Home / Electrodes
Back
Reading time: 3 min
0
1350
There is a wide variety of brands, models, and types of welding electrodes. In addition to dividing electrodes by type of coating and purpose, they can also be divided by the type of current used: direct or alternating.
This distinction meets the requirements of both welders and manufacturing plants.
From this article you will learn the differences between these types of electrodes for alternating current, their characteristics, positive and negative sides.
- Alternating current: possibilities of use
- Advantages and disadvantages of models for AC welding
- Types of welding electrode coatings
- Popular brands
- Summarize
Electrodes for alternating current: marking, how to distinguish, what current strength and which electrodes are better
There are a great variety of welding machines.
They vary in functions, dimensions and many other criteria. But one of the most important technical indicators is the type of welding current obtained at the output during the welding process. There are only two such types: constant and variable. Correct AC welding electrodes are the key to quality welder work. They have their own characteristics and precise technical characteristics.
What is alternating current in welding
Is it good or bad, which current is better? Variable or constant? No one will give you a definite answer.
To begin with, it is better to understand the features of processes with alternating current, they are as follows:
- The behavior of the arc leaves much to be desired: with alternating voltage it is the most unstable.
- The welding seam is not of the highest quality due to deviation from the axis of the welding arc.
- If the arc goes out, its combustion can only be resumed when the voltage increases.
- The metal is splattered to a large extent.
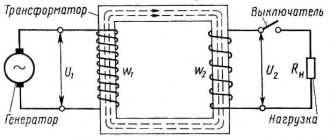
Despite all these complexities, the equipment required for AC welding is simple and inexpensive. These are, first of all, transformers - devices that are still very popular among welding masters.
It would seem that electrodes for alternating current should gradually lose their relevance: after all, many rectifiers have appeared on the market - inexpensive and with small dimensions convenient for use. However, these consumables are still in demand in many industries and handicraft workshops.
Most of the brands are universal, which is also extremely suitable for older generation domestic welders.
If you look at it, the best consumables for “change” have and show very serious production advantages. First of all, this concerns the resulting electric arc: its durability and easy ignition. Another feature of such electrodes is the low level of metal spattering during welding.
Welding transformer
Electrode diameter and steel thickness.
To carry out welding using a transformer, the following mandatory structural elements are required:
- Windings primary and secondary. The primary is made of a special insulated wire; there is no insulation on the secondary winding.
- Magnetic wire.
- Screw for controlling the position of two windings and changing the distance between them.
- Protective housing for the entire unit.
- Screw handle, running nut.
- Fan and other elements depending on the transformer model.
Despite the fact that many welding professionals regard transformers as equipment of the “outgoing generation,” they are presented on the market in the form of a wide range of models of very different values and for wallets of any thickness.
Transformers differ according to the following criteria:
- dimensions and weight;
- output current strength;
- output voltage level at idle;
- volume of electricity consumed;
Welding generator
The generator design includes the required structural elements:
- The most important part - the converter consists of an electric generating element with an alternating voltage motor. They provide changes in current indicators.
- Drive internal combustion engine.
- Indicator for monitoring and recording current strength.
- Mode switches.
- Special circuit breaker.
- Regulators for current and arc behavior.
- Terminals for connecting cables and 230V outlets.
These types of generators are available in two versions:
- Collector generators.
- Valve generators.
The main advantages of a gas generator in comparison with other welding machines are:
- Compact and therefore highly mobile.
- Convenience, relative cheapness, noiselessness.
- Wide functionality and high reliability.
- Quite high technical characteristics.
AC electrodes
Electrodes for alternating current have an interesting feature: they are universal, that is, they are suitable for working with both alternating and direct voltage. Let us immediately note that electrodes for direct current do not in any way possess such versatility.
AC electrodes are used where transformers and generators are used as welding machines. Like the devices themselves, these electrodes are in great demand, since these methods can only be used during recess.
Both units and consumables are significantly cheaper than welding technologies based on the use of constant voltage. So the popularity and demand for “change” is not going to decrease.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k-K9qgDOjb8
Electrode markings for different types of coatings.
Advantages of AC electrodes:
- The use of alternating consumables does not require rectifiers in addition to the transformer.
- The weld pool is not exposed to the harmful effects of nitrogen and oxygen from the air.
- The versatility of this type of consumables.
Disadvantages of variable consumables:
- The main disadvantage is that the quality of the welds is lower than when using constant voltage.
- Spattering of metal during welding.
- Low viscosity is under attack.
Four types of electrode coating:
- An acidic coating with the marking letter A, containing a high proportion of oxygen. This is a typical “station wagon”; such consumables can also be used on direct current.
- “Basic” coating marked with the letter B. They have a high ionization potential, which is why it is better not to work with them on alternating current.
- Rutile coating usually consists of half a special rutile concentrate, and it is very loyal to alternating current.
- Cellulose electrodes are suitable for direct current operation.
AC electrodes
Types of electrodes for welding with alternating and direct current.
The type of current is indicated in all markings of consumables - this is always the last digit. The main thing is to remember that if the last place in the marking is 0, then the electrode is not suitable for welding with alternating current.
- OZS – 12 with rutile coating. The most common type of electrodes for welding with alternating current, which is used on almost all Russian-made machines. Excellent welding of carbon steel parts, suitable for connections of critical structures. Significant advantages of these electrodes are the ability to work in any position in space, the absence of pores in the seam, a stable arc, and a completely acceptable dose of toxic gases released during the welding process.
- MP – 3 are designed for welding low-carbon steels. The advantages are similar: excellent arc stability, acceptable metal spatter. The slag crust comes off very easily. With these consumables you can cook even rusty, damp and poorly cleaned workpieces.
- ANO – 4 are also used for carbon steels. Excellent arc that ignites quickly and easily. You can cook wet and rusty products. There are no pores or cracks during seam formation. Easy separation of slag crust. There is virtually no metal spattering.
- MP-3C are distinguished by their high versatility: they are suitable for both low-alloy and carbon steels. The arc is ignited easily and instantly, the seam is protected from slag and oxides due to the rutile coating. The seams are smooth and durable, they can withstand significant loads. You can work with them in any position in space.
- ANO – 6 are used for connecting parts made of low-carbon steels. They are not afraid of rust, scale and dirt. The arc is stable and easily ignited, the seam is formed correctly.
- OZS – 4 for carbon steels, can be welded in any spatial position. The arc ignites easily. You can weld metal workpieces with edges of medium and large thickness at high temperatures. Attention! Doesn't like dirt on the surfaces being welded - they stop working.
- ANO – 21 are also intended for steels with carbon additives and low-alloy alloys. They are very easy to handle, can be worked in any position, and are also used in conjunction with an inverter and a semi-automatic transformer. The metal hardly splashes during operation, and the slag in the form of a crust is easily separated. An arc with excellent qualities - stable and soft.
- OZS – 6 are intended for carbon steels. They are characterized by a high throughput speed, which gives high labor productivity with a welding seam of excellent quality. Capable of welding oxidized surfaces.
electrodes for direct current
Differences in welding with different current polarities.
Types of electrodes used for DC welding:
- UONI - 13/55 - famous electrodes of their kind for direct current, applicable for steel alloys - with low doses of alloying elements and with the addition of carbon. They have significant advantages: the welding seam is very plastic and tough for mechanical stress, very durable. Almost no impurities and gases are formed. The arc is easily ignited. A wire of parameters Sv-08 or Sv-08A is placed in the rod.
- UONI - 13/45 are also used for joining workpieces made of carbon and low-alloy steels. The seam is not inclined to form cracks - neither hot nor cold. It is very ductile and tough, with ideal tightness, which makes it a suitable option for welding containers that will subsequently be subject to high pressure. Seams made with these electrodes do not age much longer.
- OZL – 6 are distinguished by their narrow focus: they are used in working with heat-resistant steels. Pores and cracks do not form in the seams, they are not subject to further corrosion and have the same heat resistance as the base metal. Suitable for metals with different structures.
- OZS-12 are intended for steel alloys with a low proportion of alloying additives and carbon. It is possible to work in any spatial position and is tolerant of surfaces with rust. The weld is formed with excellent characteristics: strength and durability. Stable arc. There are no releases of toxic substances during operation.
- TsL - 11 are also highly specialized electrodes, which are intended for steel alloys with additions of chromium and nickel, as well as corrosion-resistant steels. Welded seams are resistant to corrosion. The metal hardly spatters, the arc is stable, and the slag in the form of a crust is easily separated.
- ANO - 21, despite the fact that they are also intended for carbon and low-alloy steel alloys, like previous brands of electrodes, these consumables are extremely popular among craftsmen of various levels of professional training. Their features are a fine-scale structure of the weld metal, excellent arc ignition, softness, slight metal spattering, and so on.
- LB – 52U are distinguished by the high productivity of the welding process with their help. The arc is stable, the metal hardly spatters, work is possible in any position in space, and almost no cracks form in the seam.
- MR - 3 typical universal electrodes, which are rightfully present in both lists - for both alternating and direct current. Pores and hot cracks practically do not form in the weld, the arc is powerful and stable, there is little spattering of metal, and easy separation of slag in the form of a crust.
- OZCH – 2 are intended for welding cast iron. Despite their seemingly narrow functional focus, they have solid advantages in the form of versatility, ease of use, an excellent arc with excellent characteristics, ductility of the weld without cracks, and a well-separated crust with slag at the end of the process.
Electrodes for alternating current Link to main publication
Best models
We have selected brands of electrodes that are popular among professionals and beginners. Of course, these are not all the types of electrodes offered on the market, but you can start with them without fear of ruining your work:
- OZS-12 with rutile coating. This grade is widely used in welding critical metal structures, when increased quality of welds is required. The arc is very stable, no pores form in the seam, the material is non-toxic.
- MP-3. The most popular diameter for this brand is 3 mm. Used for welding steel with low carbon content. The seams are also of high quality and reliable; you can weld unrefined metal.
- ANO-4. In most cases, such electrodes are used when working with steel, which contains a large amount of carbon. They light easily, do not form cracks, slag is easily removed from the surface of the part, and, compared to other brands, there is almost no metal spattering.
- MP-3S with rutile coating. Just like the previous electrodes, they are used to work with steel with a high carbon content. This is the most common type of electrode for working with alternators. The arc ignites easily and is stable, the seam does not oxidize and is relatively smooth, reliable and resistant to mechanical stress. You can cook in any position, which is convenient in hard-to-reach places. We recommend this brand for beginners.
- ANO-6. By analogy with MP-3, they are also used for welding steel with low carbon content. You can weld without any problems on uncleaned metal and in places of mild corrosion, the arc burns evenly and stably, the weld is strong and durable.
What are the best electrodes for AC welding?
To talk about electrodes for alternating current, you must first remember what electric current is in general. This, according to definition, is the directed movement of particles carrying an electric charge.
And alternating current is a current that changes over time in magnitude and direction. When one second is taken as a unit of time, and particles carrying an electric charge change their direction a certain number of times. The change in direction is called frequency and is measured in Hertz. And in one second in our electrical networks, there are 50-60 such Hertz. Or 50-60Hz.
AC Power Supplies for Welding
At the very beginning of the welding era, there were no power sources other than variable ones. Accordingly, all welding materials, that is, electrodes, were developed to work on such devices. Rectification and conversion of alternating current to direct current occurred later.
Indicators determining the type of current
Looking ahead, it must be said that there are no electrodes that are intended only for welding with one alternating current.
Attention!!! Any electrode that operates on alternating current also works on direct current. But not every electrode operating at constant voltage can burn at alternating voltage.
Therefore, it would be more correct to talk here about universal electrodes.
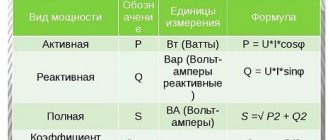
The main technological properties of electrodes are determined by such indicators as: type of current (alternating or direct); direct or reverse polarity (for direct current); current strength; deposition factor. But these properties themselves depend on the chemical composition of the rod and the quality of the coating.
Steel
For electrode rods, steel wire is used, which is divided into three groups:
•low carbon;
•alloyed;
•highly alloyed.
The grade of wire is deciphered in the following order: St - means welding, then comes the digital value of carbon content in hundredths of a percent, then there may be alloying additives, and at the end there is a letter “A” or two “AA”, which means low or very low content sulfur and phosphorus.
The chemical composition of the wire must satisfy the required quality of the welded joint.
Coatings
As you know, there are six main types of electrode coatings.
- Acid coating is designated by the letter “A”. It contains various components that contain a lot of oxygen. Ferroalloys are used to remove it. Operation on direct current is possible, but alternating current is better for electrodes with this coating.
- The main one is designated “B”. This coating is based on marble, chalk and ferroalloys. These electrodes should definitely not be used with alternating current due to the high ionization potential.
- Rutile - “R”, the coating consists of 50% rutile concentrate. Such electrodes are used for alternating current.
- Cellulose-“C” coating. Suitable for DC current.
- There are also completely “faceless” coatings with the letter “P” and mixed coatings with the letter “C”.
But the most common and “running variable” are rutile-coated electrodes. They account for about 70% of the electrodes that operate with alternating current.
Rutile coated electrodes
The slag-forming basis of this coating consists of rutile concentrate, all sorts of aluminosilicates and carbonates. Due to organic matter, which decomposes during combustion, gas protection of the molten metal is provided. And they remove oxygen from the bath with manganese.
There are two subgroups of such coatings:
1. rutile aluminum silicate;
2. rutile carbonate.
In the first group, the basis of slag protection is: mica, feldspar, koalin.
The second is mainly marble and magnesite.
The redox reactions of manganese and silicon are very important in these electrodes. These reactions greatly affect the mechanical properties of the weld metal.
The weld metal deposited with these welding materials corresponds to mild or semi-mild steel.
The amount of non-metallic inclusions and oxygen decreases with increasing slag basicity, ductility increases and crack formation is minimized.
Welding and technological properties
These electrodes have very good characteristics. Here the seam is perfectly formed, then smoothly and gently passes to the base metal. They have a very low spray coefficient. The slag is easily separated from the seam.
The arc burns steadily and evenly. When the arc length fluctuates, it is almost not prone to pore formation. And, what is very important, it is not “capricious” to wet and uncleaned surfaces, unlike electrodes with a basic coating.
They also have high resistance to crystallization cracks.
Based on the thickness of the coating, these electrodes can be used in any spatial position or only in the lower one.
According to the technological properties and content of iron powder, they are conventionally divided into three groups:
1. In the first, iron powder takes up relatively little space, only 15-20 percent. Productivity does not increase much this way, but the coating melts smoothly, the arc burns evenly and spatter is reduced. Designed for welding thin metal in workshop conditions, where short and curved welds predominate.
2. In the second group there is already more iron powder. The percentage is somewhere around 30-35. They are already called universal high performance. They weld in all spatial positions and with metal thicknesses up to 10-20mm.
3. The third group already has a high content of iron powder in the coating, up to approximately 45%. They are already highly productive. And they are used only in the lower position and over a long seam.
AC Electrode Brands
The most popular are domestic Tomsk, Losinoostrovsk and Moscow manufacturers:
- OZS-12 (SpetsElektrod, Moscow). Easy to apply a seam, insensitive to cracking, low and very affordable price. But he is afraid of dampness.
- Resanta MP-3. It ignites easily and burns stably at different arc lengths. Slag is separated easily and cleanly.
- Of the imported ones, the following are in good demand:
- ESAB-SVEL OK 46.00. They work very well even when wet. Quality and price go well together.
- Lincoln Electric Omnia 46. Small spattering, even rusty and uncleaned metal is easily “taken”. The seam is famous for its strength.
Selection of products according to other parameters
The type of current, as well as the polarity of its connection, are the most important parameters of welding operations. Welding inverters primarily produce direct current, which can be connected to the workpiece and the electrode in two circuits.
- Straight polarity. With this scheme, the plus is connected to ground, and the minus to the welding electrode.
- Reverse polarity. This scheme involves connecting the minus to ground, and the plus, respectively, to the holder with the electrode.
If you cook with an inverter using straight polarity, the surfaces being connected are subject to significant heating, which does not happen when connecting the polarity in the opposite way. This is why choosing reverse polarity is advisable in the following situations.
- When welding parts of small thickness with an inverter. Reverse polarity in such cases will help protect the material from burn-through.
- Reverse polarity is used to weld parts made of high-alloy steels, which are very sensitive to overheating.
Working with inverter welding
Direct polarity, during which the workpiece is subjected to significant heating, is optimally used for joining materials that are very thick and massive.
When performing any welding work using an inverter, the most significant are three parameters that are interconnected:
- welding current strength;
- electrode diameter;
- thickness of the parts to be connected.
The thickness of the parts being connected has a direct influence on the choice of electrodes. If it is necessary to connect thin parts (up to 1.5 mm), manual welding is not used; semi-automatic machines or devices that allow welding in a protective argon environment are better suited for this purpose.
Options for electrode position when welding
When deciding which electrodes to choose for welding structures of a certain thickness, you can be guided by the following criteria:
- for parts whose thickness is 2 mm, electrodes Ø 2.5 mm are best suited;
- when connecting parts with a thickness of 3 mm, you should choose electrodes Ø 2.5–3 mm;
- if the thickness of the parts to be welded is 4–5 mm, then electrodes Ø 3.2–4 mm are suitable;
- parts with a thickness of 6–12 mm are best welded with electrodes Ø 4–5 mm;
- when the thickness exceeds 13 mm, then the optimal choice is electrodes Ø 5 mm.
It is very important to choose the correct diameter of the electrodes, since if this parameter is exceeded, the welding current density decreases. This will lead to the welding arc becoming unstable, the penetration of parts will deteriorate, and the width of the weld will increase. Many manufacturers indicate on the packaging information about the best current values to use.
Welding electrodes
If such information is not contained on the packaging, then you can follow the following recommendations:
- for welding with electrodes Ø 2 mm, the welding current should be set to 55–65A;
- for products Ø 2.5 mm, a current of 65–80A is used;
- electrodes Ø 3 mm - current 70–130A;
- for electrodes Ø 4 mm, choose a welding current of 130–160 A;
- products Ø 5 mm - current 180–210 A;
- It is better to cook with 6 mm electrodes at a current of 210–240 A.
As it becomes clear from all of the above, for high-quality welding with an inverter, the correct choice of electrodes according to their diameter is important. You should also set the optimal welding current. If, for example, you plan to weld thin metal with an inverter, using large-diameter electrodes, or the welding current exceeds the permissible values, then pores may form in the finished weld, which will significantly reduce its quality characteristics.
» data-lazy-type=»iframe» src=»data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7″>
Electrodes for alternating current: brands, which are better, markings, features
There are a large number of classifications of electrodes. One of the common ones is the separation of welding materials depending on the type of current used. In this article we will look at electrodes used for welding with alternating voltage (where to buy, see here).
Specifics of AC welding
The welding process has several features:
- less stable behavior of the arc compared to constant;
- the welding arc deviates from the original axis, which leads to deterioration in the quality of the seam;
- arc resumption is possible at increased voltage;
- high level spattering ;
- relative simplicity and more affordable cost of equipment.
AC Welding Equipment
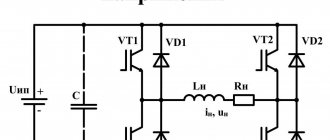
Transformers are one of the most popular types of equipment for welding work. Welding is carried out thanks to several components included in the design of the device:
- magnetic circuit;
- primary winding made of insulated wire;
- secondary winding, which most often lacks insulation;
- a threaded lead screw serves to change the position of the windings, control the distance between them and regulate the air gap;
- screw running nut;
- handle for rotating the screw;
- housing to protect the unit.
Transformer models may have additional elements: ventilation, handles and wheels for ease of transportation. The device can also be equipped with technical parts that improve its operation.
There are a large number of transformer options on the market, differing in the following parameters :
- weight and dimensions;
- the value of the output no-load voltage;
- electric current strength;
- ability to work with electrodes of various diameters;
- amount of current consumed.
The welding generator is a self-contained unit. This equipment is used for welding work in the absence of a full-fledged energy source.
The design (internal equipment) of such devices includes the following components :
- The converter includes an AC motor and an electricity generating device. This element makes it possible to change the current parameters;
- The welding unit consists of a drive internal combustion engine, an alternating current electric generator and a design that allows
- control current parameters;
- The welding generator can be valve or commutator.
The design (external equipment) consists of several parts:
- indicator displaying current strength (1);
- circuit breaker (2);
- mode switches (3 and 4);
- output 230V 16A x 2 (5);
- current and arc force regulators (6 and 7);
- terminals for connecting welding cables (8).
The main advantages of units of this type:
- high technical characteristics;
- compact dimensions ensure mobility;
- convenient and inexpensive equipment;
- high level of reliability and functionality;
- low noise level.
This information will help determine which devices are best to use for welding work on alternating voltage.
[ads-pc-2][ads-mob-2]
For AC or universal – which is correct?
Electrodes for AC welding are also suitable for DC welding, but not vice versa . This is due to the fact that alternating current has its own characteristics. Accordingly, the welding process is also characterized by several distinctive features listed above. Therefore, AC electrodes can be called universal .
Who needs AC electrodes
Alternating voltage is used in household and industrial welding. The affordability and ease of use of equipment operating on alternating current have made it in demand. Many craftsmen have similar equipment.
Generators and transformers operate exclusively during recess. Therefore, owners of such equipment have the opportunity to work on only one type of voltage and use welding electrodes for variable values.
Advantages and disadvantages
Let us now consider AC welding electrodes from the point of view of “pros and cons”.
Flaws
- In terms of connection quality, they are inferior to constant voltage welding materials.
- High level spattering .
- Relatively low impact strength.
Advantages
- Reliable protection of the weld pool from the negative effects of gases from the air: nitrogen and oxygen.
- The use of these consumables does not require a rectifier for the transformer.
- The electrodes are universal . They can work with “recess” and “constant”.
What coatings are used
There are four main types of coating:
1. Electrodes with acid coating are marked with the letter “A”. This type of coating contains components with a high oxygen content. These welding materials can operate on direct current, but this coating ensures stability even in alternating current.
2. The main one is designated by the letter “B”. Such consumables should not be used during breaks due to the significant ionization potential.
3. The coating of rutile electrodes consists of 50% rutile concentrate. This type applies to alternating current.
4. Cellulose electrodes are suitable for “permanent” use.
The most suitable and popular type of coating for “change” is rutile. Welding with rutile materials is convenient and comfortable.
Having studied this information, a welder of any level will be able to determine which welding electrodes are better for alternating current in terms of choice of coating.
[ads-pc-3][ads-mob-3]
Popular brands
The following are the most popular brands of AC electrodes. The type of electricity is indicated in the labeling by the last digit. There are several options: each number from 1 to 9 has its own meaning; if the number is 0, then you cannot cook with a variable.
Next, we will look at which brands of electrodes for alternating current are most in demand among specialists.
1. OZS-12 have a rutile coating.
This grade is used when working with critical structures and parts made of carbon steel.
Advantages: welding can be carried out in any spatial position; provide a strong and durable connection; rutile prevents the formation of pores; stable arc; small amount of toxic substances released.
2. MP-3 are intended for critical structural parts made of steel with low carbon content. Advantages: stable arc burning; minimal metal spattering; ensuring high-quality seams; the slag crust is easily separated; It is possible to weld poorly cleaned, rusty and damp metal.
3. ANO-4 are used for welding, cutting and surfacing of carbon steels. The advantages of this brand: easy ignition and arc stability; welding of poorly cleaned, damp and rusty structures is possible; practically not prone to the formation of pores and hot cracks; the slag crust is easily and quickly separated; metal spattering is minimal.
4. MP-3S are used to work with high-carbon and low-alloy steels. This brand is widely used in various fields.
Advantages: easy arc flammability; rutile coating protects the seam from inclusions of slag and oxidation; high level of welding arc constancy; the use of MP-3S electrodes ensures an even seam, resistant to mechanical stress and wear, without pores or voids; welding can be performed in any position.
Welding electrodes ANO-6
5. ANO-6 are used for welding low-carbon steels. Advantages: welding over rust, dirt and scale is possible; sharp excitation and smooth arc burning; form the seam well; have low sensitivity to the formation of cutoffs.
6. OZS-4 are designed for welding products and structures made of carbon steel.
The advantages of electrodes of this brand: rutile coating ensures connection in almost all positions, which greatly simplifies the work of the welder; insensitive to poorly cleaned metal; easy arc ignition; possibility of welding at higher modes; provide welding of products of medium and large thicknesses.
7. ANO-21 are used for welding carbon and low-alloy steels. Advantages: ease of use, which guarantees high results; welding can be carried out in all positions; used when working with an inverter and semi-automatic transformer; low metal spattering; easy slag separation; soft and stable arc.
Welding electrodes OZS-6
8. OZS-6 are designed for welding structures made of carbon steel. Advantages of this brand: provide high labor productivity; connection of oxidized surfaces is possible; guarantees a high-quality and durable seam.
Each welder has his own idea of which brand of electrodes for AC welding is the most popular and convenient.
How to properly use an inverter welding machine
In experienced hands, an inverter can produce a good seam; you need to follow three rules:
- set the optimal current strength;
- choose the correct electrode diameter;
- take into account the thickness of the parts being welded.
Diameter is the main guarantee of a high-quality seam, and the current density also depends on it. The density cannot be higher, because the arc will be unstable, which means the metal will not be welded as well and the seam will be wider.
Of course, this will not affect the quality, but if aesthetics are important, then it is better to avoid it. If you need to cook thin products, it is better to use a semi-automatic machine.
Inverter welding will produce an unreliable seam, and when choosing thick welding rods, pores will appear in the joint, which will reduce its strength.
To find out the optimal current strength when working with the selected rods, just look at the markings on the packaging. It is not recommended to deviate from this parameter.
What are the best electrodes for AC welding?
page » About welding » Electrodes for alternating current
There are a large number of classifications of electrodes. One of the common ones is the separation of welding materials depending on the type of current used. In this article we will look at electrodes used for welding with alternating voltage (where to buy, see here).
For AC or universal - which is correct?
Electrodes for AC welding are also suitable for DC welding, but not vice versa . This is due to the fact that alternating current has its own characteristics. Accordingly, the welding process is also characterized by several distinctive features listed above. Therefore, AC electrodes can be called universal .
Electrodes for alternating current welding: characteristics, features, application, pros and cons
There is a wide variety of brands, models, and types of welding electrodes. In addition to dividing electrodes by type of coating and purpose, they can also be divided by the type of current used: direct or alternating.
This distinction meets the requirements of both welders and manufacturing plants.
From this article you will learn the differences between these types of electrodes for alternating current, their characteristics, positive and negative sides.
Alternating current: possibilities of use
Variable current, variable voltage, and in common people “change” has found its application in welding work in garage conditions, in the factory production of complex metal structures.
Models with “change” are more often purchased due to their low price and ease of use. Most often, such a welding machine can be found in the hands of a novice welder, but even more “advanced” ones are happy with it.
The work requires both the presence of a device and consumables - electrodes, therefore the question of the difference between some electrodes and others arises by itself.
Answer: “change” is a universal type that is suitable for both direct current and alternating current, but direct current models are suitable only for it. This is the advantage of the former over the latter. Let's continue the conversation about the characteristics of the models.
Advantages and disadvantages of models for AC welding
The protective properties of the “changes” are another point in their favor; they will not do a bad job of protecting parts of the welding seams from negative atmospheric influences. A rectifier is not required to interact with the converter, which once again speaks in favor of this model.
Among the negative characteristics: models for alternating current are inferior to analogues for constant current. The characteristics of the seam at the exit will be lower.
Also, during the welding process, metal will spatter heavily, and heat energy from mechanical power will be poorly absorbed, resulting in a short service life.
Types of welding electrode coatings
There are 4 types of electrode coating for alternating current:
- Acidic is a mixture with a high content of iron and manganese, sometimes with titanium and silica. You can recognize them by the marking “A”. They can be used to cook raw metal, but the process releases many toxic substances.
- The main one is the most popular, marked as “B”. Such models can be used with alternating current, but with caution, since the ionization potential of the main coating is small.
- Rutile is the most suitable for working with “change”. Welding is easy, fast, there is no large spatter, the quality of the seam is good. You can recognize it by the “P” marking.
- Cellulose coating is more universal, suitable for both “change” and direct current. Marked as "C/S".