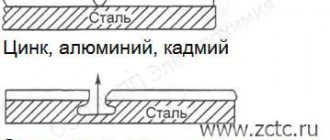
Chemical milling gives the product an ideal shape.
Chemical finishing of iron is a set of technological processes due to which the physical and chemical properties of the metal surface change. The technology is practiced only at high temperatures and in active media (solid, liquid or gaseous). The end result of chemical treatment is a change in the physical and chemical properties of the diffuse iron layer.
Purposes of processing
The considered method of finishing metal products makes it possible to increase strength indicators and enhance the anti-corrosion protection of the product. In addition, the service life of the treated substances increases. The advantages of iron diffuse surface finishing include:
- Performance. Most reactions proceed quickly, which allows the technology to be used on an industrial scale;
Chemical milling - Versatility. Practice has shown that even on a lathe it is possible to improve the performance of the element being processed with the correct choice of finishing method;
- Elimination (in most cases) of thermal or mechanical effects. The absence of these types of influence increases the performance qualities of the processed raw materials;
Etching (chemical milling) is the most common finishing method. The technology is used to work with thin metal sheets and a large number of small elements. Etching is widely used in various fields and mass production of materials with improved technical characteristics.
Studied thermal engineering, cementation of bushings
Modern metalworking technologies
Each metalworking technology described above is standard. They have been used for quite a long time, they have firmly entered into mass production. However, there are new methods that are not familiar to everyone, but are still used mainly in private practice.
Plasma cutting
Plasma is a stream of hot ionized gas. It can replace mechanical cutting methods. This is an accurate, neat, and increasingly popular method.
Electrical discharge machining
Electrical discharge machining allows you to work with products of particular complexity: ultra-small, ultra-dense, etc. Surface changes occur under the influence of electrical discharges.
Laser welding
The technology is rarely used due to expensive equipment and high demands on specialists. However, the laser accurately and firmly welds parts from any alloy, which is why the technology is still relevant.
Ultrasonic processing of metal
This is a subtype of chiselling. Used when working with fragile substances: some semi-precious stones, gypsum, alabaster, etc. Operating range – 22 KHz.
Types of chemical-thermal methods
During chemical treatment, different reactions occur, however, on the surface of the workpiece the same processes occur in the same sequence. Chemical finishing stages:
- Beginning of the reaction. At this stage, the transfer of diffusing substances to the element being processed occurs;
Chemical-thermal treatment of metals - Diffusion;
- Completion of the reaction. At this stage, the physical and chemical properties of the metal are improved;
- The final processing of the substance is often carried out on a lathe or milling machine to consolidate the acquired properties.
In modern metallurgy, several chemical treatment methods are practiced:
- Cementation is the process of saturating a metal product with carbon. Chemical processing makes it possible to obtain a unique substance with a durable shell and a soft core;
- Nitriding is the process of saturating the surface layer with nitrogen in order to improve the material’s resistance to wear and corrosion;
Types of chemical and thermal treatment - Boridation is a set of technological processes for saturating metals with boron. Raw materials saturated with boron have high wear-resistant qualities, especially against friction and dry sliding. In addition, boron creates a layer on the metal surface that increases resistance to cold welding. Also, borated materials are resistant to alkaline substances and various types of acids;
- Aluminizing is the processing of metal using aluminum on a machine. The technology makes it possible to obtain materials that are resistant to aggressive gases (hydrogen sulfide or sulfuric anhydride);
- Chrome plating is the process of enriching the upper layers of metal with chromium. Chrome plating does not increase the strength of a metal product, but it increases wear resistance and corrosion resistance. It is worth noting that hard chrome plating significantly improves the properties of metal products, for example, the treated substance increases strength, wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
Cyanidation, nitrocarburization
This is a technology for saturating steel with nitrogen and carbon. In this way, steels with a carbon amount of 0.3 - 0.4% are processed.
The ratio between carbon and nitrogen is determined by temperature. As it grows, the share of carbon increases. If oversaturated with both elements, the layer becomes brittle.
The layer size is affected by exposure time and temperature.
Cyanidation is carried out in liquid and gaseous media. The first method is also called nitrocarburization. In addition, according to the temperature regime, both types are divided into high and low temperature.
In the liquid method, salts with sodium cyanide are used. The main disadvantage is their toxicity. The high-temperature version differs from carburization in speed, greater wear resistance and hardness, and less deformation of the material. Nitrocarburization is cheaper and safer.
Nitrocarburization of steel
The final mechanical treatment is first carried out, and the fragments that are not subject to cyanidation are covered with a layer of copper 18 - 25 microns thick.
Features of chemical finishing of metal on a machine
Metal processing on a machine can only be carried out after preparing the product using special devices - primary preparation units. Preparation takes into account the physical and chemical properties of the workpiece, as well as the individual needs of each department in the enterprise.
Methods of influencing metal:
- Spraying is applied to parts that are used in dead-end or pass-through applications. The advantages of this method are the possibility of mass preparation of elements;
Methods of influencing metal - Immersion. This technology requires the production of separate containers with special solutions. Such a machine usually has mechanisms for laying out and mixing the metal product. After immersion, the material is sent to the drying chamber, where the final formation of its new physical and chemical parameters occurs. The processed parts are sent to a warehouse, from where they are transported to enterprises, where other machines will work with them; Steam blasting of metal
- The steam jet method is used to prepare large mechanisms or large metal sheets. The preparation process begins with cleaning the metal surface from grease and dust. Simultaneously with cleaning, phosphating of the treated surface occurs. It is worth noting that at this stage all work is performed manually and not on a machine. Primary processing ends with thermal exposure - the surface of the workpiece is treated with a blowtorch. Heat treatment is carried out simultaneously with the addition of active elements.
To finish the material using the listed methods, two types of equipment are used: stationary and mobile machines. It is worth noting that on a stationary machine the pressure can reach 5 atmospheres. High pressure ensures better penetration of chemical components into the upper layers of iron. Mobile equipment, as a rule, is not very powerful, so only rough processing of the workpiece is carried out with their participation.
Metal turning
The final preparation of the material is carried out on a lathe before chemical finishing. It is worth noting that on a lathe you can not only prepare, but also work with the workpiece. On such a device, thread cutting, drilling, reaming and countersinking of various holes are performed; turning grooves and cutting off parts. A stationary device is used to remove rust or remove the effects of corrosion.
Other oxidation methods
The oxidation method, known for a very long time, is immersing heated parts in linseed oil. The products are heated in an oven to 450-4700C and immersed in linseed oil for 5-10 minutes, the process is repeated several times. The result is a dense black oxide film.
Oxidation of steel is possible in acidic solutions, which, unlike the alkaline method, is carried out at temperatures up to 1000C. There are two compositions and modes of such oxidation:
- The solution consists of calcium nitrate - 15-30 g/l, orthophosphoric acid and manganese peroxide 0.5-1 g/l. Operating temperature – 1000C, holding time – 40-45 minutes.
- The solution consists of sodium hyposulfite - 80 g/l, ammonium chloride - 60 g/l, orthophosphoric acid (specific gravity 1.6) - 5 ml/l, nitric acid (specific gravity 1.4) - 2 ml/l . Operating temperature – 60-700C, holding time – 15-20 minutes. It is possible to carry out the process without heating if you increase the holding time to 40-60 minutes.
After alkaline oxidation, the parts are washed in cold water and treated with a chromium solution of 120-150 g/l, heated to 60-700C. After processing and drying, the parts are oiled.
You may be interested in the following articles:
|
Exposure to electricity
Electrical impact is a special type of metalworking associated with the use of high-intensity discharges. They are used to burn holes, form protrusions and openings. The method is designed for thick sheets. Graphite or brass electrodes serve as contact elements.
The capture of metal particles formed during the processing process is ensured by oil compositions.
Rice. 3 Cutting with graphite electrode
Working with welding equipment
By welding, permanent joints are formed, cavities and cracks are eliminated, and the geometry of the part is adjusted by welding plates or a layer of metal.
There are three welding methods.
- Gas. The components to be welded are heated by ignited gas. The fire source is acetylene, propane or butane. The work involves the use of liquefied fuel cylinders or an acetylene generator. The supply of combustible substance is regulated by the burner. Filler wire is used as a connecting element.
- Electric. There are three types of electric welding: manual, semi-automatic and automatic. In the first case, consumable electrodes are used, in the second - welding wire and protective (carbon dioxide) gas, in the third - robotic equipment that performs welding along a given contour.
- Chemical. Special compounds are used to heat and melt metal. During their reaction, a large amount of heat is released, which leads to fusion and welding of the components.
The latter welding method is used extremely rarely due to its complexity and high cost. With its help, work is carried out in hard-to-reach places.
Rice. 1 Electric welding