Investments : from 1,930,000 rubles
Payback : from 8 months
The construction sector and everything connected with it is considered the most promising for business. There is a constant demand for such materials. For example, for electrodes that are necessary for welding work. Their production is technologically simple and does not require large financial investments. No special licenses or permits are required for implementation. Products can be certified on a voluntary basis. How to succeed in this business and what is needed to produce this material, you will learn from this article.
Video description
Explanation of electrode designations.
Below we will talk about the classification of electrode elements, their purpose and properties.
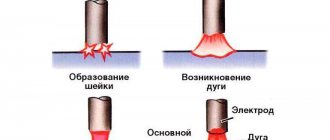
The purpose of the metal rod is to fuse the material being welded to a specific place where the workpiece is joined. The main part of the electrode serves to conduct current through itself. The end of the consumable melts under the influence of the elevated temperature of the welding arc. At the moment of melting of the end of the electrode, a complete product is formed together with the molten structure.
What does a consumable electrode consist of?
The welding electrode has a simple structure. Its main component is the rod; a special coating is made on the outside. The end that melts and comes into contact with the material being welded is made without coating.
What is this method
Electrodes for electric arc welding have a great influence on the release of a sufficient amount of heat necessary to melt the metal of the welded products, so their correct selection and proper use play a big role.
An electrode is a metal rod coated on the outside with a coating that is a special composition. During the welding process, the electrode core begins to melt. The metals of the rod and the product, being in a molten state, together form a joint. When burned, the coating releases a gas necessary to protect the welding zone from the negative influence of surrounding oxygen and nitrogen. Electrodes for arc welding solve a number of important problems.
The substances included in the coating have a low ionization potential. The consequence of this is that the arc, after its ignition, is saturated with ions that are in a free state. This stabilizes the arc burning process.
The coating takes part in the formation of slag on top of the weld, which reduces the rate at which the molten metal cools. This creates good conditions for removing impurities and non-metallic inclusions from the seam, which impair the quality of the joint.
Electrode coatings contain deoxidizers whose job is to react with oxygen, causing it to bind. With the help of electrodes, the metal forming the weld is alloyed, which improves its properties. This is ensured by substances included in the coating, such as silicon, chromium, manganese, and titanium.
Type of rods and explanation of electrode markings
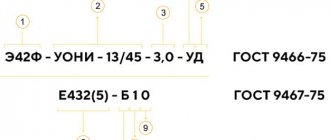
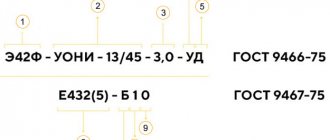
Any container in which welding rods are packaged has an alphanumeric coding, for example: E50A-UONI – 13/55 – 5.0 – UD / E514 (4) – B20
Marking of rods Source bsm21.ru
Electrodes, their markings
The first digits of the designation in our illustrative example indicate the type of rod. E50A - consumables that can be used for welding steel reinforced and non-reinforced metal. To make the abbreviation easier to understand, it is recommended to break it down into its components:
- E - rod is used for welding on an arc machine.
- 50 is the maximum value of the connection strength.
In our sample, this parameter is 50 kgf per 1 sq. mm.
- A – the joint has load toughness and good flexibility.
From this sample it is clear that it is possible to understand the decoding of the electrodes; it cannot be considered a difficult task. If you have an explanation at hand of what the digital and alphabetic signs mean, any beginner will understand.
Stripping the coating
Immediately after crimping, the electrodes enter the stripping machine. Here both ends are cleared of coating:
- one - for securing it in the electric holder during welding;
- the other is to ensure electrical contact with the product.
After cleaning, defect control is carried out again.
MEZNZH-13 (NAKS) Current - constant reverse polarity (plus on the electrode)
RUR 828.36 ? with VAT per 1 kg.
NIAT-5 Current - constant reverse polarity
RUB 2,625.48 ? with VAT per 1 kg.
OZL - 25B Current - constant reverse polarity (on the electrode plus)
RUB 5,454.60 ? with VAT per 1 kg.
ANP-13 Current - constant reverse polarity (plus on the electrode)
RUB 278.04 ? with VAT per 1 kg.
Welding rods: types and characteristics
To work with reinforced products, you need rods coded “E” and hardness codes indicated by numbers: 38, 42, 46, 50, 55, 60, 70, 85, 100, 125, 150; 42A, 46A, 50A.
In the case when it is necessary to connect types of steel products that are resistant to thermal effects, consumables coded E-09 and E-10 are used. Many types of electrodes are suitable for welding high-alloy metal, their number is more than 40. The most commonly chosen electrodes are: E-12X13, E-06X13N, E-10X17T, E-12X11NMF, E-12X11NMF.
To connect materials with previously known characteristics, the following electrodes are used: E-10G2, E-12G4, E-10G3, E-16G2KhM, E-15G5, E-30G2KhM, the total number of types is 38.
Application
Basic coated electrodes are excellent for use in the following applications:
- welding of mild steels with high sulfur content;
- steels with a high content of sulfur, carbon, phosphorus;
- welding of hardening steels, in which cold cracks can form;
- when welding low-alloy and high-alloy steels, which are used under heavy loads and high temperatures;
- if you need to weld parts of large thickness;
- when welding rigid structures.
Interpretation of welding electrodes
In an illustrative example, there is a UONI encoding - 13/55, which characterizes the brand of electrode. It is described in detail in the GOST section. Sometimes there is a designation patented by the manufacturer. Products of the OK group from the ESAB manufacturing brand are labeled in this way.
Electrode OK-46, d 3.0 ZAO ESAB-SVEL St. Petersburg Source molotok43.ru
Rod diameter
When deciphering the electrode markings, you can find digital symbols showing the cross-section of the consumable in mm. In the specified sample, this parameter is 5 mm. Based on this value, you need to know an important circumstance: the greater the thickness of the material being welded, the higher this parameter should be.
Purpose
In the representative sample, the letter “U”, placed almost at the end of the marking, indicates the choice of a consumable suitable for welding work with structures made of unreinforced steel raw materials, having a hardness limit of about 60 kgf per 1 mm2. When it is necessary to work with metal products with other parameters, then other symbols must be used, for example, “L”. Other letters:
- “B” is used for welding work on workpieces characterized by unusual qualities.
- "N" - for surfacing.
The letter "T" indicates that the rods are suitable for welding heat-resistant metal products.
Coating density parameter
The next letter after U is the letter code D, located in the representative sample, indicating how thick the coating layer is made. In our case, this layer is quite thick. In addition to D, the electrodes also have other letters: “M” - a slightly thick surface, closer to thin, “C” - medium size, “G” - impressive thickness.
Electrodes by thickness Source userdocs.ru
Manufacturers of welding electrodes
The Russian consumables market offers a wide selection of electrodes produced by domestic manufacturers. The technological capacity of production allows us to meet the needs of individuals and enterprises in various fields of activity.
Russian electrode manufacturers are divided into 3 categories:
- Large production facilities that supply the bulk of customers with materials.
- .
- Small businesses that manufacture products to meet their own needs.
We list several manufacturing companies producing electrodes:
- SVEL - Altai welding electrode plant.
A modern facility producing a wide range of coated products.
- Belorechensky electrode.
Welding materials are produced in accordance with state standards, and the products are certified.
- "Electrode-Boron".
Manufactures universal welding electrodes.
The products of Russian manufacturers are in demand in various fields of activity and are actively purchased not only in stores in our country, but also abroad.
Types of welding materials
Electrodes used in manual arc welding are divided into:
- Non-melting.
They are made from different types of materials that differ in their refractoriness: tungsten, graphite, coal. Designed to ignite and maintain the welding arc. The joints between the workpieces are filled with additives created by manually applying a consumable that melts.
- Melting.
This type of electrode melts during welding operations on the surface of the structure. Made from steel, cast iron, copper or other metal. The specific type of raw material depends on the material. The rod performs the function of an additive and also plays the role of a cathode or anode. There are electrodes coated and uncoated.
Getting the coating
The main function of the coating (coating) is to protect the weld pool from oxygen, which is destructive to the metal. The composition of the coating materials depends on the type of electrodes. All materials used undergo input control for the content of basic elements and impurities.
Preparation is carried out as follows:
- lump materials are crushed into large and medium pieces;
- then they are finely crushed in disintegrators and ball mills;
- particles are sifted through special sieves;
- Ferroalloy particles are passivated by aging in air or using heat treatment. An oxide film forms around each particle, preventing it from reacting with the binder (liquid glass) when preparing the coating mass;
- materials are dosed in a certain proportion and thoroughly mixed until a homogeneous mass is formed;
- a binder is prepared - a solution of liquid glass (sodium silicate, potassium silicate, potassium-sodium silicate, less often lithium silicate);
- The binder is added to the prepared dry mixture, and the coating mixture is mixed.
The mass has a very thick consistency, reminiscent of moist, loose soil.
TML-1U (NAKS) Current - constant, reverse polarity (on the electrode plus)
RUR 226.68 ? with VAT per 1 kg.
UONI-13/85 Current - constant, reverse polarity (on the electrode plus)
RUB 258.24 ? with VAT per 1 kg.
MEZNZH-13 (NAKS) Current - constant reverse polarity (plus on the electrode)
RUR 828.36 ? with VAT per 1 kg.
MEZOZL-6 (NAKS) Current - constant reverse polarity (plus on the electrode)
RUR 813.84 ? with VAT per 1 kg.
According to welding current parameters
Rods with a cross section of 4 mm. are selected for welding on simple welding devices. They are also used on the most productive and powerful units.
The length of this consumable is 35 and 45 cm. Suitable for welding thin workpieces up to 1 cm. Operates at a current of 220A. Welding consumables with a cross section from 5 to 12 mm. used only in welding work in the presence of additional lighting created by powerful lighting installations.
Aluminum rod FoxWeld AL Мg 5 (ER-5356) 1.6 mm 5 kg Source yandex.ru
Storage
Storing electrodes is a topic that for some reason many people avoid. And in vain. After all, a beginner can follow the welding technology and generally weld correctly, but the weld will be of poor quality due to the fact that the storage conditions have been violated. And the welder, due to his inexperience, will blame everything on a bad welding machine, inconvenient working conditions, or any other reasons.
Yes, if stored incorrectly, electrodes can indeed significantly deteriorate the quality of the finished welded joint. And all because of the moisture that the electrodes actively absorb. For this reason, it is not recommended to store electrodes in damp, stuffy areas, such as basements. Also, do not store electrodes on the ground, even if they are in a box. And don't use storage boxes at all. Replace them with a special case. You don’t have to buy it; you can make it yourself from a section of HDPE pipe.
After all, the box is just a package of electrodes; it is not intended for long-term storage in a garage or on mezzanines. Try to ensure that there are no strong temperature changes in the room. This is obvious, but many people leave electrodes in an unheated garage all winter and then wonder why the rods crumble or why the arc doesn't strike.