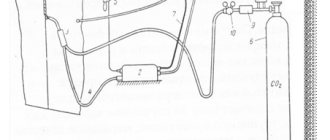
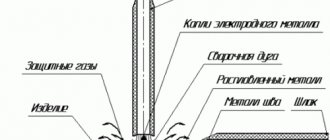
§ 45. Electric and gas welder of the 2nd category
Characteristics of the work . Manual oxygen cutting and cutting of lightweight and heavy steel scrap with petrol and kerosene cutting devices. Manual arc, plasma, gas, automatic and semi-automatic welding of simple parts, assemblies and structures made of carbon steel. Oxygen and plasma straight and curved cutting in the lower and vertical position of a metal weld, as well as simple and medium complexity parts made of carbon steel by manual marking, on portable stationary and plasma cutting machines. Tacking of parts, products, structures in all spatial positions. Preparation of products, assemblies and joints for welding. Cleaning seams after welding and cutting. Ensuring protection of the reverse side of the weld during gas shielded welding. Surfacing of simple parts. Elimination of cavities and cracks in simple parts, assemblies, castings. Heating of structures and parts during straightening. Reading simple drawings. Preparing gas cylinders for use. Maintenance of portable gas generators.
Must know: the structure and operating principle of serviced electric welding machines and devices for arc welding of alternating and direct current, gas welding and gas cutting equipment, gas generators, electric welding automatic and semi-automatic machines, oxygen and acetylene cylinders, reducing devices and welding torches; rules for using used burners, reducers, cylinders; methods and basic techniques of tack welding; forms of cutting a seam for welding; rules for ensuring protection when welding in shielding gas; types of welded joints and types of seams; rules for preparing the edges of products for welding; types of grooves and designation of welds in the drawings; basic properties of electrodes, welding metal and alloys, gases and liquids used in welding; permissible residual gas pressure in cylinders; purpose and brands of fluxes used in welding; purpose and conditions of use of instrumentation; causes of defects during welding and ways to prevent them; characteristics of gas flame; scrap dimensions according to the state standard.
Work examples
1. Transformer tanks - lining the walls for automatic welding.
2. Cradle beams, spring bars and bolsters for all-metal cars and electric section cars - welding of reinforcing angles, guides and centering rings.
3. Guardrail shoes - cutting on a ship.
4. Rolled beams - welding of points, gripping strips along the markings.
5. Strikers and templates of steam hammers - fusion.
6. Axle-box, column and center bolts - fusing of excavation areas.
7. Details of the frames of the side awning - tack and welding.
8. Metal container parts - hot straightening.
9. Diaphragms of platform frames and metal gondola cars - welding of ribs.
10. Lots - welding.
11. Rivets - cutting heads.
12. Frames and parts of brake platforms of freight cars and window frames of passenger cars - welding.
13. Casings and fences, lightly loaded components of agricultural machines - welding.
14. Casings of oil pumps and filters of automobiles - surfacing of shells in castings.
15. Header brackets, brake control rollers - welding.
16. Brackets for attaching the muffler to the car frame - welding of cracks.
17. Brackets for fastening mining equipment - welding.
18. Brackets for subframes of dump trucks - welding.
19. Covers of undercar lighting gutters - welding.
20. Corner sheets of the inner and outer skin of the tram - welding of cuts.
21. Scrap steel for charge - cutting.
22. Spring pads and linings - welding.
23. Small flasks - welding of ears.
24. Steel flasks of small sizes - welding of ears.
25. Small steel and cast iron castings - elimination of cavities in untreated areas by melting.
26. Pallets for machines - welding.
27. Profits and flyers on steel castings up to 300 mm thick - cutting.
28. Frames of transformer tanks - welding.
29. Bed mattress frames, armored and rhombic mesh - welding.
30. Reception pipes - fusing of safety nets.
31. Car wing reinforcements - welding.
32. Hydraulic clamps for dump truck mechanisms - welding.
33. Non-critical foundations, small components made of low-carbon and low-alloy steels - semi-automatic welding on a rack.
§ 47. Electric and gas welder of the 4th category
Characteristics of the work . Manual arc, plasma and gas welding of medium complexity parts, assemblies, structures and pipelines made of structural steels, cast iron, non-ferrous metals and alloys and complex parts of assemblies, structures and pipelines made of carbon steel in all spatial positions of the weld. Manual oxygen, plasma and gas straight and shaped cutting and cutting with petrol cutting and kerosene cutting devices on portable, stationary and plasma cutting machines, in various positions of complex parts from various steels, non-ferrous metals and alloys according to markings. Oxygen flux cutting of parts made of high chromium and chromium-nickel steels and cast iron. Oxygen cutting of ship objects afloat. Automatic and mechanical welding of medium complexity and complex devices, components, pipeline structures made of various steels, cast iron, non-ferrous metals and alloys. Automatic welding of critical complex building and technological structures operating in difficult conditions. Manual electric arc air planing of complex parts made of various steels, cast iron, non-ferrous metals and alloys in various positions. Welding of cast iron structures. Surfacing of defects in complex machine parts, mechanisms, structures and castings for machining and test pressure. Hot straightening of complex structures. Reading drawings of various complex welded metal structures.
Must know: the design of various electric welding and gas-cutting equipment, automatic and semi-automatic machines, features of welding and electric arc planing on alternating and direct current; basics of electrical engineering within the scope of the work performed; types of defects in welds and methods for their prevention and elimination; basics of metal welding; mechanical properties of welded metals; principles for selecting welding modes based on instruments; brands and types of electrodes; methods for producing and storing the most common gases: acetylene, hydrogen, oxygen, propane-butane, used in gas welding; gas cutting process for alloy steel.
Work examples
1. Equipment, vessels and containers made of carbon steel, operating without pressure - welding.
2. Equipment and vessels for chemical and petrochemical industries: tanks, separators, vessels, etc. - cutting holes with beveled edges.
3. Pipeline shut-off valves made of non-ferrous metals and alloys under test pressure over 1.6 to 5.0 MPa (over 15.5 to 48.4 atm) - fusing of defects.
4. Transformer tanks - welding of pipes, welding of terminal boxes, cooler boxes, current installations and tank covers.
5. Rudder stocks, propeller shaft brackets - welding.
6. Cylinder blocks of automobile engines - fusing shells in castings.
7. Crankshafts - surfacing of journals.
8. Bronze and brass inserts - surfacing on steel bearings.
9. Fittings and boiler burner bodies - welding.
10. Parts made of stainless steel sheets, aluminum or copper alloys - gas-electric cutting with beveled edges.
11. Cast iron parts - welding, fusion with and without heating.
12. Parts made of sheet steel with a thickness of over 60 mm - manual cutting according to markings.
13. Parts and assemblies made of non-ferrous metals - welding followed by pressure testing.
14. Car retarders - welding and surfacing of components under operating conditions.
15. Cast iron gear teeth - welding.
16. Thin-walled products made of non-ferrous alloys (air cooler covers, bearing shields, turbogenerator fans) - welding with brass or silumin.
17. Large cast iron products: frames, pulleys, flywheels, gears - fusing of shells and cracks.
18. Hydraulic turbine impeller chambers - welding and surfacing.
19. Blast furnace structures (casings, air heaters, gas pipelines) - cutting with beveled edges.
20. Frames of industrial furnaces and boilers - welding.
21. Crankcases of large engines and mechanical transmission housings of diesel locomotives - welding.
22. Lower engine crankcases - welding.
23. Coils of poles of electric machines made of strip copper - welding and welding of jumpers.
24. Gas exhaust manifolds and pipes - welding.
25. Hydraulic turbine control rings - welding and surfacing.
26. Housings and axles of the header drive wheels - welding.
27. Compressor casings, low and high pressure cylinders of air compressors - crack fusion.
28. Rotor housings with a diameter of up to 3500 mm - welding.
29. Stop valve housings for turbines with power up to 25,000 kW - welding.
30. Brush holder housings, reverse segments, electric motor rotors - welding.
31. Fastening and supports for pipelines - welding.
32. Brackets and fastenings for diesel locomotive pivot bogies - welding.
33. Sheets of large thickness (armor) - welding.
34. Masts, drilling and production rigs - welding in workshop conditions.
35. Aluminum furniture - welding.
36. Fundamental plates of large electrical machines - welding.
37. Struts, axle shafts of aircraft landing gear - welding.
38. Heaters - welding of a cage, a water-heating pipe with a cage, cone, rings and flanges.
39. Bearings and liners for axle boxes, drawbars - fusion along the frame and fusion of cracks.
40. Pistons of pneumatic hammers - fusing of shells and cracks.
41. Dust-gas-air ducts, fuel supply units and electric precipitators - welding.
42. Spool frames, pendulums - welding.
43. Porthole frames made of aluminum alloys - welding.
44. Conveyor frames - welding.
45. Air tanks for trolleybuses - welding.
46. Tanks for petroleum products with a capacity of less than 1000 cubic meters. m - welding.
47. Rail butt joints - welding under operational conditions.
48. Rails and prefabricated crosspieces - fusing ends.
49. Single and twisted metal mesh for pulp and paper production - soldering of ends with silver solder.
50. Crusher beds - welding.
51. Welded-cast frames and housings of electrical machines - welding.
52. Cast iron beds of large machine tools - welding.
53. Beds of working stands of rolling mills - surfacing.
54. Stators of air-cooled turbogenerators - welding.
55. Tubes for sensors with a radioactive isotope - fusing.
56. Pipe elements of boilers, armor plates, etc. - hot edit.
57. Pipelines of external and internal water supply and heating networks - welding during installation.
58. Pipelines of external and internal low-pressure gas supply networks - welding in workshop conditions.
59. Drill pipes - welding of couplings.
60. Technological pipelines of category 5 - welding.
61. Fachwerks, connections, lanterns, purlins, monorails - welding.
62. Complex cutters and dies - welding and deposition of high-speed cutters and hard alloys.
63. Brass refrigerators - welding of seams for hydrotesting at pressures up to 2.5 MPa (24.2 atm.).
64. Cylinders of car blocks - fusing of shells.
65. Car tanks - welding.
66. Balls, floats and tanks made of special aluminum alloys - welding.
Electric and gas welder ETKS
Section "Welding works"
Electric and gas welder 2nd category
Characteristics of the work .
1. Manual oxygen cutting and cutting of lightweight and heavy steel scrap with petrol and kerosene cutting devices. 2. Manual arc, plasma, gas, automatic and semi-automatic welding of simple parts, assemblies and structures made of carbon steels. 3. Oxygen and plasma straight and curved cutting in the lower and vertical position of a metal weld, as well as simple and medium-complexity parts made of carbon steel by manual marking, on portable stationary and plasma cutting machines. 4. Tacking of parts, products, structures in all spatial positions. 5. Preparation of products, assemblies and joints for welding. 6. Cleaning seams after welding and cutting. 7. Ensuring protection of the reverse side of the weld during gas-shielded welding. 8. Surfacing of simple parts. 9. Elimination of cavities and cracks in simple parts, assemblies, castings. 10. Heating of structures and parts during straightening. 11. Reading simple drawings. 12. Preparing gas cylinders for use. 13. Maintenance of portable gas generators.
Must know:
— design and principle of operation of serviced electric welding machines and devices for arc welding of alternating and direct current, gas welding and gas cutting equipment, gas generators, electric welding automatic and semi-automatic machines, oxygen and acetylene cylinders, reducing devices and welding torches; — rules for using the burners, reducers, and cylinders used; — methods and basic techniques of tack welding; — forms of cutting a seam for welding; — rules for ensuring protection when welding in shielding gas; — types of welded joints and types of seams; — rules for preparing the edges of products for welding; — types of grooves and designation of welds on the drawings; — basic properties of electrodes, welding metal and alloys, gases and liquids used in welding; — permissible residual gas pressure in cylinders; — purpose and brands of fluxes used in welding; — purpose and conditions of use of instrumentation; — causes of defects during welding and ways to prevent them; - characteristics of the gas flame; — scrap dimensions according to the state standard.
Work examples.
1. Transformer tanks - lining the walls for automatic welding. 2. Cradle beams, spring bars and bolsters for all-metal cars and electric section cars - welding of reinforcing angles, guides and centering rings. 3. Guardrail shoes - cutting on a ship. 4. Rolled beams - welding of points, gripping strips along the markings. 5. Strikers and templates of steam hammers - fusion. 6. Axle-box, column and center bolts - fusing of excavation areas. 7. Details of the frames of the side awning - tack and welding. 8. Metal container parts - hot straightening. 9. Diaphragms of platform frames and metal gondola cars - welding of ribs. 10. Lots - welding. 11. Rivets - cutting heads. 12. Frames and parts of brake platforms of freight cars and window frames of passenger cars - welding. 13. Casings and fences, lightly loaded components of agricultural machines - welding. 14. Casings of oil pumps and filters of automobiles - surfacing of shells in castings. 15. Header brackets, brake control rollers - welding. 16. Brackets for attaching the muffler to the car frame - welding of cracks. 17. Brackets for fastening mining equipment - welding. 18. Brackets for subframes of dump trucks - welding. 19. Covers of undercar lighting gutters - welding. 20. Corner sheets of the inner and outer skin of the tram - welding of cuts. 21. Scrap steel for charge - cutting. 22. Spring pads and linings - welding. 23. Small flasks - welding of ears. 24. Steel flasks of small sizes - welding of ears. 25. Small steel and cast iron castings - elimination of cavities in untreated areas by melting. 26. Pallets for machines - welding. 27. Profits and flyers on steel castings up to 300 mm thick - cutting. 28. Frames of transformer tanks - welding. 29. Bed mattress frames, armored and rhombic mesh - welding. 30. Reception pipes - fusing of safety nets. 31. Car wing reinforcements - welding. 32. Hydraulic clamps for dump truck mechanisms - welding. 33. Non-critical foundations, small components made of low-carbon and low-alloy steels - semi-automatic welding on a rack.
Electric and gas welder 3rd category
Characteristics of work.
1. Manual arc, plasma, gas welding, automatic and semi-automatic welding of simple parts, assemblies and structures made of structural steels, non-ferrous metals and alloys and medium complexity parts, assemblies, structures and pipelines made of carbon steel in all weld positions, except for the ceiling. 2. Oxygen plasma straight and curved cutting in various positions of metals, simple and medium complexity parts made of carbon and alloy steels, non-ferrous metals and alloys by manual marking on portable, stationary and plasma cutting machines in all positions of the weld. 3. Manual oxygen cutting and cutting with petrol and kerosene cutting devices to specified sizes, releasing non-ferrous metal waste and preserving or cutting out components and parts of the machine. 4. Manual arc air planing of simple and medium complexity parts made of various steels, cast iron, non-ferrous metals and alloys in various positions. 5. Surfacing of cavities and cracks in parts, assemblies and castings of medium complexity. 6. Preliminary and accompanying heating when welding parts in compliance with the specified mode. 7. Reading drawings of varying complexity of parts, assemblies and structures.
Must know:
— installation of serviced electric welding and plasma cutting machines, gas welding equipment, automatic, semi-automatic and plasma torch; — requirements for the weld seam and surfaces after air planing; — methods for selecting electrode grades depending on steel grades; - properties and importance of electrode coatings; — structure of the weld; — methods of testing them and types of control; — rules for preparing parts and assemblies for welding and welding; — rules for selecting a metal heating mode depending on the grade of metal and its thickness; — causes of internal stresses and deformations in welded products and measures to prevent them; — basic technological techniques for welding and surfacing parts made of various steels, cast iron, non-ferrous metals and alloys; — cutting mode and gas consumption for oxygen and gas-electric cutting.
Work examples.
1. Fittings made of tin bronze and silicon brass under test pressure up to 1.6 MPa (15.5 atm.) - fusing of defects. 2. Beater and cutting drums, front and rear axles of a tractor trailer, drawbar and frame of a combine and header, augers of a header, rake and reel - welding. 3. Sidewalls, transition platforms, footboards, frames and skins of railway cars - welding. 4. Balancers for spring suspension of rolling stock - cutting according to the markings manually. 5. Raid buoys and barrels, artillery shields and pontoons - welding. 6. Crankshafts of engines and cam shafts of cars - welding of defective semi-finished forgings with special steels. 7. Electrical machine shafts - welding of journals. 8. Silencers - welding. 9. Internal combustion engines (fuel and air systems) - welding. 10. Car parts (oil heater neck, gearbox housing, crankcase cover) - fusing of defects. 11. Parts made of sheet steel up to 60 mm thick - manual cutting according to markings. 12. Parts of the body frame of freight cars - welding. 13. Details of the rocker mechanism - fusing holes. 14. Bronze brake discs - fusing shells. 15. Workpieces for manual or automatic electric arc welding - cutting without bevel. 16. Frames for switchboards and control panels - welding. 17. Track rollers - welding. 18. Assembled casings, heating boilers - welding. 19. Casings of elastic couplings - welding. 20. Truck brake pads, casings, rear axle axle shafts - welding. 21. Structures, components, parts for gun mounts - welding. 22. Housings of electrical explosive equipment - welding. 23. Lifting cranes - fusing of slopes. 24. Dump truck bodies - welding. 25. Rear axles of cars - surfacing of shells in castings. 26. Car radiator lining - welding cracks. 27. Level regulator floats (fittings) - welding. 28. Projectors - welded to the ship’s hull. 29. Profits, sprues for castings of complex configuration with a thickness of over 300 mm - cutting. 30. Frames of the locomotive's drawbars - surfacing. 31. Profile window frames of the driver’s cab - welding. 32. Pantograph frames - welding. 33. Diesel locomotive frames - welding of conductors, flooring sheets, parts. 34. Tanks for non-flammable liquids and brake systems of rolling stock - welding. 35. Shaped cutters and simple dies - welding. 36. Bulkhead shaft seals - welding of the housing and pressure sleeve. 37. Small machine beds - welding. 38. Racks, bunker grates, transition platforms, stairs, railings, decking, boiler casing - welding. 39. Rear wheel hubs, rear axle and other car parts - ductile iron soldering. 40. Joints and grooves of sections, deck partitions, partitions - automatic welding on a rack. 41. Ventilation pipes - welding. 42. Copper gas exhaust pipes - welding. 43. Smoke pipes up to 30 m high and ventilation pipes made of carbon steel sheets - welding. 44. Connected smoke pipes in boilers and steam superheater pipes - welding. 45. General purpose pipes - bevel cutting. 46. Brake pipes - welding. 47. Non-pressure pipelines for water (except main ones) - welding. 48. Pipelines of external and internal water supply and heating networks - welding in workshop conditions. 49. Car tanks - automatic welding. 50. Brass gasifier balls (open) - fusing. 51. Gears - fusing of teeth.
Electric gas welder 4th category
Characteristics of work.
1. Manual arc, plasma and gas welding of medium complexity parts, assemblies, structures and pipelines made of structural steels, cast iron, non-ferrous metals and alloys and complex parts of assemblies, structures and pipelines made of carbon steels in all spatial positions of the weld. 2. Manual oxygen, plasma and gas straight and shaped cutting and cutting with petrol cutting and kerosene cutting devices on portable, stationary and plasma cutting machines, in various positions of complex parts from various steels, non-ferrous metals and alloys according to markings. 3. Oxygen-flux cutting of parts made of high-chromium and chromium-nickel steels and cast iron. 4. Oxygen cutting of ship objects afloat. 5. Automatic and mechanical welding of medium complexity and complex devices, components, pipeline structures made of various steels, cast iron, non-ferrous metals and alloys. 6. Automatic welding of critical complex building and technological structures operating in difficult conditions. 7. Manual electric arc air planing of complex parts made of various steels, cast iron, non-ferrous metals and alloys in various positions. 8. Welding of cast iron structures. 9. Surfacing of defects in complex machine parts, mechanisms, structures and castings for machining and test pressure. 10. Hot straightening of complex structures. 11. Reading drawings of various complex welded metal structures.
Must know:
— arrangement of various electric welding and gas-cutting equipment, automatic and semi-automatic devices, features of welding and electric arc planing on alternating and direct current; — basics of electrical engineering within the scope of the work performed; — types of defects in welds and methods for their prevention and elimination; — basics of metal welding; — mechanical properties of welded metals; — principles for selecting welding modes based on instruments; — brands and types of electrodes; — methods for producing and storing the most common gases: acetylene, hydrogen, oxygen, propane-butane, used in gas welding; — process of gas cutting of alloy steel.
Work examples.
1. Equipment, vessels and containers made of carbon steel, operating without pressure - welding. 2. Equipment and vessels for chemical and petrochemical industries: tanks, separators, vessels, etc. - cutting holes with beveled edges. 3. Pipeline shut-off valves made of non-ferrous metals and alloys under test pressure over 1.6 to 5.0 MPa (over 15.5 to 48.4 atm) - fusing of defects. 4. Transformer tanks - welding of pipes, welding of terminal boxes, cooler boxes, current installations and tank covers. 5. Rudder stocks, propeller shaft brackets - welding. 6. Cylinder blocks of automobile engines - fusing shells in castings. 7. Crankshafts - surfacing of journals. 8. Bronze and brass inserts - surfacing on steel bearings. 9. Fittings and boiler burner bodies - welding. 10. Parts made of stainless steel sheets, aluminum or copper alloys - gas-electric cutting with beveled edges. 11. Cast iron parts - welding, fusion with and without heating. 12. Parts made of sheet steel with a thickness of over 60 mm - manual cutting according to markings. 13. Parts and assemblies made of non-ferrous metals - welding followed by pressure testing. 14. Car retarders - welding and surfacing of components under operating conditions. 15. Cast iron gear teeth - welding. 16. Thin-walled products made of non-ferrous alloys (air cooler covers, bearing shields, turbogenerator fans) - welding with brass or silumin. 17. Large cast iron products: frames, pulleys, flywheels, gears - fusing of shells and cracks. 18. Hydraulic turbine impeller chambers - welding and surfacing. 19. Blast furnace structures (casings, air heaters, gas pipelines) - cutting with beveled edges. 20. Frames of industrial furnaces and boilers - welding. 21. Crankcases of large engines and mechanical transmission housings of diesel locomotives - welding. 22. Lower engine crankcases - welding. 23. Coils of poles of electric machines made of strip copper - welding and welding of jumpers. 24. Gas exhaust manifolds and pipes - welding. 25. Hydraulic turbine control rings - welding and surfacing. 26. Housings and axles of the header drive wheels - welding. 27. Compressor casings, low and high pressure cylinders of air compressors - crack fusion. 28. Rotor housings with a diameter of up to 3500 mm - welding. 29. Stop valve housings for turbines with power up to 25,000 kW - welding. 30. Brush holder housings, reverse segments, electric motor rotors - welding. 31. Fastening and supports for pipelines - welding. 32. Brackets and fastenings for diesel locomotive pivot bogies - welding. 33. Sheets of large thickness (armor) - welding. 34. Masts, drilling and production rigs - welding in workshop conditions. 35. Aluminum furniture - welding. 36. Fundamental plates of large electrical machines - welding. 37. Struts, axle shafts of aircraft landing gear - welding. 38. Heaters - welding of a cage, a water-heating pipe with a cage, cone, rings and flanges. 39. Bearings and liners for axle boxes, drawbars - fusion along the frame and fusion of cracks. 40. Pistons of pneumatic hammers - fusing of shells and cracks. 41. Dust-gas-air ducts, fuel supply units and electric precipitators - welding. 42. Spool frames, pendulums - welding. 43. Porthole frames made of aluminum alloys - welding. 44. Conveyor frames - welding. 45. Air tanks for trolleybuses - welding. 46. Tanks for petroleum products with a capacity of less than 1000 cubic meters. m - welding. 47. Rail butt joints - welding under operational conditions. 48. Rails and prefabricated crosspieces - fusing ends. 49. Single and twisted metal mesh for pulp and paper production - soldering of ends with silver solder. 50. Crusher beds - welding. 51. Welded-cast frames and housings of electrical machines - welding. 52. Cast iron beds of large machine tools - welding. 53. Beds of working stands of rolling mills - surfacing. 54. Stators of air-cooled turbogenerators - welding. 55. Tubes for sensors with a radioactive isotope - fusing. 56. Pipe elements of boilers, armor plates, etc. - hot edit. 57. Pipelines of external and internal water supply and heating networks - welding during installation. 58. Pipelines of external and internal low-pressure gas supply networks - welding in workshop conditions. 59. Drill pipes - welding of couplings. 60. Technological pipelines of category 5 - welding. 61. Fachwerks, connections, lanterns, purlins, monorails - welding. 62. Complex cutters and dies - welding and deposition of high-speed cutters and hard alloys. 63. Brass refrigerators - welding of seams for hydrotesting at pressures up to 2.5 MPa (24.2 atm.). 64. Cylinders of car blocks - fusing of shells. 65. Car tanks - welding. 66. Balls, floats and tanks made of special aluminum alloys - welding.
Electric and gas welder 5th category
Characteristics of work.
1. Manual arc, plasma and gas welding of various complexity of devices, parts, assemblies, structures and pipelines made of various steels, cast iron, non-ferrous metals and alloys, designed to work under dynamic and vibration loads and under pressure. 2. Manual arc and plasma welding of complex building and technological structures operating in difficult conditions. 3. Oxygen and plasma straight and horizontal cutting of complex parts from various steels, non-ferrous metals and alloys according to manual markings with cutting edges for welding, including the use of special fluxes from various steels and alloys. 4. Oxygen cutting of metals under water. 5. Automatic and mechanical welding of complex devices, components, structures and pipelines made of various steels, non-ferrous metals and alloys. 6. Automatic welding of building and technological structures operating under dynamic and vibration loads. 7. Mechanized welding of complex building and technological structures operating in difficult conditions. 8. Manual electric arc air planing of complex parts made of various steels, cast iron, non-ferrous metals and alloys in various positions. 9. Welding of block structures in all spatial positions of the weld. 10. Welding and surfacing of cracks and cavities in thin-walled products and in products with hard-to-reach places for welding. 11. Heat treatment of welded joints with a gas torch after welding. 12. Reading drawings of varying complexity of welded spatial metal structures.
Must know:
— electrical circuits and designs of various welding machines, automatic, semi-automatic and power supplies; — technological properties of welded metals, including high-alloy steels, as well as deposited metal and metal being planed; — selection of technological sequence for applying welds; — the influence of heat treatment on the properties of the weld, rules for cutting metals under water.
Work examples.
1. Embrasures of blast furnaces - surfacing of shells and cracks. 2. Equipment and vessels made of carbon steels operating under pressure and alloy steels operating without pressure - welding. 3. Fittings for open hearth furnaces - welding during repair of existing equipment. 4. Reinforcement of load-bearing reinforced concrete structures (foundations, columns, floors, etc.) - welding. 5. Pipeline shut-off valves made of tin bronze and silicon brass - surfacing under test pressure over 5.0 MPa (48.4 atm.). 6. Tanks of unique powerful transformers - welding, including welding of lifting hooks, jacking brackets, stainless steel plates operating under dynamic loads. 7. Beams and traverses of crane trolleys and balancers - welding. 8. Span beams of bridge cranes with a lifting capacity of less than 30 tons - welding. 9. Center beams, buffer beams, pivot beams, frames of locomotive bogies and wagons - welding. 10. Cylinders, caps, spheres operating in a vacuum - welding. 11. Boiler drums with pressure up to 4.0 MPa (38.7 atm.) - welding. 12. Blocks of building and technological structures made of sheet metal (air heaters, scrubbers, blast furnace casings, separators, reactors, blast furnace flues, etc.) - welding. 13. Cylinder blocks and water manifolds of products - welding. 14. Large crankshafts - welding. 15. Lead baths - welding. 16. Gas tanks and tanks for petroleum products with a volume of 5000 cubic meters. m or more - welding in workshop conditions. 17. Gas and oil product pipelines - welding on a rack. 18. Parts of gas welding equipment - soldering with silver solders. 19. Parts of especially critical machines and mechanisms (charging devices of blast furnaces, propellers, turbine blades, rolls of rolling mills, etc.) - deposition with special, hard, wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials. 20. Parts of complex configurations of critical structures - cutting with cutting edges for welding without additional mechanical processing. 21. Ball and spherical bottoms - cutting oblique holes without subsequent machining. 22. Forged, stamped and cast parts of critical machines, mechanisms and structures (propellers, turbine blades, engine cylinder blocks, etc.) - fusing defects. 23. Red copper coils - welding. 24. Caissons for open-hearth furnaces operating at high temperatures - welding. 25. Caissons of open-hearth furnaces (hot repair) - internal surfacing. 26. Collectors of complex configuration consisting of 20 or more parts made of stainless and heat-resistant steel with testing for macrostructure and radiography - welding. 27. Columns, bunkers, rafter and sub-rafter trusses, beams, overpasses, etc. - welding. 28. Bellows-type expansion joints made of stainless steel - soldering. 29. Structures of radio masts, television towers and power line supports - welding in stationary conditions. 30. Housings of cutters, loading machines, coal combines and mine electric locomotives - welding. 31. Head housings, traverses, bases and other complex components of presses and hammers - welding. 32. Cast iron bodies, covers, tees, elbows, cylinders - fusing of defects. 33. Rotor housings with a diameter of over 3500 mm - welding. 34. Stop valve housings for turbines with power over 25,000 kW - welding. 35. Covers, stators and lining of hydraulic turbine blades - welding. 36. Masts, drilling and production derricks - welding during installation. 37. Bases made of high-alloy drill pipes for drilling rigs and three-diesel drives - welding. 38. Aluminum and bronze castings, complex and large - fusing of shells and cracks. 39. Support plates for walking excavators - welding. 40. Complex molds - welding in hard-to-reach places. 41. Frames and components of cars and diesel engines - welding. 42. Kingpin and diesel locomotive frames - welding. 43. Tanks for petroleum products with a capacity of 1000 and less than 5000 cubic meters. m - welding during installation. 44. Rotors of electrical machines - welding of short-circuited rings, rods, deposition. 45. Complex beds, aprons of large lathes - welding, fusion of cracks. 46. Joints of reinforcement outlets of elements of load-bearing prefabricated reinforced concrete structures - welding. 47. Pulse tubes for instrumentation and automation systems - welding. 48. Pipe elements of steam boilers with pressure up to 4.0 MPa (38.7 atm.) - welding. 49. Pipelines of external and internal low-pressure gas supply networks - welding during installation. 50. Pipelines of external and internal gas supply networks of medium and low pressure - welding during installation and in workshop conditions. 51. Technological pipelines of III and IV categories (groups), as well as steam and water pipelines of III and IV categories - welding. 52. Lead pipes - welding. 53. Assemblies of sub-engine frames and shock absorber cylinders of aircraft landing gear - welding. 54. Brass refrigerators - welding of seams for hydrotesting under pressure over 2.5 MPa (24.2 atm.). 55. Engine cylinders - fusing of internal and external jackets. 56. Tires, tapes, expansion joints for them made of non-ferrous metals - welding.
Electric gas welder 6th category
Characteristics of work.
1. Manual arc, plasma and gas welding of particularly complex devices, parts, assemblies, structures and pipelines made of various steels, cast iron, non-ferrous metals and alloys, designed to operate under dynamic and vibration loads and under high pressure. 2. Manual arc and gas-electric welding of building and technological structures operating under dynamic and vibration loads, and structures of complex configuration. 3. Automatic welding of various structures from alloyed special steels, titanium and other alloys on specially designed machines, multi-arc, multi-electrode machines and machines equipped with television, photoelectronic and other special devices, on automatic manipulators (robots). 4. Mechanized welding of devices, components, pipeline structures, building and technological structures operating under dynamic and vibration loads, when performing welds in the ceiling position and on a vertical plane. 5. Welding of experimental structures made of metals and alloys with limited weldability, as well as titanium and titanium alloys. 6. Welding of complex structures in block design in all spatial positions of the weld.
Must know:
— a variety of titanium alloys, their welding and mechanical properties; — kinematic diagrams of automatic and semi-automatic machines, basic design of electronic control circuits; — rules for training robots and rules for working with robotic systems; — types of corrosion and factors causing it; — methods of special testing of welded products and the purpose of each of them; — main types of heat treatment of welded joints; — basics of weld metallography.
Work examples.
1. Beams of working platforms of open-hearth shops, structures of bunkers and unloading platforms of metallurgical enterprises, crane beams for heavy-duty cranes, booms of walking excavators - welding. 2. Span beams for bridge cranes with a lifting capacity of 30 tons and above - welding. 3. Boiler drums with pressure over 4.0 MPa (38.7 atm.) - welding. 4. Air separation units for oxygen shops - welding of parts made of non-ferrous metals. 5. Gas tanks and tanks for petroleum products with a volume of 5000 cubic meters. m or more - welding during installation. 6. Main gas and oil product pipelines - welding during installation. 7. Parts and assemblies made of non-ferrous metals operating under pressure above 4.0 MPa (38.7 atm.) - welding. 8. Spherical and drop-shaped containers and coatings - welding. 9. Vacuum containers, caps, spheres and pipelines - welding. 10. Locks of drill pipes and couplings - double seam welding. 11. Working wheels of gas turbine compressors, steam turbines, powerful blowers - welding of blades and blades. 12. Ammonia synthesis columns - welding. 13. Structures made of light aluminum-magnesium alloys - welding. 14. Design of radio masts, television towers and power line supports - welding during installation. 15. Structures made of low-magnetic steels - welding. 16. Steam turbine boxes - welding and cladding of shells. 17. Stator housings of large turbogenerators with hydrogen and hydrogen-water cooling - welding. 18. Housings of heavy laser engines and presses - welding. 19. Steam boilers - straightening the bottoms, welding critical components with a one-sided butt weld. 20. Feet and rustles of drill bits, drilling steam conductors - welding. 21. Rotor blades and turbine stators - soldering. 22. Oil and gas pipelines - welding to eliminate gaps. 23. Piping of oil and gas wells and peripheral filling wells - welding. 24. Wiring of pulse turbines and boilers - welding. 25. Tanks and structures made of two-layer steel and other bimetals - welding. 26. Reinforcement bars for reinforced concrete structures of split forms - welding. 27. Span structures of metal and reinforced concrete bridges - welding. 28. Pipe elements of steam boilers with pressure over 4.0 MPa (38.7 atm.) - welding. 29. Pressure pipelines, spiral chambers and impeller chambers of hydroelectric turbines - welding. 30. Pipelines for external gas supply networks of medium and high pressure - welding during installation. 31. Technological pipelines of categories I and II (groups), as well as steam and water pipelines of categories I and II - welding.
§ 48. Electric and gas welder of the 5th category
Characteristics of the work . Manual arc, plasma and gas welding of various complexity of devices, parts, assemblies, structures and pipelines made of various steels, cast iron, non-ferrous metals and alloys, designed to work under dynamic and vibration loads and under pressure. Manual arc and plasma welding of complex building and technological structures operating in difficult conditions. Oxygen and plasma linear and horizontal cutting of complex parts from various steels, non-ferrous metals and alloys according to manual markings with cutting edges for welding, including the use of special fluxes from various steels and alloys. Oxygen cutting of metals under water. Automatic and mechanical welding of complex devices, components, structures and pipelines made of various steels, non-ferrous metals and alloys. Automatic welding of building and technological structures operating under dynamic and vibration loads. Mechanized welding of complex building and technological structures operating in difficult conditions. Manual electric arc air planing of complex parts made of various steels, cast iron, non-ferrous metals and alloys in various positions. Welding of structures in block design in all spatial positions of the weld. Welding and surfacing of cracks and cavities in thin-walled products and in products with hard-to-reach places for welding. Heat treatment of welded joints with a gas torch after welding. Reading drawings of varying complexity of welded spatial metal structures.
Must know: electrical circuits and designs of various welding machines, automatic, semi-automatic and power supplies; technological properties of welded metals, including high-alloy steels, as well as deposited metal and metal being planed; selection of technological sequence for applying welds; the influence of heat treatment on the properties of the weld, rules for cutting metals under water.
Work examples
1. Embrasures of blast furnaces - surfacing of shells and cracks.
2. Equipment and vessels made of carbon steels operating under pressure and alloy steels operating without pressure - welding.
3. Fittings for open hearth furnaces - welding during repair of existing equipment.
4. Reinforcement of load-bearing reinforced concrete structures (foundations, columns, floors, etc.) - welding.
5. Pipeline shut-off valves made of tin bronze and silicon brass - surfacing under test pressure over 5.0 MPa (48.4 atm.).
6. Tanks of unique powerful transformers - welding, including welding of lifting hooks, jacking brackets, stainless steel plates operating under dynamic loads.
7. Beams and traverses of crane trolleys and balancers - welding.
8. Span beams of bridge cranes with a lifting capacity of less than 30 tons - welding.
9. Center beams, buffer beams, pivot beams, frames of locomotive bogies and wagons - welding.
10. Cylinders, caps, spheres operating in a vacuum - welding.
11. Boiler drums with pressure up to 4.0 MPa (38.7 atm.) - welding.
12. Blocks of building and technological structures made of sheet metal (air heaters, scrubbers, blast furnace casings, separators, reactors, blast furnace flues, etc.) - welding.
13. Cylinder blocks and water manifolds of products - welding.
14. Large crankshafts - welding.
15. Lead baths - welding.
16. Gas tanks and tanks for petroleum products with a volume of 5000 cubic meters. m or more - welding in workshop conditions.
17. Gas and oil product pipelines - welding on a rack.
18. Parts of gas welding equipment - soldering with silver solders.
19. Parts of especially critical machines and mechanisms (charging devices of blast furnaces, propellers, turbine blades, rolls of rolling mills, etc.) - deposition with special, hard, wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials.
20. Parts of complex configurations of critical structures - cutting with cutting edges for welding without additional mechanical processing.
21. Ball and spherical bottoms - cutting oblique holes without subsequent machining.
22. Forged, stamped and cast parts of critical machines, mechanisms and structures (propellers, turbine blades, engine cylinder blocks, etc.) - fusing defects.
23. Red copper coils - welding.
24. Caissons for open-hearth furnaces operating at high temperatures - welding.
25. Caissons of open-hearth furnaces (hot repair) - internal surfacing.
26. Collectors of complex configuration consisting of 20 or more parts made of stainless and heat-resistant steel with testing for macrostructure and radiography - welding.
27. Columns, bunkers, rafter and sub-rafter trusses, beams, overpasses, etc. - welding.
28. Bellows-type expansion joints made of stainless steel - soldering.
29. Structures of radio masts, television towers and power line supports - welding in stationary conditions.
30. Housings of cutters, loading machines, coal combines and mine electric locomotives - welding.
31. Head housings, traverses, bases and other complex components of presses and hammers - welding.
32. Cast iron bodies, covers, tees, elbows, cylinders - fusing of defects.
33. Rotor housings with a diameter of over 3500 mm - welding.
34. Stop valve housings for turbines with power over 25,000 kW - welding.
35. Covers, stators and lining of hydraulic turbine blades - welding.
36. Masts, drilling and production derricks - welding during installation.
37. Bases made of high-alloy drill pipes for drilling rigs and three-diesel drives - welding.
38. Aluminum and bronze castings, complex and large - fusing of shells and cracks.
39. Support plates for walking excavators - welding.
40. Complex molds - welding in hard-to-reach places.
41. Frames and components of cars and diesel engines - welding.
42. Kingpin and diesel locomotive frames - welding.
43. Tanks for petroleum products with a capacity of 1000 and less than 5000 cubic meters. m - welding during installation.
44. Rotors of electrical machines - welding of short-circuited rings, rods, deposition.
45. Complex beds, aprons of large lathes - welding, fusion of cracks.
46. Joints of reinforcement outlets of elements of load-bearing prefabricated reinforced concrete structures - welding.
47. Pulse tubes for instrumentation and automation systems - welding.
48. Pipe elements of steam boilers with pressure up to 4.0 MPa (38.7 atm.) - welding.
49. Pipelines of external and internal low-pressure gas supply networks - welding during installation.
50. Pipelines of external and internal gas supply networks of medium and low pressure - welding during installation and in workshop conditions.
51. Technological pipelines of III and IV categories (groups), as well as steam and water pipelines of III and IV categories - welding.
52. Lead pipes - welding.
53. Assemblies of sub-engine frames and shock absorber cylinders of aircraft landing gear - welding.
54. Brass refrigerators - welding of seams for hydrotesting under pressure over 2.5 MPa (24.2 atm.).
55. Engine cylinders - fusing of internal and external jackets.
56. Tires, tapes, expansion joints for them made of non-ferrous metals - welding.
§ 49. Electric and gas welder of the 6th category
Characteristics of the work . Manual arc, plasma and gas welding of particularly complex devices, parts, assemblies, structures and pipelines made of various steels, cast iron, non-ferrous metals and alloys, designed to operate under dynamic and vibration loads and under high pressure. Manual arc and gas-electric welding of building and technological structures operating under dynamic and vibration loads, and structures of complex configuration. Automatic welding of various structures from alloyed special steels, titanium and other alloys on specially designed machines, multi-arc, multi-electrode machines and machines equipped with television, photoelectronic and other special devices, on automatic manipulators (robots). Mechanized welding of devices, components, pipeline structures, building and technological structures operating under dynamic and vibration loads, when performing welds in the ceiling position and on a vertical plane. Welding of experimental structures made of metals and alloys with limited weldability, as well as titanium and titanium alloys. Welding of complex structures in block design in all spatial positions of the weld.
Must know: types of titanium alloys, their welding and mechanical properties; kinematic diagrams of automatic and semi-automatic machines, basic design of electronic control circuits; rules for training robots and rules for working with robotic systems; types of corrosion and factors causing it; methods of special testing of welded products and the purpose of each of them; main types of heat treatment of welded joints; Fundamentals of weld metallography.
Work examples
1. Beams of working platforms of open-hearth shops, structures of bunkers and unloading platforms of metallurgical enterprises, crane beams for heavy-duty cranes, booms of walking excavators - welding.
2. Span beams for bridge cranes with a lifting capacity of 30 tons and above - welding.
3. Boiler drums with pressure over 4.0 MPa (38.7 atm.) - welding.
4. Air separation units for oxygen shops - welding of parts made of non-ferrous metals.
5. Gas tanks and tanks for petroleum products with a volume of 5000 cubic meters. m or more - welding during installation.
6. Main gas and oil product pipelines - welding during installation.
7. Parts and assemblies made of non-ferrous metals operating under pressure above 4.0 MPa (38.7 atm.) - welding.
8. Spherical and drop-shaped containers and coatings - welding.
9. Vacuum containers, caps, spheres and pipelines - welding.
10. Locks of drill pipes and couplings - double seam welding.
11. Working wheels of gas turbine compressors, steam turbines, powerful blowers - welding of blades and blades.
12. Ammonia synthesis columns - welding.
13. Structures made of light aluminum-magnesium alloys - welding.
14. Design of radio masts, television towers and power line supports - welding during installation.
15. Structures made of low-magnetic steels - welding.
16. Steam turbine boxes - welding and cladding of shells.
17. Stator housings of large turbogenerators with hydrogen and hydrogen-water cooling - welding.
18. Housings of heavy laser engines and presses - welding.
19. Steam boilers - straightening the bottoms, welding critical components with a one-sided butt weld.
20. Feet and rustles of drill bits, drilling steam conductors - welding.
21. Rotor blades and turbine stators - soldering.
22. Oil and gas pipelines - welding to eliminate gaps.
23. Piping of oil and gas wells and peripheral filling wells - welding.
24. Wiring of pulse turbines and boilers - welding.
25. Tanks and structures made of two-layer steel and other bimetals - welding.
26. Reinforcement bars for reinforced concrete structures of split forms - welding.
27. Span structures of metal and reinforced concrete bridges - welding.
28. Pipe elements of steam boilers with pressure over 4.0 MPa (38.7 atm.) - welding.
29. Pressure pipelines, spiral chambers and impeller chambers of hydroelectric turbines - welding.
30. Pipelines for external gas supply networks of medium and high pressure - welding during installation.
31. Technological pipelines of categories I and II (groups), as well as steam and water pipelines of categories I and II - welding.
Regulatory regulation of the work of an electric welder for manual welding
This document was approved back in 1985 by a special Resolution of the USSR State Committee for Labor and Labor and the Secretariat of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions numbered 31/3-30.
Today, this document is a list of existing working specialties and positions for which certain qualification requirements are imposed. The use of ETKS is necessary for the following purposes:
- to determine the rules of tariffs for workers working in certain positions in the national economy;
- to determine the level of qualification requirements that are established for a specific employee in order to determine his suitability for the position he occupies;
- to verify the correct name of the position held by a specific employee of the organization;
- to determine the content of programs used in advanced training courses for workers in a certain field.
The activities of a manual electric welder are also regulated by this Handbook.
In accordance with the assigned category, the activities of a manual welder are regulated by paragraphs 55 to 59 of this handbook.
Based on the indicated paragraphs of the Handbook, electric welders of manual welding are divided into categories from the second to the sixth, each of which affects how an employee with a certain category assigned to him should carry out his activities.