02/15/2022 Author: VT-METALL
From this material you will learn
:
- Parameters affecting the properties of weld metal
- Factors affecting the quality of weld metal
- Weld metal crystallization process
- Strength testing of weld metal
- Causes of defects
The properties, quality, and crystallization process of the weld metal depend on many parameters. The primary ones include consumables used in welding, the properties of the metal of the workpiece, and the operating mode of the welding machine. Secondary ones are the environment in which the welding was carried out, the speed of the weld, its cooling, etc.
By selecting certain parameters, you can predict in advance how the weld will turn out. This will also help avoid common metal defects. You will learn more information about weld metal from our material.
Parameters affecting the properties of weld metal
The physical characteristics that determine the characteristics of seams formed by welding are usually called complex mechanical properties of welded joints. Such properties depend on the calculated ratio of the mechanical parameters of the weld surface, the processing zone, and the thermal features of the product structure.
When carrying out work, they are guided by the characteristics of the metal of the weld, and any joints normally have a structure close to the structure of the material of the product itself.
A welded joint is called high-quality if the ultimate strength is reached and the fluidity is at a level that ensures sufficient ductility.
The uniform strength of the weld depends on a number of technical and physical characteristics, such as
:
- consumables used (electrodes, flux, wires);
- chemical parameters of the weld metal;
- mode of operation;
- methods of soldering, cutting material;
- dimensions of the product, and the main indicator, from the point of view of the strength of the weld metal, is the thickness of the workpiece;
- material cooling rate;
- probable deformation in the plastic characteristics of the seam.
In accordance with this regulation, the physical and technical parameters of the metal are established, which simplifies the determination of its actual characteristics during the transition from the alloyed to the unalloyed type and vice versa.
VT-metall offers services:
The key standards for determining mechanical properties for welds are established in GOST 9467-60. Moreover, similar determination methods are also used for operations using flux and other welding methods. The latter include manual, arc, electric arc welding, automatic and semi-automatic.
Features of mechanical research
The main feature is that mechanical studies are destructive control methods. Those. in most cases, the samples under study are destroyed or damaged. But if destruction is not the best option in a particular case, other testing methods must be chosen.
The room where experiments are carried out must be maintained at the same temperature. The data obtained during the inspection must be recorded.
To obtain the most accurate results, several samples from the same batch are tested. It is likely that results will vary. Then the average value is derived from the obtained indicators - this will be the most accurate result.
It is advisable to use mechanical tests in the serial production of parts, when from each circulation they take the number of products regulated by standards and conduct research. It will not be possible to issue a correct conclusion using only one sample. If the product is single, it is worth using non-destructive testing methods.
Test results depend on various factors. This includes both the original state of the workpiece and the presence of defects in the metal. Therefore, before determining technical characteristics, it is necessary to carry out flaw detection of welded joints, for example, ultrasonic testing.
Factors affecting the quality of weld metal
The quality of the weld metal depends on a number of factors, such as weldability, the degree of exposure of the metal to thermal effects, oxidation, etc. It is important to take into account all such criteria so that the finished welded joints are suitable for certain operating conditions.
The weldability of metals is an indicator on which the ability of metals and alloys, with suitable processing, to form compounds with specified parameters depends. Experts distinguish between physical and technological weldability.
In any case, a significant role here is played by the physical and chemical characteristics of metals, their crystal lattice, the presence of impurities, the degree of alloying, etc., which affects the reliability of the weld metal.
Physical weldability is the ability of a material to form a monolithic compound with a stable chemical bond. This quality is characteristic of most pure metals, as well as their technical alloys and some combinations of metals and non-metals.
Technological weldability is the reaction of a material to welding and the ability to form a seam with the required characteristics.
To determine weldability criteria, the following material properties are taken into account:
:
- sensitivity to thermal effects during welding;
- tendency to grain growth while maintaining unchanged plastic and strength characteristics, structural, phase changes in the heating region;
- chemical activity, which affects the oxidation of the metal during thermal exposure;
- ability to resist pore formation, cracking in cold and hot conditions.
The quality of steels largely depends on their deoxidation ability, which is determined by the proportion of manganese, silicon and a number of other elements in the metal composition. It is also influenced by how evenly these components are distributed. Based on deoxidation, boiling steels are distinguished, marked as “KP”, semi-quiet, with the designation “PS”, and calm, that is, “SP”.
In boiling steel, impurities are distributed unevenly throughout the thickness of the rolled product, which is most clearly manifested in the case of sulfur and phosphorus and is explained by incomplete deoxidation by manganese.
In such steels, aging quickly manifests itself, crystallization cracks form on the metal of the weld and the area adjacent to it. As a result, the material becomes brittle at temperatures below 0°C.
Calm steel is characterized by a uniform distribution of impurities, making it less prone to aging. In addition, it is less affected by the temperature increase during welding.
Semi-quiet steel in its properties is between boiling and calm.
The named characteristics form the basis for the choice of welding method, methods of creating a weld, parameters of thermal effects, etc.
Weld metal crystallization process
During crystallization, the metal of the weld pool is influenced by the hot welding arc and the cold surrounding metal. In other words, the arc introduces heat, and the metal of the product removes it.
The transition of a metal from a liquid to a solid state is accompanied by the formation of crystals - this is crystallization. The weld metal undergoes this process throughout the welding process.
The weld has the structure of cast metal. During welding, the edges of the workpiece and the electrode wire fed into the bath area melt. Conventionally, the latter consists of a front or head and tail part: in the first, melting occurs, and in the second, crystallization occurs and a seam is formed.
It is customary to distinguish between primary and secondary crystallization. Primary is the transition of liquid metal to a solid state, which is accompanied by the formation of crystals. At first, the resulting crystal grows freely and has the correct shape.
But since there is a parallel development of many crystals, they gradually begin to touch each other, and accordingly, the shape is disrupted. Eventually they become rounded, more like grains, which is why the crystals are referred to as grains.
The size of the grains depends on the progress of crystallization: they can be large, distinguishable without special equipment, and small. The latter are visible only under a microscope.
The crystalline structure of a metal or alloy is called structure. It is also customary to talk about the macrostructure or structure of metals, which can be distinguished with the naked eye or with the help of a magnifying glass.
Crystallization of weld metal occurs at a much higher rate than a similar process with ingots. This is explained by the fact that the intense heating of the weld pool is quickly replaced by heat removal into the workpiece.
Crystallization occurs in separate thin layers. When the first layer of crystals has formed, the cooling of the metal slows down against the background of the release of latent heat from the ongoing process. Then the second layer hardens, and so on throughout the bath.
Crystallization layers have a thickness from tenths of a millimeter to several millimeters - the specific indicator is determined by the volume of the weld pool and the characteristics of the heat sink. The columnar crystals of each new layer become a continuation of the previous one, due to which the crystals grow from layer to layer.
In order for the process of primary crystallization to start, its centers or nuclei must be formed, which will continuously grow. This role is played by the melted grains of metal found at the bottom of the weld pool.
Further, additional crystallization centers may appear - usually these are refractory particles, grain fragments, or centers spontaneously formed in the liquid metal.
During multilayer welding, the function of the centers falls on the crystals of the previous layer. They grow by attaching atoms from the surrounding liquid metal.
Each crystal is a group of elementary columnar crystals, one end of which is connected to a common base or fused grain of the base metal. Based on the shape and arrangement of the crystals, experts distinguish between granular, columnar and dendritic or tree-like structures of the cooled metal.
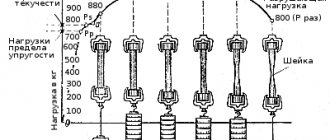
Strength testing of weld metal
Mechanical tests of welds make it possible to determine operational characteristics and, based on them, calculate possible loads.
Such tests of weld metal are carried out in various ways, but always involve the destruction of samples using multidirectional loads. Special control equipment is also used here.
First of all, several serial samples are selected in order to determine the ductility and fracture resistance of the weld using a series of identical operations.
There is a complex of studies for seams formed by various types of welding. We are talking about groups of test methods with directed stresses:
- The static method involves a gradual increase in the breaking load. To ensure constant voltage, a lot of time is allocated for testing.
- The dynamic voltage is instantaneous and does not require a long period of time to test.
- Fatigue methods involve repeated exposure to a sample, with the number of cycles reaching tens of millions, and the load changing in sign and value.
Without mechanical testing of weld metal, serial production of parts is not possible. Using static tests, butt joints are assessed, physical characteristics of seams such as hardness, creep, elongation, ductility, bending ability, etc. are measured.
To do this, the connection is compared with a sample of solid metal. Samples with a stripped and uncleaned roller are sent for research.
It is worth clarifying that the conditional yield strength is the stress against which the length of the product increases by 0.2%. The bending test allows you to control the ductility of the diffuse layer. Such a load is measured before the first crack appears in the longitudinal and transverse sections of the weld.
Such experiments are carried out with flat and tubular samples.
Using dynamic tests, the probability of fatigue deformation of the seam and impact bending strength are determined. For testing, different conditions are set, namely normal, low and high temperatures. All obtained indicators are recorded in the protocol in graph format, after which they are examined according to the type of curves.
Sometimes other, normatively approved studies and calculations of weld metal parameters may be used.
Hardness is measured in the area of the diffuse layer and the thermally affected zone. To check the structural strength of a metal, the metallography method is used, which is used to examine areas such as:
- diffuse layer of the seam;
- heat affected zone;
- metal product that has not been exposed to elevated temperatures during the welding process.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
First, about the unique capabilities of the technique:
- obtain data on the performance properties of welding;
- study the mechanical characteristics of connections;
- establish design values to determine maximum loads (data necessary for design work);
- the capabilities of the diffuse layer, the thermally affected zone, where internal defects are possible, are checked.
At low costs for studying samples, data are obtained by which the strength characteristics of serially produced parts are judged. Select the optimal welding option for various alloys.
The disadvantages are obvious. The samples are expected to be destroyed and cannot be restored. This control method cannot be used for acceptance of welded joints. Methods are needed for research at the stage of launching series into production.
A feature of mechanical testing of welded joints is the mandatory destruction of samples under multidirectional loads.
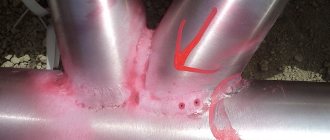
Causes of defects
Defects can appear for objective and subjective reasons. The fact is that any type of rolled metal has a certain level of weldability, which depends on the method of its manufacture and the composition of the alloy. If you plan to work with poorly welded parts, then a significant percentage of defects is initially recorded in the technological maps.
Usually seam welding is associated with problems such as
:
- violation of the integrity of the metal;
- deformation of elements under the influence of internal stresses;
- violation of the shape of the seam bead;
- changing the geometry of the surfacing bead;
- structural changes in the metal, namely, the grain size changes in the phase transition zone of the welded joint.
External defects are less dangerous than internal ones and can be detected using non-destructive inspection methods. However, it is important to understand that it is risky to form critical welds without sufficient knowledge and skills, and it is better to seek help from specialists.
Typically, a violation of the integrity of the metal of welds and the zone exposed to temperature effects occurs for the following reasons:
- the processing of the joints was carried out poorly, for example, the metal of the welded seams was poorly cleaned of scale, rust, oxide film residues, grease and dirt, violations were committed in the process of removing oxygen from the metal of the welded seam;
- surfacing wire and electrodes that are not suitable for the metal of the workpiece were used;
- equipment is faulty;
- the parameters on the welding machine regulators, such as current and voltage, are incorrectly set;
- an error was made when laying out the parts, the coefficient of linear expansion was not taken into account;
- the distance between the electrode and the workpiece is broken, causing the arc to be too long or too short.
Welding operations greatly influence the mechanical properties of low-carbon steel. And the processing of structural steels leads to structural changes in the heat-affected zone, which reduces the mechanical performance of the joint. At the same time, hardening structures and cracks appear in the weld metal.
You need to understand that the weld, the heat-affected zone, and the unexposed workpiece metal have different strengths. This means that during the study it is important to regard the welded joint as an inhomogeneous body. Destructions can occur in any of the three named zones - it all depends on where the lowest strength is observed.
Recommended articles
- Types of welds: differences from joints and descriptions of varieties
- How to cook with electric welding: technology and important rules
- Capacitor welding: process features
Today it is possible to achieve equal strength of welds and the base metal using electrodes with high-quality coatings and other consumables.
The reliability of the connections is ensured by the strength of the weld metal, and also depends on the width of the overheated metal in the thermal zone, the total width of the weld material and the overheated metal. Important factors include the nature of the application of external load, the temperature at which the product is operated, etc.
Quality control of raw materials
The quality of the base metal must meet the requirements of the certificate provided by the manufacturing plants along with the batch of metal.
In the absence of a certificate, the metal is put into production only after a thorough check: it is necessary to conduct an external inspection, a weldability test, and establish the mechanical properties and chemical composition of the metal.
During an external inspection of the metal, the absence of scale, rust, cracks, delamination and other defects on the metal is checked. Preliminary inspection of the metal in order to detect surface defects is necessary and mandatory, since it prevents the use of low-quality metal for welding products.