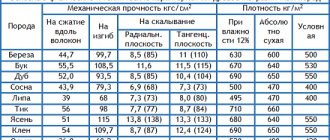
Milling is a quick and reliable way to give wood the desired shape. The working cutting tool of CNC machines is a milling cutter. Structurally, it is a rotating part with sharpened teeth. Milling cutters for CNC machines for wood are made from different alloys and are divided into categories. Their choice depends on the characteristics of the surface being treated, the type of work and the degree of hardness of the wood. It is also necessary to take into account not only the compliance of the cutter type with the task being performed and the milling mode, but also the design features of the cutting area. Our article will help you choose the right tool for programmed machines, which will introduce you to the types of cutters and their purpose.
- Types of edge cutters
What is a cutter?
The tool is a multi-blade part. Depending on the type, it can be mounted on the machine spindle or installed on the working shaft. For the manufacture of products, different types of alloys of durable metals are used.
In order for a tool to work efficiently, it is important to choose it, taking into account not only your needs, but also the technical characteristics of the machine.
Types of cutters most in demand when performing 3D processing
Most often, when creating a 3D part, the following types of cutting tools are used:
Ball straight cutters are a tool with a hemispherical tip
Designed for finishing finishing of a convex surface of any configuration. The absence of a spiral makes it difficult, when sharpening, to form the rake angle of the cutting edge of the tip. Therefore, this option is used for wood processing.
Two-way versions are in demand.
Spherical spiral - the tip has a similar shape. on a cylindrical surface this is a spiral type cutter
Therefore, the front angle of such a hemisphere ensures milling not only wood, but also metal.
They allow better processing of blind pockets with a rounded bottom than the previous option. Provides (with the required accuracy) profile processing of flutes, chamfers, ridges, fillets, and fillets.
Allows you to form profiles of varying complexity (plinths, cornices, baguettes, etc.) according to the laid down 3D model (without using a profile knife).
An excellent solution for small-scale production.
As a rule, carpentry workshops must purchase spherical spiral cutters for volumetric processing with diameters of 8 mm, 6 mm, 3 mm.
During the work, single- and double-pass versions are used. And also three-start ones with a finishing chipbreaker.
Spherical cone
They make it possible to reduce (without compromising quality) the finishing time of blind pockets with inclined walls by increasing the speed of the operation.
Due to the fact that the cutting speed along the length of such a cutter is uneven (for difficult-to-cut hard materials, this parameter is critically important when determining the cutting mode), the tool is in demand mainly in woodworking.
Here it allows you to perform volumetric processing of deep, small reliefs, decor, carvings, cornices, and other profiles with a complex cross-section (no profile knife required).
A good solution for the production of figured furniture elements.
Provides sampling to the required depth in a single pass, which speeds up work. The conical shape ensures the cutter's resistance to dynamic loads and vibrations during high-speed processing conditions.
When making a three-dimensional product, a tool is used in one- and two-way versions.
Straight conical - in fact, this is a sharpened engraving cutter
Used for engraving work on decorative wooden products. Two-way versions are used.
Spiral cone
Provides proper processing quality for blind pockets, the walls of which have slopes and the bottom has a complex configuration.
As a rule, it has a flat end (this is due to the presence of a spiral throughout the cylinder, which affects the actual thickness of the tooth).
Important. When choosing such a cutter in the catalog, you should remember that the diameter indicated in it is given for the flat area on the end of the tool, and not for the place where the conical part becomes cylindrical.
Available in single and double pass versions.
Conical models are perfect for making high reliefs (finishing is carried out immediately). The conical shape provides the tool with significant strength with small tip diameters.
Finishing processing can be carried out using radius engravers (if we are talking about small elements of the relief being performed, or when applying engraving). This tool is much cheaper (with comparable quality of work). However, its use requires more attention, since the latter has a smaller safety margin.
Types of cutters depending on manufacturing method
There are prefabricated and monolithic instruments. The prefabricated type is a blank onto which blades were soldered at the factory. The sharp part of the part is made from special tool steel or from carbide types of metals.
Monolithic types of wood cutters are made from solid metal. Most often, manufacturers use tool steel. They initially include blades. Both options have proven themselves well in woodworking enterprises.
It must be taken into account that cutters with soldered blades cannot be sharpened.
There are also cutters with replaceable blades (a subtype of prefabricated tools). They can and should be changed as they wear out. This is the most practical option for those who do milling all the time.
General information
Milling cutters for various types of processing differ in the shape of the cutting edges and methods of sharpening. Backed ones have a curved shape and frontal sharpening; They are used when working with profiles. Pointed ones with a straight profile are used for drilling; they are sharpened on the front or back sides. There are cutters with two cutting edges. This design makes it possible to make tools and processing cheaper, increase work speed and improve the quality of the finished product.
Over time, the cutting edge of the tool becomes dull and wears out. To avoid frequent replacement, cutters are made from high-strength alloys with a long service life.
Take the test
Types of blades
Types of cutters for a wood router also differ in the type of blades. They come in high-speed (marking: HM) and carbide (marking HSS). The first option is great for working with soft woods, and the second is great for hard woods.
The blades can be positioned vertically or at an angle. The inclined type of blades makes it possible to carefully cut a layer of wood without chipping along the edges. Vertical blades cut lumber.
What should you pay attention to when choosing a cutting tool?
First of all, the type of workpiece to be processed (surface hardness) should be taken into account. This directly affects the choice of tool: models with tungsten, molybdenum additives (high-speed steel), or carbide versions. It is important to understand that the latter is a very expensive pleasure. In addition, they are highly specialized (adapted for a specific task).
The following is the answer to the question of what exactly this tool is supposed to do:
- perform rough processing (cut away the surface layers of the material, carry out the initial formation of a model from a workpiece, its cutting or cutting);
- mill grooves (grooves, depressions, grooves, recesses);
- carry out high-precision processing of the edges of the workpiece and its corner parts;
- carry out fine finishing (the optimal solution for this is to use a diamond-coated tool);
- create flat and three-dimensional images.
Variants of parts depending on geometry and design
There are many options for cutters to meet production needs. The main ones are: cylinders, corner, end, shaped, end. Each of them is designed for a specific type of woodworking.
If you want to find out more information about the types of wood cutters for machines, the specialists of the Mnogofrez online store are always ready to advise you on all technical issues. You can also buy tools for machine tools from us at an affordable price.
Contact us and you will be pleased with your choice!
SEE ALSO: Woodworking cutters • Purpose of cutters by number of passes • DJTOL tool series and alloys
Requirements for this tool
Machines with a computerized control system operate accurately and at high speed, but require careful equipment. To process metal, wood, synthetics and composite materials with different hardness coefficients, cutters with a certain sharpening angle of the cutting edge are needed.
There are factors that influence the result of work:
- the strength of the product itself and the ability to withstand loads;
- the location of the blades in the cutter and their geometric shape;
- wear resistance, allowing the tool to maintain its original sharpening for a long time;
- minimal vibration during the production process.
There is a design variety of cutters for CNC; they are made exclusively from special grades of hardened steel. But there are only two technologies:
- Specialists produce serial tools from a single piece, using high-speed hard steel for this. Among the main advantages are precise execution, guarantee of rigidity, and the ability to work with maximum load.
- The steel body, a hard alloy with a fine-grained structure, is soldered to reproduce the complex geometry of the cutting edge. Scope of application – production of tools (shaped, diamond or large-sized), cutters for woodworking (hand tools).
Optimal selection of cutters
The minimum that is included in a good set of cutters is:
- two edge cutters, one metric, the other inch;
- end mills with diameters of 6, 12 and 18 millimeters;
- a simple groove cutter, and for dovetail cutting;
- figured molding cutter;
- disk cutter.
This is the required minimum, but for professional work you may need a much larger arsenal.
How to choose the right cutter
CNC tools come in a wide variety . To make a choice, you need to consider the type of operation that will occur. It is very important to know what material the workpiece is made of. A high-quality device is distinguished by its technological indicators:
- Good balance.
- Excellent wear resistance.
- High strength.
To use the same tool for a long time, it is necessary to sharpen it periodically. It is advisable to purchase equipment for such an operation directly from the cutter manufacturer.
Scope of application
There are quite a few tools used on CNC machines. Each of them is used for a specific purpose. Therefore, all the tools were divided into several groups, taking into account their area of application.
- Rough milling. A large layer of metal is first removed. The desired shape is formed. Used for cutting sheet metal.
- Drilling grooves. Such equipment for CNC machines is capable of performing the following technological operations:
- Formation of grooves.
- Formation of grooves.
- Processing of recesses.
- Cutting recesses.
- Precise work. Machining corners, milling the edges of the upper surface of the part.
- Finishing. The operation is mainly performed with diamond cutters. They create depressions of various shapes, having the most complex configuration. After such processing, it is enough to clean the finished part and completely remove the remaining chips.
- Artistic drawings.
Types and design features
Milling cutters for wood milling machines are classified according to technological purpose and several parameters, including:
- design;
- cutting edge inclination;
- configuration
According to the design, one-piece and prefabricated tools are manufactured. The cutting edges are located parallel to the axis of rotation - straight and inclined. The configuration of the cutters determines the topography of the machined surface.
Milling cutters for wood milling machines are available for standard collet sizes in three sizes: 6, 8, 12 and 32 mm. For imported equipment, the shank is measured in inches and is not suitable for domestic milling machines and machines.
Grooved
Groove cutters for a wood router follow the shape of a cut on a wooden part. They have a shank for mounting in a collet, cutting edges on the sides and end. Based on the type of cut in the cross-section, slot cutters are distinguished:
- straight;
- V-shaped;
- fillets;
- T-shaped;
- dovetail;
- shaped.
According to their design, groove cutters for a wood milling machine are produced in one piece, with edges cut into the body of the workpiece at an angle, and in composite ones with shaped inserts.
Edge
Designed for processing edges and ends of parts. According to their shape, cutters are divided into:
- straight;
- trapezoidal;
- molded - figured;
- rebated.
In straight cutters for a wood milling machine, the working part has the shape of a cylinder. After processing, a smooth edge is obtained. Trapezoidal models follow the shape of a cone. They cut off sharp corners. The cutting edges of molding cutters are shaped, with a configuration opposite to the relief of the workpiece.
Important!
Edge cutters for a wood router have a bearing or a copy ring on the shank below the cutting edge. It rests on the edge of the part or template. As a result, the cutting line, straight and curly, is smooth and clean.
Edge cutters for a wood milling machine are installed for processing flat parts along the contour and manufacturing linear products: skirting boards, decorative frames, cornices, borders. Edge cutters are used in the manufacture of furniture and building structures. They cut a groove in the end to connect two parts, select a quarter.
Combined
Reliable joining with a rigid fit is ensured by combination cutters. They process the end, cutting out grooves and tenons. To connect two parts, one must be rotated 180⁰ around its axis, and the ends will completely coincide and are connected according to the tongue-and-groove principle.
To ensure that there are no transitions along the plane at the joint and a smooth plane is formed, the longitudinal axis of the workpiece should be determined before processing. After this, the copying ring is adjusted so that the middle of the cutter runs strictly along the axis of the end.
Important!
To connect flat parts at right angles, the end of one is machined, and on the second mating element, tenon grooves are cut along the edge of the plane.