Cold heading machines National Machinery
National Machinery , founded in 1874, is a manufacturer of high-tech equipment for cold heading and heated heading.
In Soviet times, National presses were the basis for hardware production. In total, about 600 units of National .
National Machinery machines are now used in more than 60 countries around the world, and parts produced from them are used in the automotive, mechanical engineering, bearing, aerospace and other industries.
National machines allow you to produce a wide range of products from steel, aluminum, brass and other metals using the upsetting method:
- fastening elements: bolts, screws, nuts, rivets in all their variety;
- fittings, bushings, spark plug housings, gun casings;
- fingers, ball fingers of various shapes;
- balls and rollers of rolling bearings;
- fittings for plastic windows, furniture, etc.
National Machinery presses can be designed to produce parts using both cold heading and heated heading , and are also equipped with a variety of additional equipment to suit customer needs:
- wire unwinding and calibration devices,
- bar feeder;
- pressing force control system;
- conveyors of finished products and waste.
Through continuous development and research, advanced technological capabilities, and a worldwide sales and service network, National Machinery is firmly positioned as the "world leader in metal forming technology."
Currently, National Machinery develops and manufactures machines that fundamentally change the concept of high-speed precision stamping. The innovative design improves efficiency and simplifies set-up, and ensures the highest upsetting accuracy. Whether you're making a spark plug, fastener or fitting, National's machines will produce a shape close to the final part.
National Machinery's advanced developments are implemented in FORMAX series machines.
FORMAX machines manufactured by National Machinery
The model range of FORMAX machines is represented by the FORMAX 2000 , FORMAX Plus , FORMAX Plus for large parts, FORMAX for very long parts, LeanFX and FORMAX XXV .
| Main technical characteristics of FORMAX machines produced by National Machinery |
FORMAX machines, for the first time in the history of cold heading, implemented the concept of quick tool change by using the FORMAPAK system , which allows you to set up the tool on a special stand outside the machine while the machine is in operation.
FORMAPAK block includes:
- matrix block;
- block of punches;
- transfer system carriage;
- transfer finger opening cam shaft;
- cutting cassette.
After installing the configured FORMAPAK block into the cold heading machine, computer control simplifies the final adjustment of the machine mechanisms: electric drives perform accurate and repeatable adjustment of the matrix ejectors in automatic mode.
Key advantages of FORMAX machines:
The machine slide has a two-axis design, which uses fixed guides to ensure zero clearance during the working stroke of the machine. The zero-clearance guide system aligns dies and punches with high precision, providing tight concentricity tolerances on manufactured parts previously thought unattainable. |
Linear wire feed replaces the outdated traditional roller wire feed, providing unmatched cut accuracy without the need for a wire stop. Unlike traditional feed rolls, the linear feed system's grips are designed to cover the entire range of wire diameters, so only one set of grips is required for the job. The linear feed system also ensures greater precision in cut workpieces by eliminating the problems associated with the brake and clutch of a traditional feed mechanism. |
FORMAX machines are the only machines equipped with slider guide seals, which protect the guides from foreign materials that cause increased and premature wear. |
The FORMAX 2000 Series machines feature the Straight Across zero-clearance workpiece transfer system, designed for high speed operation and improved stability over traditional transfer systems. |
FORMAX Plus series machines are equipped with a Pick-Move-Place workpiece transfer system, which provides excellent control of complex shaped parts as they move between stations. This system is ideal for parts with a heavy head and parts that are difficult to handle. The increased transfer finger opening width allows the use of larger punches. |
FORMAX 2000
The main advantages of FORMAX 2000 series machines :
- quick tool change system ;
- slider guides with zero clearance;
- precise linear wire feed mechanism;
- sealing the slider guides to protect them from damage and wear;
- Straight Across transfer system.
Straight Across transfer system used in the Formax 2000 series machines is designed to work at high speeds, carrying out precise transfer of workpieces along a linear path.
| ||||||||||||||
| * maximum performance is indicated for models with the shortest slide stroke length |
FORMAX Plus
FORMAX Plus series machines have the same advantages as the FORMAX 2000 series machines, but at the same time provide expanded production capabilities due to the following features:
- increased pressing force;
- increased diameter of the cut workpiece;
- expanded space of the instrumental zone;
- wire feeding mode every second stroke of the slider;
- Pick-Move-Place transfer system.
The Pick- Move- Place transfer system used in the Formax Plus series machines is designed for the production of short and other difficult-to-grip parts .
| ||||||||||||||
| * maximum performance is indicated for models with the shortest slide stroke length |
FORMAX Plus for large parts
FORMAX Plus series large parts machines are designed to produce large, complex parts with the highest precision. These machines have unique automatic configuration, changeover and control functions, thanks to which the operator can make a complete changeover within 30 minutes.
Formax Plus machines for large parts feature full automation of the changeover process:
- automatic tool changer;
- automatic adjustment of punch wedges;
- automatic feed length adjustment;
- automatic adjustment of matrix ejectors;
- automatic synchronization of the transfer system.
| ||||||||
| * maximum performance is indicated for models with the shortest slide stroke length |
FORMAX Plus for very long parts
The ability to produce long parts on a cold heading machine is an important technological advantage, but as a rule this leads to the need for a significant reduction in equipment productivity. However, the FORMAX series machines are an exception for very long parts.
This series of FORMAX machines is designed to produce very long parts without loss of productivity.
For example, the FX45 XL allows you to produce parts from wire with a diameter of 16 mm with a core length of up to 215 mm with a productivity of 200 pcs./min .
| ||||||||
| * maximum performance is indicated for models with the shortest slide stroke length |
LeanFX
LeanFX series is designed specifically for the production of standard parts and fasteners . LeanFX machines are distinguished by high productivity and FORMAX accuracy, while some functions have been simplified, which has significantly reduced the price of the equipment. LeanFX is ideal for high volume production .
Many of FORMAX's innovative features are also used in the LeanFX design:
- linear feed;
- slider guides with zero clearance;
- protective seal for slider guides;
- Straight Across transfer system
LeanFX machines have simplified yet effective features such as:
- manual adjustment of feed length and ejectors;
- operator console integrated with the control cabinet;
- conveyor with magnetic tape for finished parts.
LeanFX machines are equipped with Straight Across or Cold Former transfer system (version with 5 dies).
| ||||||||||||||
| * maximum performance is indicated for models with the shortest slide stroke length |
FORMAX XXV
FORMAX XXV is the latest automatic machine for the production of wire parts with a diameter of up to 25 mm.
FORMAX XXV machines feature advanced technologies, including:
- servo drives for adjusting mechanisms;
- robotic tool changer.
FORMAX XXV also has the most important classic advantages of FORMAX machines:
- expanded space of the instrumental zone;
- high performance;
- slider guides with zero clearance;
- high precision linear feed;
- Pick-Move-Place transfer system.
FORMAX XXV machines are presented in models with short and standard slide stroke, with the number of matrices from 5 to 7.
For more information about this unique cold heading machine, please contact us.
Heated disembarkation
Heated upsetting is the process of deforming metal heated to a temperature at which the ductility of the material increases, but recrystallization, grain growth, or metallurgical destruction does not yet occur. This process allows the part to be successfully upset to its final shape and tolerance, eliminating the need for further machining.
The process temperature is determined depending on the part material, geometry, final technical requirements and tolerances, and can vary in the range of 200-850°C.
Heated heading is widely used in the production of aerospace products, for example, when heading parts that require significant deformation during the stamping process, as well as parts made from materials such as:
- industrial stainless steels;
- FA 286 SS;
- high-carbon and alloy steels;
- Inconel;
- alloy "Waspaloy";
- titanium (6-2, 6-4).
FORMAX machines can be equipped for heated planting, and the following devices and systems can be installed:
- high frequency converter;
- induction coil;
- double-circuit cooling system: ○ frequency converter and induction coil; ○ matrix block, induction coil bracket and oil reservoir for matrix lubrication;
- oil heater for lubrication of dies;
- wire temperature sensor (pyrometer);
- fire extinguishing system.
Carbon steel grades for fastening production
Approximately 90% of the fastenings in the world are made from carbon steel. The reasons for the popularity of the material are its high value, ease of processing and low workability compared to other metal alloys.
The mechanical strength of fastening elements made from carbon steels lies directly in the percentage of carbon in the alloy stock. Based on this criterion, they began to divide into three groups:
- low-carbon;
- mid-carbons;
- legovani.
Low carbon steels have less than 0.25% carbon. The material has high plasticity and flexibility, is easy to process and cook, and is inexpensive to manufacture. Low-carbon steels are suitable for the production of fastening of coal material with a limit of up to 600 MPa.
The marking of such alloys consists of the letter designation “St” and numbers from 0 to 6. The number is the intellectual number of the brand. The higher the number, the more carbon there is in the alloy. Popular brands for making fastenings – Art.3, Art.5.
To designate special authorities, additional letter indices began to be used, which are assigned to the right of the digital designation. This can be classified according to the deoxidation stage:
- kp - boiling water;
- ps – calm;
- sp - calm.
The letter G is placed between the index and the brand number, which means that in the alloy there are advances instead of manganese.
Medium carbon or structural steels contain 0.25 to 0.85% carbon. These alloys can be subjected to additional heat treatment to improve mechanical strength. Structural steels are vicorized for the production of metallic compounds, the value of which exceeds 600 MPa.
Mid-carbons began to be marked with double-digit numbers, which indicate hundredths of a percentage instead of carbon. The letter G in the designated brand indicates a high content of manganese.
The most popular grades of structural steel for fastening are St.10, St.20, St.35, St.40.
Alloy steels are called steels that contain more than 1.65% manganese, 0.6% silicon and copper, and less than 4% chromium. The presence of light elements in the alloy storage promotes the mechanical and chemical power of fastening viruses.
The designation of the grade of bright alloy steel consists of a letter-digital connection, which means a chemical warehouse for the alloy. The following symbols may be used to enter the steel warehouse of lightweight elements:
- nickel – N;
- chromium – X;
- silicon – C;
- manganese – G;
- tungsten – B;
- molybdenum – M;
- aluminum – Yu;
- titanium - T;
- copper – D;
- vanadium – F;
- cobalt – K;
- boron – P;
- zirconium – C;
- nobiy – B.
The number after the letter indicates the percentage of the additive in the warehouse. Since there are no numbers, the alloying element in the alloy is close to 1.5%. For the designated grades of bright alloyed structural steels, the first two digits are indicated instead of carbon in hundreds of units. High-acid alloys bear the letter A at the end, especially high-acid alloys – Ш.
For the production of fasteners, alloy steel grades are used: St.35Х, St.40Х, St.30ХГСА, St.35ХГСА, St.40G2.
Cold heading machines Nakashimada
The Japanese company Nakashimada was founded in 1911 and has become world famous as a manufacturer of high-precision cold heading machines.
It is thanks to their incredible precision that Nakashimada machines are used to produce parts for watches, computers, mobile devices, in the automotive and aviation industries.
For many years, Nakashimada has been following the path of combining the best traditions and new technologies, producing cold heading machines that are so popular with the largest hardware manufacturers around the world.
The model range of Nakashimada slot machines is represented by the following series: NS, NP, MH/ MF, BT/ BTX/ MST .
| Main technical characteristics of Nakashimada slot machines |
Series NS. 1-matrix 2-strike machines
The machines in this series are used by leading screw and rivet manufacturers around the world, allowing them to produce standard fasteners of the highest quality.
Over 25 years of innovative development, more than 800 cold heading machines of the NS series have been manufactured.
The new rigid machine bed design provides increased stability during high speed operation, longer machine life and increased productivity.
The punch blocks are mounted on a vertical carriage and are securely fixed during operation. The mechanism for vertical movement of the punches ensures ease of setup and maintenance, higher speed of operation of the machine, accuracy and concentricity of the parts produced, as well as exceptional tool life.
All sliding surfaces, including the slider, are hand-finished to micron precision to ensure tight tolerances and long service life.
NP series. 2-matrix 3-strike machines
This series of machines is designed for the production of high-precision parts. Over a 30-year history of innovative developments, more than 1,000 cold heading machines of the NP series have been manufactured, used by the largest manufacturers of hardware, parts for the automotive and aviation industries around the world.
The unique 2-die, 3-impact configuration with a fingerless transfer system , coupled with die and punch ejection mechanisms, allows for the production of complex shaped parts, short parts, and parts that are difficult to handle. The use of this transfer system eliminates the problems of precise timing and registration that are typically associated with finger transfer. Also, due to the fact that the second punch hits both the first and second dies, this series is characterized by the capabilities of a 2-die, 4-impact machine, which is especially useful when landing parts with piercing or trimming.
MH/MF series. Automatic machines for the production of very small products
Nakashimada cold heading machines of the MH/MF series (Micro Headers / Micro Formers) are designed for the production of precision miniature parts . Over the years, more than 1,400 cold heading machines of the MH/MF series have been manufactured, used by major manufacturers of parts used in electronics, computers, watches and mobile phones .
These reliable machines are distinguished by the tightest tolerances of components and structural parts, which allows them to be used for the production of high-precision products using the cold heading method. All MH/MF series machines are equipped with a fingerless transfer system , which includes a unique mechanism for horizontal movement of the dies. This mechanism successfully solves the problem of transferring very small, short and difficult to transfer parts.
Series BT/BTX/MST. Multi-position cold heading machines for the production of bolts and complex parts
Multi-position machines of these series, presented in configurations from 2-matrix 2-impact to 7-matrix 7-impact, allow the production of a wide range of products: from simple bolts to the most complex products.
When developing the BT/BTX series, the goal was to create a new world standard for cold heading machines for the production of bolts and complex parts . Wear resistance, accuracy and productivity are increased without sacrificing ease of use and environmental friendliness.
Nakashimada's MST series of multi-position cold heading machines provides hardware manufacturers the ability to produce precision parts of the highest quality. Over a 20-year development history, more than 400 high-performance cold heading machines of the MST series have been manufactured, used by our customers to produce precision parts. The quality of Nakashimada MST series automatic machines has earned a special reputation in the aviation industry.
Fastening production: technology, steel grades
At the same time, strong vibrobes are scoured by water in all industrial and vibrator galuzes, and they vibrate on a large scale. With the recent development of modern technologies, it has become possible to produce metals of different sizes, classes of value and precision.
The fortifications began to become violent a century ago. Even the ancient Egyptians, Greeks and Romans were familiar with germs, which became the prototypes of modern screws and bolts. Mass production of fastening began to develop during the industrial revolution and the mass transition from manual to machine work. Until the beginning of the 20th century, metal parts were prepared by hand using lathes. This method saves a lot of time and does not allow the removal of fasteners of the required accuracy class.
In the 20th century, the serial production of fastening with vicaries began one of the most economical technological processes - steel processing with a vice. We allow you to produce large batches of products and change their quality. If necessary, secondary operations are performed, for example, cutting operations. Read about the technologies used for the production of fastenings, which are used in the production of current fabricators, as well as about the selection of steel grades required for the production of metals in our article.
Service maintenance of cold heading equipment
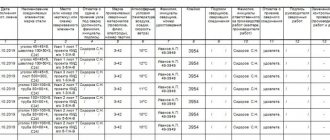
Our service department is made up of experienced engineers who regularly undergo training at equipment manufacturers in Europe to improve their skills, which ensures prompt and high-quality performance of work for the customer. We offer:
- equipment inspection and drawing up a defect list;
- installation of equipment;
- commissioning works;
- training;
- warranty and post-warranty service;
- maintenance and repair;
- remote software maintenance via modem or Internet;
- supply of consumables and spare parts.
We will always be happy to answer all your questions.
Overhaul and modernization of equipment
We have extensive experience in carrying out major repairs and modernization of cold heading equipment.
When carrying out a major overhaul, the machine is completely disassembled, mechanisms are troubleshooted, components are restored or replaced, lubrication systems, hydraulics, pneumatics, and electrical systems are updated or completely replaced.
If necessary, the machine is equipped with missing units and components, a noise-proof casing and additional equipment.
Typical work required when restoring a cold heading press is listed below.
- Dismantling of equipment at the client's plant
- Cleaning the press bed and individual components
- Defect detection
Checking the condition of the press: examining all individual components for wear and suitability for reuse. Based on the results of the inspection, a written defect report is drawn up.
- Reassembly
The press is reassembled after repair/replacement of its components.
- Wire insertion mechanism
- Replacement of wire input mechanism shafts, including sealing rings.
- Replacement of the input mechanism roller holders if they are worn out.
- Replacing the bearing pin of the upper roller race.
- Overhaul of the entire freewheel mechanism.
- Refinement of the inner and outer rings. Replacement of clamp elements with springs.
- Replacement of the connecting rod hinge pin and spacer washers.
- Replacement of the bushing body.
- Brake mechanism overhaul.
Roller pressing device:
- Replacement of bearings and pins.
- Replacement of the hinge pin and cylinder eye.
- Replacing seals in the cylinder.
- Wire entry mechanism drive
- Replacement of pins and bushings of bearing supports of connecting rods.
- Grinding the lever axes, installing new bearings.
- Complete overhaul of the length adjustment mechanism for wire insertion.
- Replacing the wire straightening and drawing device.
- Wire stop
- Checking and repairing the wire stop position adjustment system.
- Replacement of bronze linings of the slider guides and grinding of the top strip.
- Parting system
- Check the cutter slide and cutter arm for cracks.
- Replacing the cutting device slide pin, incl. bushings.
- Replacement of guide bushing and pressure spring.
- Replacing the pressure element of the cutting knife adjustment device. Checking the knife seat.
- Replacing the axis of the cutting device lever.
- Replacing the bearing bushing of the cutting device lever.
- Replacement of the roller tappet and pin, as well as the bearing.
- Crankshaft and cams
- Measure and check the crankshaft for cracks. Grinding the crankshaft bearing seats. Replacement of plain bearings.
- Installing a new bearing bushing into the ejector mechanism connecting rod and grinding the eccentric.
- Checking the condition of the cams and gears, replacing the bearing support.
- Press slider and connecting rod, pipe for transferring parts
- The surfaces of the press slide guides are fine-tuned and adjusted to the press body.
- Grinding the end surface of the front plate of the slider.
- Replacing the connecting rod pin.
- Replacing the split main bearing shell, incl. connecting rod pin bushing.
- Replacement of bronze guide plates.
- Grinding the pressure surfaces of the installation wedges.
- New installation wedges.
- Replacement of all bearings.
- Ejectors / pusher / matrix block / trimming mechanism
- Grinding the ejector lever axis, replacing bushings.
- Reworking the working surfaces of the cams and replacing the fingers.
- Replacement of bushing bodies, adjusting spindle and ejector pins when worn.
- Modification of the cams of the ejector camshaft and grinding of the shaft journal. Replacement of bearing bushings of the drive lever and ejector cam shaft.
- Grinding the drive arm bearing seat.
- Replacing the split bearing shell, incl. hinge pin.
- Replacing the locking bolt.
- Check the drive arm and camshaft where it connects to the locking bolt for cracks.
- Complete overhaul of the ejector lever spring system. Replacement of all springs. Checking the condition and repairing spring guides.
Trimmer lever
- Replacing the bearing bushing of the ejector mechanism lever.
- Replacement of roller tappet, pin and bushing.
Matrix block
- Replacing the matrix block.
- Grinding the pressure plate and the installation wedge along the surface adjacent to the matrix block. Replacing the mounting plate.
Pusher
- Complete replacement of the bearing support, replacement of the pressure spring and bearing pin.
- Workpiece transport system drive
- Complete repair of the transport system drive.
- Polishing the working surface of the drive mechanism cam.
- Replacement of roller tappet, bushing and pin.
- Replacing the cam lever bearing support.
- Check the condition of the rack and pinion for wear.
- Checking and repairing the clamping mechanism cylinder.
- Finger opening mechanism for workpiece transport system
- Replacement of all bearing supports.
- Replacement of roller tappet, pin and bushing. Replacement of pressure springs.
- Workpiece transfer system
- Checking the condition of the transfer system slide body, replacing worn parts.
- Installing the cam shaft on new bearings. Polish the surface of the cams or, in case of wear, replace them.
- If worn, replace connecting rods.
- Complete redesign of the workpiece transfer system slider, fit in the housing.
- Transfer system folding device
- Replacing the swivel eye and pin.
- Air brake
- Installing the brake disc on the flywheel.
- New air brake according to CE standard.
- Machine lubrication system
- Replacement of hoses, pipes, filters, control pressure gauges.
- Repair of dosing devices of the drip lubrication system.
- Pneumatic equipment
- Damaged hoses, pneumatic units, valves and lines are updated or replaced.
- Main motor
- Replacing the motor.
- Replacing V-belts.
- Electrical equipment
The upgraded electrical system includes the following elements:
- Siemens programmable logic controller.
- Touch control panel.
- Control cabinet..
- Distribution boxes.
- Electrical cables and wires.
- Sensors and actuators of the control system.
- Press force monitoring system.