Non-ferrous is a group of different metals and their alloys.
Let's take a closer look at what non-ferrous metal scrap is.
There are two groups of metals:
- colored;
- black.
Iron and its alloys are called black
The rest are non-ferrous or non-ferrous.
Their list is diverse:
- aluminum;
- copper;
- nickel;
- manganese;
- titanium;
- zirconium, etc.
are in demand today both in production and in scientific activities . Their areas of application are varied.
Scrap metal collection points are happy to buy non-ferrous metal scrap at competitive prices, and in order to avoid getting into trouble when handing it over, you need to be familiar with the types and know the standard classification of non-ferrous metals.
Classification of non-ferrous metals according to GOST
The current GOST 1639-2009 clearly indicates what belongs to non-ferrous metal scrap.
The classification of scrap is divided into four main sections that characterize it:
- Name;
- physical parameters;
- chemical composition;
- quality.
GOST metals and their alloys.
The section displays 13 types that are accepted in organizations for receiving recyclable materials.
Below is a table in which you can see a list of non-ferrous metals in one list and the number of individual types of scrap:
| Metal | Types of scrap |
| Aluminum | 32 |
| Tungsten | 17 |
| Cadmium | 2 |
| Cobalt | 3 |
| Magnesium | 8 |
| Copper | 13 |
| Brass | 23 |
| Bronze | 15 |
| Molybdenum | 9 |
| Lead | 11 |
| Mercury | 6 |
| Tin | 10 |
| Nickel | 26 |
Pure metal can rarely be found , since most scrap is made up of alloys.
Upon acceptance, belonging to one or another type is assessed by the element that is greater in percentage terms in recyclable materials.
This ratio can be determined using special equipment.
Categories of ferrous scrap according to GOST 2787-75
In addition to classes, scrap and ferrous metal waste are divided into categories:
- A (carbon compounds);
- B (doped compounds).
The category designation is included in the index assigned to each type of ferrous scrap. For example, category 5A may include pieces of carbon steel reinforcement with a diameter of more than 10 mm and a length of more than 1 meter, and 5B - oversized pieces of scrap (including the same reinforcement), but made of alloy steel.
| Classes | Categories | Kinds | N type | General designation |
| Steel scrap and waste | A | Steel scrap and waste N 1 | 1 | 1A |
| A, B | Steel scrap and waste N 2 | 2 | 2A, 2B | |
| A, B | Steel scrap and waste N 3 | 3 | FOR, ZB | |
| A, B | Steel scrap and waste N 4 | 4 | 4A, 4B | |
| A, B | Oversized steel scrap and waste (for recycling) | 5 | 5A, 5B | |
| A, B | Briquettes N 1 from steel shavings | 6 | 6A, 6B | |
| A, B | Briquettes N 2 from steel shavings | 7 | 7A, 7B | |
| A, B | Packages N 1 | 8 | 8A, 8B | |
| A | Packages N 2 | 9 | 9A | |
| A | Packages N 3 | 10 | 10A | |
| A, B | Scrap for packaging N 1 | 11 | 11A, 11B | |
| A | Scrap for packaging N 2 | 12 | 12A | |
| A, B | Steel ropes and wire | 13 | 13A, 13B | |
| A | Steel filings N 1 | 14 | 14A | |
| A, B | Steel filings N 2 | 15 | 15A, 15B | |
| A, B | Vinyl steel filings (for recycling) | 16 | 16A, 16B | |
| Cast iron scrap and waste | A, B | Cast iron scrap and waste N 1 | 17 | 17A, 17B |
| A | Cast iron scrap and waste N 2 | 18 | 18A | |
| A | Cast iron scrap and waste N 3 | 19 | 19A | |
| A, B | Oversized cast iron scrap and waste No. 1 (for recycling) | 20 | 20A, 20B | |
| A | Oversized cast iron scrap and waste N 2 (for recycling) | 21 | 21 A | |
| A | Oversized cast iron scrap and waste N 3 (for recycling) | 22 | 22A | |
| A | Briquettes made from cast iron shavings | 23 | 23A | |
| A, B | Cast iron shavings | 24 | 24A, 24B | |
| Outside the classroom | A, B | Domain additive | 25 | 25A, 25B |
| A, B | Oversized blast furnace additive (for processing) | 26 | 26A, 26B | |
| A | Rolling and forging scale | 27 | 27A | |
| A | Welding slag | 28 | 28A |
Types
Non-ferrous metal scrap is divided into types according to the following criteria :
- origin;
- chemical composition;
- physical state.
The origin of the scrap may be as follows:
- industrial waste;
- marriage;
- substandard;
- scrap of finished products.
The chemical composition of non-ferrous metal scrap, which is determined in the laboratory, shows which metal or alloy it belongs to.
The most valuable recyclable materials are unalloyed metals with a low content of impurities. Physical parameters are just as important when passing as chemical ones.
According to these characteristics, scrap is divided into the following classes :
- A – directly refers to scrap and lump waste;
- B – includes shavings, tangled wire and small pieces;
- B - powdered waste (mainly found only in rare metals: tungsten, cobalt, molybdenum and titanium);
- G - other recyclables.
Classes of ferrous scrap metal
From the standpoint of the mentioned standard, two classes of ferrous scrap are distinguished. The division is based on the proportion of carbon content in the metal:
- steel scrap and waste (contain less than 2.14% carbon, which is true for iron-carbon alloys with a low percentage of impurities);
- cast iron waste and scrap (characterized by high carbon content in iron).
Sometimes a third class is added to these classes - stainless steel. But its position in the classification cannot be decided unambiguously. On the one hand, stainless steel is the result of the interaction of iron and carbon (which is also structural steel and cast iron), and on the other hand, during its production alloying elements are added - impurities (mainly non-ferrous metals), which significantly change the properties of steel.
In addition to the listed classes, secondary ferrous metals are distinguished outside the class: blast furnace additive, scale, welding slag.
Safety
All non-ferrous scrap must be checked for:
- presence of radiation and harmful chemical contamination;
- explosion hazard.
When transporting scrap metal, it must be accompanied by documentation on radiation and explosion safety.
The concentration of harmful substances must not exceed the values specified in GOST 12.1.005.
The Russian Ministry of Natural Resources has identified five classes of chemical, radiation and explosion hazards of non-ferrous metal scrap:
- Hazardous waste with great harm to the ecosystem. These include mercury, polonium and plutonium.
- Highly hazardous waste, the consequences of which take nature thirty years to remove. These are alloys of lead, cobalt and molybdenum.
- Moderate danger , in which it takes ten years to restore the ecology. This is scrap mixed with copper, nickel, iron, zinc, aluminum and silver.
- Low hazardous waste, removal of the consequences takes three years. This includes scrap bronze.
- Low danger , such scrap does not harm the environment. This is the most common class among colored scrap.
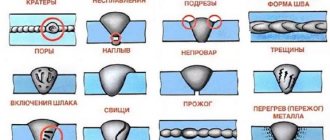
Due to the expected harm to humans and nature, all operations with non-ferrous scrap require a license from the points accepting secondary non-ferrous metals. Checking for all types of hazards is carried out according to the following scheme:
Subtleties of working with non-ferrous metal
Do not forget about safety precautions when working with non-ferrous metal!
Every time when conducting research on any batch of scrap, the percentage of harmful and toxic substances is checked. It is for this reason that studies are carried out to determine the presence of radiation, explosiveness, and the presence of harmful chemicals. Absolutely all batches of scrap must have a certificate of conformity in accordance with GOST.
According to the regulations and standards, an inspection is carried out and the class, type of substance, fire hazard and a number of other indicators are established.
Marking
According to GOST, all transported scrap must be marked with the following indication:
- names;
- GOST designations;
- designations of the type of recyclable materials;
- alloy grades.
Marking of non-ferrous metals and alloys must be firmly attached to the cargo during transportation and storage.
To determine the grade of metal, you need to look at the stamp book , a special document with all the markings of the metal or alloy you are interested in.
Waste from metal forming (drawing, pressing, forging, stamping)
Metal forming
This is the most economical - low-waste, method of producing metal products, where the share of scrap does not exceed 25%. For comparison, during mechanical processing (cutting, for example), the level of scrap metal is up to half the mass of the finished product. Among the available pressure processing methods, cold stamping is the most effective, characterized by a waste level of up to 10%.
The most common types of waste from metal forming are slag from the combustion of coke and scale. The latter option is present in the following methods:
- pressing – the composition of the scrap contains up to 15% petroleum products, the waste is kept separately in pits after dismantling the equipment;
- forging of ferrous metal;
- stamping of forgings - the presence of petroleum products in this waste exceeds 15%;
- mechanical cleaning of parts made by hot stamping.
Separately, it is necessary to consider the formation of colored scale in metallurgy, which accompanies the production of copper wire using drawing technology with simultaneous annealing.
Kinds
The large number of non-ferrous metals and various characteristics required their classification into separate types.
industrial systematization is in use , reflecting the historically established components of the metallurgical industry and the science of the same name.
The name itself does not fully reflect the essence of non-ferrous metal.
Only gold and copper are colored, while the rest are the usual grey-black shades.
Science usually distinguishes the following types of non-ferrous metals and alloys:
- lungs;
- heavy;
- noble;
- refractory;
- scattered;
- rare earth;
- radioactive.
industry in Russia today is on the rise and includes:
- metal mining;
- ore beneficiation;
- metal smelting
Basic non-ferrous metals
The main non-ferrous metals include:
- copper;
- aluminum.
Aluminum is an excellent electrical conductor. It is flexible, which is both its advantage and disadvantage.
To give it strength add :
- manganese;
- copper;
- magnesium, etc.
Such alloys are used for the production of :
- airplanes;
- sea and river ships;
- space shuttles;
- in construction;
- in the food industry.
Aluminum and its alloys are the cheapest type of non-ferrous metal scrap.
You can find it in a variety of household items, including:
- siding;
- gutters;
- roofing
Copper is a commonly found non-ferrous metal.
It also has good characteristics:
- plastic;
- good electrical conductor;
- good heat conductor.
It is in great demand in alloys and is used in various economic sectors.
Its alloy with zinc and tin is known - brass.
It can be found in:
- cars;
- hours;
- expensive jewelry.
find copper for scrap metal in:
- power cables;
- water pipes;
- household products.
Copper is highly valued at recycling centers.
Rare
Rare earth metals are used to improve the qualities of other metals and became widely used with the development of industrial production in the 20th century.
These are the following metals:
- scandium;
- yttrium;
- lanthanides.
The name itself suggests that there is very little of these non-ferrous metals in the earth's crust. Also, previously, refractory oxides that form rare non-ferrous metals were called “earths” . They are extracted from oxides.
Today, rare earth metals can be found in all digital devices:
- smartphones;
- players;
- computers;
- in hybrid engines;
- in other electronics.
Alloys made from them have high characteristics , for example:
- anti-corrosion;
- strength;
- heat resistant.
Heavy
Let's consider heavy non-ferrous metals, collecting them in several lists.
The heaviest non-ferrous metals on Earth:
- osmium;
- iridium.
Rarely found in soil , it is generally the most expensive non-ferrous metal.
Also included in this group are:
- copper;
- lead;
- zinc;
- tin;
- nickel.
All of them have a high density and, accordingly, a lot of weight, which is why they get the name – heavy.
Lead is widely known and used in many industries , contained in:
- rock
- soil.
It is made from:
- batteries;
- explosives;
Lead is also used to create protective aprons from radiation .
Has the following characteristics:
- low thermal conductivity;
- plastic;
- toxicity.
Therefore, lead must be used carefully, following all safety regulations.
Tin used to be called an alloy of lead and silver.
Today, tin is used in the metallurgical industry and the production of various alloys, which include:
- bearings;
- packaging foil;
- bronze;
- food tin;
- wires
Nickel is a heavy non-ferrous metal with high heat-resistant and anti-corrosion characteristics. Nickel is used in alloys. In stainless steel it is the main component.
Made from nickel :
- coins;
- armor;
- chemical equipment;
- wire;
- foil;
- a thread;
- powder;
- alkaline batteries.
in demand in:
- shipbuilding;
- electrical engineering.
Lungs
The definition of “light non-ferrous metals” includes metals with low density.
List of the most popular light non-ferrous metals:
- aluminum;
- tin;
- magnesium;
- titanium;
- beryllium;
- lithium.
The lightest non-ferrous metal is lithium. It is widely used in various alloys.
is used in:
- chemical industry;
- metallurgical industry;
- military-industrial complex;
- thermonuclear energy.
Lithium is also used in the manufacture of:
- optics;
- alkaline batteries;
- ceramic products.
The ductility of magnesium is not as good as that of copper and aluminum, which affects the welding properties of this metal. But it can be easily cut with a special tool. At the same time, the mechanical properties leave much to be desired. This it to be widely introduced into industrial production .
Metal processing waste from the production of finished metal products
Sources of scrap metal can be divided into three categories:
- products that have become unusable;
- structures, parts or mechanisms that have reached their maximum service life;
- waste generated during processing of metal blanks and products.
The last group is characterized by such types of scrap as chips, slag, scale, trimmings, etc. Distinctive features that characterize metal processing waste in the production of finished metal products are a high percentage of scrap and its qualitative composition. The second factor is associated with the specifics of the outer layer of the metal workpiece, which has better strength characteristics than the core. The exact proportion of waste generated from metal processing depends on the type of specific process.
Popular types at collection points
The most popular non-ferrous metals at collection points:
- aluminum;
- copper;
- brass;
- zinc alloys (for example, TsAM);
- bronze;
- nickel;
- lead;
- titanium;
- tin;
- tungsten.
If you want to find out what is more profitable to rent out, then read this article.
Recycling of metallurgical waste
The work of modern enterprises engaged in the metallurgical sector is aimed not only at the production of blanks and metal products, but also at the processing of solid waste: any serious metallurgical plant has at its disposal the production resources for their processing.
Recycling of secondary raw materials includes two processes that are equally applicable to both ferrous and non-ferrous metals: recycling and recycling.
Disposal
The recycling process involves recycling TPO for reuse. Recycling involves cutting, sorting, cleaning and treating waste to produce materials of practical value. Examples of recycling are slag pumice or mineral wool: being products of metallurgy, they are not metal, but silicate materials obtained from industrial waste.
Advantages of using recycled materials
After processing of scrap metal is completed, a material is obtained that has the same properties as the primary raw material. It can not only be used to make rolled metal of good quality, but also used in various fields of activity.
The process of obtaining secondary raw materials has a number of advantages. The most significant among them are:
- low (compared to the extraction of metal from ore) negative impact on the ecology of the settlement and the entire region;
- significant savings in energy spent on scrap processing;
- reducing iron ore production and preserving natural reserves;
- quickly obtain metal ready for use.
Scrap recycling is an important activity that helps solve the problem of metal shortages. When the process is carried out correctly, the desired result is quickly achieved, and financial costs are significantly reduced.
Acceptance rules
At points, scrap metal is accepted in batches. This means that all scrap brought on one vehicle with a single package of accompanying documents is assessed and weighed. The results of the actual analysis for alloyed metals, dates of dispatch, company details or personal data of the sender must be indicated. The package of documents includes certificates confirming ownership of the scrap. Special alloys and high-alloy steel waste must be packaged. The total weight is determined by the net weight (clogging, machine weight and tare weight are subtracted from the gross weight).
Sorting
Initially, it is designed to distribute scrap into piles, placing materials with approximately the same characteristics in each. To obtain a high-quality product, as well as to optimize the processing process, scrap metal is sorted according to the following criteria:
- Dimensions of pieces;
- Chemical properties: classification is carried out taking into account 28 indicators, including the content of carbon and its compounds;
- Presence of impurities.
Equipment for sorting scrap, although not cheap, quickly pays for itself by increasing the speed of work and minimizing human errors.