Home / Devices
Back
Reading time: 2 min
0
1092
Those who have had to use welding devices at home have probably heard about such a miracle of technology as a wire welding machine. What is it, what is it for and what is it good for?
A wire machine is a semi-automatic device that uses not electrodes, but metal wire and gas or flux.
The peculiarity of the operation of such a device is that the built-in mechanism in a semi-automatic mode supplies filler material - wire - to the welding zone.
- general characteristics
- Process technology
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Conclusion
What is MIG/MAG
The wire has such qualities as flexibility and thinness. And its use allows you to reduce the spattering of molten metal, increase the size of the weld pool and the depth of welding. Using semi-automatic wire machines, you can weld different grades of steel, non-ferrous metals, and other materials.
Modern wire welding machines use MIG/MAG technology. What do these English abbreviations mean? MIG is Metal Inert Gas and MAG is Metal Action Gas.
That is, what kind of gas is used in the welding process is of key importance here. If it is inert helium, then the technology should be called MIG, and if welding is carried out with CO2 gas, which is classified as active, then MAG.
The welding process with machines that support MIG/MAG technology is quite simple. Even craftsmen without serious experience in the profession can achieve decent seam quality and a good level of productivity.
With a semi-automatic welding machine it is possible to work spotwise and create continuous seams up to 40 meters long. Anyone today can purchase one of these devices in specialized stores, and it will definitely come in handy in the household.
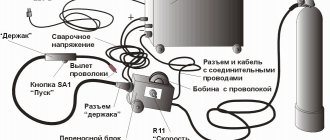
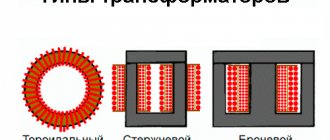
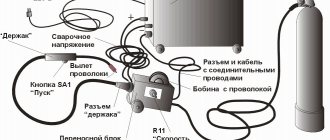
In the design of a semi-automatic wire welding machine, three main elements can be distinguished: a transformer (or inverter) that generates an electric arc; a conveyor responsible for feeding the wire electrode; and a control unit, whose main task is to synchronize all processes.
Device, principle of operation
The welding station includes:
- Source of arc formation (transformer, rectifier, inverter). In addition to the voltage converter, it includes a control unit and a mechanism for automatically feeding a flexible electrode. The latter can be made in the form of a separate autonomous device - these units belong to the professional series.
- Shielding gas and wire supply hose. It ends with a conductive burner mouthpiece.
- Power cable connected to the workbench or directly to the workpiece (ground clamp).
- Gas system: gas cylinder, pressure reducer, hose.
The equipment is portable (household series) or transportable (semi- and professional series), equipped with two (four) wheels. Power is supplied from a stationary power supply 220V or 380V.
220V units are less powerful than 380V units, but are successfully used to solve household problems or are used in small mechanic shops (for example, car repair shops).
Operating principle:
- The preparation procedure (including the gas system) and switching on are described in detail in the instructions for each model.
- The arc is ignited through a tungsten tip. After the flame is formed, the necessary adjustment of the current parameters occurs. The gas component is started and the wire feed is turned on.
- The flexible rod acts as a consumable electrode, that is, it is a filler wire. The task is to create a weld in the form of a weld bead of metal.
Operation without shielding gas
MIG/MAG technology by default involves the use of wires in combination with a shielding gas - argon, helium, nitrogen or carbon dioxide. But home craftsmen are reluctant to use this method, because creating a gas environment entails a number of costs and inconveniences.
For welding work, you will need to have a cylinder with some kind of inert or active gas. From time to time, these cylinders will need to be refilled at a specialized station.
Moreover, refilling will become especially expensive and costly if the welding machine is not used very often. Moreover, the presence of cylinders and additional equipment leads to the fact that the welding machine loses its mobility.
However, there is an alternative - in practice, wire MIG/MAG welding machines can be used effectively without gas. To do this, you need to purchase flux-cored wire.
It is relatively inexpensive, and its presence allows the master to practically forget about complex preparatory procedures. You just need to insert this wire into the place intended for it, turn on the device and start working.
Flux-cored welding wire for semi-automatic and automatic welding is slightly thicker than usual. This is due to the fact that inside it there is a rod made of a substance that improves the welding process (this is flux).
Thus, the wire can be bent, cut into pieces, and so on - this will not affect its performance characteristics in any way.
Which semi-automatic welding machine is better to buy?
After the most popular models of semi-automatic welding machines have been studied, you need to make a choice in favor of one device. It depends on your capabilities, goals and scope of work. But based on feedback from experts and users, we can conclude:
- For household work, the Resanta SAIPA-135 model is suitable.
- For a professional with simple work – Elitech IS 250PN.
- For car service and garage work - BlueWeld Starmig 210 Dual Synergic.
- For three-phase network and different conditions - Svarog MIG 3500 (J93) (TIG, MIG/MAG, MMA).
- For professional purposes and for complex work - Fast and Furious 502 (TIG, MIG/MAG, MMA).
We reviewed the best models of semi-automatic welding machines, studied their characteristics, and highlighted their advantages and disadvantages. You just need to familiarize yourself with the devices and choose the appropriate device.
10 semi-automatic welding machines worthy of attention
Wire selection
You should not choose the cheapest (most likely made in China) option. After all, the quality of the future connection depends on the additive. GOST 2246-70 specifies more than 75 types of wire for semi-automatic welding machines.
In addition, there are several dozen more types of wire products, whose characteristics are determined by the Technical Conditions (TU).
The wire should be selected so that it matches the metal being welded . That is, for example, aluminum wire is only suitable for aluminum products. At the moment, both ordinary aluminum (steel, copper, nickel, etc.) wires and products with a flux layer inside can be found on the open market.
But to create a high-quality seam, the wire machine must have an impeccable feeding and pulling algorithm. So far, only devices made in the European Union can boast of this.
By the way, flux-cored wire itself, made from the same aluminum, can have a very high cost, which will certainly not suit all home craftsmen.
The best manufacturers of semi-automatic welding machines - which company to choose
A number of manufacturers who have won the trust of consumers due to their quality and reliability:
- Resanta . The leading brand of electrical equipment on the Russian market comes from Latvia. The manufacturer has been working in this field for more than 15 years and offers high-quality equipment available to both professionals and amateurs.
- Fubag . A German brand that produces professional equipment for construction and repair. Over 40 years of operation, FUBAG has become a recognized leader in the European market and supplies products to many countries around the world.
- Inforce . Professional tools are produced under the INFORCE brand. All products undergo double quality control: in production and by company specialists.
- Aurora . The high quality of equipment sold by the Aurora manufacturer has been known for more than 10 years. The welding equipment presented by the brand has certificates of compliance with both European and Russian standards.
- Patriot . A large manufacturer of gardening, power equipment and power tools. Since 1999, Patriot has been actively developing sales in the markets of Russia and the CIS countries.
But each model from the same manufacturer has its own distinctive features, so before purchasing you should study the characteristics of the device. A selection of the best devices can help you with this; they indicate the pros and cons of the models, customer reviews and costs.
Refueling and consumption
In order for the welding operation to proceed quickly and without errors, you need to correctly thread the wire into the machine. This is done as follows:
- Usually welders buy one or more wire spools at a time. After unwinding a small piece, straighten the outermost 10 centimeters using wire cutters;
- then you should examine whether there are any traces of corrosion or contamination on the wire surface. If everything is fine, then you need to advance the wire thread a few centimeters into the so-called liner (this is a tube in the area of the device sleeve);
- Now you need to turn on the semi-automatic welding machine and start working, not forgetting to make sure that the bends of the sleeve are not too strong and sharp. Because of this, the wire may well get stuck and break in it.
It is equally important during welding or in advance to find out at least the approximate consumption of welding wire. N
and the consumption rate is influenced by such parameters as the chemical composition of the metal, the thickness of the wire itself, and the technical characteristics of the welding machine.
In many cases, it is believed that the weight of the wire should be equal to 1.5% of the weight of the parts being welded. And the weight of the deposited material is always 6-10% less than the weight of the wire (this 6-10% “eats” the waste).
Open sources also indicate that the consumption of flux-cored wire per second during semi-automatic welding can range from 3 to 25 cm. Obviously, much will depend on the speed of the master welder.
How to cook
Wire welding differs from the “gas” method in its more gentle consumption of materials and low energy intensity of the process. In fact, these are two main advantages.
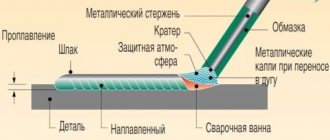
The welding process itself is as follows. The wire inserted into the welding machine passes through a small sleeve into the holder, and then forms an electric arc that is in direct contact with the metal workpieces being welded.
The filler material (flux) burns and melts under the influence of an electric arc, releasing carbon dioxide. And it, in turn, reliably isolates the weld pool from oxygen in the surrounding atmosphere and creates obstacles to excessive melting of parts.
In general, semi-automatic welding without gas has few differences from the standard “arc” process. But still, the use of cored wire imposes certain limitations. Flux-cored wire is quite fragile, and the welder will have to handle the machine holder very carefully.
The very fact of the release of carbon dioxide makes this method unacceptable for creating ceiling joints. Even vertical seams will be difficult. But with traditional horizontal seams, no insurmountable difficulties should arise.
However, in some cases, someone who welds with wire without gas will probably have to go over some areas again in order for the flux to be completely removed from the surface.
There are also certain restrictions on the size of welds. A wire electrode with a diameter of up to two millimeters is physically incapable of creating a wide and deep connection.
In addition, it is important to observe polarity and correctly connect the cathode and anode of the wire apparatus. The greatest power must be transmitted to the holder; it must be used to melt the wire additive.
There is no point in using ordinary wire in such a welding process - without the protective gas environment, the molten metal will either all splash out to the sides (if the current is too high), or will often “stick” (if the current is insufficient).
Required device parameters
In order to work correctly with flux-cored wire electrodes, welding machines must have the following parameters:
- welding current strength from 35 A;
- power from 1.5 kW or more;
- The diameter of the wires used is from 0.5 to 2 mm.
The current strength can be adjusted using rheostats located in the control unit. When selecting the optimal wire size, the welding conditions (thickness of the metal products being joined, type of alloy or metal) must be taken into account.
As for the power of the wire machine, it directly affects productivity and cost. The greater the power, the more the wire apparatus costs and the greater its efficiency.
DC transformer machines for welding with consumable electrodes.
The design is similar to previous devices, but a diode or thyristor rectifier is installed at the output. The alternating current is rectified, but some power is lost. The design is more complex, heavy and expensive. But working on direct current is more comfortable, the arc is more stable. In addition to welding ferrous metals, it is possible to work with stainless steel and non-ferrous metals using appropriate electrodes. Direct current has polarity, so this must be taken into account when selecting and connecting electrodes. There are also electrodes for direct current, and there are universal ones. Recently, many manufacturers are refusing to produce this type of hobby-class devices.
But in professional activities they are widely used.
The characteristics for these devices are the same as the previous type.