Without exception, all welders working in production have a specially equipped workplace, which is also commonly called a welding station. It can be stationary or mobile and is equipped depending on the tasks assigned to the specialist.
- Stationary station equipment
- General requirements
Basic equipment
To fully equip a welding station, it is necessary to equip it with electrical equipment, additional equipment and auxiliary means:
- a current source for the formation of a welding arc, which is a welding transformer or inverter;
- current-carrying cables in a reliable braid that can withstand high current strength and constant mechanical stress.
- conductors must have appropriate fastening at the end for connection to terminals, electrode holders and ground;
- gas burners for working with gas welding equipment;
- fixtures and other tools for welding work: clamps, clamps, holders;
- welding table;
- protective equipment: heat-resistant suit, special gloves, welder’s mask, headdress with a lapel.
A distinctive feature of a mobile welding station is that it does not have any boundaries. This is explained by the fact that a specialist needs to constantly move to perform his duties within a certain area: construction site, welding shop, production site, etc.
It is worth paying attention to the fact that this classification relates exclusively to the organization of procedures, but does not in any way regulate the nature of the manipulations performed.
Workplace arrangement options
In practice, it is customary to distinguish between two types of welding stations. Stationary is mostly used for working with small-sized workpieces. The mobile one is in demand at large production sites, in the construction or laying of various types of pipelines.
Basic requirements for organizing a workplace for welding work:
- Good lighting should be provided in the area. The minimum value is 80 Lux. It is advisable to combine natural light and artificial light.
- All electrical equipment must be grounded.
- The base must be strong and solid. As a rule, this is concrete or brickwork.
- Work pockets should be provided at the workplace where documentation or graphic materials could be stored.
- Good ventilation must be provided.
- The working surface of the welding table must be made of steel or cast iron. Nearby there should be connectors for connecting the welding machine and additional equipment.
- There should be a rubber mat or a thick wooden shield under the specialist’s feet.
- To perform work in a sitting position, you need a dielectric chair made of non-flammable material.
If the workplace is set up outdoors, then you need a canopy that will well protect the welder and equipment from rain. In sunny weather, you can work in an open area, but protection from direct sunlight is often required. Then the canopy can be replaced with high shields.
What is a welding post
A welding station is essentially a makeshift welder's office. Yes, there are no comfortable chairs, tables or jugs of water, but there is everything necessary to perform a complex of welding work. In other words, a welding station is a workspace where a welder can work comfortably and safely, and he always has consumables and other necessary equipment at hand.
The welding station must be equipped in compliance with all safety and labor protection requirements. This is a mandatory condition that allows specialists to maintain their health and get the most out of them. When setting up the post, special attention is paid to fire safety. But in order to achieve all the necessary conditions, you should study the specifics of different welding posts.
Depending on the equipment used, welding stations can be:
- Gas welding . The main distinguishing principle is that the energy obtained as a result of gas combustion in a special burner is used to melt metal blanks. Due to the specific nature of gas welding, it is important to equip a good ventilation system for organizing a work office. The surface of the desktop and the space around it must be made of non-combustible materials.
- Electric welding . Working with electric welding is no less dangerous than working with gas welding. In addition to good ventilation, effective protection of employees from electric shock is also necessary.
In any case, no matter what method of welding or cutting metal is used in a closed workspace, it is very important to carefully consider the arrangement of the ventilation system. In addition to the hood, supply systems are also installed for natural or forced supply of fresh air.
Depending on the needs, welding stations can be:
- Stationary . It is a limited space in a room, equipped specifically for welding metals. They are often equipped with rotary tables for convenience.
- Mobile . They are mobile structures that one person can carry or move within the work site. The best option in cases where welding of large structures is required. They can be located indoors (workshop, production site, shipbuilding dock, etc.) or in an open area (construction, creation of large-sized non-standard structures, etc.).
A stationary welding station is best suited for joining small and medium-sized metal workpieces. But for working with large-sized structures this is not the best option. A special cabin, which serves as the “walls” of such an area, is made of galvanized metal sheets. They are characterized by high resistance to high temperatures, as well as IR radiation.
A clear advantage of a mobile welding station is the fact that there is no need to create any special conditions for work. If necessary, protection from precipitation is provided by a canopy, and from wind - by side hard screens. If conditions permit, parts are welded without protection from the weather.
Tools and additional equipment are contained in the drawers of the tool cabinet, and artificial lighting (if required) is provided locally. In mobile posts, as in stationary ones, care should be taken to ground the equipment that is connected to the power supply network.
Copper pipes
The chemical composition of the metal used for the production of copper pipes is regulated in Russia by GOST 859-2001. According to it, in all grades of copper the Cu (+Ag) content is more than 99%. Small impurities of iron, tin, lead, antimony and other elements are acceptable. Copper pipes come in annealed (soft) and unannealed (hard) varieties .
The first are obtained as a result of annealing - heating to 600-700°C with gradual cooling. This operation returns copper to its natural ductility, lost during machining (stamping or rolling) during manufacturing. Annealed pipe has some technological advantages over unannealed pipe .
While inferior to it in strength, it is much superior to it in ductility. The value of its elongation at break can reach 40-60%. This means that the annealed pipe can be bent if necessary without fear of rupture. Observing, of course, certain relationships between the diameter of the pipe and the bending radius (R = 3d-8d, depending on the bending method).
Annealed copper pipes can prevent a water pipe from bursting when it accidentally freezes - thanks to the plastic deformation of the metal, which prevents the pipe from rupturing. Anyone who has at least once encountered the replacement of steel “frozen” pipes is able to fully appreciate this advantage. Annealed pipes are supplied in coils of 50 and 25 m, unannealed pipes are supplied in the form of measured pieces (rods) 3 and 5 m long.
Unannealed and annealed copper pipes
Types of welding stations
Stationary post
The classic design of a stationary welding station involves the installation of a special protective cabin without a canopy.
Requirements for organizing a stationary workplace:
- The area of the room along the internal perimeter must be at least three square meters.
- The surface of the walls is finished with non-combustible materials.
- The cabin frame can only be made of metal.
- The height of the work table depends on the method of performing the work. For a sitting position it is 60 cm, and for a standing position it is 90 cm. Ideally, if the structure can be lowered or raised depending on the situation.
- A tarpaulin canopy is hung at the entrance.
- The minimum permissible cabin height is 2 meters.
- The lower part of the walls is raised above the floor level to improve ventilation. The gap should be at least 25 cm.
- The working surface requires a metal or cast iron sheet with a total area of at least one square meter.
- The inside of the cabin is treated with a special compound in a light gray shade. It has high fire-resistant characteristics and absorbs ultraviolet radiation. This is necessary to prevent accidental ignition of the surface of the walls of the room.
Gas welding station
To organize a gas welding station, you will first need the appropriate equipment: an acetylene generator, burners and hoses for gas supply, oxygen cylinders and reducers.
A portable gas welding station is a trolley on which cylinders, gearboxes and all the necessary equipment are located. The cart is most often made of pipes, and the wheel axle is located at the center of gravity to make it easier to move and hold.
The gas welding station equipment consists of the following elements:
- table with metal top;
- hood. It is usually installed above the table or slightly to the side;
- sources of light.
Gas cylinders are located slightly away from the workbench to prevent hot splashes from getting on the gearboxes. Gas is supplied to the work site through hoses. Large enterprises often provide for gas supply through centralized pipelines.
According to existing standards, for safety reasons, the distance between the work table and cylinders with acetylene and oxygen must be at least 10 meters. The same footage (no less!) must be maintained between cylinders and any sources of open fire. In cases where you have to work in narrow or hard-to-reach places, a supply of fresh air is required.
Mobile post
A mobile welding station is necessary when performing work with large-sized structures. Often, such a workplace is located outdoors. Therefore, it requires additional equipment for protection from sunlight, wind and precipitation. The protection consists of a hinged canopy and folding rigid shields (screens) from the wind. To accommodate consumables, additional tools and small equipment, the mobile workplace is equipped with metalwork carts with drawers.
During welding work, harmful volatile substances are released in large quantities. They pose a health hazard to the specialist. However, ventilation is not required: the mobile welding station is located in an open area and the gases quickly evaporate.
But a local lighting system may be required. In conditions of poor natural light, an additional light source will be required. It is placed directly above the table on stands. Good lighting reduces eye strain, improves working conditions, which helps increase specialist productivity. Electrical equipment, including the welding machine itself, must be grounded in order to minimize the likelihood of electric shock to the welder.
It is necessary to take into account that when installing enclosing structures, a gap of about 50 cm should be left between the panels. This is necessary to ensure a sufficient flow of fresh air. The welder must have protective equipment - a special suit, shoes, mask, mittens and headgear. It is imperative to always have a working main tool - a holder. It must be reliable and safe, protect the welder’s hand from a source of high temperature, hold well and quickly release the electrode.
Proper equipment of a mobile welding station gives the welder the opportunity to work without discomfort and in completely safe conditions. This in turn brings:
- good final result of the work;
- reducing the time required to complete welding work;
- reducing the likelihood of specialist illness.
Gas cutting equipment
In the most general case, cutting metal with gas involves the following operations:
- cutting sheet steel at the procurement area;
- dismantling of metal structural elements at the assembly site;
- manual cutting of parts and assembled units;
- recycling of outdated structures and mechanisms and other types of work that do not require special precision.
The equipment for the above gas cutting of metal (hereinafter referred to as gas cutting) includes:
- gas-burner . It is equipped with a head located at an angle of 90° or 60° to the axis of the tool. The latter has several nozzles through which oxygen and heating gas escape;
- gas cylinders;
- pressure regulator;
- gas hoses (sleeves).
Acetylene generators
An acetylene generator is a device that creates acetylene by mixing calcium carbide with water.
Acetylene generator. East. https://weldering.com/acetilenovyy-generator
The process of mixing and chemical interaction occurs in stationary or mobile gas welding stations. They subsequently serve as sources of acetylene, a flammable gas for gas welding.
In accordance with GOST 30829-2002 “Mobile acetylene generators. General technical conditions" (hereinafter referred to as GTU), acetylene generators consist of the following main components:
- gasifier . This unit is designed to produce acetylene from water and calcium carbide;
- gas collector It performs two tasks: storing all generated gas;
- compensation of unevenness between gas formation and gas consumption of acetylene;
- localization of an oxygen-acetylene or air-acetylene mixture flame;
In addition, generators can be equipped with other functional elements:
- filters;
- pressure regulators, etc.
In accordance with the General Specifications, acetylene generators are classified according to the following parameters:
- according to the method of interaction of calcium carbide with water: VK – water on carbide;
- KB – carbide in water;
- K – contact, with process options: BB – water displacement;
- PC - immersion of carbide in water.
- N – low pressure. Parameter value (hereinafter referred to as PV), MPa: ≤ 0.02;
Additional technical requirements:
- generator productivity should not exceed, cubic meters/hour: 3;
- weight of unloaded generator, kg: ≤ 20.
When choosing equipment for gas cutting, you should carefully compare its capabilities with the tasks you face.
Gas welding kits and stations
Gas welding stations in everyday use have the following names:
- gas welding kits;
- gas welder's tool, etc.
Gas welding stations, depending on their size and power, are divided into mobile (transportable or portable) and stationary (in large industries). The mobile set is a special metal structure: a transport trolley or a portable box.
Gas welding station “PGSP-10/12”
The gas welding post (hereinafter referred to as ASG) is intended for transporting gas welding equipment and tools to the place of work and welding. The PGS is equipped with the following devices:
- cylinders . They are filled with oxygen and flammable gas (acetylene, propane, etc.);
- burners and cutters;
- combination and security keys;
- rubber hoses (gas hoses);
- clamps.
The ASG is equipped with a frame, which allows it to move easily and be used to perform a wide range of works:
- repair;
- emergency;
- installation.
The advantage of ASGs is that they allow welding work to be carried out far from sources of replenishment of consumables:
- during installation of pipelines;
- inside refrigeration systems;
- when carrying out plumbing work, etc.
The disadvantage of ASG is the need to refill cylinders with oxygen and flammable gas. This disadvantage becomes especially noticeable under conditions of intensive work, which requires increased gas consumption.
When choosing equipment you should:
- carefully decide: what you intend to do, what is the amount of work to be done;
- depending on the decision made, choose equipment.
When assessing the technical condition of the ASG, be sure to check the calibration and control documentation for the pressure gauge and valves.
Gas cylinders
The set of ASG equipment for gas welding includes cylinders that are necessary for storing and transporting working gases. The latter are in a cylinder under pressure in one of the following states:
- compressed;
- liquefied
- dissolved.
Gas cylinders for welding have volumes, cubic meters. dm: 0.4…55. They are used in mobile (portable or transportable) and stationary ASGs. Cylinders with a capacity of 40 liters are more in demand.
Cylinders for ASG are manufactured in accordance with GOST 949 - 73 “Steel cylinders of small and medium volume for gases at Рр<=19.6 MPa (200 kgf/cm2). Technical specifications" (hereinafter referred to as TU), made of seamless steel pipes. They have the shape of a cylindrical vessel with a convex bottom and a narrow neck. Various devices are mounted on the neck:
- flanges;
- fittings;
- valves.
In the neck of the vessel there is a cone-shaped hole in which a thread is cut for a valve - a shut-off control device. The latter has a flywheel, the rotation of which opens or closes the gas supply valve.
A ring with an external thread for a safety cap designed to protect the valve is tightly installed on the neck of the cylinder. To ensure stability of the cylinder in a vertical position, a shoe with a square platform is placed on its lower part - a container with gas is placed on it.
Gas cylinders for welding or cutting metals vary in color.
Each gas has its own color cylinder
Each gas has its own color. The color coding of cylinders with the most commonly used gases is shown in Table No. 1. Table No. 1.
| Gas | Cylinder color | Lettering color | Stripe color |
| Oxygen | Blue | Black | – |
| Propane | Red | White | – |
| Acetylene | White | Red | – |
| Carbon dioxide | Black | Yellow | – |
| Nitrogen | Black | Yellow | Brown |
| Argon | Grey | Green | Green |
| Oil and Gas | Grey | Red | – |
The gas cylinder has its own individual passport, which indicates its technical parameters. In addition, all containers regularly undergo mandatory testing and inspection, the results of which must be indicated in this passport. It is attached to the body of the cylinder under the neck. When choosing cylinders, check their passports and the condition of the gas locking mechanism.
Cutters
This is the equipment for gas cutting that you cannot do without at all. Gas cutters on our website are discussed in detail in the article “Gas cutters”. Therefore, we will not repeat ourselves, and we recommend that you contact the specified address.
Burners
A gas welding torch is a device that allows proportional mixing of oxygen with flammable gas or flammable liquid vapor to produce a stable welding flame of the required power. Welding torches are mandatory participants in the gas welding process. They are intended for:
- heating the metal;
- welding of parts.
Therefore, they must satisfy a number of special requirements that are important when performing gas welding work:
- be able to create, shape, maintain and regulate a stable flame of the selected mode;
- have high mechanical strength;
- ensure safety during operation;
- have a small mass.
The burners are made of durable and high-quality material. As a rule, the welding torches themselves are made of brass, and the mouthpieces are made of copper. In some cases, light aluminum alloys are used for their manufacture. This significantly reduces the overall weight of the equipment.
Welding torches have different powers, which makes it possible to weld metal of different thicknesses. According to the flow pattern of combustible gas into the mixing chamber, gas burners are divided into two types:
- injection . They are used at low pressure of incoming flammable gas (less than 0.5 atmospheres);
- non-injector . They are used when the pressure of the flammable gas in the cylinder is higher than the specified value. In this case, gas can enter the burner without the help of an injector (on its own).
Schemes of acetylene torches. East. https://tm.msun.ru/tm/books/pats/lab3/lab3.html.
Explanation of the figure: a) injection burner; b) injection-free burner; 1 – burner barrel; 2 – nut; 3 – tip; 4 – mouthpiece; 5 – mixing chamber; 6 – injector; 7 – valve; 8 – connecting fitting.
Depending on functionality, gas burners are divided into the following groups:
- by method of application : manual;
- machine;
- single-flame;
- small Acetylene consumption, l/h: 25…400;
In accordance with GOST 1077-79 “Universal single-flame burners for oxy-acetylene welding, soldering and heating. Types, main parameters and sizes. General technical requirements", single-flame universal gas burners are divided into four types according to power output:
- G1 – micropower;
- G2 – low power;
- G3 – average power;
- G4 – high power.
The most common are burners of low and medium power (thickness of the metal being processed, mm: ≤ 0.2¬07 and ≤ 0.5¬30, respectively).
Oxygen and flammable gas must be mixed in a certain ratio. For example, the following ratio requirements apply to burners that are used with acetylene: Vк/Va = 0.8-1.5. The torch must maintain a constant mixture composition during welding.
When choosing, pay attention to the technical condition of the valves.
Trolleys for cylinders
The use of gas cylinders in metal processing is associated with certain inconveniences - they weigh quite a lot. This is especially true when moving them. The cart for cylinders, included in the equipment for gas cutting of metal, eliminates this drawback. In addition, the process becomes safer and more efficient. With its help, you can move cylinders over short distances without much effort. These carts for gas cylinders are safe because they have a reinforced axle for the wheels. In addition, more reliable and safe trolleys have a special design that allows gas cylinders to be moved at an angle of 45°. This design of the device has its advantages: it is more convenient and safe.
Please pay attention when purchasing, do not buy a cart that violates the safety regulations. According to the rules, cylinders are secured with a chain.
There are carts designed to transport one cylinder, two containers and other attributes necessary for welding (welding station). The cylinders are secured using a special galvanized chain. Carts for transporting cylinders with oxygen, propane and other flammable gases have the following load capacity, kg:
- for one container: 150;
- for two: 250.
Moreover, carts designed to transport two gas cylinders are equipped with a third wheel to reduce the load. It performs rotary-support functions. Its diameter is usually smaller than the two main ones:
- the main two wheels have a diameter, mm: 250 or 330;
- third (auxiliary) – mm: 160.
Let's look at examples of the most popular trolleys for gas cylinders among welders:
- series "GB 1" . Used to transport one cylinder (acetylene, oxygen, carbon dioxide, etc.). The trolley is easy to use, simple and, as a result, very reliable. The cylinder is fixed to the cart body with a galvanized chain. Equipped with a reinforced axle for mounting wheels. It is equipped with both pneumatic wheels and cast rubber.
- series "GB 2" . Used to transport two cylinders. In order to reduce loads and for ease of use, this trolley model has a third: a rotary support wheel, the diameter of which is 160 mm. The design of the trolley is reliable, simple, and easy to use. Fixing the cylinders to the cart body and equipping them with wheels is similar to the “GB-1”;
- series "PR" . Cart for transporting one propane cylinder. Fixing the cylinders to the cart body and equipping them with wheels is similar to the “GB-1”;
- “KP” series (oxygen + propane). Trolley for transporting two cylinders. It is equipped with an additional support wheel with a diameter of 160 mm. Fixing the cylinders to the cart body and equipping them with wheels is similar to the “GB-1”;
- series "KP-2 U" . Used to transport two cylinders and hoses (complete welding station). Fixing the cylinders to the cart body and equipping them with wheels is similar to the “GB-1”;
- series "GB-2B" . The welder's trolley is equipped with two powerful cast wheels with a diameter of 330 mm and has a design feature: it holds, without the help of a third wheel, 2 gas cylinders at an angle of 45°. The cylinders are fixed to the trolley using a galvanized chain;
- series "GBR" . The trolley is designed to transport 1 oxygen gas cylinder. Fixing the cylinder to the cart body and equipping it with wheels is similar to the “GB-1”.
When choosing a trolley, pay attention to the design of the wheel fastenings.
Valves
The classification of shut-off valves for cylinders depends on their contents. Therefore, valves are divided into the following types:
- fittings for liquefied gas cylinders;
- fittings for oxygen cylinders;
- fittings for propane-butane cylinders.
As an example, consider the design of an oxygen cylinder valve. Its diagram is shown in the figure.
Oxygen cylinder valve. East. https://experttrub.ru/zadvizhki/ventil-kislorodnyj-ustrojstvo.html.
Explanation of the figure: 1 – nut; 2 – spring; 3 – handwheel; 4, 7 – fiber gaskets; 5 – spindle; 6 – union nut; 8 – coupling; 9 – valve body; 10 – plug; 11 – valve body; 12 – seal.
Valve design and operating principle:
- valve body (hereinafter – designations in the valve figure: 9). This is a steel part that resembles a “tee” in shape. A conical thread is cut on its lower part (identical to the thread on the receiving hole of the cylinder). In the upper part of the body there is a cylindrical thread. It is intended for the union nut (6) holding the spindle (5). On the side outlet of the housing there is a cylindrical thread intended for the valve plug (10);
- locking element. This is a prefabricated unit (assembly), consisting of: a bypass valve (11), which regulates the flow movement through the body;
- stock It transmits torque from the flywheel (3) to the valve (11);
In addition, valves for high-pressure cylinders are equipped with gaskets and seals (4, 7, 12). These sealing structural elements are located between:
- body and union nut;
- nut and flywheel;
- valve and body.
The operation diagram of the valve on a gas cylinder for welding is very simple:
- A plug is screwed from the side fitting on the body. Instead, the welding hose reducer (sleeve) is screwed on;
- The valve flywheel is unscrewed with a smooth movement. He moves the valve, and the contents of the cylinder flow to the workplace;
- To shut off the gas flow from the cylinder, you need to do everything in reverse order.
When choosing a valve, you should pay special attention to the quality of the gaskets and the technical condition of the threads.
Gearboxes
Gas reducers are devices designed to reduce the pressure of a gas (gas mixture) at the outlet of a cylinder (gas pipeline, etc.) to the operating level. In addition, they automatically maintain this parameter constant, regardless of its changes in these cylinders or gas pipelines.
Gearboxes must comply with the GOST R 54791-2011 standard “Equipment for gas welding, cutting and related processes. Reducers and flow meters for gas pipelines and gas cylinders with gas pressure up to 300 bar (30 MPa).”
A diagram of a typical gearbox without a flow meter is shown in the figure.
Diagram of a typical gearbox without a flow meter. East. https://docs.cntd.ru/document/gost-r-54791-2011.
Explanation of the figure: 1 – setting screw; 2 – spring thrust washer; 3 – body; 4a – inlet fitting; 4b – inlet fitting nut; 5 – input filter; 6 – pressure gauge seal; 7 – high pressure gauge; 8 – pressure reducing valve cap; 9 – pressure reducing valve spring; 10 – spring thrust washer; 11 – reducing valve; 12 – safety valve cap; 13 – safety valve spring; 14 – safety valve seat; 15 – low pressure gauge; 16 – reducing valve seat; 17 – transfer rod; 18 – transfer disk; 19 – membrane; 20 – output connection; 21 – union nut; 22 – fitting for the hose; 23 – membrane seal; 24 – reducing spring; 25 – gearbox cover; 26 – thrust washer of the reducing spring; 27 – outlet valve.
Gas reducers: classification
- according to the principle of organizing the regulatory process : direct action. Gas through the fitting, entering the high-pressure chamber and acting on the valve, tends to open it;
- reverse action. The gas tends to close the valve. In practice, reverse-action gearboxes are most widely used, since they are more convenient and safe to use;
- B – balloon;
- A – acetylene;
- О – single-stage with spring pressure setting;
- at the inlet: 250 – for compressed gases;
- by gas consumption. This parameter, depending on the type of gearbox and its purpose, can vary from several tens of liters per hour to several hundred cubic meters per hour;
- According to the principle of operation, gearboxes are divided into: direct action. Gradually and simultaneously, both pressures decrease: working and in the cylinder;
- single-chamber. Used in cases of low pressure constant requirements;
Table No. 2.
| Type of gas | Code designation |
| Acetylene | A |
| Oxygen | ABOUT |
| Hydrogen | N |
| Compressed air | D or Air (air) |
| LNG (including propane, butane and propylene) | R |
| MAF | Y |
| Natural gas | M |
| CO2, nitrogen, inert gas | N |
The most common types of gearboxes are:
- oxygen. It has an unusually wide application: in industrial enterprises for gas welding, cutting, soldering, etc.;
- when performing welding in extreme conditions (underwater, in space) and many other types of work;
- with a constantly specified operating pressure, which is set at the manufacturer;
In addition to what is described above, the reducer can also serve as a pressure relief valve.
Welding station equipment
Regardless of the functionality, be it a stationary or mobile welding station, the specialist’s place of work must fully comply with the following set of requirements:
- grounding of all energy-consuming devices is mandatory;
- good degree of illumination of the desktop. A combination of natural and artificial lighting is considered optimal;
- floors must be made of brick or concrete;
- the table top is made of cast iron or steel and is connected to ground;
- Drawers are provided for storing tools;
- in cases where sedentary work is required, a chair made of dielectric material is required;
- A rubber mat is spread under your feet.
When working in an open area, additional protection from sunlight, wind and precipitation will be required.
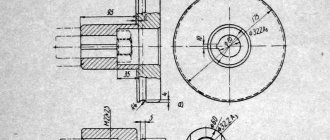
Stationary station equipment
A stationary workplace must meet a number of requirements:
- Such a workplace is made in the form of a cabin that does not have a roof. The total area of the allocated space should not be less than 3 square meters. The optimal height of the fences is 2 m. The entrance opening should be covered with a canopy made of fire-resistant tarpaulin.
- The lower part of the fence should be raised above the floor to a height of 25-30 cm.
- The material for the worktop tabletop can be steel or cast iron. The surface area is made no less than a square meter.
- It should be possible to adjust the height of the table so that the welder can change it to work while sitting (50-60 cm) or standing (90 cm).
- The perimeter walls are made of fire-resistant material. On the inside they are painted a light gray shade that absorbs ultraviolet radiation.
- It is necessary to provide a hood that would effectively remove combustion products. For effective air exchange, fresh ventilation will be required. According to safety requirements, the productivity of such a system is calculated to be no less than 40 cubic meters of air per hour.
- The standard lighting brightness is 60-80 lumens. It is ideal if it is possible to provide a combined illumination of the post: natural in combination with artificial.
All equipment connected to the power supply network must be grounded. In addition, one general switch is installed, which allows you to disconnect all equipment from the supply network at once.
Mobile post equipment
An excellent option for a production workshop or other large workspace, as well as when creating large-scale structures.
Primary requirements:
- Electric welding and additional equipment are combined on a mobile cart.
- The length of the power cable must be sufficient to move within the work area or facility.
- There is no need to install a ventilation system. On the street, combustion products of consumables are carried away as a result of the natural movement of air masses.
- The portable post is equipped with a canopy and protective shields that can be quickly assembled to protect from precipitation, wind or sun.
- In the same way, it is necessary to provide for the possibility of installing fences to protect bystanders from flashes of the welding arc.
- For ease of work, the welder must have a sufficient number of tool carts to store his equipment, additional equipment and equipment.
Desktops
Considering that small metal parts are welded at stationary work stations, special tables are provided for convenience. Structurally, industrial workbenches are designed for work in a standing or sitting position. If the table is made independently, then you need to take into account that the optimal height for working while sitting is 60 cm, and for standing – 90 cm.
The table cover is made of sheet steel or cast iron 2 cm thick. The total surface area is at least 1 square meter. It is important that the table has drawers in which the welder can store electrodes and other consumables, tools and small equipment. If there are none, then you need to additionally acquire a special plumbing trolley.
Rubber mats should be placed under the table itself and along its perimeter to prevent electric shock to the welder. And one more small touch - a metal chair with a dielectric seat, which allows you to do part of the work in a sitting position.
Methods for connecting copper pipes
The most convenient way to connect copper pipes is with fittings, of which there are many available. With all the abundance of types of these parts, there are only three main forms used most often: tees (provide branches from the pipe), corners (change the direction of the pipeline by 90°) and couplings (connect two pipes).
Copper solder fittings
If you wish, you can do without fittings at all, or, in any case, with a minimal amount of them. True, for this you need to have a special, expensive tool that allows you to perform certain operations with pipes, namely bending, expanding and flanging. Using bending, you can do without corner fittings. Expansion (increasing the diameter of the pipe end) allows you to do without couplings when soldering pipes. By using flanging, you can avoid purchasing tees (or corners, if you cut the pipe and install a plug at its end). You just need to keep in mind that when using flanging, the outlet pipe must be smaller in diameter than the main one. To perform all these operations with pipes, you must have manual or electric tools: a pipe bender, a beading machine and an expander. When using pipe benders, the bending radius must be no less than 3.5d (d is the diameter of the pipe) for a diameter of up to 15 mm, and 4d for a diameter of 18 mm. When using a bending spring - no less than 6d.
Manual pipe bender
Springs for bending copper pipes
An excessively small radius may cause the pipe to rupture or collapse. Annealed pipes can be bent to a smaller radius, but a tight bend (less than 3d) is unfavorable from a flow point of view. Annealed pipes can also be carefully bent by hand. In this case, to avoid flattening, the bending radius must be no less than 8d.
Poorly executed bends, in which the pipe has flattened and the cross-section has lost its round shape or the inner surface of the bend has gathered like an accordion, cause turbulent flows in the pipe bend, which leads to erosion-corrosion damage.
Unannealed (solid) pipe, up to a diameter of 18 mm, can be cold bent with a pipe bender. Larger diameter pipes should be softened at a temperature of 500-600°C before bending.
The operation of the expander is based on the radial expansion of the segments of the cam mechanism inserted inside the pipe. The expandable copper pipe must be annealed (soft). Thanks to the lever system, pressing on the tool handles creates the necessary force required for plastic deformation of the metal. Everything is very simple - insert the cam tip into the pipe, squeeze the handles and get a socket into which you can insert a pipe of the same diameter. You can make a coupling from a piece of pipe by expanding both ends of the workpiece. If necessary, the end of the unannealed (solid) pipe can be annealed yourself.
Pipe expander
The flanging operation is somewhat more complicated than the expansion operation. It consists of two stages: drilling a hole with a special calibration drill and the flanging itself. After the hole is drilled, it is necessary to insert into it a mandrel with sliding antennae lubricated with grease, and attach the outer part of the device to it, which serves as a stop when drawing. After that, a power tool is connected to the outer part. Rotation of the spindle pulls the mandrel out of the hole. In this case, by spreading the antennae, flanging is carried out - bending the edge of the drilled hole outwards.
Pipe flanging
Now you can insert a bend into the pipe, which is a piece of pipe with a smaller diameter. To prevent it from protruding too much from the inside and preventing the movement of water, two protrusions are formed on its walls using a special tool. The latter rest against the socket, ensuring that the outlet is immersed in the hole to a strictly defined depth.
The described beading method involves the use of power tools, but there are also manual models.
Manual beader
Equipment for different types of welding
The organization of welding stations is associated, first of all, with the parameters of the equipment being used. The main ones are weight and requirements for the power supply network.
The welding station must be equipped not only with welding equipment and accessories for it. In addition, additional tools are required for trouble-free operation of welding machines, and, if necessary, minor repairs. For uninterrupted operation, you will also need a certain supply of consumables: various types of additives, flux in powder form or inert gas.
Technological maps, individual regulations, diagrams, drawings and other documentation will help you assemble a workstation more accurately. It is customary to distinguish two large groups of common equipment: electric and gas.
Stationary posts focused on the use of electrical equipment are often equipped with powerful AC or DC devices. Power supply often requires a connection to a three-phase network. The most popular additional equipment: AC transformers complete with or without rectifiers, generators, electric arc stabilizers.
When work is planned using gas (inert or active), the package includes cylinders containing hydrogen, argon, helium or other gas necessary for work. For gas welding, you will need cylinders with oxygen and working gas - acetylene or propane. The stationary gas welding station can be equipped with cylinders of different weights, starting from 10 liters.
The table can be very massive or small and compact. The only condition is that the area of the tabletop should not be less than 1 square meter. Vices and clamps will be its indispensable additions. In addition to this, additional equipment often includes various types of fasteners, pipe benders, rolling devices, etc. For mobile kits, small-sized equipment is used: gas welding machines with small cylinders, inverters and semi-automatic welding machines.
There are mobile installations located on the basis of automotive vehicles, including passenger cars. They are equipped with gasoline or diesel generators and are autonomous. Such posts are intended for field work. They are often found in natural disaster zones, on sections of highways after accidents; used in road and field work.
Soldering copper pipes
The process of soldering copper pipes consists of sequentially performing the following operations:
- pipe cutting,
- chamfering,
- cleaning the connected parts from oxides,
- coating them with flux,
- connection assemblies,
- heating it and applying solder.
cutting
The most convenient way to cut pipes is with a pipe cutter. Many types of this tool are produced, but they all have a similar design and consist of a body, support rollers, a cutting knife in the form of a disk, and a screw that presses the knife to the pipe. The main difference between the models is the shape of the body, which determines the required rotational force when cutting. The longer the lever that the pipe cutter turns, the easier it is to cut. To cut pipes located close to enclosing structures, compact pipe cutters with a minimum size are used. They require more force than regular sized pipe cutters.
Cutting a copper pipe with a pipe cutter
The cutting sequence is as follows. The pipe cutter is installed on the pipe so that the edge of the cutting roller coincides with the cutting line. The screw is clamped, pressing the roller to the pipe, and cutting is carried out by turning the tool around the axis of the pipe. After every 1-2 revolutions, you need to rotate the screw to press the roller towards the pipe. The pipe can be cut with a regular metal saw or jigsaw. You just need to try to make the cut perpendicular to the axis. To do this, it is better to buy or make a template - a miter box.
The use of pipe cutters gives a straight edge to the pipe, but can lead to a slight reduction in the diameter of the pipe; in this case, scoring occurs only inside the pipe. Using a hacksaw avoids pipe deformation, but produces a lot of burrs.
Chamfering
After cutting, it is necessary to remove the internal and external chamfers. The pipe cutter slightly bends the edge of the pipe inward; if this bend is not removed, it will create turbulence and resistance to the flow of water or gas. The outer chamfer can be removed to facilitate assembly. There are special sickle-shaped knives for chamfering. Sometimes they are built into pipe cutters, sometimes they are a separate tool. Chamfering tools are also produced in the form of bushings (the internal chamfer is removed with one side, and the external chamfer with the other). As a last resort, you can use a mounting knife or any other knife.
Deburring
Chamfer remover
Stripping
After chamfering, you need to clean the mating parts of the parts from oxides. External surfaces are cleaned with fine abrasive sandpaper (P600 grit), stainless steel wire mesh, or a special tool with a hole framed with a wire brush. For internal surfaces, brushes, sandpaper or mesh are used, screwed onto some kind of pin or, in extreme cases, your own finger. The surface is cleaned to a shine. If abrasive sandpaper was used, after cleaning it is necessary to remove any remaining abrasive from the parts. The presence of foreign substances on the surface reduces the quality of any soldering, including copper soldering.
Mechanical cleaning of copper pipe from oxides
Mechanical cleaning of copper pipe from oxides
Flux processing.
Coating with flux must be done immediately after stripping, since after just a few minutes the cleaned surface will be again covered with oxides that prevent wetting with solder. Paste-like flux is applied with a brush to the outer surface of parts inserted inside others. Apply an amount sufficient to completely cover the mating surfaces, but without excess.
Flux application
When the flux is applied, it is recommended to immediately connect the parts - this will prevent foreign particles from getting onto the surface treated with flux.
Assembly
When assembling, you need to slightly rotate the parts relative to each other so that the flux is well distributed over the surface and make sure that the pipe reaches the stop. Then you should remove excess flux with a dry cotton cloth and secure the parts in the desired position or place them on fire-resistant materials on which heating can be carried out without the risk of fire.
Assembling parts and removing excess flux
When installing a copper pipeline using a gas torch, a fireproof screen should be used.
Fireproof screen
Basic requirements for arranging welding stations
Regardless of what equipment the post is equipped with, the fire safety requirements are almost the same. All their points are aimed at ensuring safe working conditions and making them as comfortable as possible. Primary requirements:
- The welder's place should be protected with shields or screens made of fireproof materials. the top should be left open;
- welding work using inert gases is allowed only in those booths where there is no top, the light opening between the fences and the base is 30 centimeters or more, and the walls of the fences are at least 2 meters;
- the inside of the post along the perimeter is sheathed with fireproof materials;
- The cabin area must be at least 4.5 square meters. This space is enough to accommodate welding equipment, accessories, various devices, systems for storing tools and consumables;
- when operating a plasma cutting machine, the height of the fences must be at least 2.2 meters, and the surface inside must be covered with fireproof materials;
- You should not install two welding machines inside one booth at once. And if this is really necessary, then a separating light-protective screen must be installed between them. It will prevent the possibility of a fire.
When arranging a welder’s workplace, the organization of a ventilation system is important. The production site foreman must check the ventilation performance of each station, since the safety of not only a specific welder, but also the work site as a whole directly depends on the efficiency of air exchange.
Practitioners advise:
- Ensure parallel operation of two exhaust systems at once: general and local.
- Local hoods are equipped with filters that purify the air from harmful aerosols and combustion products.
- When performing welding work in a protective environment, air is supplied dispersedly into the booth. In other cases, it may be pumped into the upper area of the cabin.
- It is desirable that the walls inside are matte. Then the welding glare will not be reflected.
If all the requirements for organizing the supply and exhaust ventilation system are met, then the workplace is ready for use. Before starting welding work, the specialist must wear protective clothing and a mask. Otherwise, he risks damaging his eyes and getting burns from hot metal drops.
Solders and fluxes for copper soldering
Copper and its alloys can be soldered using both low-temperature and high-temperature soldering. There are a sufficient number of soft and hard solders that provide good quality pipe soldering.
The use of low-temperature solders allows soldering to be performed at a temperature that has little effect on the strength of copper, but they produce a seam with worse mechanical characteristics. Solders for high-temperature soldering provide greater strength to the seam and allow high operating temperatures of the system, but in this case the copper is annealed and more skill is required, since it is easy to burn out the metal.
Low-temperature soldering is most in demand in water supply and heating. There are many low temperature lead-free solders that provide fairly good quality copper soldering. These are alloys of tin with antimony, copper, silver, bismuth, and selenium. The main part (up to 95-97%) of them is tin, the rest is other elements. Silver-containing solders, for example, S-Sn97Ag3, containing 97% tin and 3% silver, have the best technological properties. Copper-containing solders, in particular S-Sn97Cu3 (97% tin and 3% copper), have somewhat worse, but quite good qualities. There are three-part solders containing tin, silver and copper (for example, a composition with 95.5% tin, 3.8% silver and 0.7% copper). The most versatile and widely used is tin-copper solder. The disadvantage of tin-silver alloys is their higher cost compared to tin-copper alloys.
Solder S-Sn97Ag3 containing 97% tin and 3% silver
Solder S-Sn97Cu3 containing 97% tin and 3% copper
These solder compositions provide good seam quality and meet all the requirements for strength, durability and reliability of water supply and heating systems. Solders of other compositions are practically not used. Lead-tin solders are also suitable for low-temperature soldering of copper, but if a pipeline for drinking water is being soldered, they must be abandoned due to the harmfulness of lead. Compositions containing zinc chloride are mainly used as fluxes for low-temperature soldering. However, it is hardly worth paying special attention to its composition when purchasing flux. There are many effective fluxes for soldering copper; you just need to purchase any composition designed for this. For example, F-SW 21 or rosin-vaseline paste, consisting of rosin, zinc chloride and technical petroleum jelly. The paste form is the most convenient for applying to parts.
Flux F-SW 21
Taking into account the large contact area of pipeline elements, low-temperature solders provide sufficient strength of the connections. It makes sense to resort to high-temperature solders only in cases where there is a special need for it. For example, if the brazed pipeline is expected to operate at high temperatures (above 110°C) - in heating systems using high-pressure steam or other cases. For soldering gas pipelines made of copper pipes, only high-temperature soldering is used, as a connection with the greatest strength and reliability; low-temperature soldering is not used in gas supply.
The following are the values of permissible pressures in pipelines made of copper pipes with a diameter of 6-28 mm, soldered with low-temperature (soft) and high-temperature (hard) solders. Solder type Soft Temperature of the transported medium, °C 30-65-110 Allowable pressure, atm. 16-10-6 Solder type Hard Temperature of the transported medium, °C 30-65-110 Allowable pressure, atm. 40-25-16 For copper pipes with a diameter of 6-28 mm.
For high-temperature soldering of copper, copper-phosphorus solder of the composition Cu-94%, P-6% (L-CuP6 and similar ones - PMF 7, PMF 9, etc.) is most widely used. The introduction of a 6% phosphorus additive very sharply reduces the melting point of copper (to 710-750°C), which makes it possible to use this composition as solder.
Copper-phosphorus solder L-CuP6 containing 94% copper and 6% phosphorus
Copper-phosphorus solders in the case of copper-to-copper soldering do not require the mandatory use of fluxes. Another advantage of this solder is that the thermal expansion coefficients of the solder and copper of the soldered parts are almost identical. Self-fluxing solder with the composition: 92% Cu, 6% P, 2% Ag (copper-phosphorus with silver - L-Ag2P) has also become widespread. All hard solders are produced in the form of solid rods.
Due to the brittleness of the connection resulting from the chemical reaction of phosphorus with some metals, copper-phosphorus solders cannot be used for soldering non-ferrous metals with a nickel content higher than 10%. These solders are also not recommended for soldering aluminum bronze. They cannot be used when soldering steel and cast iron. When joining elements from different copper alloys with copper-phosphorus solders: copper with bronze or copper with brass or bronze with brass, it is always necessary to use flux for high-temperature soldering.
Flux for brazing
For low-temperature and high-temperature soldering, it is preferable to use matched solder and flux for a particular type of soldering from the same manufacturer.
Requirements for welding stations
General requirements
Requirements for the organization of welding stations are based on compliance with safety regulations and ensuring comfort in carrying out work. It is important to ensure that all energy consuming installations are grounded. To place them, it is highly advisable to make a base of concrete or brickwork. The post must have everything necessary to store not only tools, but also documentation.
Briefly about the basic requirements. Ventilation is required. The table is made of steel or cast iron. The welder must stand on a rubber mat while working.
For cases where the welder works while sitting, it is necessary to provide a special chair with a non-conductive seat. It should be durable, but light and small so that it can be moved with one hand if necessary. Naturally, the seat should be comfortable, since sometimes a specialist has to work for several hours without a break.
Productive work is impossible without adequate lighting. The brightness should not be excessive, but at the same time, even small details should be well illuminated. As practice shows, 80 Lumens are enough to work. The light source should be placed directly above the table. If this is not possible, then it is permissible to place the lighting device in close proximity to the workplace.
Even if we are talking about multi-station welding, you still need a switch, by turning which you can turn off the electricity supply in an instant. This may be needed in an emergency and to de-energize the area at the end of the working day.
A little theory about copper soldering
The prevailing opinion about the good solderability of copper and its alloys is true only when it comes to copper itself and its alloys with zinc, tin, lead, phosphorus, antimony, iron, nickel, and manganese. These metals actually have oxides that are relatively easy to remove with fluxes. But copper alloys alloyed with chromium, aluminum, silicon, titanium and some other elements have oxides on their surface that are difficult to dissolve with fluxes. Fortunately, more often you have to deal not with them, but with commercially pure copper or those alloys that form easily removable oxides. So the statement that soldering copper does not cause much trouble can be considered true in most cases.
When soldering in general and copper tubes in particular, lap joints are usually used. They make it possible to ensure sufficient structural strength even if soft solders with relatively low strength are used. It is believed that to ensure satisfactory solder joint strength, the overlap should be at least 5 mm. In practice, much higher values are usually used, which provides a good margin of safety.
Mutual overlap of elements in the pipeline is ensured through the use of fittings or pipe expansion and flanging operations. Parts of pipes and fittings are inserted into each other. In this case, between the elements being connected, just such a gap is provided (0.1-0.2 mm) that is necessary for the action of capillary forces, which are a prerequisite for most types of soldering. Under their action, the molten solder is spontaneously drawn into the gap, distributed evenly over the entire contact surface and tightly seals the connection. Capillary forces allow solder to be fed from below.
Soldering copper pipes