Electrical power, designated in the diagrams by the letter P, is a physical quantity that characterizes the rate of conversion or transmission of electricity. The standard concept is the effort to move an electric charge along a route from point F1 to point F2.
The electrical power of a device is a key parameter that determines the potential for its operation in the electrical network. Used to calculate circuits and operating modes of equipment to ensure the safety of electrical networks. The greater the power of the device, the faster they perform the desired action.
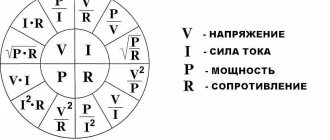
Formulas for calculating voltage, current, power, resistance Source amperof.ru
Electrical current through voltage and current
Since the potential difference calculated by the formula (F1-F2) determines the voltage (U), it is easy to conclude that the relationship established by Ohm’s law cannot be used. Electrical power (P) is also qualified by the current strength (I) on a specific section of the line. Final expression: P = U x I.
What is the load determined in terms of current and resistance?
Through a simple conversion, the electrical energy consumption is determined using the following formula: P = I2 x R. This shows the dependence of the power on the nominal value of the resistor connected to the line of the network element. For a complete circuit, the source resistance (internal) and the conductance of the connection point are indicated.
The concept of electrical power and methods for calculating it
From an electrical engineering point of view, it is a quantitative expression of the interaction of energy with conductor material and elements during the flow of current in an electrical circuit. Due to the presence of electrical resistance in all parts involved in conducting electric current, the directional movement of charged particles encounters an obstacle along the way. This causes the collision of charge carriers, electrical energy transforms into other forms and is released in the form of radiation, heat or mechanical energy into the surrounding space. The conversion of one type to another is the power consumption of the device or section of the electrical circuit.
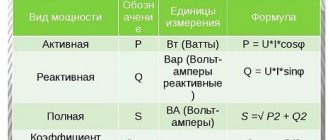
Depending on the parameters of the current and voltage source, power also has distinctive characteristics. In electrical engineering it is denoted by S, P and Q, the unit of measurement according to the international SI system is watts. Power can be calculated through various parameters of instruments and electrical appliances. Let's look at each of them in more detail.
Through voltage and current
The most relevant way to calculate power in DC circuits is to use current and applied voltage data. To do this you need to use the calculation formula: P = U*I
Where:
- P – active power;
- U – voltage applied to a section of the circuit;
- I is the strength of the current flowing through the corresponding section.
This option is only suitable for active loads, where direct current does not provide interaction with the reactive component of the circuit. To find power you need to multiply current and voltage. Both quantities must be in the same units of measurement - Volts and Amperes, then the result will also be in Watts. You can use other methods kV, kA, mV, mA, μV, μA, etc., but the power parameter will proportionally change its decimal value.
Through tension and resistance
For most electrical devices, such a parameter is known as internal resistance, which is taken as a constant for the entire period of their operation. Since domestic or industrial units are connected to a source with a known voltage rating, determining the power is quite simple. The active power is found from the previous relationship and Ohm's law for a section of the circuit, according to which the current in the section is directly proportional to the magnitude of the applied voltage and has inverse proportionality to the resistance:
I = U/R
If the expression for calculating the current load is substituted into the previous formula, you will get the following expression for determining the power:
P = U*(U/R)=U2/R
Where,
- P – load value;
- U – applied potential difference;
- R – load resistance.
Through current and resistance
There is a situation when the potential difference applied to an electrical device is unknown or requires labor-intensive calculations, which is not always convenient. This issue is especially relevant if several devices are connected in series and you do not know how the consumed electricity is distributed between them. The definition approach here is no different from the previous method; it is based on the basic statement that the electrical load is calculated as P = U×I , with the difference that we do not know the voltage.
Therefore, we will also derive it from Ohm’s law, according to which we know that the voltage drop on any section of a line or electrical installation is directly proportional to the current flowing through this section and the resistance of the circuit section:
U=I*R
after substituting the expression into the power formula, we get:
P = (I*R)*I =I2*R
As you can see, the power will be equal to the square of the current multiplied by the resistance.
Apparent power in AC circuit
AC networks are fundamentally different from direct current in that changes in electrical quantities lead to the appearance of not only an active, but also a reactive component. As a result, the total power will also consist of active and reactive energy:
Where,
- S – total power
- P – active component – occurs when electric current interacts with active resistance;
- Q – reactive component – occurs when electric current interacts with reactance.
Also, the components are calculated through trigonometric functions, like this:
P = U*I*cosφ
Q = U*I*sinφ
which is actively used in the calculation of electrical machines.
Rice. 1. Power triangle
What is it and how to calculate the load
Electric current load is a quantity characterizing its properties. Shows how much energy is consumed by electrical appliances. The current power is measured using a special device - a wattmeter.
If you connect a meter in series, you can check the current strength. When connecting in parallel, the voltage is determined. The amount of circuit consumption is calculated using the formulas: P = I x U or P = U2/ R = I2 x R.
The electrical load is equal to the voltage across the consumer multiplied by the amount of current flowing through it.
P = U x I
The formula indicates which measurements determine this parameter. If the load is active, it is measured in Watts, the reactive unit of electrical power is VA.
Reactive unit of electrical power - VA Source infourok.ru
How to determine the maximum current load
The useful power shows the maximum value in a situation where the load resistance R is compared with the same parameter inside the source - r.
R = r.
P max = E2 / 4r, where E is the driving force of the current source.
To calculate the maximum current load for an electrical device, you need to know the rated load parameter and the AC input voltage. The technical data sheet of the device, manual or emblem contains the first indicator.
For example, when the appliance rating (P) is 12 W, the maximum current consumption at AC voltage will be for:
- 120 V – I = 12/120 = 0.100 A or 100 mA.
- 220 V – I = 12 / 220 = 0.055A or 55 mA.
If necessary, the amount of electricity consumed is expressed through a complex value. For this purpose, basic relationships are used, impedance is used instead of resistance.
Calculation of light bulb power
The selection of incandescent lamp power depends on the desired level of illumination of the living space. One 100 W light bulb, working in the dark for at least 12 hours, consumes 1.2 kW of power. For a month this will be 36 kW, for a year - at least 432 kW. If there are 10 light bulbs in an apartment, then the total annual consumption will be 4320 kW. If the price for 1 kW of electricity is 5 rubles, the amount turns out to be decent – 21,000 rubles. Therefore, replacing incandescent lamps with energy-saving light sources: LED lamps, LED strips and the like allows you to save money. In addition, reducing the power of such light bulbs does not reduce the luminous flux. The reduced supply voltage of LED strips also reduces the amount of power consumed.
Electrical Appliances Parameters
Every modern apartment must be equipped with electrical appliances. To connect them to the network, it is necessary to draw up a schematic diagram where the loads connected to individual lines will be distributed in coordination with each other. It is necessary to build in a circuit breaker based on the PUE to prevent emergency situations.
First, the electrical wiring parameters are clarified. Then they are checked according to the group diagram for connecting to the network of household electrical appliances.
Standard characteristics of electrical power consumption (W):
- desktop computer – 170-1,250;
- LCD TV – 120 – 265;
- laptop – 40-280;
- air conditioning – 1,200 – 2,500;
- iron – 450-1850.
To protect the network, you need an automatic machine; we choose it taking into account all the significant factors.
Automatic switch for protecting the electrical network Source vmasshtabe.ru
It is important to pay attention to loads that have increased reactive energy parameters.
What is it measured in?
The unit of measurement of electrical power is W for Russia. By international standards - W. This is the energy provided per unit of time. One W is equal to a joule per second (J/s). Moreover, a joule is a unit of electrical power, a second is a unit of time.
For small values, multiple prefixes are used: “milli-”, “micro-”, for large values - “mega-”. For example: 5,800 W = 5.8 kilowatts = 5.8 kW.
When you multiply 1 Kilowatt by 1 hour, you get a Kilowatt-hour (kW x h). This is a unit of measurement of the amount of electricity provided to subscribers. It is used by energy enterprises that own the appropriate equipment (generators and transformer substations). They generate and convert the produced electricity, which is then distributed to consumers.
In the same way, the energy capacity of batteries is measured in units of ampere hours (Ah). Portable types of energy storage batteries are measured in milliampere hours (mAh).
The energy in batteries is measured in milliamp hours (mAh). Source listtopa.ru
For the unit of measurement Watt, according to international standards, the letter designation W is allocated after James Watt. He was the first to use the term “horsepower,” which today is an obsolete unit of the W parameter.
Energy conversion indicators:
- horsepower (HP) - 746 W;
- kilo Watts (kW) – 1×1000 W;
- megawatts (MW) −1×1000000 W;
- gigawatt (GW) – 1×1000000000 W.
Today, "horsepower" is used to indicate the second measure of engine power in vehicles.
Power determination
Let's say we need to harvest wheat from a field of 100 hectares. This can be done manually or using a food processor. Obviously, while a person cultivates 1 hectare of area, a combine harvester will have time to do much more. In this case, the difference between man and technology is precisely what is called power. This leads to the first definition.
| Power in physics is the amount of work done per unit of time. |
Let's consider another example: between point A and point B the distance is 15 km, which a person can cover in 3 hours, but a car can travel in just 10 minutes. It is clear that they will do the same amount of work in different times. What does power show in this case? How quickly or at what speed something is done.
In electromechanics, this quantity has another definition.
| Power is a scalar physical quantity that characterizes the instantaneous rate of energy transfer from system to system or the rate of conversion, change, and consumption of energy. |
Recall that scalar quantities are those whose value is expressed only as a number (without a direction vector).
Human power depending on activity
| Kind of activity | Power, W |
| Slow walking | 60–65 |
| Running at a speed of 9 km/h | 750 |
| Swimming at a speed of 50 m/min | 850 |
| Football game | 930 |
What determines the load of electric current?
Existing electrical wiring lines experience resistance during the movement of electrons, which characterizes voltage loss. Circuits where an alternating current source is present have one feature - the key role here is played by a sinusoidal oscillation of electrical indicators.
Sinusoidal oscillation of electrical indicators. Source urpsvet.ru
The following information will allow you to select the best calculation method based on actual network conditions.
Instantaneous electrical power: calculating the value
This indicator establishes the instantaneous values of the measured data. The key definition is considered taking into account the fact that a single simple charge (q) moves in a certain time Δt. To perform a specific action, the energy of electric current PF1-F2 = U/ Δt or (U/ Δt) x q = U x (q/ Δt) is expended. The formula takes into account the movement of q over the period Δt. Since the current, according to the classical definition, is equal to the charge moving from F1 to F2 (I = q/ Δt), the final expression is derived: PF1-F2 = U x I.
Conditionally assuming that the time period is very short, we obtain the instantaneous power for part of the electrical circuit P(t) = U(t) x I(t). The same conclusions can be drawn taking into account the corresponding resistance parameter: P (t) = (I (t))2 x R = (U(t))2/ R.
Electrical power: DC circuit
The previously mentioned formulas are shown without correction factors. They are used to calculate a circuit connected to a direct current source. Using an ordinary device - a multimeter, with the switch in the correct position, the resistance of the load connected to the network is set.
With its help, the load resistance is set. Source hammer-shop.ru
Electrical power: AC circuit
For such lines, it is unacceptable to use formulas that determine instantaneous parameters, since the final indicator changes from a minimum value to a maximum value with the network frequency. A typical single-phase 220 V network is characterized by a 50 Hz sinusoidal signal. It is allowed to use the simple formula P = U x I when connecting devices with resistive parameters:
- Heating elements of washing machines;
- spirals of infrared heaters;
- incandescent light bulbs.
Using this formula, the load is set.
Energy can be of two types: reactive and active.
Active is the true electrical power that produces real work in the load, W shows this parameter. It converts energy into mechanical, thermal and other forms.
If you turn on a powerful unit or capacitor, the voltage inside the network drops. Such loads create an oscillating circuit that receives energy from the power source. In this situation, only P act components perform useful functions. The active indicator is calculated in the following way:
- U x I – direct current (alternating current with a resistive load);
- U x I x cos fi – for a single-phase 220 V line;
- U x √3 x cos fi = U x 1.7321 x cos fi – 3-phase network, U x √3 x 380V.
There are other types of energy, but more on that later.
Active and passive energy Source ppt-online.org
Reactive power
This indicator shows the loads that are created in devices due to fluctuations in the energy of the electromagnetic field.
Reactive power, regardless of the absence of useful work, must be taken into account to correctly evaluate key network data. Cables and wires, when current passes through them in any direction, heat up. This happens quite cyclically. Energy effects at high intensity:
- damage cable cores and protective insulation;
- contribute to the occurrence of a short circuit;
- destroy the windings of transformers and drives.
Reactive power is expressed as VA (volt-amperes) and is calculated by multiplying the voltage by the current and the shear angle:
P r = U x I x sin fi.
When connecting a load with capacitive parameters, the value becomes negative, when inductive it becomes positive. Since the characteristics of the magnetic field change, the unit of measurement for reactive power is VA.
If the parameters of total electrical power are shown as vectors, a triangle appears. The length of its sides will be equal to the amount of electricity consumed by a particular component. The angle between the apparent power (Pap) and the active power (ϕ) is used for calculations. The total value is determined by the expression: P total = √((P act)2 + (P react)2).
Energy consumption
Calculating energy consumption for a house or apartment is not particularly difficult. To do this, you need to perform the following algorithm of actions:
- make a table of all electrical appliances used in the house, including lighting lamps;
- put in separate columns: device power, operating hours per day;
- for each energy consumer, calculate (by multiplying the power by the operating time) the average daily consumption;
- sum up all the obtained power values.
Such a calculation will give a real picture of electricity consumption. Using this data, you can control consumption and adjust the daily power consumption of each device.
It does not matter how power consumption is calculated or measured. The main task of the process is to correctly select the cross-section of conductors for wiring, supplying power cables and ensure that automatic protection is triggered. The cable supplying voltage to the room must withstand the simultaneous switching on of all consumers located in it for a long time. Its choice directly depends on the accuracy of determining the power of consumers.
What is power in electricity
Voltage is the work done to move a unit of charge. Current is the number of coulombs moved in 1 second. When multiplying the first parameter by the second, the total amount of work done in 1 second is obtained.
The strength of electricity is a numerical current meter that characterizes its energy qualities. The power indicator equally depends on voltage and current strength. How is current power measured? To measure this parameter, a Wattmeter is used; the unit of measurement is designated in the same way - W (Watt).
By using the dependence of the power parameter on current and voltage, specialists can transmit electricity over long distances. For these purposes, energy is converted at step-down and step-up transformer substations (transformer substations).
Power at currents: direct and alternating
Calculation of voltage drop in a cable
When it becomes necessary to calculate how much installed equipment will consume, you need to remember that there is a difference between the P value when applying DC and AC voltage.
The formula P for constant current shows P as the product of the instantaneous values of I and U. In this case, the moment in time can be absolutely any.
The expression P under conditions of sinusoidal electron motion takes into account the angle by which the phases of the current and voltage are shifted. The cosine of this angle is multiplied by the product of current and voltage over a period of time T. This is the period of time during which the current changes its value from positive to negative:
T = 1/f, where f is the frequency of 50 Hz.
Electrical power and inactive power
Equipment certificates contain active load - power factor, which is an important characteristic. It shows how efficiently a household appliance consumes electricity.
Fig.8
This is a number from −1 to 1, it is never equal to one. This coefficient depends on the type of load: C, L or R. The first 2 negatively affect PF = cos φ of the system. If its parameter is large, the current consumed by the devices increases. Many power loads are inductive, causing the current to lag behind the voltage.
Inactive energy arises in electrical AC circuits of alternating current networks. It is calculated simply: the square root of the sum (Pa2 + Pr2). If the reactive load is zero, then the passive load is equal to the modulus |Pa|.
The presence of nonlinear current distortions in electrical networks is caused by non-compliance with the direction that occurs between U/I, since the energy has a pulsed nature. In nonlinear modes, the apparent current power (EP) increases. Such a load is inactive and consumes Pr and current distortion energy. The unit of measurement is the same as regular power W.
Determination of power consumption
Calculating electricity consumption by power can be done in several ways. They are described below.
Nameplate data
Over time, a generally accepted practice has developed - to indicate the technical parameters of household appliances on nameplates. To find out the power consumption, just read the data on the plate.
Nameplates:
Calculation by formula
Knowing the voltage in the current source (household outlet, batteries or accumulator) and the current that the device consumes, there is nothing easier than determining the power consumption of an electrical device. In this case, the calculation formula will look like this:
N = VxI. Where N is power (W); V—voltage (V); I - current strength (A).
Multimeter:
For example, using a multimeter in ammeter mode, they find out the current strength for which the electric saw is designed - 8.2 amperes. Since the equipment operates from a household power supply of 220 volts, it will be quite simple to calculate the power consumption of the saw: 220 × 8.2 = 1800 W = 1.8 kW.
Circuit for measuring current with a multimeter:
Measurement with a wattmeter
This is a universal way to calculate electricity consumption using such a device. Currently, it is quite easy to purchase it online in one of the Chinese online stores.
Wattmeter:
Wattmeter is a power meter for various electrical consumers. The device determines the power characteristics of a device for any purpose operating from a household electrical network. On its back there is a plug that is inserted into the socket. In the front part of the case, under the display, there is its own socket. The equipment under test is connected to it.
Using this tester is one of the ways to calculate the electricity consumption of any household electrical appliance. The power meter is a kind of bridge that connects the consumer with the current source. They take measurements over a certain period of time. Then you can calculate how much money a refrigerator or washing machine “spends”. The tester has a built-in battery, which is needed to remember previously obtained readings and calculate the monetary costs for consumed electricity. In other words, a wattmeter can be characterized as an individual electric meter that serves one electrical appliance.
Elimination method
With this method, the electric meter acts as a power meter. Let’s say that there is electrical equipment in the house that does not have a nameplate, the documentation for it has long been lost or did not exist at all. There is the easiest way to calculate electricity consumption - this is the elimination method. Proceed as follows: de-energize all appliances in the apartment or house, turn off the lights, and turn the block toggle switches on the electric meter to the “Off” position. except one.
Taking electric meter readings:
The desired device is turned on for as long as possible. The amount of electricity consumed for 1 hour should be recorded. If circumstances do not allow this, then switching on is carried out within a time period that is a multiple of 60 minutes.
For example, if the equipment worked for 10 or 20 minutes, then the result is multiplied by 6 or 3 accordingly. If the device consumed 800 W within an hour, this means that its power is 0.8 kW/h. If you display the average number of operating hours of an electrical consumer per month, you can determine the costs that this equipment brings. To do this, the indicator is multiplied by the cost of 1 kW/h.
Power consumption calculator
You can use an online calculator as a power meter. One of its options can always be found on the Internet. The main purpose of the network service will help you determine the power of all electrical consumers located in a house, apartment or office. The results obtained are indicative in nature, but with their help you can calculate the electricity consumption of different types of consumers.
Using the calculator, homeowners can calculate future energy costs. Knowing the weak points in the overall picture of energy consumption, you can optimize the operating mode of the main electrical appliances. This can bring significant savings to the family budget.
The calculator is easy to use. The relevant data about lighting devices is entered into the interface windows - the power and number of lamps of different types, then information about electrical appliances is entered: a refrigerator, a TV, a washing machine and other household appliances, a computer, related office equipment and various power tools. After this, the current electricity tariff is entered into the “Cost of 1 kW” window. By clicking the “Calculate” button with the cursor, you get the estimated value of energy consumption for the month, as well as the amount to pay for electricity.
Informative way
There is a lot of information on the Internet about the capacities of various household appliances. Homeowners know and can compile a list of electricity consumers indicating their average power taken from the network. Residents can also count a certain number of operating hours of devices per day. From here the final result of electricity consumption for the month is obtained.
For power plants (this includes equipment with electric motors), a correction factor of k = 1.2 should be introduced, taking into account the sharp increase in starting power. The following table shows a standard list of household appliances. It may differ significantly from the list, which will include homestead equipment - these are machines, pumps, lawn mowers and much more.
Average power of household appliances:
After reading this article, it becomes clear what the power consumption of electrical appliances is and how it can be calculated. The accuracy of any calculation of electricity costs is verified by the bill of the local electricity company. If there is a significant discrepancy in the results, it is necessary to reconsider the methodology for calculating the power consumption of all electrical appliances. You need to know that all calculation methods will not be accurate, but they will be able to tell you where you can save energy.