Pure copper is not used for the manufacture of products. It is used as ready-made alloys, the compositions of which are regulated by generally accepted standards. In Russia, the main regulation is GOST 859-2001. He describes in detail the grades and compositions of copper alloys, as well as the permissible areas of their use. Since copper is a non-ferrous metal with unique physical and chemical properties, it is actively used in industry, production, construction and domestic conditions. There is also a separate classification of copper scrap, which is purchased on the secondary market. Our company accepts copper at a price of 340 rubles per kg. Details about the conditions and costs of specific types of copper alloys are presented on the website.
Our prices for copper intake
| Type of copper | Price per kg, rub |
| Scrap copper glitter | 685-712 |
| A piece of copper | 675-706 |
| Copper mix | 660-692 |
| Scrap copper burner | 670-705 |
| Scrap tinned copper, burnt waste | 550-585 |
Copper. Discussion.
Konstruktor
, yes, of course, I think so too. if it is food grade copper, . Nowadays there is a lot of technical equipment, but somehow people lived without stainless steel Aptekar, 27 Aug. 09, 19:17
Last ed. 01 Sep. 09, 09:53 from Alexander555
Copper marking in Russian marks: the letter “M” is used to denote copper. Next are numbers showing the degree of purity in% (00-highly pure, 0-pure, 1,2,3-technically pure). The last marking element is a letter indicating the method of copper production: (k - cathode, y - cathode remelted, b - oxygen-free, p - deoxidized, f - deoxidized with phosphorus). Copper grade M00 M0 M1 M2 M3 Purity 99.99 99.95 99.90. 99.70. 99.50.
Copper grades M1p, M2p and M3p, with a total impurity content identical to copper grades M1, M2 and M3, differ from them in that they are more completely deoxidized and the oxygen content in them is reduced from 0.05-0.08% to 0. 01%. Therefore, they additionally contain from 0.002% to 0.012% phosphorus. The M1f copper grade differs from M1r in an even greater amount of phosphorus from 0.012% to 0.04%, for greater deoxidation and, accordingly, a complete absence of oxygen. CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF COPPER ACCORDING TO GOST 859 (%) Brand Cu+Ag Impurities, not more than (%) copper % Bi Sb As Fe Ni Pb Sn S Zn OP М1ф 99.90. 0.001 0.002 0.002 0.005 0.002 0.005 0.002 0.005 0.005 - 0.04. М1р 99.90. 0.001 0.002 0.002 0.005 0.002 0.005 0.002 0.005 0.005 0.01 0.012. M1 99.90. 0.001 0.002 0.002 0.005 0.002 0.005 0.002 0.004 0.004 0.05 — M2 99.70. 0.002 0.005 0.01 0.05 0.2 0.01 0.05 0.01 - 0.07 - M3 99.50. 0.003 0.05 0.01 0.05 0.02 0.05 0.05 0.01 — 0.08 —
The use of various grades of copper in plumbing products is determined by GOST 52318, and in Europe - EN 1057. In construction products: GOST 495-92, in Europe - EN 1172.
For construction purposes and plumbing, for roofing and the manufacture of pipelines for any purpose, copper grades M1f and Cu-DHP, which are analogues, are most often used. The complete absence of oxygen in them guarantees the absence of “hydrogen disease”, excellent weldability and good strength properties.
I got it here, if you're interested, check out the whole article.
Source
Foods Rich in Copper
Macro- and microelements in full are contained in seafood. Seafood also contains large amounts of copper.
Squid, fish, shrimp, mussels and edible algae, when regularly present in the diet, can provide the body with a sufficient supply of this element.
Copper is also present in plants and “regular” animal foods. It accumulates in plant products mainly because copper microfertilizers are used to improve the yield of many crops.
Therefore, the mineral is present in vegetables, fruits, and cereals. They contain copper along with molybdenum, and this increases their value as sources of microelements, because these two minerals “work in pairs” in the body.
Some plants “purposefully” accumulate copper. Thus, ginseng, known for its numerous beneficial effects, is distinguished by its high content.
Raw egg yolks also contain high dosages of copper, but due to their specific taste and the risk of salmonella infection, raw eggs should not be eaten.
Liver, fermented milk products, and meat are rich in copper from animal sources.
Copper. Discussion.
Last ed. 28 Dec. 15, 18:08 from Andrey
who knows what edible copper is? alekslug, 24 Nov. 07, 21:24
I used copper pipe to connect the pressure cooker to the refrigerator. An unpleasant taste and smell appeared. And each time after distillation it was possible to clean the pipe with a cleaning rod and see that a large amount of oxide was formed there.
Copper is very harmful to the liver. If you are not afraid of cirrhosis, you can use it
2All: I went to the website of our bourgeois colleagues homedistiller.org where copper is popular (pipe copper). They write that it even improves SR, connects the org. acids. Convenient installation, fittings, solder are easily accessible. Has anyone considered/done plumbing copper? mascod, 21 Dec. 07, 08:50
2Andrey: do you have a pipe made of food grade/plumbing copper or from an air conditioner/brake pipe? mascod, 22 Dec. 07, 05:49
Some expensive American one for air conditioners.
I replaced it with silicone, IMHO this is best.
2Culinary: where to get food grade stainless steel for the refrigerator and column? I find it only in the form of mugs and bowls
mascod, 22 Dec. 07, 17:59
2Culinary: where to get food grade stainless steel for the refrigerator and column? I find it only in the form of mugs and bowls
mascod, 22 Dec. 07, 17:59
In the markets (bazaars, in the old days), look in the economic or technical sectors, everything that they managed to steal from production or from any other sources is dragged there. Walk around these sectors, ask around, you will see who is selling all sorts of pieces of iron and pipes, place an order for them, they will drag you from somewhere. Culinary, 22 Dec. 07, 20:27
What makes copper so good is that it can be chemically coated with tin or silver. Moreover, it is much easier with silver. Villager, 23 Feb. 08, 18:38
What makes copper so good is that it can be chemically coated with tin or silver. Moreover, it is much easier with silver. Villager, 23 Feb. 08, 18:38
The question is, if you take copper and anneal it, it will not reduce harmful substances. wwn, 01 March 08, 23:40
As befits an Odessa resident, I’ll answer a question with a question. What harmful substances should be reduced in copper? And what harmful substances are present in the copper tube? Copper itself is not entirely useful. Whoever doesn’t believe, let him eat a tablespoon of copper sulfate. True, if you think about it this way, table salt will also be harmful if you eat it with spoons. wwn, all classic French alambiques intended for the production of cognac are made of copper without any tinning or silvering. They were made a hundred or more years ago, and are still in great use today. Moreover, it is legally prohibited to make any changes to their design. We are not talking about copper, but about the impurities that may be present in it. And about those compounds that can result from the interaction of unknown copper impurities with unknown components of moonshine. Naturally, no calcination will bring either harm or benefit.
What makes copper so good is that it can be chemically coated with tin or silver. Moreover, it is much easier with silver. Villager, 23 Feb. 08, 18:38
would be more detailed. very interesting!! Ivan, 20 March 08, 09:29
Source
Formula, equation, properties of copper sulfate
The copper salt of sulfuric acid has the following chemical formula:
CuSO4
At temperatures above 650 °C, thermal decomposition of the compound begins:
CuSO4 →CuO + SO2 + O2↑
This produces oxygen gas, copper oxide (2) and sulfur dioxide.
A qualitative reaction to copper sulfate is interaction with alkalis:
CuSO4 + 2NaOH → Cu(OH)2↓+ Na2SO4
During the reaction, a blue precipitate is formed - copper hydroxide (2), as well as a soluble sodium salt of sulfuric acid. Adding barium chloride to a copper sulfate solution is also a way to identify the compound:
CuSO4 + BaCl2 → BaSO4 ↓+ CuCl2
A white precipitate formed by barium sulfate is clearly visible, indicating the presence of sulfate ions in the solution.
Copper sulfate is hydrolyzable and can react with simple and complex substances. The compound interacts with alkalis, as well as with other salts, and has pronounced redox properties.
Copper sulfate molecule
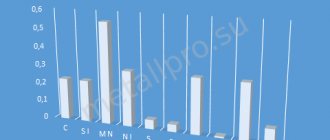
Impurities in copper alloys
Impurities contained in copper (and, naturally, interacting with it) are divided into three groups.
Forming solid solutions with copper
Such impurities include aluminum, antimony, nickel, iron, tin, zinc, etc. These additives significantly reduce electrical and thermal conductivity. The grades that are primarily used for the production of conductive elements include M0 and M1. If the copper alloy contains antimony, its hot pressure treatment becomes significantly more difficult.
Impurities that do not dissolve in copper
These include lead, bismuth, etc. Although they do not affect the electrical conductivity of the base metal, such impurities make it difficult to process by pressure.
Impurities that form brittle chemical compounds with copper
This group includes sulfur and oxygen, which reduces the electrical conductivity and strength of the base metal. The sulfur content of the copper alloy greatly facilitates its machinability by cutting.
Copper grades and their applications
Benefits for the body
Like iron, copper is important for maintaining normal blood composition. In particular, this trace element takes part in the production of red blood cells and is important for the synthesis of hemoglobin and myoglobin (oxygen binding protein contained in the heart and other muscles). Moreover, it is important to say that even if the body has sufficient iron reserves, the creation of hemoglobin without copper is impossible. In this case, it makes sense to talk about the complete indispensability of Cu for the formation of hemoglobin, since no other chemical element can perform the functions assigned to cuprum. Copper is also an important component of enzymes on which the correct interaction of red blood cells and white blood cells depends.
The indispensability of Cu for blood vessels lies in the microelement’s ability to strengthen the walls of capillaries, giving them elasticity and proper structure.
The strength of the so-called vascular framework - the internal coating of elastin - depends on the copper content in the body.
Without copper, the normal functioning of the nervous system and respiratory organs is also difficult. In particular, cuprum is an important component of the myelin sheath, which protects nerve fibers from destruction. The benefit for the endocrine system consists of a beneficial effect on pituitary hormones. For digestion, copper is indispensable as a substance that affects the production of gastric juice. In addition, Cu protects the digestive tract from inflammation and damage to the mucous membranes.
Together with ascorbic acid, Cu can strengthen the immune system and protect the body from the harmful effects of viruses and bacteria. Enzymes that fight free radicals also contain copper particles.
Being a component of melanin, it affects skin pigmentation processes. The functioning of the amino acid tyrosine (responsible for hair and skin color) is also impossible without Cu.
The strength and health of bone tissue depend on the amount of this micronutrient in the body. Copper, by promoting collagen production, affects the formation of proteins necessary for the skeleton. And if a person experiences frequent fractures, it makes sense to think about a possible Cu deficiency in the body. Moreover, cuprum prevents the leaching of other minerals and trace elements from the body, which serves as a prevention of osteoporosis and prevents the development of bone diseases.
At the cellular level - supports ATP functions, performs a transport function, facilitating the supply of necessary substances to every cell of the body. Cu takes part in the synthesis of amino acids and proteins. It is a significant component for the formation of collagen and elastin (important components of connective tissues). It is known that cuprum is responsible for the processes of reproduction and growth of the body.
According to recent studies, Cu is an essential component for the production of endorphins, hormones that improve mood and relieve pain.
And one more good news about copper. A sufficient amount of microsubstance will protect against early aging. Copper is part of superoxide dismutase, an antioxidant enzyme that protects cells from destruction. This explains why cuprum is included in most anti-aging cosmetic products.
Other useful functions of copper:
- strengthens the immune system;
- strengthens the fibers of the nervous system;
- protects against the development of cancer;
- removes toxic substances;
- promotes proper digestion;
- takes part in tissue regeneration;
- activates insulin production;
- enhances the effects of antibiotics;
- has bactericidal properties;
- reduces inflammation.
Standards for Copper Alloys
State standards stipulate the rules for marking copper and its alloys, the designation of which corresponds to a certain structure.
The fact that this is one of the copper grades is indicated by the letter “M” in its designation. After the initial letter in the marking of copper and its alloys there are numbers (from 0 to 3), conventionally indicating the mass fraction of the base metal in their composition (for example, M3 copper). The numbers are followed by capital letters, by which you can determine how this grade of copper was obtained. Technological methods for producing copper include the following:
- cathode (k);
- deoxidation method, which assumes a low content of residual phosphorus (p);
- deoxidation method, which assumes a high content of residual phosphorus (f);
- without the use of deoxidizers - oxygen-free (b).
Examples of markings for such grades and copper alloys may look like this: M2p, M1b.
Chemical composition of copper GOST 859-2014
A number of copper grades, distinguished by unique characteristics, are actively used in various industries.
- M0 - this grade is used for the production of conductive elements and for adding to alloys of high purity.
- M1 - this grade is also used to produce current-conducting elements, rolled products of various profiles, bronze, parts for cryogenic equipment, electrodes for welding copper and cast iron, wire and rods (used for welding work under a submerged arc layer and in an environment of inert gases), consumables for performing gas welding of copper parts that do not experience significant loads during operation.
- M2 - this brand allows you to obtain products that are well processed by pressure. M2 copper is also used for cryogenic equipment parts.
- MZ - parts from this grade of metal are produced by the rolling method.
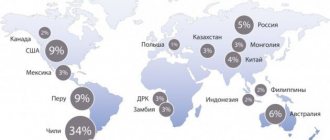
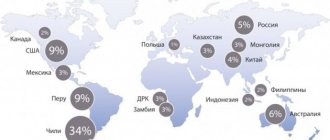
Spatial distribution of copper reserves in Russia
GOST 859-2001, which specified the requirements and characteristics of copper alloys, was replaced in 2014 by a new state standard (859-2014), which was recorded by the relevant Order of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology. The new standard in its main points is almost identical to GOST 859-2001.
GOST 859-2001 on copper grades
This state standard document applies to cast and deformed semi-finished copper products, as well as copper manufactured in the form of cathodes.
Daily requirement
Nutritionists have determined the average copper intake for adults. Under normal conditions, it ranges from 1.5 to 3 mg per day. But the children's norm should not go beyond 2 mg daily. At the same time, babies under one year old can receive up to 1 mg of microelement, children under 3 years old - no more than one and a half milligrams. Copper deficiency is extremely undesirable for pregnant women, whose daily requirement is 1.5-2 mg of the substance, since cuprum is responsible for the proper formation of the heart and nervous system of the unborn baby.
Some researchers are convinced that dark-haired people need more copper than blondes. This is explained by the fact that brown-haired people use Cu more intensively for hair coloring. For the same reason, early gray hair often occurs in dark-haired people. Eating foods high in copper will help avoid depigmentation.
People with:
- allergies;
- osteoporosis;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- anemia;
- heart disease;
- periodontal disease.
Copper m1 m2 m3 difference
Due to their properties, various grades of copper are very popular in the industrial environment. This metal is good because it is flexible and, regardless of the operating environment, with the exception of exposure to sulfur dioxide and ammonia, it is resistant to corrosion.
The external distinctive feature of copper is its pink-red color. Depending on the purity, copper is divided into types with the technical designations M1, M2, M3. This metal comes into production in the form of wire, sheets, pipes, and rods.
This is due to different application situations.
Based on its composition, copper is divided into oxygen-free and deoxidized; the symbol is M0 and M1, respectively. Oxygen-free is used in the manufacture of parts for electrical, electronic, and electrovacuum industrial products. O2 in oxygen-free brands is no more than 0.001%, and in deoxidized ones - 0.01%.
The breakdown of copper grades is presented in the table:
Variety of copper products
Rods made from this metal vary in shape and can be round, square, or hexagonal. In addition, they are divided into cold-deformed, so-called “drawn”, hot-deformed, or “pressed”. Their production takes place in strict compliance with GOST 1535-91, using copper grades such as M1, M1r, M2, M3, M3r according to GOST 859.
The degree of hardness of the finished rods is: medium, hard and soft. Copper grade M2 is used, as well as M1, M1r, M2r, M3, M3r according to GOST 859, in accordance with the GOST 1173-93 standard.
There is also a division according to normal accuracy in thickness and increased in width, normal accuracy in thickness and width, increased accuracy in thickness and optimal accuracy in width.
Copper wire can be soft or hard. In production, copper grade M1, GOST 859, GOST 434-78 is used.
Pipe manufacturing
In order to produce high-quality copper pipes suitable for further use, you need to know which brand to use, as well as comply with certain technical requirements that are prescribed in GOST 617-90. Thus, in industrial production the M3 brand is used, as well as M1, M1r, M2, M2r, M3r, GOST 859 and chemical. composition GOST 15527 L96.
Pipes come in the following varieties: pressed and cold-deformed, hard, medium-hard and soft.
Production of strips and sheets
Strips and sheets are made in accordance with GOST 495-92, for this they use copper with the following markings: M1, M1r, M2, M2r, M3, M3r GOST 859.
Normal and high precision production methods are used for cold-rolled sheets and strips.
The size of hot-rolled sheets varies from six hundred to three thousand mm in width, and in length - from one thousand to six thousand.
According to the degree of hardness, cold-rolled sheets and strips on an industrial scale are soft, hard, and medium.
Variety of copper alloys
The most common alloy in industry is brass. It is a compound of zinc and copper. When a third, fourth, fifth, etc. appears in this composition. element, brass becomes complex, or special. In this case, it receives an aluminum, iron-manganese, manganese-tin-lead prefix.
This alloy is well suited for work involving casting, pressing, and cutting, since, unlike the usual composition of copper, it is characterized by increased resistance to fracture, elasticity and endurance. These qualities facilitate the processing of parts.
Brass rods are made in compliance with GOST 2060-90. Manufacturing accuracy is increased, normal and high. Plasticity – hard, medium, and soft.
Brass wire is produced taking into account GOST 1066-90, brass grades L68, L80, L63, LS59-1 are used. The chemical composition is regulated by GOST 15527.
Reactions with copper sulfate, compounds
Copper sulfate hydrolyzes well, forming an electrolytic solution with an acidic environment:
CuSO4 → Cu 2+ + SO42-
This produces a fairly strong electrolyte. Electrolysis proceeds with the release of free oxygen, copper and sulfuric acid:
2CuSO4 + 2H2O →2Cu + 2H2SO4 + O2
The compound interacts with metals:
CuSO4 + Zn→ZnSO4 +Cu
A substitution reaction is characteristic, during which pure copper precipitates.
Copper sulfate is characterized by interactions between ion exchange and various precipitation. Most often, copper sulfate reacts in this way with other salts:
3CuSO4 + 2Na3PO4 – Cu3(PO4)2 ↓+3Na2SO4
As a result, greenish crystals of copper orthophosphate fall out. Sometimes the exchange reaction occurs with a change in oxidation states, then we are talking about redox reactions:
2CuSO4 + 4NaI → 2CuI + I2 + 2Na2SO4
Cedi sulfate reacts with sodium iodide, free iodine is released.
Copper sulfate can be reduced with hydrogen when heated:
CuSO4 + H2 → Cu + H2SO4
It often forms complex salts, such as ammonia:
CuSO4 + 4NH4 → [Cu(NH3)4]SO4
The reaction produces a bright purple solution and tetraamine copper sulfate is formed.
Copper m1 – Copper grades according to GOST 859 M1, M2, M3
alexxlab | 12/05/2018 | 0 | Questions and answers
- Copper grades according to GOST 859 M1, M2, M3
- Copper M1 / Auremo
- Copper M1r / Auremo
- properties, characteristics, composition. Mass fraction of impurities in copper M1 GOST 859-2001
- Copper grades - classification, physical properties, application +
- MV copper (vacuum copper) + Anodes, graphite, solder... › Russian metal We offer MV copper to order.
- Electrical copper M1E + Anodes, graphite, solder... › Russian metal We supply electrical copper M1E to order.
Copper grades according to GOST 859 M1, M2, M3
Due to their properties, various grades of copper are very popular in the industrial environment. This metal is good because it is flexible and, regardless of the operating environment, with the exception of exposure to sulfur dioxide and ammonia, it is resistant to corrosion.
The external distinctive feature of copper is its pink-red color. Depending on the purity, copper is divided into types with the technical designations M1, M2, M3. This metal comes into production in the form of wire, sheets, pipes, and rods.
This is due to different application situations.
Based on its composition, copper is divided into oxygen-free and deoxidized; the symbol is M0 and M1, respectively. Oxygen-free is used in the manufacture of parts for electrical, electronic, and electrovacuum industrial products. O2 in oxygen-free brands is no more than 0.001%, and in deoxidized ones - 0.01%.
The breakdown of copper grades is presented in the table:
Designations
| Designation GOST Cyrillic | M1 |
| Designation GOST Latin | M1 |
| Translit | M1 |
| By chemical elements | Cu1 |
Description
M1 copper is used : for the production of current conductors; rental; high-quality tin-free bronzes; cryogenic equipment products; round drawn thin-walled pipes; cold-rolled foil and strip, cold-rolled and hot-rolled sheets and plates for general purposes; wires for the manufacture of metal shielding braids of the PML type, intended for shielding wires and cables; hot-rolled and cold-rolled anodes used for galvanic coating of products; cold-deformed rectangular tape with a thickness of 0.16−0.30 mm, intended for coaxial trunk cables; radiator tapes intended for the manufacture of cooling tubes and radiator plates; drawn pipes of rectangular and square cross-section, intended for the manufacture of conductors for stator windings of liquid-cooled electrical machines; profiles for the manufacture of rotors of submersible electric motors; round welding wire and round welding rods drawn and pressed with a diameter from 1.2 to 8.0 mm, intended for automatic welding in an inert gas environment, submerged arc and gas welding of non-critical structures made of copper, as well as the manufacture of electrodes for welding copper and cast iron.
Characteristics and properties of fluxes
The properties and composition of the solder must be completely suitable for the metals with which it will be soldered. Also, the solder intended for soldering pipes must be at a lower temperature than the metal so that it does not get damaged. Therefore, there are two types into which materials are divided:
- Low-temperature solders have a low melting point, which does not reach 450 degrees Celsius. In this case, the load on the adhesions should not be too high. The metal and its physical properties remain unchanged.
- High temperature solders provide greater strength and quality, but their melting point can be above 800 degrees Celsius.
Choice and its features
The higher the melting point, the more it affects the metal from which the pipes are made. Therefore, it is worth knowing what load will be placed on the pipes and choosing the appropriate solder. If the load is expected to be light, then you can choose soft, low-melting solder. If the pipes are intended for the food industry, then it is necessary to choose a solder that is non-toxic and does not cause harm to human health.
Important! When choosing solder for copper pipes, you need to know the melting point and composition of the material for which it is intended!
Product Names
Generally accepted standards indicate the official name copper sulfate. Internationally, the name Cupric Sulphate is accepted.
In addition to the food industry, E519 is used in pharmaceuticals, photography, agriculture, and the textile industry.
In the countries of the European Union, the food additive is named according to the encrypted code - E519 (sometimes indicated with a dash between the letter and numbers).
Other names are also known among industrialists or chemical industry workers. The most popular are copper sulfate, crystalline hydrate, divalent copper sulfate, individual names in German and French.
Average copper consumption and status.
Typical diets meet or exceed the RDA for copper. The amount of copper consumed in the average human diet ranges from 800 to 1000 mcg per day for children aged 2 to 19 years. In adults 20 years of age and older, the average daily intake of dietary copper is 1,400 mcg for men and 1,100 mcg for women. Total intake of dietary supplements ranges from 900 to 1100 mcg/day for children and from 1400 to 1700 mcg/day for adults over 20 years of age.
According to an analysis of data from the 2009–2012 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 6–15% of adults aged 19 years and older who do not take a copper supplement have a copper intake below the EAR.
General information
According to chemical reference books, it has a common name - copper sulfate, the formula of which is CuSO4. The main difference between different types of this substance is its saturation with liquid - water.
Content:
- General information
- Product Names
- Type of dietary supplement
- Packaging and Application
- Benefits and harms
- Application in other areas
In addition to pentahydrate, you can find anhydrous sulfate with a similar formula, which has a gray-white or slightly greenish tint. There is also a mineral called Bonatite, which is called trihydrate.
Standard copper sulfate has the appearance of crystals of a characteristic blue color. When consumed by humans, a slightly metallic taste is felt. The substance is able to dissolve in water, methyl alcohol and hydrochloric acid.
Some time ago, E519 was available in the food industry of the Russian Federation. With its help, they created an unusual bluish color of some products and used it as one of the best preservatives. The most common is the production of olives. In 2010, the use of copper sulfate was vetoed. Despite its common consumption as food, modern research shows some toxic effects leading to mutations within the body.
Lack of copper in the body
Copper deficiency in the body is easy to notice. Common symptoms:
- blood diseases manifested by low hemoglobin;
- the appearance of bruises on the body at the slightest blow;
- tendency to infectious and colds;
- baldness;
- increased cholesterol levels;
- thyroid diseases;
- abnormal heart rhythm;
- pale skin;
- feeling of weakness, loss of strength;
- feeling of lack of air;
- damage to the cardiovascular system;
- osteoporosis (due to impaired mineralization in the bones);
- pigmentation;
- distress syndrome in newborns;
- A lack of copper in a woman’s body leads to insufficient production of sex hormones.
The causes of deficiency are caused by various factors. More often, the problem arises due to improper selection of diet, the habit of consuming semi-finished products, and fast foods.
Other reasons are poor-quality drinking water, impaired absorption of the substance due to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, prolonged treatment with antibiotics, hormonal drugs, antacids, and corticosteroids.
Effect on the human body, pharmacological action
With the right dosage and course of treatment, copper sulfate does not have a negative effect on health. Pharmacological action consists of disinfection, wound healing, adaptogenicity. This is a valuable medicine that must be used wisely to achieve the best therapeutic effect. Therefore, treatment with copper sulfate should be supervised by a doctor.
Acceptable norms for taking copper sulfate
The toxic dose of copper sulfate when taken orally is 0.5 g per 1 kg of weight. At this concentration, the first symptoms of poisoning begin to appear. The maximum permissible consumption rate must necessarily be less than this value. Fatal poisoning occurs with simultaneous administration of 45-125 g.
Benefits of copper sulfate
Copper sulfate is valued in many fields of activity. Due to its strong antiseptic properties, it is able to suppress the development of bacterial infections of various origins, and can be used to treat diseases of the oral cavity (gingivitis, stomatitis, inflammation of the tonsils), as well as gynecological inflammations. Copper sulfate effectively destroys pathogens; solutions, powders and ointments based on this substance are used.
Copper salt of sulfuric acid is necessary in industry. It is distinguished by its high reactivity and low toxicity, which is why it can be used for treating residential premises, water and for direct work with metal products. Due to its high hygroscopicity, anhydrous copper sulfate powder is capable of retaining moisture for a long time and is a component of air humidifiers.
Harm of copper sulfate
Copper sulfate is harmless when used correctly. When contacting it, it is important to follow safety measures and not neglect hygiene procedures. There is no E519 in domestically produced food products, so a negative impact on humans through food is excluded.
Copper sulfate can be toxic to fish, aquatic plants and invertebrates in high doses. Therefore, before use, you need to read the instructions and consult a veterinarian.
When disinfecting premises, inhaling copper sulfate aerosol can lead to burns to the respiratory tract and severe poisoning.
Application
Until 2010, additive E 519 was approved for use in the food industry as a preservative, color stabilizer, and food for baker's yeast. Due to its unpleasant taste, the substance was rarely used.
Currently, copper sulfate is excluded from the list of additives approved for food production in Russia, EAEU countries, Norway, Great Britain, and EU countries. Stabilizer E 519 is approved in Japan, presumably Ukraine. The status of the substance in the United States is unclear.
Medicine
Copper sulfate is a strong antiseptic.
The substance has astringent properties, accelerates the formation of hemoglobin, and acts as an antidote for poisoning with phosphorus compounds. It is an effective emetic and is prescribed when it is necessary to quickly cleanse the stomach. The drug in the form of powder or homeopathic capsules is used to treat infectious diseases (for example, sore throat), anemia.
A solution of copper sulfate is used for conjunctivitis, furunculosis, urinary tract infections, purulent wounds, and phosphorus burns.
Important! The substance is extremely toxic! Treatment is carried out only as prescribed by a doctor.
Agriculture
Copper sulfate is a popular fungicide.
It effectively fights various pests and fungal infections (scab, gray mold, moniliosis, anthracnose and many others).
The solution is used to treat the soil before seasonal planting to protect crops from contamination by fusarium and other infections, and to disinfect wounds on tree trunks. Sometimes it is used as a fertilizer when there is insufficient amount of copper (for example, in peat areas), and the seeds are treated to prevent infection by mold fungi.
Veterinary
Used as an antiseptic and anthelmintic drug.
The solution is sprayed into rooms and stalls to kill fleas, mosquitoes, and some types of ticks. Animal hooves are treated for the treatment and prevention of digital dermatitis, hoof rot, and plantar ulcers.
Additive E 519 is used to treat aquarium fish from parasitic and bacterial infections (fin rot, oodiniosis, costiosis and others).
The product is poisonous to invertebrate inhabitants, plants, and some types of fish. The dosage must be strictly observed.
Using copper sulfate, rust and mold are removed from various surfaces, wood is protected from rotting, and mineral paints and acetate fiber are produced. Additive E 519 has found application in electroplating, metallurgy, and various chemical industries.
Recommended intake values for copper.
RDA - recommended average daily intake to meet the necessary requirements for a substance, suitable for 97-98% of healthy people.
AP(AL) - adequate consumption. These levels are assumed to ensure nutritional adequacy. Established when scientific data is not sufficient to establish an RDA.
RSP (EAR) - estimated average daily requirement. Average daily intake calculated to meet the needs of 50% of healthy people. Typically used to estimate nutrient intakes of groups of people and plan adequate diets for them. Can also be used to estimate nutrient intake of individuals.