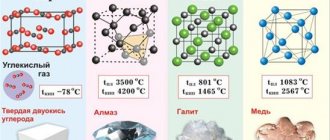
Physical properties
At room temperature and without applying pressure, all substances are solid. But there is gallium, which already at 30 degrees of heat begins to deform and melts in your hands. Characteristics you can note:
- High plasticity. Only manganese, tin and zinc are fragile.
- Can be light or heavy. Compare aluminum with osmium.
- The melting point is very high. There are exceptions, for example, mercury, which is why it is used in classic thermometers.
- Color – gray, silver, bluish. Colored items, such as yellow or red, are rare.
- Increased conductivity of heat and electricity, especially in copper, is why copper wires are popular.
History of discovery and study
The first sample of lithium metal was obtained thanks to the work of Humphry Davy. Using an electric current, he decomposed the molten hydroxide of this alkali metal. After some time, Leopold Gmelin experimented with lithium-containing salts. He was able to detect that they paint the flames a dark color.
The main credit for the discovery of a new chemical element and the growth of its popularity belongs to Johann August. In 1817, he discovered a new substance in petalite, an aluminosilicate. After some time, lithium was found in other mineral formations. It received this name due to the fact that it was first found in stones. The name of the stone in Greek is “lithos”.
Petalite
Classification and types of metals
There are pure, single-component structures and alloys. The most classic example is the different types of steel. They differ according to GOST in accordance with the addition of alloying additives. The higher the carbon content, the stronger the material. There is also a generally accepted distinction; below we present the subtypes.
Black
They are mined from metal ore. In production they occupy 90% of all raw materials. Usually these are cast iron and steel. To change the characteristics, more or less amount of carbon and alloying additives are added: copper, silicon, chromium, nickel. One of the very popular subspecies is stainless steel, which is distinguished by its shiny surface and unique properties - lightness, high strength and resistance to humidity and temperature changes.
What applies to non-ferrous metals
The second name is non-iron, that is, alloys do not contain iron, but consist of more expensive materials. Substances have different colors and have unique qualities:
- durability;
- long-term preservation of properties;
- the formation of an oxide film that prevents corrosion.
Thanks to this, certain varieties can be used in medicine, jewelry, the chemical industry, and in the manufacture of electrical wires. Non-ferrous metals include aluminum, zinc, tin, lead, nickel, chromium, silver, gold and others.
Copper and its alloys are popular metals
Copper ore was one of the first to be processed by man because it is subjected to the cold method of forging and stamping. Pliability has led to demand everywhere. Oxygen in the composition leads to a red tint. But decreasing the valency in various compounds will lead to yellow, green, blue color. Excellent thermal conductivity is considered an attractive quality - second only to silver, which is why it is used for wires. Connections can be:
- solid - in combination with iron, arsenic, zinc, phosphorus;
- with poor solubility with bismuth, lead;
- fragile - with sulfur or oxygen.
Metals include aluminum and alloys
Al was discovered in 1825 and is distinguished by its ease and simplicity in metalworking. It is made from bauxite, and the reserves of this rock are practically inexhaustible. Next, the element is combined in various proportions with copper, manganese, magnesium, zinc, and silicon. Less often with titanium, lithium, beryllium. Features depending on additives:
- good weldability;
- corrosion resistance;
- high fatigue strength;
- plastic.
It is used for the manufacture of jewelry, cutlery, as well as for glass melting, in the food and military industries, for the creation of rockets and for the production of hydrogen and heat in aluminum energy.
All about the metals magnesium, titanium and their alloys
Mg is the lightest substance of this group. It does not have strength, but it has advantages, for example, plasticity, chemical activity. Due to its high structural ability, it is added to compositions to increase weldability and ease of metalworking with a cutting knife. It must be taken into account that magnesium is very susceptible to rust. Titanium has similar qualities - lightness, ductility, silver color. But the anti-corrosion film appears upon first contact with oxygen. Distinctive features are low thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, and lack of magnetism. Metal containing titanium is a substance used in the aviation, chemical, and shipbuilding industries.
Anti-friction alloys
A characteristic feature of this group is its ease of use under mechanical stress. They create virtually no friction and also reduce it in other composites. Very often they act as a solid lubricant for components, for example, for bearings. The composition usually includes fluoroplastic, brass, bronze, iron graphite and babbit.
Soft
These are those whose metal bonds are weakened. For this reason, they have a lower melting and boiling point and simply become deformed. Sometimes you can make a dent with one finger press, or leave a scratch with your fingernail. These include: copper, silver, gold, bronze, lead, aluminum, cesium, sodium, potassium, rubidium and others. One of the softest is mercury; it is found in nature in a liquid state.
What does hard metal mean?
In nature, such ore is extremely rare. The rock is found in fallen meteorites. One of the most popular is chrome. It is refractory and can be easily processed into metal. Another element is tungsten. It melts very poorly, but when properly processed is used in lighting applications due to its heat resistance and flexibility.
Metal materials in the energy sector
We would not have such a developed electrical network and a lot of devices that consume electricity if a number of substances were not distinguished by the presence of free electrons, positive ions and high conductivity. Wires are made from lead, copper and aluminum. Silver would be great, but its rarity affects the cost, so it is rarely used.
Features of Ferrous Secondary Metals
This is waste that is generated as a result of one of the metalworking stages - forging, cutting. These could be scraps or shavings. They are sent to steel-smelting furnaces, but before that they must pass inspections in accordance with GOST. Scrap is called ferrous metal, it is distinguished into steel and cast iron according to price. Its use is in great demand instead of ore processing.
Alkaline earth alloys
These are solid substances that have high chemical activity. They are very rarely found in their pure form, but are used in compounds. Their importance cannot be overestimated from the point of view of human and animal anatomy. Magnesium and calcium are essential microelements.
Alkali metal concept
They are able to dissolve in water, forming an alkali. Due to its increased chemical activity (reaction occurs with violent action, ignition, release of gas, smoke) it is almost never found in nature. After all, at the external level there is only one electron, which is easily given to any substance. Hydroxides are very important in industry.
General characteristics of materials from the d- and f-families
These are transition elements that can be both oxidizing and reducing agents. Properties depend on the environment in which they are located. But there are also common ones:
- there are many electrons in the outer level;
- several oxidation states;
- increased valence;
- strength;
- ductility;
- ductility.
What are the side subgroups of metals in the periodic system?
In fact, these are varieties of the previous category - transitional elements. This is a line from scandium to zinc. They are often smelted and have virtually the same characteristics as the above materials from the d- and f-families.
All that remains is to pack the rolls and apply the customer’s markings.
0
Source:
Interestingly, different customers have different requirements for packaging. As a rule, this depends on the method of long-distance transportation (only by rail across Russia or further transportation by sea with a large number of loading/unloading cycles). The most vulnerable are the ends of the rolls, which can be damaged by contacts and even become severely jammed, which will render the entire roll unusable.
0
Source:
As I said above, Severstal supplies galvanized steel to such concerns as Renault-NISSAN, VOLKSWAGEN, HYUNDAI-KIA, Ford, GM, etc.
Comparison of properties
The second part of the elements in the periodic table is characterized by a variety of characteristics, so it is almost impossible to provide a complete summary table. We offer a table that shows 4 distinctive features:
| Signs | Metals | Nonmetals |
| Position in P.S. | Under the diagonal boron-astatine | Above her |
| Atomic structure | Large atomic radius, pure electrons in the last layer - from 1 to 3 | Small, from 4 to 7 - respectively |
| Physical properties | Electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, gloss, malleability, plasticity, in terms of state of aggregation, mostly solid | Dielectrics, non-shiny, brittle, gases, liquids and volatile solids |
| Crystal lattices | Metal | Molecular, atomic |
| Chemical properties | Restorers | Oxidative (sometimes reduced) |
We talked about metal, what kind of material it is, how it is used. If you need metalworking machines, order them from. We have manual and semi-automatic band saws in stock and on order, as well as pendulum, vertical and two-post units. The price of goods has been reduced by 1.5 - 2 times compared to foreign analogues. To clarify the information you are interested in, contact our managers, we will be happy to help you select equipment.
The steel coils are first unwound and then welded to form a continuous sheet.
0
Source:
This is done using a special cunning machine, which allows the process to be continuous, despite the fact that the welding process requires stopping the conveyor for a short time. By the way, the line for the production of hot-dip galvanized sheets was designed by the Belgian company, and it was put into operation in 2005.
0
Source:
This is done using a special storage device in the form of a movable accordion. As you understand, in order to connect the ends of the two rolls, you need to pause. And the galvanizing process is continuous. This is what the drive was created for: it delivers the sheet for galvanizing, unwinding the accordion from this unit.
Casting molds
The most ancient type of molds are those made from sand-clay molding mixture, or “earth.” Historically, centers of metallurgy arose near the deposits of sands that were ready in their composition for casting, for example, near the world famous Kasli iron plant. Mixtures are divided into coating and filling mixtures.
molds made from sand-clay molding mixture
To construct any matrix, a model is required - a life-size mock-up of the future product, but somewhat larger in size - equal to the amount of casting shrinkage.
The model is placed in the center of the formwork, or flask, and a layer of coating mixture is applied to it - heat-resistant and plastic. Then they begin to fill the flask layer by layer, carefully tamping each layer, with the filling mixture. The requirements for filling mixtures are much lower than for coating mixtures - they must withstand the pressure of the poured metal, maintaining the configuration of the casting, and ensure the release of melting gases. Afterwards, the model is removed from the mold and the melt is poured in its place.
For castings of complex configurations, with intricate details and internal cavities, composite models and molds made of several parts are used.
Metal molds
Casting is also carried out in metal molds. They are used for large runs of cast parts, in cases where high dimensional accuracy and low surface roughness of the casting are required, as well as for some metals that are active in a heated state. The melting temperature of the mold material must be significantly higher than the temperature of the melt being cast.
Basic methods of metal casting
Casting into the ground
Traditional way. A simple or composite model is made from wood or other modeling materials, then a matrix is made from a sand-clay mixture based on the model. Read more about this method in the corresponding article.
Earth casting technology
The model is removed from the mold, its parts are assembled together, and a gating system is created. The form is pricked with thin sharp needles to ensure gas removal. They make a casting, wait for it to cool,
Metal casting
A split mold, called a mold, is made from metal parts. Matrix parts are produced by casting or, if high surface quality and dimensional accuracy are required, by milling. The molds are lubricated with non-stick compounds and filled.
Metal casting
After cooling, the molds are disassembled, the castings are removed and cleaned. The metal matrix can withstand up to 300 operating cycles.
Casting using gasified models
The model is made not of wood or wax, but of a low-melting and gasifying material, mainly polystyrene. The model remains in the mold and evaporates when the metal is poured.
Casting using gasified models
Advantages of the method:
- the model does not need to be extracted from the matrix;
- you can make models of as complex castings as you like; complex and composite molds are not needed;
- The complexity of modeling and molding has been significantly reduced.
Gasification casting is becoming increasingly popular in modern metallurgical industries.
Metal casting methods
The main metal casting methods are as follows:
Traditional method
The metal enters the mold under the influence of gravity. Sand-clay or metal matrices are used. The disadvantage of the method is the high labor intensity of making molds and other operations, difficult working conditions and low environmental friendliness
Low pressure casting
The essence of the method is that a crucible with metal and matrices for castings are located in a sealed chamber. A metal wire made of titanium alloy is lowered from the mold into the molten metal. At this time, low excess pressure of air or inert gas is supplied to the chamber. The metal enters the matrix under pressure, the flow rate is very high and at the same time regulated. The form is filled completely and evenly.
The method makes it possible to obtain high-quality castings, including especially thin-walled ones. The surface quality is also superior to castings produced by the traditional method. Foundry gases are removed through an exhaust pipeline into the cleaning system, from where they enter the atmosphere. The method is characterized by highly automated operations, improved working conditions for personnel and high environmental friendliness. In addition, with such casting, both materials and energy consumption are significantly saved.
High pressure casting
The method is used in both ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy and allows one to obtain the most accurate and uniform castings. Metal under high pressure enters the matrix at a speed of up to 120 m/s and instantly fills it.
Parts obtained by this method require virtually no finishing machining. Using this method, you can cast parts of almost any configuration, with thin walls, with ready-made holes and even with ready-made threads.
Injection casting
The injection method differs from conventional injection molding in that the metal enters the matrix in the form of a powder mixed with a binder. The molds are made from high-strength steels.
The high fluidity of the mixture allows you to fill the smallest relief details of forms of the most complex configuration, including internal cavities. The advantage of this method is the high precision of the surface, making additional mechanical processing unnecessary or reducing it to a minimum. Another advantage is the highest physico-chemical homogeneity of the casting.
There are other methods of casting parts that have niche applications.
Areas of application
Used in making:
- Thermoelectric converters.
- Highly efficient lasers.
- Pyrotechnics. It is used to color fireworks flames red.
- Soldered.
- Metal halide lamps, alkaline batteries.
- Lubricants.
- Glass, coatings for porcelain products.
Main areas of application:
- nuclear energy;
- metallurgy;
- medicine.
Alkali metal perchlorate is used as an oxidizing agent.
Battery
Use of the word METAL
The second homonym is the word METAL. With one L at the end - this is an imperfect verb, masculine, past tense, having the infinitive “throw”: “The athlete threw a javelin.”
In this case, all past tense verbs from the word “throw” are written with one L: “throw, throw, throw.” Although in the neuter gender this verb is most often written in the perfect form, with prefixes: “swept away, swept away.”
Example sentences
- Yesterday all our eighth graders threw a ball in physical education.
- In his youth he was an athlete: he threw a javelin.
- Angry, she threw everything she could get her hands on at the wall.
- The wind blew the hay all over the field.
- The laundry was randomly swept all over the street.
- Pavel was very tired: he had been throwing hay all day to make it before the rain.