What is affected by the number of turns in a transformer?
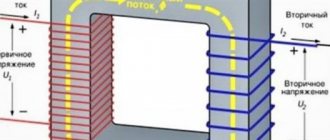
If we talk about the secondary windings of the transformer, then the value of the number of turns in them mainly affects the output voltage. Things are more complicated with the primary winding, since the voltage on it is set by the supply network. The parameters of the primary winding affect the no-load current, and, consequently, the efficiency. When changing the parameters of the primary winding, it will be necessary to recalculate all secondary windings.
And it is worth noting that it is better not to open the secondary winding of the CT.
Calculation method
The full calculation of the transformer is quite complex and takes into account the following parameters:
- supply voltage and frequency;
- number of secondary windings;
- current consumption of each secondary winding;
- type of core material;
- weight and size indicators.
At the household level, for the manufacture of devices powered by a standard 220V 50Hz network, the design can be significantly simplified.
The technique does not require special knowledge of complexity, and if you have experience, it takes little time.
The following data is required for the calculation:
- Number of exits.
- Voltage and current consumption of each winding.
The design of any transformer is based on the total power of all secondary loads:
Pс=I1∙U1+ I2∙U2+… In∙Un
To take into account losses, the concept of overall power has been introduced, for the calculation of which a simple formula is used:
P=1.25∙ Pс
Knowing the power, you can determine the core cross-section:
S=√P
The resulting cross-sectional value will be expressed in square centimeters!
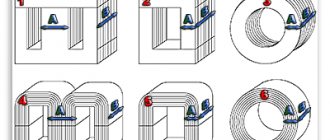
Further calculations depend on the type and material of the selected core. Magnetic cores are of the following types:
- armored;
- rod;
- O-shaped.
The methods for manufacturing magnetic cores also differ:
- typesetting - from individual plates;
- twisted, split or solid.
Armored or rod magnetic cores are usually split, while O-shaped ones are structurally made exclusively in one piece. In this respect, they are no different from continuous rod cores.
To determine the number of turns, use the following ratio, showing how many turns are needed per 1 volt of voltage:
W=K/S,
where K is a coefficient that depends on the material and type of core.
To simplify calculations, the following coefficient values are adopted:
- For stacked magnetic cores made of W- or U-shaped plates K=60.
- For split magnetic cores K=50.
- For O-shaped cores K=40.
As you can see, the shortest length of the winding wire, and therefore the best weight and size indicators, will be for O-shaped cores. In addition, designs with such cores have a small field of parasitic magnetic scattering and maximum efficiency. They are rarely used only because it is technically difficult to wind a winding around a closed core.
Knowing the parameter W, it is easy to determine the number of turns for each winding:
n=U∙W
To take into account the voltage drop on the primary winding, wound with a large amount of thin wire, the number of turns in it should be increased by 5%. This is especially true for small-sized, low-power structures.
You can reduce the no-load current by increasing the W value for each of the windings, but you should be aware that an excessive increase can lead to saturation of the magnetic circuit, which will lead to a sharp increase in the no-load current and a decrease in the output voltage.
At the final stage, the diameter of the conductors of each winding is determined. The calculation formula is as follows:
d=0.7√I
The diameter of the winding wire is determined for all windings without exception.
The resulting values are rounded to the nearest larger standard wire diameter.
Low power factor: causes and consequences
A low indicator leads to a maximum elimination of the energy component. Special devices are used for compensation, which reduce electricity consumption and increase the efficiency of the device.
Load losses in network elements
Loading leads to redistribution and reduction of the energy component. The voltage level drops, which causes significant overheating of the device. The consequence is loss of efficiency and performance, rapid failure of equipment.
The specialist minimizes load-type forces. This allows you to increase the starting torque of the device.
Alternative method for dimensions
The approximate parameters of the transformer, based on the available core, can be determined in another way, and then conclusions can be drawn about the possibility of further use.
Knowing the cross-sectional area of the magnetic circuit in square centimeters, you can estimate the maximum power that this converter is capable of providing:
PG=S2
It should be borne in mind that this power is dimensional, and the real one will have a smaller value:
P=0.8 PG
Usually, provided that the calculated power matches the required one, the primary winding connected to the 220 V network can be left untouched, recalculating only the parameters at the outputs.
Required information
To manufacture a winding product, it is necessary to be guided by a lot of information. The quality and service life of the finished power supply will directly depend on this. You should approach the calculation process competently, taking into account indicators such as magnetic inductance, efficiency and current density. Otherwise, the product will turn out to be unreliable and will soon fail. The main characteristics include:
- Mains input voltage. It depends on the source to which the transformer will be connected. The standard ones are: 110 V, 220 V, 380 V, 660 V. In practice, it can be anything, depending on the characteristics of the intermediate circuits.
- The output voltage of the transformer is the value required to ensure stable operation of the consumer. It is often necessary to manufacture a product with multiple ratings or with adjustable voltage. Then it is necessary to take into account its maximum value.
- Load current. With a fixed value, the rigid characteristics of the device are calculated, but often it is necessary to provide an adjustable value, then it will be necessary to take into account its maximum value.
- Network frequency. We use the European standard, that is, 50 Hz.
- Load power. This is not the main parameter, because it can be determined by voltage and current.
- Number of output windings. Some electronic devices use power supplies with multiple output voltages. For the manufacture of power electronics, mainly one rating is used, for example, for welding transformers.
You will also need to take into account the type of core , because the principle of calculating product performance directly depends on its design. There are many varieties of both designs and materials. If taking the latter into account makes no sense due to minor errors, then shape and size are of great importance. Therefore, different calculation algorithms are needed, depending on this criterion. Let's start with the simplest and most common.
It is not always necessary to carry out calculations using the required data. Often there is some kind of iron available, then you will need to determine the power of the transformer based on the cross-section of the magnetic circuit. Online programs available on the Internet allow you to determine parameters in any order.
Using a Multimeter
Using a multimeter, you can find data for recalculating the windings of an existing transformer. To do this, you need to make an additional coil from any available wire. After connecting the device to the network, it is necessary to measure the voltage on the additional coil. Now you can easily calculate the required number of turns per volt and recalculate the transformer to meet the required requirements.
Table of volts per turn
In order not to constantly carry out calculations, you can use the table, which shows the average data of the windings depending on the power:
| Power, P | Section in cm2, S | Number of vit. /B, W | Power, P | Section in cm2, S | Number of vit. /B, W |
| 1 | 1.4 | 32 | 50 | 9.0 | 5.0 |
| 2 | 2.1 | 21 | 60 | 9.8 | 4.6 |
| 5 | 3.6 | 13 | 70 | 10.3 | 4.3 |
| 10 | 4.6 | 9.8 | 80 | 11.0 | 4.1 |
| 15 | 5.5 | 8.4 | 90 | 11.7 | 3.9 |
| 20 | 6.2 | 7.3 | 100 | 12.3 | 3.7 |
| 25 | 6.6 | 6.7 | 120 | 13.4 | 3.4 |
| 30 | 7.3 | 6.2 | 150 | 15.0 | 3.0 |
| 40 | 8.3 | 5.4 | 200 | 17.3 | 2.6 |
How to measure wire diameter.
If you have a micrometer lying around at home, you can use it to measure the diameter of the wire.
It is better to first heat the wire in a match flame and only then remove the weakened insulation with a scalpel. If this is not done, then part of the copper can be removed along with the insulation, which will reduce the accuracy of the measurement, especially for a thin wire.
If you don’t have a micrometer, you can use an ordinary ruler. You need to wind 100 turns of wire around the tip of a screwdriver or another suitable axis, compress the turns with your fingernail and attach the resulting set to a ruler. Dividing the result by 100, we get the diameter of the wire with insulation. You can find out the diameter of the copper wire from the table below.
Example.
I wound 100 turns of wire and got a set length of -39 mm.
39 / 100 = 0.39 mm
Using the table, I determine the diameter of the copper wire - 0.35 mm.
Winding wire data table.
| Diameter without insulation, mm | Copper cross section, mm² | Resistance 1m at 20ºС, Ohm | Permissible load at current density 2A/mm² | Diameter with insulation, mm | Weight 100m with insulation, g |
| 0,03 | 0,0007 | 24,704 | 0,0014 | 0,045 | 0,8 |
| 0,04 | 0,0013 | 13,92 | 0,0026 | 0,055 | 1,3 |
| 0,05 | 0,002 | 9,29 | 0,004 | 0,065 | 1,9 |
| 0,06 | 0,0028 | 6,44 | 0,0057 | 0,075 | 2,7 |
| 0,07 | 0,0039 | 4,73 | 0,0077 | 0,085 | 3,6 |
| 0,08 | 0,005 | 3,63 | 0,0101 | 0,095 | 4,7 |
| 0,09 | 0,0064 | 2,86 | 0,0127 | 0,105 | 5,9 |
| 0,1 | 0,0079 | 2,23 | 0,0157 | 0,12 | 7,3 |
| 0,11 | 0,0095 | 1,85 | 0,019 | 0,13 | 8,8 |
| 0,12 | 0,0113 | 1,55 | 0,0226 | 0,14 | 10,4 |
| 0,13 | 0,0133 | 1,32 | 0,0266 | 0,15 | 12,2 |
| 0,14 | 0,0154 | 1,14 | 0,0308 | 0,16 | 14,1 |
| 0,15 | 0,0177 | 0,99 | 0,0354 | 0,17 | 16,2 |
| 0,16 | 0,0201 | 0,873 | 0,0402 | 0,18 | 18,4 |
| 0,17 | 0,0227 | 0,773 | 0,0454 | 0,19 | 20,8 |
| 0,18 | 0,0255 | 0,688 | 0,051 | 0,2 | 23,3 |
| 0,19 | 0,0284 | 0,618 | 0,0568 | 0,21 | 25,9 |
| 0,2 | 0,0314 | 0,558 | 0,0628 | 0,225 | 28,7 |
| 0,21 | 0,0346 | 0,507 | 0,0692 | 0,235 | 31,6 |
| 0,23 | 0,0416 | 0,423 | 0,0832 | 0,255 | 37,8 |
| 0,25 | 0,0491 | 0,357 | 0,0982 | 0,275 | 44,6 |
| 0,27 | 0,0573 | 0,306 | 0,115 | 0,31 | 52,2 |
| 0,29 | 0,0661 | 0.2bb | 0,132 | 0,33 | 60,1 |
| 0,31 | 0,0755 | 0,233 | 0,151 | 0,35 | 68,9 |
| 0,33 | 0,0855 | 0,205 | 0,171 | 0,37 | 78 |
| 0,35 | 0,0962 | 0,182 | 0,192 | 0,39 | 87,6 |
| 0,38 | 0,1134 | 0,155 | 0,226 | 0,42 | 103 |
| 0,41 | 0,132 | 0,133 | 0,264 | 0,45 | 120 |
| 0,44 | 0,1521 | 0,115 | 0,304 | 0,49 | 138 |
| 0,47 | 0,1735 | 0,101 | 0,346 | 0,52 | 157 |
| 0,49 | 0,1885 | 0,0931 | 0,378 | 0,54 | 171 |
| 0,51 | 0,2043 | 0,0859 | 0,408 | 0,56 | 185 |
| 0,53 | 0,2206 | 0,0795 | 0,441 | 0,58 | 200 |
| 0,55 | 0,2376 | 0,0737 | 0,476 | 0,6 | 216 |
| 0,57 | 0,2552 | 0,0687 | 0,51 | 0,62 | 230 |
| 0,59 | 0,2734 | 0,0641 | 0,547 | 0,64 | 248 |
| 0,62 | 0,3019 | 0,058 | 0,604 | 0,67 | 273 |
| 0,64 | 0,3217 | 0,0545 | 0,644 | 0,69 | 291 |
| 0,67 | 0,3526 | 0,0497 | 0,705 | 0,72 | 319 |
| 0,69 | 0,3739 | 0,0469 | 0,748 | 0,74 | 338 |
| 0,72 | 0,4072 | 0,043 | 0,814 | 0,78 | 367 |
| 0,74 | 0,4301 | 0,0407 | 0,86 | 0,8 | 390 |
| 0,77 | 0,4657 | 0,0376 | 0,93 | 0,83 | 421 |
| 0,8 | 0,5027 | 0,0348 | 1,005 | 0,86 | 455 |
| 0,83 | 0,5411 | 0,0324 | 1,082 | 0,89 | 489 |
| 0.86 | 0,5809 | 0,0301 | 1,16 | 0,92 | 525 |
| 0,9 | 0,6362 | 0,0275 | 1,27 | 0,96 | 574 |
| 0,93 | 0,6793 | 0,0258 | 1,36 | 0,99 | 613 |
| 0,96 | 0,7238 | 0,0242 | 1,45 | 1,02 | 653 |
| 1 | 0,7854 | 0,0224 | 1,57 | 1,07 | 710 |
| 1,04 | 0,8495 | 0,0206 | 1,7 | 1,12 | 764 |
| 1,08 | 0,9161 | 0,0191 | 1,83 | 1,16 | 827 |
| 1,12 | 0,9852 | 0,0178 | 1,97 | 1,2 | 886 |
| 1,16 | 1,057 | 0,0166 | 2,114 | 1,24 | 953 |
| 1,2 | 1,131 | 0,0155 | 2,26 | 1,28 | 1020 |
| 1,25 | 1,227 | 0,0143 | 2,45 | 1,33 | 1110 |
| 1,3 | 1,327 | 0,0132 | 2,654 | 1,38 | 1190 |
| 1,35 | 1,431 | 0,0123 | 2,86 | 1,43 | 1290 |
| 1,4 | 1,539 | 0,0113 | 3,078 | 1,48 | 1390 |
| 1,45 | 1,651 | 0,0106 | 3,3 | 1,53 | 1490 |
| 1,5 | 1,767 | 0,0098 | 3,534 | 1,58 | 1590 |
| 1,56 | 1,911 | 0,0092 | 3,822 | 1,64 | 1720 |
| 1,62 | 2,061 | 0,0085 | 4,122 | 1,71 | 1850 |
| 1,68 | 2,217 | 0,0079 | 4,433 | 1,77 | 1990 |
| 1,74 | 2,378 | 0,0074 | 4,756 | 1,83 | 2140 |
| 1,81 | 2,573 | 0,0068 | 5,146 | 1,9 | 2310 |
| 1,88 | 2,777 | 0,0063 | 5,555 | 1,97 | 2490 |
| 1,95 | 2,987 | 0,0059 | 5,98 | 2,04 | 2680 |
| 2,02 | 3,205 | 0,0055 | 6,409 | 2,12 | 2890 |
| 2,1 | 3,464 | 0,0051 | 6,92 | 2,2 | 3110 |
| 2,26 | 4,012 | 0,0044 | 8,023 | 2,36 | 3620 |
| 2,44 | 4,676 | 0,0037 | 9,352 | 2,54 | 4220 |
Return to top menu