- Table of types of turning
- Types of turning
- Metal turning tools
- Turning equipment
- Which company should you choose as a contractor?
There are several types of turning parts, which are the most popular for machining metal and giving the metal workpiece the required dimensions. The main factor is the equipment on which the metal will be processed on lathes, because this determines what operations can be carried out. The second no less important factor is the tool, and in particular the cutters with which the part will be processed directly. The parameters by which quality turning work is judged are accuracy, frequency and compliance with the drawing or sample according to which the work will be performed.
By observing these factors, you will minimize defects. Let's look at what types of metal turning exist, what equipment and tools are best to use in order to avoid production defects and the production of low-quality parts.
Table by type
| Process | Task |
| Machining of cylindrical surfaces | Surface treatment of the workpiece to obtain the required parameters and dimensions. |
| Turning of the outer conical surface of a part | Processing a workpiece to shape the part and remove the base layer of metal. |
| Turning of shoulders and ends | Machining shoulders and ends on a lathe for finishing the part. |
| Lathe cutting of workpiece | Cutting workpieces to size on a lathe using a cutting tool. |
| Hole machining | The main types of processing: drilling, boring and reaming holes in a workpiece or part. |
Cutting a product or workpiece
is performed by cutting cutters, with the tool moving transversely to the center of the part. Depending on the size of the part, various methods of fixing an almost cut or cut part are used. Tool breakage at the end of cutting is prevented by using supporting rests and reducing the cutter feed (by 45-55%) when approaching the center of the part by half the radius of the workpiece. Small parts fall into a tray, part catcher or are fixed in a turret fixture.
Types of turning
- Processing of cylindrical surfaces.
If we take into account the complexity of turning steel parts, the use of turning modes, the choice of the type of cutters and tools, this operation can be classified as one of the simplest. Turning is a mechanical process of cutting material through the mechanical action of a cutting turning tool on a metal workpiece to create parts and give shape, parameters and the desired frequency. During the processing process, the cutter cuts a given thickness of the metal layer from the workpiece, reducing the outer diameter.
For turning external surfaces, cutters of the through and thrust type are used. Parts that are manufactured entirely by turning are often custom-made shafts, axles, and fasteners. Turning is also used to refine finished parts or modernize them by changing the size and shape.
- Turning of the outer conical surface of a part.
Such processing of products on lathes can be performed exclusively on CNC lathes using program control, where it is possible to process along two axes - transverse and longitudinal tool feed. The machine operator with a CNC module makes adjustments to a specific part from the drawing and sets the exact coordinates of the movement of the cutting tool and the rotation of the chuck. On CNC lathes, parts are produced as quickly as possible and chamfers are removed, which significantly increases the productivity and accuracy of work.
- Turning of shoulders and ends.
The operation is performed with a workpiece clamped in a lathe chuck using through-cut turning tools. The required parameters and frequency are obtained by increasing the spindle rotation speed, the cutting tool moves towards the center of the part.
- Lathe cutting of workpiece.
In cutting-off turning operations, only cut-off cutters are used. The movement of the cutter occurs towards the center of the workpiece. An important point is to support the workpiece at the final stage of cutting as the cutting tool approaches the center of the part in order to avoid chipping the cutter.
If you need to cut long parts or workpieces, use a special tool called a steady rest. It serves to fix the middle part of the workpiece and serves as a supporting, auxiliary tool.
- Hole machining
The most popular types of turning are drilling, boring and reaming. If we take the most popular turning method of these three, then this is, of course, drilling. Drilling is necessary before boring or reaming operations. The part is clamped in turning jaws, the drill is clamped in a mandrel, which is fixed in the headstock. The drilling process on a lathe is performed exclusively in the center of the part.
Internal boring, internal stepped boring, internal grooves are made when securing the part in a chuck mounted on the headstock of the lathe.
Design of complex surfaces of bodies of rotation, shaped turning
To obtain bodies of revolution with a curved generatrix on universal machines, it is necessary to use through or shaped cutters using a copier or a hydrocopying support. Often, such operations require highly qualified turners, and profitability is achieved only with mass production.
Modern CNC lathes have wide technological capabilities. Shaped surfaces are very diverse; their production in many cases is ensured not by the geometry of the tool, but by the form-building movements of the working parts of the machine according to the program. The use of shaped tools for working on CNC machines is extremely rare. Obtaining the full variety of part surface shapes can be achieved through proper design of the processing program. The accuracy of circular and linear interpolation allows for smooth transitions between frames.
This makes it possible to get by with a relatively narrow range of tools when processing various parts. The programmable point of the cutter is either its tip or the center of the rounding at the tip.
On CNC lathes, it is especially effective to use tools with multifaceted non-grinding inserts made of carbide and super-hard materials. They ensure stability of the geometry, the ability to use the maximum power of the machine, increased tool life, and simplify the setup of the machine when the tool wears out. When one of the cutting edges wears out, the plate is rotated, introducing a new edge into the work. The error in the position of the new face usually does not exceed 0.05-0.1 mm and can be easily eliminated using correctors of the CNC system.
Metal turning tools
The frequency and accuracy of turning depends, firstly, on the quality and condition of the lathes themselves, and secondly, on the processing speed, the thickness of the metal layer being removed and the quality of the cutting tool. It is necessary to learn how to correctly select the optimal rotation speed of the spindle of a lathe, correctly select the type of cutter required for a particular operation, and optimally select the thickness of the metal layer to be removed. By choosing the right parameters you will receive high quality parts.
It is worth taking into account that when selecting the spindle rotation speed, you need to take into account the type of steel being processed. Since for different steels you need to choose different speeds, as well as choose the most suitable type of cutting tool. You can find out and select the optimal speed and the right tool to obtain higher-quality parts by turning in specialized tables and documentation on the topic of metal machining.
Various cutters are also used for roughing and finishing turning. Roughing is the preliminary stripping of a metal workpiece. Finishing is the final processing to size of the part. For roughing, preliminary turning, it is better to choose cutters with a larger cutting plate, which will allow you to remove a thicker layer of metal without breaking the cutter. The incisors will be divided into bent, straight, and reinforced.
Here it is worth saying that during turning, the quality and accuracy are directly affected by the parameters and types of cutters. In order to achieve the most accurate parameters and efficiency of turning, you need to be more precise in choosing the shape of the cutting tool. The concept of angle will help you in this matter.
The required angle of the cutter is obtained by sharpening its tip. It is also worth considering the position of the cutter during turning; the smaller the angle, the more resistant the cutter will be. If we look at an example, let’s say when turning parts with a large diameter and harder steel, it is better to choose an angle from 35 to 40. When turning smaller diameters and softer steel, it is better to choose an angle from 60 to 90 degrees.
Boring holes
Precise holes, large-diameter stepped holes, and internal grooves can be produced using boring operations. The product is clamped into the headstock chuck and supported by a steady rest (in the case of significant length or weight). In this case, access to the end processed by the boring cutter remains free. The accuracy of boring on a CNC lathe exceeds the accuracy of drilling, and is often ensured by processing technology, cutting tools, lathe experience, systems for fine-tuning cutting tools and the technical condition of the equipment.
Turning equipment
There is a wide variety of lathes for different types of turning work, but screw-cutting lathes remain the most common and universally used. They are widely used in all types of industrial enterprises, factories, private workshops and in repair centers of various types. Their popularity is justified by their versatility and great technical capabilities.
Universal screw-cutting lathes consist of the following parts:
- A headstock, which includes a rotating spindle with a chuck and a lathe gearbox, a tailstock with a slide clamp and fastening for a mandrel for drills or a rotating center;
- Feed box;
- Stanina and more.
To obtain the highest quality turning and milling of parts, machines with a CNC module are used. They are not very different in design, but due to software control we obtain more accurate dimensions and tolerances. In addition to the universal screw-cutting lathe, they are often used in metalworking:
- Turning and rotary;
- Turning and turret;
- Semi-automatic turning machines (used for small serial parts such as fasteners);
- CNC lathes.
In conclusion, it is worth saying that if you comply with all the above parameters and subtleties of the turning operation, you will achieve good results in the quality of parts and avoid a large number of defects or unforeseen problems with turning equipment.
Drilling, countersinking, reaming holes
The main method of making holes is drilling. Drilling is the process of making cylindrical holes using a metal-cutting tool. Drilling usually precedes operations such as boring or reaming. Processing can be done either in the center of the part (when clamping it in a three-jaw chuck) or with an offset of the center of the hole. Offset (eccentricity) is achieved by fixing the workpiece in a four-jaw lathe chuck or on the headstock faceplate. On a turning center, it is possible to use a driven tool and make holes both on the spindle axis and with an offset along the X axis. When using a radial drive unit, it is possible to process holes located along the X axis.
In a universal machine, the processing tool: countersink, drill, reamer is fixed in the conical hole of the tailstock directly or through a clamping chuck. in CNC machines - in the toolholder position using special cutting blocks and mandrels.
With the development of tools for machining short holes, the sequence of the drilling process and preparation for it undergoes significant changes. Modern tools allow drilling into solid material and do not require preliminary centering of the holes. High surface quality is achieved and, often, there is no need for subsequent finishing of the hole. The use of modern drills with replaceable inserts allows processing at high speeds and large volumes of generated chips, which in CNC machines are washed out of the hole by flows of coolant supplied under a certain pressure through internal channels.
For precision turning, it is necessary to have correct and uniform sharpening of the cutting edges of the drill, perpendicularity of the end of the workpiece to the tool axis, and the absence of burrs and surface irregularities.
Using Renishaw monitoring and setting systems, software in CNC machines allows you to set tool length and diameter compensation parameters and perform breakage detection during machining. The tool feeding in the machine occurs mechanically. The drill ensures a clean surface of the hole Ra 6.3...3.2, a countersink - Ra 2.5, a reamer - Ra 1.25...0.8.
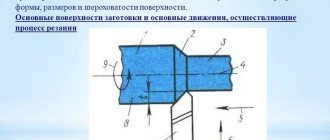
Scheme of processing on a lathe
To launch a new series of products at any enterprise, schematic images are developed that play the role of technical specifications for turners. They make it possible to greatly simplify and save time on metal work, since the craftsman does not have to independently select the mode, speed, and required cutter. The circuits are first checked to avoid various defects. This also allows you to calculate more accurate product parameters, which is especially important for serial turning production.
The diagram shows:
- method of fixing the cutter;
- its position in relation to the workpiece;
- turning process using symbols.
It presents the main parameters, which can be adjusted if necessary to achieve maximum precision in processing parts.
The essence of metal turning
The technology of metal turning is that the excess metal layer is cut off from products until the part takes on the required shape, size and surface roughness. For such processing, metal-cutting machines called lathes are used.
Lathes are suitable for processing rotating parts - shafts, gears, pulleys, bushings, rings, couplings, nuts, etc.
Basically, with the help of lathes, surfaces that have a cylindrical, conical shape, as well as shaped and end surfaces, and ledges are processed. On machines, grooves are turned, parts of workpieces are cut off, holes are machined by drilling, boring, countersinking, and reaming; threads are cut and rolled.
Metal turning work to order and on an industrial scale is performed using cutting tools. Working on machines involves the use of various cutting tools - cutters, drills, countersinks, reamers, taps, dies, threading heads, etc.
The cutting process is similar to the wedging process, and the working part of the cutting tools resembles a wedge.
Due to the application of force to the cutter, its cutting edge is wedged into the workpiece, and the front surface of the tool, continuously compressing the layer of metal lying in front, overcomes the adhesion of the particles of the processed surface and separates them from the main mass. The layer cut off during turning, which is metal shavings, is called allowance.
In the process of working on a metal lathe, two movements are combined. The first (main) of them involves rotation of the workpiece, which is fixed in a chuck or faceplate, the second - the feed movement - is performed by the tool in order to give the workpiece the specified parameters in size, shape and surface quality.
Thanks to the many options for connecting these movements, turning equipment allows you to work with parts with different configurations, as well as perform other technological operations. Using machines you can:
- cut threads of various types;
- drill, bore, ream, countersink holes;
- cut off parts of the workpiece;
- grind grooves of various configurations on the surface of the product.
A wide range of functions of turning equipment allows you to do numerous jobs. This is what is suitable for processing:
- nuts;
- shafts of various configurations;
- bushings;
- pulleys;
- rings;
- couplings;
- gear wheels.
Of course, upon completion of turning, a finished product must be obtained that meets certain standards. Quality in this case implies that the parts must have dimensions, shape, surface roughness and relative position accuracy that meet the requirements.
To ensure proper quality control in the process of metal turning, measuring instruments are used: if we are talking about large enterprises that produce serial products, maximum calibers; in the case of manufacturing parts in small batches, or individually - with calipers, micrometers, internal gauges and other measuring devices.
Features of the equipment and its operation
Lathes can be automated (CNC) or designed for manual operation. Modern CNCs are equipped with a numerical control panel for independent, automatic solution of the required task. The only exception is the blank installation function - this action must be performed by the operator. Devices of this type are characterized by high accuracy and ease of use.
The use of manual lathes involves the need to install the workpiece, cutter, carry out calculations, direct the support to the starting point, select the rotation speed and feed mode. In addition, during work the master must independently change all the specified parameters.
A separate category also includes machines:
- turning-screw-cutting - on them the products are given a taper, threads are cut, corrugations are rolled, grooves are turned, etc.;
- turning-turret - allow processing of parts with complex configurations, for example, rods, forgings, castings;
- rotary turning (one-, two-column) - turning of large-diameter products;
- multi-cutting semi-automatic;
- in the form of processing complexes (for turning and milling work).