Steel cylinders are used
for storing and transporting compressed, liquefied and dissolved gases under pressure . Cylinders have different capacities - from 0.4 to 55 dm3.
Cylinders are steel cylindrical vessels, in the neck of which there is a conical hole with a thread into which a shut-off valve is screwed. Each gas has its own valve designs, which excludes the installation of oxygen valves on an acetylene cylinder and vice versa. A ring with an external thread is tightly fitted onto the neck to screw on a safety cap, which serves to protect the cylinder valve from possible shocks during transportation.
Cylinders for compressed, liquefied and dissolved gases are made from seamless carbon and alloy steel pipes. For liquefied gases at an operating pressure of not more than 3 MPa, the use of welded cylinders is allowed.
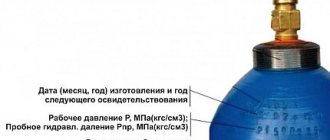
Depending on the type of gas contained in the cylinder, the cylinders are painted on the outside in conventional colors, and the name of the gas is also applied with paint corresponding to each gas. For example, oxygen cylinders are painted blue, and the inscription is made with black paint, acetylene - in white and red paint, hydrogen - in dark green and red paint, propane - in red and white paint. Part of the upper spherical part of the cylinder is not painted and the passport data of the cylinder is stamped on it: type and serial number of the cylinder, trademark of the manufacturer, weight of the empty cylinder, capacity, operating and test pressure, date of manufacture, quality control department stamp and Gosgortekhnadzor inspection stamp, next date tests. Cylinders are periodically, every five years, inspected and tested.
The main types of cylinders used for storing and transporting oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen and other gases are shown in the table.
Oxygen cylinders
For gas welding and cutting, oxygen is delivered in steel oxygen cylinders of type 150 and 150 L. The oxygen cylinder is a steel seamless cylindrical vessel 3, having a convex bottom 1, onto which a shoe 2 is pressed; At the top, the cylinder ends with a neck 4. The neck has a conical hole into which a shut-off valve 5 is screwed in. A safety cap 6 is screwed onto the neck to protect the valve.
The most widely used for gas welding and cutting are cylinders with a capacity of 40 dm3. These cylinders have the following dimensions: outer diameter - 219 mm, wall thickness - 7 mm, height - 1390 mm. The weight of the cylinder without gas is 67 kg. They are designed for a working pressure of 15 MPa, and a test pressure of 22.5 MPa.
To determine the amount of oxygen in the cylinder, you need to multiply the capacity of the cylinder (dm3) by the pressure (MPa). For example, if the capacity of a cylinder is 40 dm3 (0.04 m3), pressure is 15 MPa, then the amount of oxygen in the cylinder is 0.04x15 = 6 m3.
Figure 1 — Oxygen cylinder
At the welding station, the oxygen cylinder is installed in a vertical position and secured with a chain or clamp. To prepare an oxygen cylinder for operation, unscrew the cap and fitting plug, inspect the valve to determine if there is any grease or oil on it, carefully open the cylinder valve and blow through its fitting, then close the valve, inspect the union nut of the reducer, attach the reducer to the cylinder valve , set the operating oxygen pressure with the adjusting screw of the gearbox. When you finish withdrawing gas from the cylinder, you must ensure that the residual pressure in it is not less than 0.05-0.1 MPa.
When handling oxygen cylinders, it is necessary to strictly observe operating and safety rules, which is due to the high chemical activity of oxygen and high pressure. When transporting cylinders to the welding site, you must firmly remember that it is prohibited to transport oxygen cylinders together with flammable gas cylinders. If the oxygen cylinder valve freezes, you need to warm it up with a rag soaked in hot water.
The reasons for the explosion of oxygen cylinders may be contact with fat or oil on the valve, falling or hitting the cylinders, the appearance of a spark when too much gas is drawn off (the neck of the cylinder is electrified), heating of the cylinder by some heat source, as a result of which the gas pressure in the cylinder will become higher than permissible.
Table 1 - Types of cylinders for liquefied gases
| Cylinder type | Pressure, MPa | Tensile strength, MN/m2 | Relative extension, % | ||
| conditional | hydraulic | pneumatic | |||
| 100 | 10 | 15,0 | 10 | 650 | 15 |
| 150 | 15 | 22,5 | 15 | 650 | 15 |
| 200 | 20 | 30,0 | 20 | 650 | 15 |
| 150L | 15 | 22,5 | 15 | 900 | 10 |
| 200L | 20 | 30,0 | 20 | 900 | 10 |
Features of oxygen as a chemical substance: what you need to know when providing storage
Handling any substances, including oxygen, requires a person to strictly adhere to established safety rules. Contact with oil and fat components is therefore unacceptable, since interaction with them will inevitably lead to ignition and subsequent heating of the container and contents, followed by an explosion. Organic materials such as peat and wood are also explosive if they are soaked in liquid oxygen. That is why during storage or transportation the valve is protected by a safety cap, which, in turn, is screwed onto the outer ring located at the neck. It is important to know in advance the volume of the oxygen cylinder in m3 in order to prepare all the necessary conditions for its storage, since safety precautions require compliance with special rules and regulations for this.
Thus, the volume of an oxygen cylinder used in different areas of human activity may be different, since the consumption of this substance is different. In enterprises it will be significantly higher than in medicine or in everyday life. That is why containers from 0.3 liters to 100-150 liters are produced, so that each area can find the optimal volume for itself and use it effectively in its daily work.
Acetylene cylinders
Powering gas welding and cutting stations with acetylene acetylene cylinders is now widespread They have the same dimensions as the oxygen one. An acetylene cylinder is filled with a porous mass of activated charcoal (290-320 g per 1 dm3 of cylinder capacity) or a mixture of coal, pumice and infusorial earth. The mass in the cylinder is impregnated with acetone (225-300 g per 1 dm3 of cylinder capacity), in which acetylene dissolves well. Acetylene, dissolving in acetone and being in the pores of the porous mass, becomes explosion-proof and can be stored in a cylinder under a pressure of 2.5-3 MPa. The porous mass must have maximum porosity, behave inertly towards the metal of the cylinder, acetylene and acetone, and not produce sediment during operation. Currently, (GOST 6217-74) with a grain size from 1 to 3.5 mm is used as a porous mass Acetone (chemical formula CH3COCH3) is one of the best acetylene solvents; it impregnates the porous mass and dissolves it when filling cylinders with acetylene. Acetylene delivered to consumers in cylinders is called dissolved acetylene.
Figure 2 - Acetylene cylinder
The maximum acetylene pressure in the cylinder is 3 MPa. The pressure of acetylene in a fully filled cylinder changes with temperature:
| Temperature, °C | -5 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 |
| Pressure, MPa | 1,34 | 1,4 | 1,5 | 1,65 | 1,8 | 1,9 | 2,15 | 2,35 | 2,6 | 3,0 |
The pressure of filled cylinders should not exceed 1.9 MPa at 20°C.
When the valve of the cylinder is opened, acetylene is released from the acetone and enters in the form of a gas through the reducer and hose into the burner or cutter. Acetone remains in the pores of the porous mass and dissolves new portions of acetylene during subsequent fillings of the cylinder with gas. To reduce acetone losses during operation, it is necessary to keep acetylene cylinders in a vertical position. At normal atmospheric pressure and 20°C, 28 kg (l) of acetylene are dissolved in 1 kg (l) of acetone. The solubility of acetylene in acetone increases approximately in direct proportion with increasing pressure and decreases with decreasing temperature.
To fully utilize the cylinder capacity, it is recommended to store empty acetylene cylinders in a horizontal position , as this promotes uniform distribution of acetone throughout the entire volume, and with the valves tightly closed. When acetylene is removed from the cylinder, it carries away some of the acetone in the form of vapor. This reduces the amount of acetylene in the cylinder during subsequent fillings. To reduce the loss of acetone from the cylinder, acetylene must be withdrawn at a rate of no more than 1700 dm3/h.
To determine the amount of acetylene , the cylinder is weighed before and after filling with gas and the amount of acetylene in the cylinder in kg is determined from the difference.
Example. The mass of the cylinder with acetylene is 89 kg, empty - 83 kg, therefore, the amount of acetylene in the cylinder is equal to: by weight - 89-83 = 6 kg, by volume - 6/1.09 = 5.5 m3 (1.09 kg/m3 - density of acetylene at atmospheric pressure and temperature 20°C).
The mass of an empty acetylene cylinder consists of the mass of the cylinder itself, the porous mass and acetone. When taking acetylene from a cylinder, 30-40 g of acetone per 1 m3 of acetylene is consumed along with the gas. When removing acetylene from a cylinder, it is necessary to ensure that the residual pressure in the cylinder is at least 0.05-0.1 MPa.
The use of acetylene cylinders instead of acetylene generators provides a number of advantages : compactness and ease of maintenance of the welding installation, safety and improved working conditions, increased productivity of gas welders. In addition, dissolved acetylene contains fewer impurities than acetylene obtained from acetylene generators.
The reasons for the explosion of acetylene cylinders can be sudden shocks and impacts, strong heating (over 40°C).
Scope of use
Compressed oxygen is a popular gas, the scope of which depends on the type of raw material. The medical substance is used during the resuscitation of patients. The element has a beneficial effect on the heart and lungs, so therapeutic procedures are often prescribed for health problems. The component is taken to saturate cocktails during oxygen starvation.
Technical gas heats up quickly and maintains high temperatures for a long time. The resulting continuous jet burns through metal of any density, which allows you to cut or solder parts. The characteristic is useful both in construction and in domestic use. In metallurgy, the substance increases the efficiency of furnaces, thereby improving the quality of the finished product.
Cylinders for pronan-butane
Propane-butane cylinders are manufactured in accordance with GOST 15860-84 welded from sheet carbon steel. The main application was found in cylinders with a capacity of 40 and 50 dm3. Propane-butane cylinders are painted red with the word “propane” written in white.
A cylinder for propane-butane is a cylindrical vessel 1, to the top of which a neck 5 is welded, and to the bottom - a bottom 2 and a shoe 3. A brass valve 6 is screwed into the neck. Backing rings 4 are pressed onto the cylinder body. A cap is used to protect the cylinder valve 7.
The cylinders are designed for a maximum pressure of 1.6 MPa. Due to the high coefficient of volumetric expansion, cylinders for liquefied gases are filled to 85-90% of the total volume. for propane cylinders 24 kg of liquid propane-butane is poured into a cylinder with a capacity of 55 dm3. The maximum gas extraction should not exceed 1.25 m3/h.
Figure 3 — Prop-butane cylinder
Equipment
The main additional element of the oxygen tank is the valve. It is made from brass. A protective cap must be installed over the valve; it can be aluminum or plastic. Usually the cap comes as an integral part. But they are often lost, so the protective device can be made from any material with your own hands. Reliability and tightness are important here. The valve is screwed into the cylinder itself using a conical thread
The second most important element is the shoe. It is on him that the entire weight load falls. It is made from steel strip, which is shaped into a square cross-section. GOST does not define exactly how it should be fixed to the cylinder, so some manufacturers weld it, others press it in.
Storage and transportation of cylinders
Transportation of cylinders is permitted only on spring vehicles, as well as on special hand carts or stretchers. When transporting containers without containers, the following requirements must be met:
- All cylinders must have safety caps screwed on completely;
- oxygen cylinders must be placed in wooden sockets (it is allowed to use metal linings with sockets covered with rubber or other soft materials);
- oxygen cylinders should only be laid across the body of the car so that the safety caps are on one side; it is allowed to lay cylinders within the height of the sides;
- cylinders must be loaded by workers who have undergone special training.
Transportation of oxygen and acetylene cylinders in a vertical position is allowed only in special containers. The combined transportation of oxygen and acetylene cylinders on all types of transport is prohibited, with the exception of transporting two cylinders on a special trolley to the workplace. In summer, cylinders should be protected from sunlight with a tarpaulin or other covering. Cylinders within the workplace may be moved by tilting in an inclined position. At workplaces, cylinders must be firmly secured in a vertical position.
Requirements for marking gas cylinders according to GOST R ISO 14175
In order not to be misleading, we clarify that this marking has nothing to do with the data that must be indicated on the spherical part of each cylinder in accordance with regulatory documents for equipment operating at excess pressure (the date of the next technical inspection, the mark of the organization that carried out technical examination, etc.).
So, each vessel or gas cylinder must have a tag or label attached to it, which must contain the following information:
- name of manufacturer or supplier
- trademark
- gas designation according to standard
- health warnings
- safety warning
Main settings
The liquid substance oxygen is colored blue; when it freezes, it changes to blue . O2 dissolves better than all gases in water and does not form oxides with inert gases, so similar mixtures are used in industry.
The physical properties are:
- The composition in the air is up to 21%.
- In the gaseous state it has no color, smell or taste.
- Dissolves in organic substances, absorbed by coal and metals in powder form.
- Boils when frozen below -183 0 C.
- The density under normal conditions is 0.0014 g/cm 3 .