How to properly assemble a cutter with cylinders (oxygen + propane), what is the order of preparatory work? Please tell me a good cutter model.
MAYAK-2-01 gas welding cutter
To work correctly with such equipment, theory alone will not be enough. Before you start, you definitely need to practice at positions with specialists who have experience. Wrong actions can even lead to a tragic accident. Safety precautions should come first here.
Torch Basics
The cutting process with a gas cutter occurs by burning the metal in a stream of oxygen supplied under pressure.
The alloy must first be heated to the required operating temperature using a burning mixture of acetylene and oxygen. The only metals that can be cut using this method are various grades of carbon and non-alloy steel. Stainless steel, non-ferrous metals and alloys cannot be cut with an oxygen-acetylene cutter. To perform this type of work, in addition to the appropriate set of gas equipment, you will need the following:
- Fire extinguisher.
- Protective equipment: special glasses; thick leather gloves; sturdy work shoes with leather soles.
- Appropriate clothing – fire-resistant clothing is recommended, but if not available, well-fitting cotton clothing will do. You should not wear items made of synthetic or flammable fabrics, loose fit, or with torn or worn edges.
- Tools for measuring and marking: ruler, square and pencil made from soapstone.
- Lighter for gas cutter - designed to properly ignite the flame of the cutter. Using regular matches and lighters is very dangerous.
Rules to follow when cutting
According to safety regulations, there are several main rules for cutting containers in which gaseous substances were previously stored. You need to know how to properly cut a gas cylinder before starting work - this is very important! To perform the necessary actions, you will need:
- the gas cylinder itself is, of course, empty;
- hacksaw for metal work;
- construction funnel;
- bucket;
- watering hose;
- grinder with protective kit.
After all the tools are prepared, you can read the information or watch a video on how to cut a gas cylinder with a grinder in order to do all the work quickly and efficiently.
Preparing a place and conditions for safe and comfortable work
To ensure safe work using a cutting torch, you must follow the following rules and recommendations:
- To perform the work, choose only a place in a perfectly ventilated room or in the open air.
- You can cut away from flammable substances and materials.
- The floor in the room should be concrete or earthen.
- The surface of the earth or concrete must be cleared of any foreign objects and materials within a radius of at least 5 m, since sparks from the metal being cut scatter over several meters and can set fire to dry rags, shavings, paper, dried plants or leaves.
- The metal to be cut is placed on a suitable support so that the cutter can be used at a comfortable working height. For these purposes, it is best to use a steel table.
- Do not allow the flame to touch the concrete (especially if it is fresh) - this will cause its expansion and subsequent intense cracking with small fragments of concrete flying out of it.
- It is strictly forbidden to use flammable surfaces as workers, or on which flammable or explosive materials are spilled.
- The location of the metal cut is marked as shown in the video.
How to cut a gas cylinder with a grinder
After an old propane gas cylinder has become unusable, do not rush to throw it away. In some cases, it can be used to make various products with your own hands, for which it is often cut. This process is characterized by quite a large number of features, which we will discuss in more detail later.
Preparing and setting up gas cutting equipment
In order to work safely with a gas cutter, it is important not only to correctly select the appropriate set of equipment, but also to connect and configure it correctly. First, the corresponding tubes are connected to the oxygen and acetylene cylinders. Oxygen hoses and containers are usually green, acetylene hoses are red.
Safety valves (a device that delays flashback flames) should be installed at both ends of the hoses.
The next step is to check that the acetylene supply is working properly. First, close the flow control valve - the T-shaped handle is rotated back several times. On the cylinder, in its upper part, open the valve - turn it 1 turn of the hand. They do this for safety reasons. The acetylene pressure in the cylinder should not be allowed to exceed 1 atm - in case of high pressure, this gas becomes unstable and can even spontaneously explode or ignite. To check that the acetylene pressure is adjusted correctly, do the following:
- The main valve of the container is unlocked, then the control valve is opened by turning the handle in a clockwise direction. This must be done very slowly, monitoring the readings of the pressure gauge installed at the low pressure outlet. The control valve is opened until the pressure reaches 0.34–0.54 atm.
- Then blow air from the hose - open the acetylene valve of the cutter until the sound of escaping gas appears. After this, look at the readings of the low pressure gauge. When purging, the pressure value should be stable (if not, then make sure that the regulator is installed correctly).
- The valve on the cutter is closed.
They check and adjust the oxygen supply - turn off the oxygen supply regulator (twist it down), and then adjust the pressure. To reduce the oxygen supply, twist the pressure gauge knob a few turns back. Then perform the following steps:
- The main valve on the oxygen cylinder is fully opened. It is double-seated and if it is partially opened, due to the high pressure in the cylinder (150 atm), oxygen escapes around the sealing ring of the valve stem connection.
- Slowly open the supply regulator, monitoring the readings of the pressure gauge installed at the low pressure outlet until the oxygen pressure is adjusted within the range of 1.7–2.7 atm.
- Blow out the atmosphere from a hose - open the oxygen valve on the cutter. The cutter has 2 valves for oxygen: one is closer to the hose, controls the flow into the chamber where oxygen is mixed with acetylene to heat the steel (burning the mixture), as well as for supply to the oxygen nozzle for cutting; the other is located further and supplies oxygen to a separate cutting nozzle (until this valve is opened or the special cutting lever is released, oxygen should not leave the cutter mouthpiece). First, the first valve is opened - it is turned several times, ensuring a sufficient flow of oxygen to carry out both functions. After this, open the second (front) valve slightly until the hose is cleared (3–5 s for a 7.5 m long tube).
- The front valve is closed.
What you should pay attention to?
Disassembling even an old gas cylinder requires special care from the master and consistency of all actions.
For novice craftsmen who have not yet had to deal with sawing a propane receiver, we have prepared some useful tips:
- the degree of severity of the smell of propane when rinsing the cylinder is an indicator of a high probability of fire or explosion;
- It is better to unscrew the cylinder valve away from living quarters;
- cutting a propane tank near a fire or any other source of fire is contraindicated;
- it is forbidden to stand in front of the gas outlet from the receiver, especially if there is a characteristic hissing sound;
- The markings on the cylinder should be marked in advance so as not to end up making mistakes with the calculations.
If there is a strong smell of propane, it is better to rinse the receiver again, and only then proceed to sawing off the valve.
If the smell is still pungent, it is better to postpone work for a few days and wait until it completely disappears.
Immediately after cutting, the container must be cleaned of old paint, and then thoroughly cleaned with sandpaper to create the most even surface possible.
The easiest way is to install a flap wheel on the grinder, which will facilitate the further process of surface treatment, including painting.
Ignition of the torch and heating of the metal
Before igniting the torch, you must:
- make sure that all connections (valves, pressure gauges, hoses, other fittings) are tight - any gas leak can instantly cause a fire;
- check the place of work again for the absence of flammable materials, strangers (especially children), and animals;
- make sure you are ready to work;
- Wear safety glasses and gloves.
Then the acetylene valve on the cutter is opened, allowing the oxygen in the mixing chamber to escape. A few seconds are enough for this. Then they tighten the valve until you can hear that acetylene is barely coming out. A special lighter for it is placed in front of the cutter, as shown in the video, so that its inner part touches the mouthpiece. Then press the lighter lever. When the sparks produced ignite the acetylene, a small yellow flame should form in front of the mouthpiece.
By tightening the gas supply valve, the flame length is increased to approximately 25 cm. The torch should start at the very mouthpiece of the cutter. The flame will come off or jump when too much acetylene is supplied.
Slowly open the front oxygen valve. In this case, the flame should change color from yellow to blue - at this moment, the supply of such an amount of oxygen will be provided, which is sufficient for the complete combustion of acetylene. The oxygen supply should be increased until the inner tongue of blue flame decreases and contracts towards the mouthpiece.
The oxygen valve is opened even further - the size of the torch is increased until the length of the internal flame becomes barely greater than the thickness of the steel being cut (for cold-rolled sheets with a thickness of 9.5 mm, it is enough to exceed the flame length by 1.3 mm). When you hear a "snuffing sound" or the blue flame appears feathery and unstable, there is too much oxygen being supplied. It is reduced until the entire flame stabilizes and the internal one takes the shape of a clear cone.
The very tip of the internal flame is brought to the surface of the steel being processed. It is heated until a pool of molten glowing metal forms at the point of contact. The tip of the flame must be kept motionless at a distance of approximately 10 mm from the surface of the steel as shown in the video, so that all the heat is concentrated in one area.
Cutting steel with a gas cutter
The handle of the gas cutting valve is slowly released down - a stream of oxygen is supplied, igniting the molten metal. If a violent reaction immediately begins to occur, then the steel has caught fire and you can continue to gradually increase the oxygen pressure until its stream cuts right through the material. When the reaction does not proceed, the metal is not heated enough to ignite in a stream of oxygen. It is necessary to add oxygen to the heating flame and allow it to heat the steel.
When the oxygen stream begins to cut, the cutter mouthpiece begins to slowly move along the cutting line. In this case, almost all processing products (molten slag, sparks) are blown away by a jet to the rear side of the cutting zone as shown in the video. If this flow comes back or slows down, then you need to reduce the speed of the cutter or stop it and heat the material even more (it is better to work very slowly than to try to cut too quickly). Cutting continues until the intended cut or separation of metal is completed.
Examples of using cut gas cylinders
Human invention provides many uses for such modified containers, for example:
- container for an artificial reservoir in the country;
- part of the autonomous heating system;
- barbecue/smokehouse/woodshed;
- hearth for forge/fireplace.
You can come up with other types for using cut gas cylinders. If you haven’t done this kind of work before, it’s best to find out in advance how to cut a gas cylinder; a video will be an ideal option because it will allow you not only to imagine, but to see the process as it should be.
Advantages and disadvantages
Cutting metal with propane has a number of advantages, among which are the following:
- Gas cutting is in demand in situations where there is a need to cut metal of considerable thickness or create products according to templates that require the production of a curved cut that cannot be made with a grinder. You also cannot do without a gas cutter even when faced with the task of cutting out a disk from thick metal or making a blind hole of 20-50 mm.
- A gas cutter is a very easy-to-use tool and is lightweight. All home craftsmen who have experience working with gasoline models are aware of the inconveniences associated with large weight, size and noise. In addition to the fact that vibration creates significant inconvenience, the operator is forced to provide serious pressure during operation. Gas models seem to be a more attractive alternative due to the absence of all the above-mentioned disadvantages.
- Using metal cutting with gas allows you to speed up the work by 2 times, which cannot be done using a device equipped with a gasoline engine.
- Among most gases, including gasoline, propane has a lower price. For this reason, it is better suited for carrying out a significant amount of work, for example, if there is a task of cutting steel into scrap metal.
- When using propane cutting, it is possible to create a narrower cut edge than when working with acetylene cutters. At the same time, the method under consideration allows you to create a cleaner cut than what can be done using gasoline torches or a grinder.
Among the disadvantages that propane cutters have, only one should be highlighted: they can only be used for a limited range of types of metals. They are suitable for cutting exclusively low and medium carbon steels, as well as ductile cast iron.
Features of use
Such tools are not suitable for cutting high-carbon steels for the reason that they have a fairly high melting point, which is almost the same as the flame temperature.
This leads to the fact that instead of the release of scale, which looks like a column of sparks, from the back side of the sheet, it mixes with the molten metal along the edges of the cut. As a result, oxygen cannot reach the thickness of the metal, which is why it fails to burn through the material. Difficulties when cutting cast iron are created by the shape of the grains, as well as the graphite between them. True, this does not apply to malleable cast iron. It is impossible to solve the problem if you have to deal with aluminum, copper and their alloys.
It is important to dwell on the following point: the category of low-carbon steels is represented by grades from 08 to 20G, medium-carbon steels - grades from 30 to 50G2. A characteristic feature of carbon steel grades is the presence of the letter U in front of their names.
What is the process of cutting metal with gas?
Gas cutting of metals is currently a fairly simple technology in which work occurs without the use of complex equipment and additional energy sources. This method is used by specialists to carry out work in agriculture, construction and various types of repairs. Equipment for gas cutting of metal is mobile and can be quickly transported for use at another facility.
Let's look at the basic principle of cutting with oxygen. First, the material is heated by a heater to an average temperature of +1,100 °C. After which oxygen begins to flow into the cutting zone, comes into contact with the hot surface and lights up. A stable supply of oxygen produces a powerful jet of burning gas that easily cuts sheet metal.
For successful gas cutting, it is necessary that the material has a combustion temperature lower than its melting temperature. Otherwise, it will be difficult to remove the molten metal from the cutting area, unlike burnt metal.
Consequently, we can conclude that metal cutting with gas occurs due to its burnout in the zone of action of the gas jet. The main piece of gas cutting equipment is the cutter. It creates a mixture of air and gas due to dosing and subsequent mixing of oxygen with liquid fuel vapors or gases. After which the cutter ignites the resulting mixture and additionally provides oxygen to the cutting area.
Gas cutting is one of the temperature methods of processing materials. Its advantage was its high productivity and the ability to process workpieces of almost any thickness. One welder can cut several tons of material per shift. Workers point to one of the main advantages - the ability to work regardless of energy sources. This is especially important when work is carried out in the field, where there is no power source.
We recommend articles on metalworking
- Steel grades: classification and interpretation
- Aluminum grades and areas of their application
- Defects in metal products: causes and search methods
There are exceptions to the list of metals that oxy-fuel cutting is used to work with: aluminum, stainless steel, copper and brass.
Cutting Features
The cutter must be moved smoothly along the cutting line and monitor the angle of inclination, which deviates 5-6 degrees against the movement of the tool. When the metal thickness is more than 0.95 m, the deflection is increased by cutting through the metal to a depth of about 20 mm, and the deflection angle decreases again. We have already explained in detail how to cut with a cutter so that the cut is even in the previous section.
How much gas is consumed?
Gas consumption when cutting metal with a propane-oxygen cutter depends on the thickness of the structure and the configuration of the cut. For clarity, we present the table below:
| Workpiece size (thickness), mm | Hole time, sec | Cut size (width), mm | Consumption, per m 3 cuts | |
| propane | oxygen | |||
| 4,0 | 5—8 | 2,5 | 0,035 | 0,289 |
| 10,0 | 8—13 | 3,0 | 0,041 | 0,415 |
| 20,0 | 13—18 | 4,0 | 0,051 | 0,623 |
| 40,0 | 22—28 | 4,5 | 0,071 | 1,037 |
| 60,0 | 25—30 | 5,0 | 0,087 | 1,461 |
Gas consumption is significantly reduced when surfacing or soldering is performed.
Nuances
The main task of the performer is to maintain the speed correctly:
- normal mode - sparks fly at right angles relative to the surface of the workpiece;
- low speed - flying away from the performer and an angle of less than 85 degrees.
After the process is completed, the oxygen supply is turned off first, and the propane is turned off last.
Negative deformation
Beginning welders are concerned with the question of how to properly use a propane-oxygen cutter so that warping of the surface of the part does not occur. First you need to figure out what factors contribute to the occurrence of these defects:
- with uneven heating of the surface;
- a high cutting speed was selected;
- there was a sharp cooling of the heating area.
To eliminate the occurrence of the listed factors on the workpieces, they are first securely fixed and heated, and the speed is increased gradually. If warping does occur, then the original shape can be returned by firing or tempering, and the sheets can be straightened on rollers.
Kickback hazard
If the jet burns in an incorrect mode, a bang occurs and the flame is drawn inside the product, which leads to an explosion, as the fire spreads through the hoses and reaches containers with gases. To prevent a dangerous situation, the cutter is equipped with a non-return valve, which cuts off the flame and prevents it from spreading.
Terms of use
They are similar to safety precautions when welding, but have specific additions:
- It is not recommended to neglect protective equipment, as this leads to injury in the form of skin burns or damage to the cornea of the eyes from flying sparks, so goggles and gloves with long bells up to the elbow are required.
- The performer's clothing and shoes are made of non-flammable material.
- Gas cylinders are located no closer than five meters from the cutting site.
- The flame of the cutter is directed only in the direction opposite to the hoses.
- Cutting is carried out in rooms equipped with strong ventilation or in open areas.
If the equipment is idle for a long time, it is necessary to carry out preventive maintenance before using the cutter for its intended purpose.
What gases are used for cutting metal
There are several methods for classifying gas cutting. It depends on the gases used and other features. From them you can choose the optimal one for performing a particular operation or task. For example, electric arc cutting with oxygen is possible if the equipment is connected to an electrical network. And it is more convenient to process low-carbon steel with a gas-air mixture with propane.
Among professionals, the most popular methods are:
- Propane cutting. Cutting metal with gas, for example, propane, as well as oxygen, is perhaps the most popular, but has its limitations. It is used for low-alloy and low-carbon steels, titanium alloys. If the material contains an alloying component or carbon in an amount of more than 1%, a different method is required. Cutting is also possible with other gases: acetylene, methane, etc.
- Air arc cutting. A fairly effective cutting method is oxygen-electric arc cutting. Melting occurs using an electric arc. The remaining melt is removed with an air jet. When performing the operation in this way, oxygen is supplied along the electrode. The disadvantages of this method include shallow cuts. However, they are compensated for by almost any width of the workpiece.
- Oxygen-flux cutting. Its feature is the supply of an additional component to the cutting zone - powdered flux. It allows the metal being processed to become more pliable during the flux-oxygen cutting process. This method is used for metals that form hard-melting oxides. During its application, an additional thermal effect is created, in which the gas jet effectively cuts the metal. Oxygen-flux metal cutting is used for processing copper and copper alloys, alloy steels, reinforced concrete and slagged metals.
- Spear cutting. This method is used to work with industrial process waste, large amounts of steel and emergency scrap. A special feature is the increasing speed of work. The technology involves the use of a high-energy gas jet, which leads to significant savings in steel spears. The speed of work increases with the rapid, complete combustion of the material being processed.
Gas consumption when cutting metal can be seen in the table:
The dependence of gas consumption on the volume of work is strongly influenced by the selected cutting method. The standards for cutting metal with gas when using the oxygen-flux method contain information about the incomparably lower use of gas than when using the air-arc method.
In addition to the processing method, the gas and oxygen consumption when cutting metal depends on a number of parameters, such as:
- welder qualifications - an inexperienced specialist will need more gas per meter of workpiece than a master;
- equipment parameters and its integrity;
- thickness and grade of metal from which the workpiece is made;
- cutting characteristics - width and depth.
The table below provides the information a technician needs when making a propane cut:
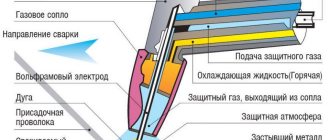
Basic design of a cutting torch
Design features of the cutter.
Injection or two-pipe cutter
This is the most popular model due to its design. The name “two-pipe” comes from the division of technical oxygen into two streams. This is done to functionally separate the work of oxygen.
The upper flow of oxygen flows at high speed through the nozzle of the internal mouthpiece. This is an extremely important part of the device - it is directly responsible for the metal cutting phase. This flow is regulated by a special valve, which is usually placed on the outer panel.
The second flow of oxygen goes straight to the injector. The operating procedure in the injector chamber is as follows: oxygen enters the chamber under high pressure and at high speed, as a result of which a rarefied pressure zone is formed in this space. Oxygen is injected in this case.
Nominal gas flow.
Through special side holes in the walls of the chamber, flammable gas is drawn into it - in this case it is ejected. The gases are mixed, the velocities are equalized, and as a result, a flow of a mixture of gases is formed at the exit from the chamber, the velocity of which is lower than that of the injected oxygen, but higher than that of the ejected combustible gas.
At the next stage, the formed mixture of gases enters the tip - first into its head, and then exits through the nozzle between the mouthpieces and forms the same flame in the form of a torch, which heats the metal to its combustion temperature. All gas flows are regulated by their own valves on the outside of the housing - for supplying oxygen and separately for supplying flammable gas to the injector.
Injectorless or three-pipe gas cutter
In this case, the device of the gas cutter is more complicated. Oxygen enters it through two tubes, and the third tube is rightfully occupied by flammable gas. In this welding torch, gases are mixed inside the head; there is no chamber here. This system is safer than the two-chamber model.
The fact is that there is no risk of the so-called “reverse strike”, which consists of a very unpleasant and dangerous phenomenon: the penetration of burning gases in the channels and tubes of the device in the opposite direction.
This model has a significantly higher cost. In addition to this drawback, the three-pipe cutter has one more nuance: when working with it, a very high pressure of flammable gas is required - higher than with an injection apparatus.
Oxygen-propane cutter
The process of dismantling metal structures will require the use of specialized tools. The preparation of parts is carried out by cutting; for this purpose, metal cutting is used both with a gas installation of propane-oxygen type and with other devices.
Mechanical devices are suitable for processing structures of small thickness; thick sheets are processed with a gas cutter. The operating principle of the installation is the same, regardless of the design.
Various technical specifications are described on how to use the mechanism correctly; it is necessary to comply with safety requirements and other features.
Oxygen-propane cutter
Operating principle and types
The principle of operation is based on supplying a pure stream of oxygen through the nozzle of a gas cutter. Regardless of the design features of the autogen, execution occurs due to the combustion of metal under the influence of a propane-oxygen environment. The main requirement for using the device is that the combustion temperature must be higher than melting, otherwise the material will melt and drain, which interferes with high-quality work.
Most steel alloys are not susceptible to the action of an oxygen-propane cutter, due to restrictions on the maximum proportion of alloyed impurities. The presence of carbon in the element can lead to unstable functioning or stop the process. The impact on metal occurs in several steps:
- The temperature rises to the point where the steel begins to burn. To obtain the required flame, pure ozone is mixed with the combustible mixture in the required proportions.
- After the zone is heated, both the heated steel is oxidized by the oxygen environment and materials are released from the processing area.
The classification of hand cutters is divided according to several parameters, depending on the type of work. Main characteristics:
- a type of flammable gas, methane, propane - butane, acetylene and others are used;
- power, parameter for obtaining a mixture for heating;
- The nozzle design, which affects the production of gas, is used both with injection systems and without injection.
Injection cutter-burner
Power is divided into several types, from low to high cutting power. With low power, products with a thickness of 3 to 100 mm are affected; with the medium type of installation, it is possible to cut materials up to 200 mm thick, and with high power – 300 mm. There are varieties capable of processing products up to 500 mm thick; such installations are used both in industry and in domestic settings. Some components of the characteristics depend not only on the power, but also on the design of the cutting torch.
Design
The most common type of device used in machining steel structures is the double-tube injection cutter. The combustible mixture is divided into several streams, which allows you to adjust the flame power to suit the work. The adjustment mechanism is located on the outer part of the body; there are lever-type devices.
The flow moves through the tube to the tip through the head, releasing at high speed through the central nozzle. The mouthpiece is responsible for the main functionality of the cutter, the cutting part of the process. Part of the gas is transferred to the injector, which, when released under high pressure, creates a vacuum, thereby connecting the combustible mixture. The mixing process determines the equalization of the flow rate by which the action is performed.
The formation of the mixture is carried out by the head of the tip, into which it enters through the lower tube. A torch is formed between the outer and inner mouthpiece, as a result of the formation of a flammable mixture. The two-channel system is equipped with control valves that allow you to adjust the supply of both oxygen and auxiliary gas to the injector.
Cutting torch design
The design without an injection type is more complex, since there are tubes for two flows of oxygen and separately for gas. The mixture of the flammable composition occurs directly inside the head; this design is considered safer. Operations will require higher supply pressures of both oxygen and flammable gases.
The dimensions of the cutters are fixed by GOST standards; for production with small parts, P1 models with a total length of no more than 50 cm are used. More powerful designs are produced longer in shape, there are specific elongated designs designed to perform tasks with difficult access to the cutting site.
Advantages and disadvantages
The gas burner is designed for cutting products in production conditions, with a large volume of tasks. Before using the device, it is important to understand what key features metal cutting with propane and oxygen has:
- The mechanism of action is convenient when making curved cutting lines. Stable power allows you to separate metal products of various thicknesses into parts. In situations where it is impossible to use a tool such as an angle grinder, a gas torch is used. The task of making a round product or a blind hole is performed with a gas torch without requiring much effort.
- A gas cutter has an advantage over gasoline models. In addition to being lightweight, the mechanism does not produce excessive noise during operation and is also compact.
- The use of a device based on the influence of flammable gas makes it possible to double the speed of execution, which is beyond the power of mechanical tools.
- Propane, as a liquid gas, has a low price. Therefore, it is used not only when processing products for production needs, but also when recycling metal and other activities.
- The use of propane as a flammable mixture allows for high-quality cutting. Cutting is carried out along a narrow line, which is the main factor in quality work.
Standards and dimensions
Welding using a welding torch with gas.
All standard measurements regarding gas cutters are specified in GOST 5191-79. Naturally, the weight and size of the devices are directly related to their power. Weight, for example, comes in only two sizes: the cutters of models P1 and P2 weigh 1.0 kg, and the high-power model P3 weighs 1.3 kg and not an gram more or less.
By the way, the type of combustible gas is also related to the power and size. If powerful P3 cutters operate only on a mixture of oxygen and propane, then smaller devices such as P1 and P2 can operate with any type of gas.
Insert gas cutters:
In addition to the classic models with different powers, there is a separate category - the so-called plug-in gas cutters with a special marking RV. According to GOST, they have a very strange name: tips for a gas torch for cutting metal. In general, they differ from traditional cutters: the mixing of the combustible mixture and oxygen is carried out at the tip itself.
These devices are much lighter in weight than cutters. PB1 weighs 0.6 kg, and PB2 and PB3 only 0.7 kg each. But don't let this apparent elegance fool you. Let's not forget that these are tips for the torch, complete with which they will weigh no less than conventional cutters. What is the advantage then?
The fact is that they can be purchased in addition to an existing burner and, thus, save some money. And the compactness of the entire set, packed in a special case. And one more important detail concerns the nature of flammable gas. The fact is that acetylene is much more expensive than propane.
But for metal welding, acetylene is much more desirable: a torch with it produces a flame with a temperature 400°C higher than the same one with a mixture of oxygen and propane.
Portable models: small ship – short voyage
Cutter device.
The market now offers many portable options for autogens - this is exactly how they are positioned. They are sold as an attachment for a compact collet gas cylinder. But in essence and the principle of operation, these are burners. Most of them provide a flame temperature no higher than 1300°C.
There are, of course, portable models of the “professional” range - collet cutters that produce a higher torch temperature - up to 2000 - 2500 ° C, which is generally close in performance to a classic oxygen-propane cutter. But physics is physics: even in these models there is no main component that cuts metal - an oxygen jet that oxidizes this very metal.
Where is a portable cutting torch good? When cutting easily fusible metals or alloys such as tin, brass, bronze, copper. But even these “children’s” options are not cut, but melted. Therefore, compact attachments - cutters are used more for soldering or welding small workpieces made of non-ferrous metals. These can be parts of household devices such as a refrigerator or air conditioner. Welding, not a cutter, in a word.
In any case, be careful when choosing such models; their proposed “portability” is not always justified in the end.
Examples of using cut gas cylinders
The parts of the cylinder can be used to achieve a variety of purposes. The following cases are examples:
- Furnace body.
- Containers for storing liquids.
- Grill.
- Smokehouse.
Gas cylinder stove
The scope of application is wide, but it is worth considering that the metal is not characterized by high corrosion resistance. An exception is a propane gas cylinder, which is coated with paint using a special technology.
Equipment
The main equipment for gas cutting is a cutter. The kit includes: a nozzle for welding and melting.
Thanks to the cutter, you can control the dosage of the gas mixture and oxygen. Also, with the help of this equipment, the flammable mixture is ignited and a flame is supplied to the processing site.
The cutter consists of two blocks: cutting and heating. The first is represented by an oxygen stream outlet tube, a valve and an internal type mouthpiece.
The heating block includes valves that are designed to regulate the pressure of the gas mixture and oxygen. There is also a supply tube, an external mouthpiece, a mixing chamber and an injection cell.
Cutters are either manual or machine. The latter are stationary, so for repair work it is preferable to use manual ones.
Additionally, the following gas cutting equipment is used:
- reducer – designed to reduce pressure;
- device for changing pressure;
- steel cylinder with gas and oxygen;
- connecting hoses.
Before using the equipment, it is important to check its serviceability in order to avoid explosion of the cylinder or reducer. The cutter is pre-purged with oxygen.
Is it possible for metal to deform?
Gas cutting involves a thermal effect on the material; as a result, deformation changes cannot always be avoided. Deformation consists of lengthening, shortening or bending of a product. The cut part can be turned inward or outward.
There are factors that contribute to metal deformation:
Oxygen cutting process diagram
- uneven heating;
- high flame speed;
- sudden cooling of the heating area.
It is necessary to exclude the effect of these factors, otherwise the resulting defect will have to be corrected. There are several simple ways that allow you to return the workpiece to the correct shape: use firing or tempering, apply steel straightening on rollers.
Deformation can be avoided if the product is pre-fixed and heated, the gas mixture flow rate is observed, and the correct cutting technology is followed. It is important to carry out all the steps sequentially and select the cutting mode based on the thickness and type of material. You cannot start processing with high gas mixture supply rates.
If you don’t have much experience, you should start working with small pieces, rather than cutting products from solid sheets.
Safety requirements
Gas equipment that is used in the process of cutting metals, namely an oxygen-acetylene cutter, is classified as explosive and flammable. Therefore, before using a gas cutter, you should follow all mandatory safety recommendations.
To do this, the workplace should be equipped with:
- fire extinguisher. The use of a gas cutter is accompanied by an open flame and high temperatures, so fire extinguishing equipment must be present at the post;
- protective clothing, consisting of: a cotton suit, if possible, impregnated with a fire retardant compound;
- gloves or leggings made of canvas or fairly thick leather;
- boot with leather sole;
- safety glasses with built-in light filters.
When working with a cutter, you should never wear clothing made from synthetics or other easily flammable fabrics, or that do not fit tightly to your body or have heavily worn edges. All this can lead to fire and, accordingly, danger to health and life.
Only various grades and types of unalloyed carbon steel can be cut with gas. Stainless steel, non-ferrous metals and various alloys cannot be cut with a propane cutter.
Using a gas receiver in cut form
Due to the massive connection of all houses to the gasification system, gas receivers have lost their popularity. That is why today many craftsmen have set out to make new designs from used cylinders that perform completely different functions.
The first thing that comes to mind when looking for options for using a gas receiver is a homemade potbelly stove. In this case, a propane cylinder is an ideal body for the stove, since the thickness of its walls is 3 mm, and this is just enough for safe operation.
Particularly popular is the grill made from a gas cylinder. To make such a mobile grill, you will need a simple cylinder, a burner from an old gas stove, a grill grate and a tray.
The internal coating of the housing allows you to safely cook food in the Dutch oven even with the lid closed. A gas grill made from a used receiver is ideal for a spacious summer cottage where you can gather a large group of friends.
From several cylinders you can build a real smokehouse with separate containers for cold and hot smoking, a barbecue and a grill compartment. The design can be adapted both for skewers and for grilles, which allows you to cook meat and fish in different ways. When making such a complex structure, you should understand the principle of operation of the smokehouse, so it is recommended to rely on the drawing.
The process of disassembling an old gas cylinder requires special care on the part of the master, since even a slight remaining gas inside the container, when interacting with a spark from an angle grinder, can provoke an explosion. The process of sawing a gas receiver is preceded by a preparatory stage, which includes releasing gas and filling the cylinder with water.
How to choose a better cutter?
Operating principle of a gas cutter.
We offer a block of useful information that will help you better navigate the specifications and technical characteristics of cutters in advance:
- Nipples are made of brass and aluminum. Brass options are more durable.
- If possible, choose models with aluminum rather than plastic handles. No matter how heat-resistant the plastic is, it will “float” in any case faster than aluminum.
- The handle should be quite massive: the diameter should be at least 40 mm.
- The valves should work well. This means turning without much effort.
- Lever-controlled devices are more convenient and economical to use, they save gas.
- Valve spindles must be made of stainless steel, and not brass, which is too short-lived. There are “combined” options; they occupy a middle position in terms of durability.
- The best materials for the cutter body are metals: brass, copper, stainless steel.
- We remember that acetylene cutters are more expensive. We monitor the material from which the parts that have direct contact with the flammable gas are made before mixing in the chamber. Attention! They should not be made of copper or its alloys, where the copper content is not less than 65%.
- If the design of the device is collapsible, this is better: it is easier to clean and repair.
- Only copper! Only copper outer mouthpiece!
- The correct internal mouthpiece for an acetylene-type cutting torch should also be made of copper. But in an oxygen cutter for metal it is made of brass. These are the nuances.
- Be sure to check with the seller the status of spare parts and consumables.
Advice from experienced people: how to use
Instructions on how to use a gas cutter can be divided into general provisions and professional “minor” notes, which in fact are the most valuable practical assistants.
Table of cutting metals with a gas cutter.
First the general points:
- Only with a mask! We carry out any work with any gas cutter only in a welder’s mask or special glasses. Working with an autogen is an activity with a sea of risks; safety precautions must be carried out for real and not childishly.
- We choose clothing and gloves with fire-resistant properties. If there are none, well: at least the minimum requirement is not to wear synthetic clothes.
- There must be a fire extinguisher at the workplace with all the correct expiration dates, etc. Fire extinguishing equipment must also be placed nearby in accordance with fire safety regulations.
- Before work you need to stock up:
- a ruler, a special pencil, a square and a tape measure;
- a special lighter, which is usually included with the equipment.
- When working, it is important to choose the right location. The torch flame must be located in front of the supply hoses. The hoses, in turn, should be positioned so that they do not interfere with you during the process.
- Another safety rule: gas cylinders should not be closer than 5 meters to you during operation.
- Ventilation should be excellent throughout cutting, preferably working outdoors.
- The floor in the workshop should be either concrete or earthen.
- If you haven't worked with your cutter for a long time, or are starting to use a new device, check the channels: they should be clean. In addition, always check the vacuum level in the chamber that is formed by oxygen. First, remove the propane hose - this must be done with the valves on both the cutter and the cylinder tightened. Then open the oxygen and gas valve on the cylinder at operating pressure. The injector is checked simply: put your finger on the gas nipple, if everything is correct, you will feel air being sucked into this nipple. Close the oxygen, all the valves and then connect the hose with flammable gas to the cutter: you can work.
Scheme of cutting metal with a cutter.
Stages of action during cutting, propane cutters:
- First, an oxygen cylinder: set the operating pressure.
- Then a cylinder with flammable gas: we also set the working pressure. The reference point is oxygen pressure. The propane pressure should be about ten times less. If the device is three-pipe, then the difference will be five times.
- Slowly open the oxygen and gas valve, ignite the gas and use the valves to create the pressure of the heating flame.
- The manual gas cutter is ready for work, now the actual cutting of the metal with the cutter.
- A stream of igniting oxygen begins to flow to the combustion site. If the metal is heated sufficiently, the desired reaction will begin immediately. In this case, the oxygen supply pressure can be further increased until the metal is completely cut through.
- Now the autogen can be moved in the desired direction - along the line of the planned cut. The speed of movement must be determined as you go, it will depend on how the sparks and slag flow or are blown down from the burner.
- After cutting, carefully inspect the work area for any remaining pieces of molten metal. God forbid you step on these - they will even burn through the thick soles of your boots.
- Cooling of parts is carried out either with water or naturally.
- After finishing cutting, you need to finish the work process, which is no less important than starting work.
- First we tighten the oxygen valve.
- The flame valves are closed next - the propane valve first, the oxygen valve next.
- We tighten the valves on the cylinders.
- We release the hoses from the gas: open and then alternately close the valves of the heating mixture on the device.
Sources
- https://tutmet.ru/polzovatsja-rezat-rabotat-gazovym-rezakom-nastrojka.html
- https://stanok.guru/oborudovanie/raznoe/rezka-metalla-kislorodno-propanovym-rezakom.html
- https://printeka.ru/metally/kak-pravilno-rezat-gazovym-rezakom-metall.html
- https://tutsvarka.ru/oborudovanie/gazovyj-rezak
- https://msmetall.ru/instrument/kak-rezat-relsy-rezakom.html
- https://WikiMetall.ru/oborudovanie/kak-polzovatsya-rezakom.html
How to cut a balloon safely
When making a gas cylinder from propane or other gas, fairly high quality metal is often used. That is why many are considering the possibility of cutting it to obtain blanks, which are later used to create various products. When considering how to cut a gas cylinder, it is recommended to pay attention to the following points:
- The body can be a good workpiece for making a stove, water tank or barbecue.
- Before actual work, the oxygen gas cylinder should be emptied, since the gas at its high concentration is not only flammable, but also explosive. Therefore, before cutting, you should check the filling level of the gas cylinder.
- As a rule, there are no significant problems with oxygen and carbon dioxide gas cylinders. This is due to the fact that ordinary iron is used in their manufacture.
- Propane gas tanks can cause some pretty serious problems. This is due to the fact that it is quite difficult to empty them completely; this requires preliminary preparation.
Gas cylinder explosion
Before you begin, you also need to prepare the required set of tools. As a rule, it can be found in almost any garage and workshop.