What the article is about:
RDS welding with alternating current and its disadvantages
The quality of welds and the welding process itself largely depends on the characteristics of the welding current. Simple models of devices cook using alternating current. However, today there is more modern equipment on sale that can be switched from constant to variable.
In order to understand what the pros and cons of devices operating on alternating current have, you need to compare them with equipment that uses direct voltage.
In this article:
But in welding units that generate direct and alternating current, different physical processes occur inside that determine the characteristics of the welding arc. The nature of the current is also different.
- What is alternating current
. In alternating current there is a frequency or oscillation. In a household network it is 50 Hz. This means that chaotically moving electrons moving along a sine wave are capable of changing their direction up to 100 times per second (2 times per cycle). Devices operating on alternating current are designated as AC (alternating current). - What is direct current
? In direct current, electrons (negatively charged particles moving from negative to positive) move in only one direction. The movement is not chaotic, but orderly. There are no fluctuations (frequencies), the voltage is more stable. Welding machines operating on direct current are designated as DC (direct current).
What is polarity?
When talking about direct current, it is worth mentioning polarity. Polarity is the direction of movement of negatively charged particles. In physics they always move from the minus terminal to the plus terminal. Alternating current does not have such a clearly defined direction.
In welding machines operating on direct current, the welder can choose which socket to install the connector of the holder (torch) and which ground cable. Since electrons always move from minus to plus, in each case the welding current will have certain properties.
With direct polarity (the holder is negative and the mass is positive), negatively charged particles move from the holder to the product. This promotes:
- rapid heating of the metal;
- increases penetration depth;
- saves consumption of coated electrode.
Straight polarity is relevant for welding thick steels.
Reverse polarity means connecting the holder to positive and the ground cable to negative. This triggers the electrons in reverse - the heat is concentrated not on the workpiece, but at the tip of the electrode, reducing heat input to the workpiece. Reverse polarity is used when welding thin sheets of iron to avoid burn-through. But using reverse polarity leads to overheating of the electrode tip and its accelerated melting.
Voltage inverter circuit
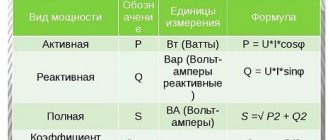
The most common voltage inverter circuit consists of four IGBT transistors VT1...VT4, connected in a bridge circuit, and four freewheeling diodes, designated VD1...VD4, connected in parallel to controlled semiconductor switches in the opposite direction. The converter powers an active-inductive load. It is the most common one, so it was taken as a basis.
The inverter input terminals are connected to Uip. If such a source is a diode rectifier, then its output is necessarily shunted by capacitor C.
In power electronics, transistors with an insulated gate IGBT (they are shown in the diagram) and GTO, IGCT thyristors are most widely used. When operating with lower powers, MOSFET field-effect transistors have no competition.
At time t1, VT1 and VT4 open, and VT2 and VT3 are closed. A single path is formed for the current to flow through the load: “+” Uip – VT1 – load RнLн – VT4 – “-” Uip. Thus, in the time interval t1 - t2, a closed circuit is created for the flow of in in the corresponding direction.
Circuit operation mode
To change the direction of in, control pulses are removed from the bases VT1 and VT4 and signals are sent to open the second and third VT2,3. At point t2 on the t time axis, the first and fourth VT1,4 are closed, and the second and third are open. However, since the load is active-inductive, it cannot instantly change direction to the opposite. This will be prevented by the energy stored in the inductance Lн. Therefore, it will maintain the same direction until all the energy stored in the inductance in the form of a magnetic field, equal to Wм = (Lн∙i2)/2, is dissipated.
In this regard, in the time interval t2 - t3, the current will flow through diodes VD2 and VD3, maintaining the same direction to RнLн, but will pass in the opposite direction through U or capacitor C if the energy source is a diode rectifier. Therefore, it is necessary to install capacitor C if the converter is connected to a diode rectifier. Otherwise, the flow path will be interrupted, resulting in a strong overvoltage that can damage the consumer insulation and damage semiconductor devices.
At time t3, all the energy stored in the inductance will drop to zero. Starting from moment t3 to moment t4, under the influence of the applied Uip, through the open semiconductor switches VT2 and VT3, in will flow through LnRn in the other direction.
At point t4, located on the t time axis, the control signal from VT1,3 is removed, and VT1 and VT4 are opened. However, in continues to flow in the same direction until the energy stored in the inductance is consumed. This will happen in the time interval t4 – t5.
Circuit operation
Starting from moment t5, in changes direction and flows from Uip through LнRн along the path through VT1 and VT4. Further, all processes occurring in the electrical circuit will be repeated. On LnRn, the voltage shape will be rectangular, but the current on the active-inductive load will have a sawtooth shape due to the presence of inductance, which does not allow it to instantly rise and fall. If the consumer is purely active in nature (inductance and capacitance are practically equal to zero), then the shapes in and un will be in the form of rectangles.
Since VT1...VT4 were opened in pairs throughout the entire length of the corresponding half-cycles, the maximum possible in was formed at the output of the converter, therefore, in of the maximum value flowed through LnR. However, it is often necessary to ensure a smooth increase in power at the consumer, for example, to gradually increase the brightness of lighting or the engine speed.
It should be clarified that the signals coming from the control system of the control system are not sent directly to the bases of the semiconductor switches, but through the driver. Since modern control systems are built on meringue microcontrollers that produce low-power signals that are not capable of opening an IGBT, an intermediate link – a driver – is used to increase the power of the opening pulse. In addition, the driver often performs many additional functions - it protects the transistor from short circuits, overheating, etc.
Which devices produce what current?
Now let's look at which welding machines produce alternating or direct welding current.
Transformers
Rectifiers
Inverters
It is transformers that generate alternating current for welding. To do this, their design uses two windings - primary and secondary. They are wound on a steel core, which significantly increases the weight of the device. Alternating current from a household network of 220 V or three-phase 380 V is supplied to the primary winding. Due to the large number of turns, an electromagnetic field arises with concentration on the core. The secondary winding is supplied with a reduced voltage of about 70-90 V and an increased current of up to 160-300 A, depending on the number of turns of the transformer winding.
Transformers are used only for RDS welding with coated electrodes. Depending on the power of the welding current, the thickness of the metal being melted is determined.
Welding rectifiers contain two transformer windings inside, but are supplemented with a rectification unit that converts alternating current into direct current. Most often, converters are designed for a 380 V network in order to evenly load the power phases.
Rectifiers are used in factories and workshops where high-quality penetration of thick metals of 5-20 mm is required. But due to the massive design they take up a lot of space. They are often equipped with wheels for moving around the workshop. To move them to a height, loops are provided for the hook of a crane or hoist.
Inverters are available at 220 and 380 V. Their incoming alternating current with a frequency of 50 Hz is rectified and smoothed using a filter. Then the current returns to alternating again, but its frequency increases significantly and amounts to 20-50 kHz. There are models capable of outputting frequencies up to 100 kHz. After this, the current is again converted to direct current and filtered.
This process ensures an extremely smooth current, resulting in a stable arc and high weld quality. Inverter machines are used for welding MMA, MIG, TIG. Due to the compactness of internal components, some inverters weigh only 3-4 kg. Most household models for RDS do not weigh more than 10 kg. But there are also industrial versions with a current of 400-500 A and a weight of 30-50 kg.
Most inverter machines only operate on DC power, but there are professional AC/DC versions that can switch to AC power. This expands their application possibilities.
Transformer KaVik TDM-252 AL
Quick view
Rectifier ESVA VS-300B
Quick view
Inverter BARSVELD Profi TIG-217
Quick view
Voltage inverter with regulation of output parameters
The easiest way to change the value of un is to regulate the value of the supplied Uip, if such a possibility exists. For example, for an adjustable rectifier this is not a problem. But such sources of electrical energy as a battery, supercapacitor or solar battery do not have this capability. Therefore, regulation of the frequency and value of the output un is entirely the responsibility of the inverter.
To regulate the value of u, one pair of diagonally opposite transistors should be opened somewhat earlier than in the case discussed above. Therefore, the control system algorithm should provide for a shift of control signals. For example, VT1 and VT4 are applied to open relative to the control pulses supplied to the bases VT2 and VT3, at a certain angle called control angle α.
Please note that the amplitude value of un remains unchanged and is approximately equal to the value of Uip, but the effective value of un will decrease as the control angle α increases. Let's look at how this works.
In the time interval from t1 to t2, a pair of transistors VT1 and VT4 is open; in flows from right to left, as shown in the diagram. At moment t2 the first transistor closes and the second opens. The current remains in the same direction, and the load turns out to be short-circuited, as a result of which the voltage across it drops to almost zero, and iin decreases accordingly.
Next, a command is received from the control system and VT2 opens and VT4 closes. However, the energy accumulated in the inductance does not allow the current in to change its direction, and it flows through the same circuit, only through diodes VD2 and VD3 opposite the power source. The duration of this process continues until time point t4. At point t4, under the influence of the applied Uip, in changes sign to the opposite.
Difference between AC and DC welding
Understanding the differences between alternating and direct current, as well as the features of welding machines that produce them, let’s consider the difference in welding.
AC Welding
DC welding
The arc on alternating current burns less stably; random attenuation is possible with a slight change in the gap between the electrode and the product. There is a characteristic crackling sound. It is more difficult to manipulate the arc, sometimes it “walks”, and it is more difficult to set the shape of the seam.
When welding with alternating current, there is metal spattering, the arc “spits”. AC electrodes are consumed faster. During the execution of ceiling and vertical welds, the transfer of filler metal is complicated; some of it accumulates downwards under the influence of gravity.
But welding machines operating on alternating current are cheaper than rectifiers and inverters. They have the simplest design and internal components that can easily withstand harsh conditions at a construction site, garage, or workshop. There is practically nothing to break here - only the winding can burn out from overheating. If you do not overheat the transformer, it will serve for many years.
The devices are not afraid of dust, and the current strength is adjusted by moving the primary winding closer or further from the secondary. All elements are simple and reliable, the equipment has increased maintainability with low cost of components.
Welding with direct current is characterized by a stable arc, it is easier to weld a seam by controlling the scaliness, width and height of the bead. The arc does not crack, but rustles. Liquid metal splashes less, and the drop is better transferred to the product. Direct current is more convenient for welding not only in the lower position, but also in the vertical and ceiling positions.
When the incoming voltage “jumps,” DC machines only lose operating current, but the arc remains stable. The quality of the weld no longer depends 100% on the experience of the welder, but is ensured by the best characteristics of the welding current.
But inverters are more expensive than transformers. They have more complex internal equipment and expensive repairs. Inverter welding machines are sensitive to dust, shock, and shaking. When using on a construction site or in a workshop, you should be careful and regularly blow dust out of the internal circuits.
Pure sine inverters
Inverters with pure sine wave allow you to connect any devices, since they have the correct voltage form at the output, which allows you to connect any equipment and devices without the risk of failure, so most often these inverters are used in homes to organize backup power. You can connect pumps, energy-dependent heating boilers with electronics, modern refrigerators and other household appliances to them. Without having a negative impact on her work. Often these devices combine the functions of an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) and an inverter. Those. When the central power grid is turned off, the devices connected to it are automatically switched to battery power in a fraction of a second. Without interrupting the operation of connected devices.
Areas of use
Based on this comparison of the operation of devices with alternating and direct current, we can conclude that the transformer is suitable for periodic welding of non-critical structures made of low-carbon steels.
It is advisable that welding be carried out in the lower position. At the same time, the welder must have certain qualifications, otherwise the seams will be very bad. The transformer will “survive” in construction conditions, frequent transportation, and dusty rooms. This is the optimal brew for a summer house, garage, to save money. Video source: Vitaly M
But AC transformers can also be useful for professional applications. For example, when welding coated electrodes on aluminum or rusty metal that cannot be cleaned. They are better than inverters because constantly changing the direction of electron flow helps break down aluminum oxide or contaminants on the surface. Direct current is not capable of this (only in combination with a pulse)
Inverters are better for beginners to learn how to cook. It is easier to work with them in all spatial positions, as well as to weld:
Changing the polarity will help weld thin metal 1-2 mm without burns. But inverters require more careful care and careful handling, otherwise frequent breakdowns will be expensive.
For professional activities or a private workshop, it is better to buy AC/DC welding machines. By switching from alternating to direct current, you can weld any metal efficiently and enjoy the pleasant rustle of the electric arc.
Automotive inverters
Voltage converters with a modified sine wave (quasi-sine), often called car inverters, allow you to connect not very precise equipment that does not have electronics and control circuits, such as a drill, grinder, light bulbs and other devices of this kind. They have a fairly low efficiency and high current consumption for their own needs, and for the most part are designed for a short time of continuous operation.
Features of reverse polarity when welding
Metal welding with this method of connecting equipment has the following characteristics:
- The seam of the welding joint is less deep in penetration into the metal, with a more pronounced width;
- The method is most suitable for joining medium-thick workpieces or thin sheets of metal;
- During operations with thick workpieces, the seam becomes brittle under the influence of loads;
- Electrodes whose structure is destroyed when overheated are not suitable for work;
- The electric arc is less stable, especially when operating at low currents, which leads to uneven connections;
- When welding high-alloy steels, it is necessary to strictly follow the technological process of the work cycle.
Welding inverters
Separately, it is worth highlighting special inverters, which can significantly increase the efficiency of the welding machine and quickly connect two metal parts without effort and make the structure reliable. These inverters have many advantages:
- They are distinguished by high power and performance.
- Reliability and durability of welds.
- The ability to choose a compact model and move it to the place where a person will work.
- High efficiency of almost 90%. This figure is much higher than that of conventional transformers.
- Moderate consumption of electrical energy and efficiency.
- During operation of the welding machine, metal spatter is separated in smaller quantities, which saves not only energy.
- The ability to regulate the current supply, making it smooth.
- A welder can perform metal work even without much experience in this field.
The versatility of the device allows it to be used in different areas, and the ability to choose the best model in terms of price and quality ratio is considered one of the important advantages.
Control board operation
To power the board elements, a voltage stabilizer is used, rated at 15 V and installed on a heat sink. The supply voltage comes from the main rectifier. One of the functions of the power stabilizer is to supply voltage to the relay, which provides a “soft start” of the device. When voltage is applied, the capacitors begin to charge: at the same time, the voltage increases and, in order to protect the diode assembly, a limiting circuit is used, which includes a powerful (8 W) resistor. As soon as the capacitors are charged, the inverter will start working, the relay will close its contacts, and the resistor will not participate in further operation.
Welding machine control.
In addition to the voltage stabilizer, the electronic circuit of the inverter contains many other systems that ensure high performance of the device. The main ones of these electronic units are:
- Control system and drivers: the main element here is a PWM controller chip, which is “engaged” in controlling the operation of powerful transistors;
- Regulating and control circuits: the main element is a current transformer, whose task is to control the current strength of the output transformer;
- System for monitoring supply voltage and output current: consists of an op-amp (operational amplifier) assembled on a microcircuit (for example, LM324). The purpose of the system is to enable emergency protection, if necessary, to monitor the operation and serviceability of the main elements of the electronic unit.
Advantages of an inverter unit
Inverters are lightweight and small in size, which is very important when performing welding work; the weight of the device is only 4-4.5 kg. High efficiency and electrical safety, which is ensured by a large number of protection circuits - overheating, overload or electrical overvoltage. Low level of power consumption, inverters consume 1.5-3 times less than conventional welding machines. This feature allows you to use the unit even with a network voltage of 180V.
When turned on, it creates minimal electromagnetic interference in the network. Smooth and easy current control. The result is high-quality welds, such a high result is achieved thanks to the easy ignition of the electric arc with its stable combustion. There is no significant spattering of welded metal during operation. Various electrodes can be used. There is a system for quick ignition of electrodes - Hot Start.
How to determine?
It's not that hard to find out. First you need to turn the battery with the front side facing you. It is located on the side where the stickers with characteristics and logo are located. Also, the pole terminals are located closer to the front side.
On many batteries you can immediately see the “+” and “−” signs, which accurately indicate the polarity of the contacts. Other manufacturers indicate information in the markings or highlight the current leads in color. Usually the plus is red and the minus is blue or black.
In the marking, reverse polarity is indicated by the letter “R” or “0”, and direct polarity by the letter “L” or “1”.
Battery polarity
Polarity refers to the arrangement of current-carrying elements on the top cover or front side of the battery. In other words, this is the position of the plus and minus. The current leads are also made of lead, as are the plates inside.
Direct and reverse polarity
There are two common layouts:
- straight polarity;
- reverse polarity.
Straight
During the Soviet period, all domestically produced batteries were with straight polarity. The pole terminals are arranged according to the diagram - plus (+) on the left and minus (-) on the right. Batteries with the same circuit are still produced in Russia and the post-Soviet space. Foreign-made batteries that are made in Russia also have this terminal arrangement.
Reverse
On such batteries, the minus is located on the left and the plus on the right. This arrangement is typical for European-made batteries and therefore this polarity is often called “Europolarity”.
Accumulator battery
The different position schemes do not provide any special advantages. It does not affect the design and operational features. Problems may arise when installing a new battery. A different polarity will force the battery to change position and the wire may not be long enough. Also, the driver can simply mix up the contacts, which will lead to a short circuit. Therefore, it is important to decide on the type of battery for your car when purchasing.
User guide
Do not forget that the inverter apparatus belongs to electrical equipment, therefore it must be properly operated, maintained and stored.
Below are the main tenets that need to be adhered to. Then your inverter will last for a long time.
If the protection against dust and water is high, then you can use it even in the field.
The housings of all devices, without exception, are equipped with signaling lights - light indicators. Keep an eye on them while welding.
If the lamp lights up, you need to stop working until the welding device has completely cooled down. This system prevents your welding machine from overheating.
Before starting to apply a seam, inspect the metal parts for the presence of rust, scale, dirt, and paint residues. Be sure to clean metal surfaces and degrease them.
Upon completion of welding (even if you are interrupted for ten minutes), disconnect the device from the power supply. Safety regulations prohibit welding work in the presence of people or pets.
Types of inverters on the modern market
Welding inverters on the market today can be divided into two main types.
Household
A device such as a household inverter is designed to perform periodic welding work. These devices are inexpensive, but they can be used from time to time; they are not intended for intensive daily work. Such inverters are optimal if you sometimes need to perform simple and short-term welding work. Most of these devices are made in China.
Professional
Such equipment is intended for daily long-term use; its design is initially designed for active use. The cost of these inverters, naturally, is quite high, but it is adequate to their quality characteristics.
The market also offers semi-professional inverter devices, which, in terms of their technical characteristics and cost, are between household and professional equipment. In addition to the above types, there are universal devices, which are also called combined. Their versatility lies in the fact that they can be used to perform welding using various technologies. Due to its wide functionality, such inverter equipment also falls into the professional category.