculate not only the welding speed, but also the current or arc voltage depending on the thickness of the metal and other indicators. You will learn several useful formulas, and for beginners we have compiled a small hint table.
How to calculate welding speed
Welding speed is directly dependent on the size of the current, so you should first understand it. Welding current is calculated using formulas.
There are formulas by which the welding speed is calculated depending on the current value. This, in turn, can be calculated using the welding current formula. By correctly applying the formula for calculating the welding current, you can find its value and select the optimal welding speed, which depends on various characteristics.
So, for example, knowing the parameters of the deposited metal and the current value, you can apply the following formula:
αн is the deposition coefficient; γ —density of the electrode metal in g/cm3; Fн - metal area in cm2.
The deposition coefficient αн depends on the characteristics of the electrode. The metal area refers to the cross-sectional area of the welded seam under the condition of a single-pass option or one layer if a multi-layer coating is carried out.
To calculate this characteristic it is not necessary to use the welding speed formula. Regulatory documents can help, which contain recommendations on the choice for each type of metal. When asking how to calculate the welding speed, you can focus not only on the formulas, but also on the values indicated in them.
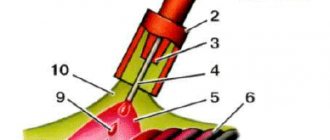
Electrode deposition rate
Author:
Igor
Date of:
14.07.2017
- Article
- Photo
- Video
Before carrying out welding work, it is necessary to calculate the deposition rate of the electrodes. This term denotes an important quantity characterizing the productivity of the welding process. KN allows you to determine how much electrode is used to form a seam, without taking into account the loss of material associated with this process.
How much electrode deposition is required for a weld?
Influence of speed on weld configuration
As the welding speed increases, the weld width decreases. The depth of penetration first tends to increase, and then it begins to decrease.
Compensation is carried out by increasing the current value. At a high welding speed, undercutting of the welded seam may occur, on both sides. This is due to heating that is insufficient to obtain a high-quality seam.
If the metal is thick, it makes sense to weld it with narrow seams, while ensuring high speed. Slow welding can lead to the appearance of defects in the metal in the form of pores.
Calculation tables
With experience, you will definitely gain experience and immediately select the necessary settings for semi-automatic welding in a shielding gas environment. Beginners cannot avoid trial and error, but tables specially created for this will help make the work easier at first.
Combine this theoretical knowledge with your experience and experiments - and you will definitely achieve great success.
Table No1. Recommendations for setting when welding low-carbon or low-alloy steel when forming a butt weld in a protective gas environment in the lower position with a current of reverse polarity (for example, carbon dioxide and its mixture with oxygen or argon).
Table No2. Recommendations for setting up for working with rotary butt joints using carbon dioxide, and its mixture with oxygen or argon, reverse polarity current.
Table No3. Recommendations for setting up when creating an overlap weld using carbon dioxide and its mixture with oxygen or argon, reverse polarity current.
Table No4. Recommendations when working with carbon steel, in a vertical spatial position, using carbon dioxide and its mixture with oxygen or argon, reverse polarity current.
Table No5. Recommendations for setting up semi-automatic welding in a shielded gas environment when creating a horizontal connection using carbon dioxide, reverse polarity current.
Table No6. Recommendations for setting when working with ceiling joints using carbon dioxide, reverse polarity current.
Table No7. Recommendations for working with the “point” method.
Manual welding
The speed of manual arc welding is chosen by the welder himself, so a lot depends on his qualifications. His choice is influenced by:
- properties of the base metal;
- characteristics of the electrode used;
- position of the seam in space.
The requirement that is imposed on the result of the choice is that it must guarantee a slight elevation of the molten metal located in the weld pool above the edges of the main one. A smooth transition of the liquid metal to the base metal without the occurrence of defects in the form of sagging and undercuts must also be ensured. When high-alloy steels are welded, welding is carried out at high speed in order to prevent overheating.
This parameter depends on the coating of the electrodes used. When using electrodes with a rutile coating, the welding speed is selected in the range of 6-12 m/h, with cellulose-coated electrodes - 14-22 m/h.
From the welding speed table for manual arc welding, you can find the value of this parameter depending on the thickness of the metal material.
Criteria for selecting automatic submerged arc welding mode
The main parameters for selecting various automatic welding modes with flux protection include: the thickness of the edges of the products being joined, the requirements for the geometry (size and shape) of the seams (they depend on the depth to which the metal is melted), and the width of the connection.
We recommend articles on metalworking
- Steel grades: classification and interpretation
- Aluminum grades and areas of their application
- Defects in metal products: causes and search methods
When choosing an operating mode, the wire diameter is determined based on the thickness of the parts. Then the welding current is calculated based on the diameter of the electrode. Then it is calculated at what speeds the wire should be fed into the weld pool and welding should be performed.
The electrode wire used for automatic welding must have a solid cross-section, and the diameter can range from 1 to 6 mm. And this is with a current from 150 to 2000 A. Arc voltage - from 22 to 55 V. The data in the table below allows you to approximately determine the modes of automatic submerged arc welding:
| Material to be welded | Metal thickness, mm | Seam type | Edge shape | Gap, mm | Electrode diameter, mm | Current strength, A | Voltage, V at current: | Welding speed, m/h | ||
| variable | constant (reverse polarity) | |||||||||
| 3 | Unilateral | Without cutting | 0–1,5 | 2 | 250–500 | 28–30 | 26–28 | 48–50 | ||
| 5 | Unilateral | Without cutting | 0–2 | 2 | 400–450 | 28–30 | 26–28 | 38–40 | ||
| 10 | Unilateral | Without cutting | 2–4 | 5 | 700–750 | 34–38 | 30–34 | 28–30 | ||
| 10 | Bilateral | Without cutting | 1–3 | 5 | 650–700 | 34–38 | 30–34 | 32–34 | ||
| 20 | Unilateral | Without cutting | 5–7 | 5 | 950–1000 | 40–44 | 32–36 | 18–20 | ||
| 20 | Bilateral | Without cutting | 2–4 | 5 | 750–800 | 38–42 | 32–36 | 22–24 | ||
| 30 | Bilateral | Without cutting | 6–8 | 5 | 950–1000 | 40–44 | – | 16–18 | ||
| 6 | Unilateral | V-shape, 60° | – | 3 | 250–280 | – | 30–32 | 25–28 | ||
| 10 | Bilateral | V-shape, 60° | – | 3 | 350–380 | – | 30–32 | 17–20 | ||
| 12 | Bilateral | V-shape, 60° | – | 5 | 500–550 | – | 30–32 | 30–36 | ||
| Welding titanium and its alloys | 4 | Unilateral | – | – | 3 | 340–360 | – | 32–34 | 45–55 | |
| 8 | Bilateral | – | – | 3 | 350–380 | – | 32–34 | 45–55 | ||
| 16 | Bilateral | – | – | 4 | 590–600 | – | 32–34 | 40–50 | ||
| 6 | Unilateral | Without cutting | – | 4 | 520–540 | – | 40–42 | 40 | ||
| 12 | Unilateral | Without cutting | – | 5 | 800–820 | – | 42–44 | 16 | ||
Semi-automatic welding
A semi-automatic welding machine is a device in which the role of an electrode is played by a wire fed to the welding site automatically. When welding with a semi-automatic machine, it is necessary to set two speeds. Both are installed by a welder. The first of these is the speed at which the wire is fed. The right choice will ensure a stable burning of the welding arc.
Second, the welding speed depends on the speed at which the torch moves. Thick-walled joints are welded at high speed to form narrow seams. At high speeds, it is necessary to ensure that when the gas leaves the protection zone, there is no oxidation of the end of the wire and the metal surface. Just as with manual arc welding, the current strength and feed speed of the electrode, in this case the wire, must be set by the welder himself, guided by his experience and qualifications. You have to start, in particular, from the type of metals being fused.
Using a semi-automatic welding machine, you can join two metal parts quickly and efficiently. This machine can weld metals of various widths. Compared to manual welding, semi-automatic welding has significant advantages.
Before starting the process, it is necessary to calculate the main characteristics - current, arc voltage and welding speed. The last parameter can be calculated knowing the selected current and voltage, since the semi-automatic welding speed depends on them.
Current and voltage, in turn, are selected in accordance with the thickness of the metal. It turns out that the speed of semi-automatic welding depends on the thickness of the metal.
First, the current strength is calculated using the formula. It is calculated depending on the diameter of the electrode and the current density. Knowing the calculated current strength and the diameter of the electrode, using the formula, you can determine the value of the welding arc voltage. After this, you can select the optimal welding speed.
Automatic welding modes and basic parameters
Technical conditions (TS) for welding various products contain all the information necessary for the work of the master. In the absence of such data, the specialist selects the desired welding mode by conducting experiments on workpieces made of a similar alloy.
Several different methods of creating connections are used. However, when using an automated process, preference is given to electric arc welding with flux protection. Experts call it the most effective. In this article we will touch on automatic welding modes and the calculation of the main parameters for their implementation.
Note. Submerged arc welding in automatic mode is advisable if the thickness of the workpiece (mm) is in the range of 5–50.
Main features of the process:
- It is necessary to carefully and scrupulously process the edges of the seam. The reason is the porous structure of the connector, which often causes cracks to form, and this applies to the entire seam.
- Welding should be carried out immediately after processing the edges.
- The requirements for workpiece and electrode materials are quite high.
Important welding parameters are:
- Welding current (I).
The depth of penetration largely depends on the amount of current passing through the arc. It is influenced by the composition of the alloy, the thickness of the workpiece, as well as the pattern of the upcoming welding.VT-metall offers services:
For the redistribution of heat between the workpiece and the (consumable) electrode, the polarity of the electric current is extremely important: straight is used by specialists in order to increase the amount of deposited material in the weld. However, it leads to spattering of metal from the weld pool and reduces the stability of the arc.
But more often they use reverse polarity. It is preferred for working under flux protection with most metals, with the only exception being aluminum.
- Welding speed (V).
The correct shape of the joint section largely depends on how optimal the choice of welding speed was. It has a direct impact on the time of welding processes (metallurgical and thermal), as well as on the life of the liquid state of the bath. Speed has the opposite effect on heat input and heat consumption.With a change in the connection speed, the section shape coefficient, width and depth of the seam change.
- Welding current voltage (U).
Voltage affects the size of the contact spot of the arc when it comes into contact with the metal. Increase leads to its increase. Low tension results in a concave weld bead with no reinforcement. In addition, undercuts appear along the seam line. High voltage promotes a narrow penetration zone and creates a stronger weld. - Electrode (wire) diameter, (∅).
The current density is inversely proportional to the diameter of the electrode wire at a certain current.The current density increases with decreasing electrode diameter. As the current density increases, the shape factor of the connection decreases.
The benefits of making the right choice
Correctly selected parameters will ensure a high-quality metal connection that can last for many years. The use of ready-made formulas makes it easier to select parameters. But this does not exempt you from studying GOSTs and other regulatory materials.
An experienced welder must cope with a non-standard situation and make adjustments. The correct choice of welding characteristics, in particular, the speed at which it will be carried out, will allow you to obtain high-quality and durable seams.
Relevance
The first thing you should definitely pay attention to if you decide to use this method of work is the qualifications of the master. It will be difficult for a beginner to understand the settings and choose materials wisely.
Work experience plays an important role and should not be underestimated. Professionals especially like to repeat how important it is to spend decades on self-study, become familiar with books, study standards and, of course, practice.
Without this, it is difficult to achieve success and quality. It’s hard to disagree with this, but let’s not give up on young specialists, because we all started somewhere.
How to refuel, installation on automatic and semi-automatic
How to thread welding wire into a semi-automatic machine is shown in the video. Here it is worth noting the key points that the author draws attention to.
- When putting on a new cassette, be sure to hold the end of the wire to prevent the coil from unwinding.
- The wire should fit into the groove of the roller.
- For pulling, use the electric drive idling (without gas supply) at the highest feed speed.
- Avoid getting caught in the sleeve or current collector.
The author of the video did not mention anything about adjusting the clamping device. The use of cored wire requires special attention. For welding with less spatter, a four-roll feed mechanism is recommended for flux-cored wire to better distribute the clamping force.
Where can I buy
The sale of various types of consumables is carried out by companies collected in a separate section. Familiarization with the information presented will allow you to find out where to buy welding wire.
In addition to the possibility of purchasing products from suppliers, it is also recommended to familiarize yourself with the range offered by manufacturers. Leading global enterprises, for example, ESAB and DEKA, have a wide network of representative offices, which allows you to purchase consumables and be completely confident in the quality of the products.
source
Current polarity
There are machines for manual arc welding that have direct current at the output. It is with direct current that two options for connecting the workpiece to be welded and the electrode appear:
- direct polarity - the workpiece to be welded is connected to plus, and the electrode holder - to minus;
- reverse polarity - the workpiece to be welded is negative, the electrode holder is positive.
Reverse polarity when connecting is used when welding high-alloy steels and thin sheet metal, because less heat is generated at the negative pole, which will avoid overheating and, as a result, burning of the metal.
Straight polarity is good for welding thick-walled parts. For example, low alloy steels (with a carbon content of less than 0.2%) can be welded in any polarity.
Reels and reel seats
Aluminum welding wire ER4043 (1.6 mm; spool 6 kg) ELKRAFT 93614. Photo AllInstruments.ru
Welding wire is wound onto reels, from which it is removed during operation. The reel is securely secured in semi-automatic machines using devices called reel holders. The devices for fastening the reels must correspond to those on the reel seat.
When the semi-automatic machine is turned off, the coil of wire tends to continue its movement, which can lead to the formation of loops on the wire. The design of the reel seat has a braking device , for example, in the form of a friction clutch. Adjusting it with a nut prevents the spool from unwinding freely and maintains the correct winding of the wire.