Metal welding has been known since at least the 17th century. But at that time, the types of metal welding were few: blacksmithing and casting. The options we are familiar with appeared only at the moment when the electric arc began to be used and the types of welding became more diverse. Today, the classification of the types of welding used is much more diverse.
There are currently three main options for performing work:
- mechanical;
- thermal;
- thermomechanical.
The introduction of electronics made it possible to increase productivity and accuracy and automate the process.
Physics, chemistry, a little poetry
Welding is the process of permanently joining different structures by heating, deformation, or both.
In short, from a physics point of view, welding uses either heat or pressure, or heat and pressure together. In short, from a chemical point of view, welding uses a huge number of different types of flux-cored tapes, fluxes, electrodes, gases and other components. It depends on the materials and conditions. Thanks to chemistry, we have a huge number of technical options.
Important! We will not burden you with complete lists of welding types or all the classifications that exist. We don't have enough paper to write, you don't have the patience to read. Understand the logic of grouping welding methods so that you can easily find information on each specific type. There are many sites on the Internet dedicated to welding: you can find everything you need.
Requirements for welding seams
The requirements that may be placed on welding seams largely depend on the final purpose of the finished structure. Nevertheless, several general requirements can be identified that connections of this type must satisfy. The hardness and tensile strength of the welded joint must have the same indicators (or similar) as those of the base metal. Tests are carried out on special equipment with a sample of the finished product.
Visually check the quality of the seam as follows. After completing the welding work, the seams are cleaned of slag and oxides, and all auxiliary devices are also removed. The seam should be uniform, fine-scaled and have a uniform width. There should be no sagging, burns, narrowing or breaks. The metal that is deposited must be homogeneous and not have pores or surface cracks.
Principles of classifications, overview
Classification of arc welding methods.
The classification of welding types is carried out according to a variety of criteria; they neatly fit into a semantic framework. What criteria are the most important? Let's go through some of them; first, it's better to see the big picture.
How many types of welding exist today? You can say the number 150 with the word “about”. Maybe 250. But we don’t recommend naming numbers. While you are reading this article, the number of species may change - technology does not stand still. But what kind of welding there is according to materials, physical processes, popularity, control methods - we need to talk, these are precisely the very principles of classification that we need to understand.
An example of a simple, understandable classification by energy source in welding:
- electricity;
- electric arc;
- friction;
- gas flame;
- laser radiation;
- electron beam;
- ultrasound.
Another example of a list by type of weld. There are many of them, whole bunches of different types:
- butt, corner welds - along the connection of the edges;
- by shape, length - horizontal, vertical, circular, straight, intermittent, continuous, long, short, medium seams;
- by type of material used - seams for steel, non-ferrous metals, bimetals, polyethylene, etc.;
- by volume of deposited metal - reinforced, weakened, normal welds;
- in shape - longitudinal, transverse seams;
- by the number of layers – continuous, intermittent, tack, multi-layer.
The “sewing” list can be continued, but it is important for us to understand the general principles, so let’s finish with the lyrics and move on to the main methods.
Possible defects in welding joints and seams
Electric welding is a complex process and not always everything goes smoothly.
As a result of operational errors, seams and joints may have various defects, including:
- Craters. Small depressions in the weld bead. They may appear as a result of a broken arc or an error in the execution of the final fragment of the seam.
- Pores. The welding seam becomes porous as a result of contamination of the edges of the parts with rust, oil, etc. In addition, porosity can appear when the seam is cooled too quickly, at high welding speeds and when working with undried electrodes.
- Undercuts. They look like small indentations on both sides of the suture bead. Appear when the electrodes are displaced in the direction of the vertical wall when welding corner joints. In addition, undercuts occur when working with a long arc or when the welding current is too high.
- Slag inclusions. There are pieces of slag inside the welding bead. This can happen if the edges are dirty, the welding speed is high or the welding current is too low.
These are the most common weld defects, but there may be others.
Additional information on welding vertical and horizontal seams using electric welding is presented in this article.
Basic concept of the welding process
Welding is a technological process of creating reliable connections by heating or plastic deformation with the establishment of interatomic bonds subsequently. The structure of the products is continuous. Energy is supplied to the electrode and welding material through an inverter. First, the metal of the electrode melts, this creates a weld pool, in this pool the electrode is mixed with the base material, and the slag that floats to the surface serves as a protective film. The welding process is nothing more than the hardening of the metal after all of the above influences. Electrodes come in several types - consumable (the electrode rod melts) and non-consumable (with a non-consumable electrode, filler wire is used, which melts separately in the bath).
How to cook using arc welding
Preparatory work
- straightening of parts intended for welding. Metal can be straightened either manually, on leveling plates, or on various sheet straightening rollers. Severely deformed metal sometimes requires hot straightening.
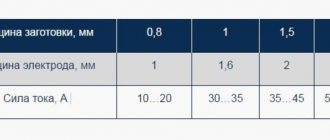
- marking. The sheet is marked according to the drawing (or sketch) using measuring tools and templates. When marking a part, you should keep in mind that during the welding process the parts are shortened. Therefore, it is necessary to leave an allowance of 1 mm for each transverse joint, and 0.1-0.2 mm for each linear meter of a longitudinal seam;
- cutting;
Cleaning
The base material and filler material are subjected to this operation. They should be free of scale, rust, oils and other contaminants: even a small amount of contaminants will lead to defects in the weld, reducing its strength, and therefore the reliability of the finished product. The edges and adjacent areas 25-30 mm wide should be cleaned especially carefully;
Edge preparation
The shape of the edges depends on the thickness of the sheet. They must be blunted with the same radius, and the gap between them must be the same along the entire length of the future weld;
Assembly
This operation accounts for up to 30% of the total labor intensity. For convenience, various templates and tools, and welding fixtures are used. Assembly must be done in the order that the previous operation does not interfere with the subsequent one.
Technological properties of welding works
There are many technological varieties of types of welding work depending on the material and equipment, the most common of them are: arc, electroslag, gas, light, plasma and electron beam.
Types of welding by type of mechanization and uninterrupted technological properties: air, vacuum, foam, flux and submerged types.
Based on the degree of metal melting, welding is divided into atmospheric and jet welding. Jet welding is characterized by molten material at the weld.
What does a novice welder need to get started?
To start training, you will have to select the appropriate equipment and equipment.
Particular attention should be paid to personal protective equipment, since welding work is a process harmful to vision and respiratory organs.
It will be necessary to equip a workplace; if it is in a workshop, then the room should be equipped with effective exhaust hood and sufficient lighting.
If you decide to start training outdoors, be sure to do so on dry ground and under a canopy that will protect you and the equipment from rain.
The workplace should be spacious, not cluttered, and not restrict the welder’s movements.
Cables should be laid out in such a way that they will not be stepped on or tripped over when moving around workpieces.
It is better to choose scraps of rolled stock and steel sheets as blanks for practicing skills. It is not recommended to start with critical structures.
Welding process
Regardless of the number of types of welding, there are 3 main stages of the welding process, inherent in all technological varieties, these are:
- Formation of contact;
- Education Communications;
- Creating a seam.
Forming a contact
The formation of contact occurs as a result of bringing the metal to the melting or boiling point; the main thing is not to confuse the weld pool with the melting of iron.
Formation of chemical and metallic bonds
The second, most important step is the formation of a weld pool; it always looks the same, regardless of the type of welding. The bath appears as a result of the fusion of metal and auxiliary material, for example an electrode, under the influence of temperature, and appears as a white spot. The quality of the seam depends on the width and length of this spot.
Creation and types of strong connection
The main qualitative characteristics of seams are their width and height.
By type of connection there are (the most common):
- butt – parts in one plane (pipes, sheets, etc. are welded).
- overlapped - the parts are arranged in parallel, only one overlaps the other (sheets are welded, the thickness of which is no more than 12 mm).
- end - weld 2 ends of the elements.
- angular - elements are located at an angle to each other.
Nuances for beginners in welding
There are several nuances that can be useful to anyone who wants to learn how to cook correctly:
- Do not forget about grounding and the importance of regularly checking the quality of contact between the clamp and the workpiece.
- Check the cable insulation regularly.
- The current strength is selected immediately after connecting the ground.
- Before igniting the arc, the electrode should be installed at an angle of approximately 60 degrees to the plane of the part, and the distance between its end and the part should be about 0.5 cm.
Electrode positions when welding
By mastering increasingly complex types of seams and joint configurations, the home craftsman will be able to learn how to weld correctly and will provide his household with all the necessary welded structures.
We will weld tightly, inexpensively, call
Tacking structures before welding.
Basic welding methods are a common but incorrect classification in this context. “The most popular” would be more correct.
Here are three well-deserved winners:
- Manual arc - gold.
- Gas - silver.
- Semi-automatic - bronze.
Each winner belongs to a different welding family; in theory, it is better to describe them in their rightful places together with their close “relatives.” But we will do the wrong thing - we will introduce welding champions at the beginning of the review.
Manual arc welding RD
People's favorite No. 1, the most common type in everyday life and in industry. The three main words in RD are simplicity, cheapness, and transportability. The physics of the process consists of melting a special coated electrode, which leaves behind a mark in the form of a weld seam. Different electrodes are used, depending on the metal. The arc is the distance between the electrode and the surface of the metal, which plays the role of a second electrode.
Essentially, an arc is a powerful discharge in a gas space (air). During RD, three objects melt: the edges of the two surfaces connected to the electrode. The better the triple melting products are mixed (to do this, the electrode is moved left and right), the better the quality of the seam.
RD welding has serious advantages over other types:
- the RD method is easy to learn;
- you can cook in any position in space;
- You can cook a wide variety of metals; there are electrodes for sale for every taste;
- accessible transportable equipment
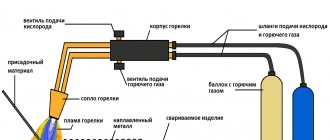
Gas welding
People's champion No. 2, well-deserved silver medal.
This is when welders carry gas cylinders with them: they need a mixture of oxygen with some flammable gas - acetylene, propane or butane. The physics of the process is also melting, but the heat is supplied not by an electrode, but by a gas burner. The metal surfaces are melted by the torch, the process occurs smoothly and rather slowly. The thicker the metal layer, the slower it melts. Why gas welding is better than other methods:
- Non-ferrous metals are excellently welded;
- the equipment is simpler than electrical methods;
- the ability to control the mixture and flame;
- no powerful energy source is needed, the method is autonomous.
You can’t do without disadvantages, the “gas” disadvantages are as follows:
- very slow heating of surfaces;
- low heat concentration due to dissipation;
- high cost of electricity.
In terms of the cost of electricity, arc methods can compete with gas methods: with RD, electricity is also wasted mercilessly. But in the end, the gas method, due to its “low speed,” is much more expensive.
Important! Where there is a pair of words “flammable gas”, there is always a second pair “safety precautions”. Safety rules are well regulated, but compliance with the requirements requires additional costs of money and time. By the way, gas welding is more than 100 years old - here it is, a stainless classic, applause.
Semi-automatic welding
Classification of the welding arc.
Bronze champion, closes the popular top three, but in terms of his prospects he will easily surpass the first prize-winners. In fact, this is a type of arc type familiar to us, a progressive evolution of the RD. It features a large number of technological nuances, options, and instructions. It is enough for us to know that the “automatic part” of the method is the feeding of the welding wire.
The manual part is the welding process itself with wire feed control. You can cook with gas (carbon dioxide for beginners, argon for professionals), or without gas, with direct current. The option without gas is popular in garages and summer cottages; in this case, a special flux-cored or flux-cored wire is needed. When it burns, a gas with vapor is formed that protects the combustion area.
Semi-automatic is the only method at a service station: body work is carried out only with its help. The semi-automatic machine uses gas and a special wire instead of the usual electrode. Gas from the torch with wire is supplied to the welding sleeve. As a result, the process is protected from environmental influences. The process modes are determined by the welder depending on the thickness of the metal.
The semi-automatic method has serious advantages over other types:
- excellent seam quality;
- high speed;
- ease of use;
- welded as non-ferrous and ferrous metals;
- You can cook rusted or galvanized metals;
- wide selection of materials, modest financial costs.
Types of Welding Machines
There are a large number of models of welding machines of different types on the market.
Of all their diversity:
- transformers;
- rectifiers;
- inverters;
- semi-automatic;
- machine guns;
- plasma;
In a home workshop, transformers are most often used because of their low cost, and inverters because of their simplicity and ease of use. The rest require either special working conditions, achievable only in production, or special training and long-term acquisition of skills.
Transformer
The design of such devices is extremely simple - it is a powerful step-down transformer, in the secondary winding of which a working electrical circuit is connected.
Transformer welding machine
Transformer advantages:
- unpretentiousness;
- survivability;
- simplicity;
- cheapness.
Flaws
- very large weight and dimensions;
- low arc stability;
- AC operation;
- causes voltage surges in the supply network.
Such a device requires skill and extensive experience from the welder. It is not suitable for teaching a novice welder how to weld correctly.
Inverters
The inverter device has a much more complex design. The inverter unit repeatedly converts the input mains voltage, bringing its parameters to the required ones. Due to the transformation of high frequency current, the dimensions and weight of the transformer are many times smaller.
Inverter
Inverter advantages:
- low weight and dimensions;
- stabilized voltage and current in the circuit;
- additional anti-stick and hot start functions;
- possibility of precise adjustment of current and arc parameters;
- does not cause voltage surges in the supply network.
The inverter also has disadvantages:
- high price;
- low frost resistance.
It’s best to start learning how to cook properly with an inverter. The stability of the arc parameters and additional functions that make starting easier and preventing “sticking” will allow the beginner to concentrate on the seam and quickly master the technology.
We cook metals
We’ve sorted out the people’s favorites, let’s move on to the “correct” classifications.
Let's start with the real heavyweights - types of metal welding, which are divided into three groups according to:
- Physical signs.
- Technical characteristics (mechanization, process continuity, metal protection).
- Technological characteristics (separate classifications for each method - for example, types of electrodes).
According to physical characteristics, we have three main classes for all types of metal welding:
Thermal class - the welding process involves melting with thermal energy:
- gas;
- arc;
- laser;
- radiation, thermite, etc.
Important! The main types of fusion welding are the most common in everyday life and in industry. This is the most populous class; the vast majority of welding methods belong to it.
Mechanical class using mechanical energy:
- ultrasonic;
- cold;
- friction;
- explosion, etc.
Metal welding table.
Thermo-mechanical class, methods of combined action of thermal energy and pressure:
- blacksmiths;
- diffusion;
- contact, etc.
As an example of metal welding, we present MAWP - mechanized argon arc welding with a consumable electrode. A true hybrid for electro-gas joining of metals. Without it, welding of non-ferrous metals or complex alloys is impossible.
Advantages of MADP:
- connection of any alloys;
- stability of the product’s shape due to low heating;
- electrodes need to be changed rarely;
- widest scope of use;
Flaws:
- difficult for beginners;
- low execution speed.
The right choice is the basis for success
You can view the products and purchase welding equipment on the company’s official website. Here you can leave a request for the purchase of equipment for gas welding. In separate sections of the site, manual arc welding machines and argon arc welding machines are presented. Owners of small and medium-sized enterprises involved in the production of metal products will be interested in semi-automatic MIG/MAG welding machines.
We cook polyethylene
Applications of plastic welding.
What can you cook besides metals? Ceramics. Glass. But in second place of honor are plastics or polymers, primarily polyethylene pipes. You can work with polyethylene using thermistor, electrofusion methods, or electrical resistance: these terms are listed in the technical literature. Don’t be alarmed, all options can be called briefly – NC welding. NZ – embedded heaters.
The essence of the process is the melting of polyethylene at the joints using metal spirals of an electric heater, which is embedded in the part. The method is extremely popular, it has great prospects in industry: it is used in various pipelines, replacing old metal pipes with new polyethylene ones, installation and repair, and the development of new polymer technologies.
When working with plastics, another method is used: welding or welding with a heated tool. The simplest option for supplying heat to heat polymer surfaces. There are many options for welding tools for working with NI - from a simple electric soldering iron for small parts to special welding machines of various sizes. Self-respecting plumbers keep this kind of equipment in their work suitcases without fail.
By the way, welding methods NZ and NI are included in the list of mandatory methods of a professional welder with confirmed qualifications, for example, certification from NAKS - the National Agency for Welding Control.
Now classification by type of process mechanization:
- Automatic
- Automated
- Mechanized
- Manual, let's start with it.
Manual welding
Examples of welded joints.
Despite the rapid growth of new automated methods, manual methods are indispensable in many cases, this type of welding has long occupied a legitimately important place in modern technology.
Advantages of manual methods:
- can be cooked in hard-to-reach places;
- in different positions in space;
- you can quickly move from one material that we melt to another;
- selection of electrodes for every taste for all types of steel;
- The equipment is easy to transport and easy to maintain.
In addition to the familiar electric arc method, this group includes a manual version of argon arc welding with the same operating principles as the mechanized version described above.
Manual types include do-it-yourself spot welding, a contact method that is possible at home, unlike other contact methods used only in industry.
Classic gas welding also refers to manual methods.
Types of metal protection during welding
Hot metal spatter is a major problem in any welding job. This happens not only with the manual electric arc method, but also with the semi-automatic method, even in a protective gas environment. The splashes harden and form carbon deposits and other defects on the surface of the structure, thereby reducing the quality of the finished metal structures.
In some cases, for example, due to the location of the seam in a hard-to-reach place, it is not possible to remove metal splashes mechanically: by cutting down or grinding. Therefore, it is recommended to pre-treat the seam area on the surfaces of the elements being welded with special means for protection - paste or liquid from the adhesion of metal splashes.
Today, many protective compounds are produced for various types of metal welding:
- liquid products, packaged in canisters and bottles, are applied to metal surfaces with a brush or sprayed through a spray bottle;
- aerosols produced in special bottles;
- pastes packaged in metal or plastic jars with a wide neck.
It is recommended to apply all protective agents in strict accordance with the manufacturer's instructions supplied.
Welders with extensive experience sometimes use their own recipes for protective compounds. For example, chalk, dissolved in water to the consistency of a paste, protects surfaces well from the adhesion of metal splashes. This homemade paste is applied to the area around the future seam, leaving the edges clean.
Upon completion of welding work, it is necessary to thoroughly clean the surfaces of the seam and the area around it from the protective coating. Many products for protecting metal surfaces from splashes contain oil and fat-containing components that significantly reduce adhesion. Therefore, before applying a protective layer, it is necessary to thoroughly degrease the area of the metal surface being treated.
The inventors of welding technologies have made a great contribution to the development of scientific and technological progress. Along with the already known methods of creating an inextricable connection, new types of metal welding have appeared. CMT technology (Cold Metal Transfer), based on cold metal transfer, allows you to perform many types of welding work with high quality.
New methods of fusing metal surfaces are being successfully introduced into all areas of industry, mechanical engineering and construction. It was thanks to welding that humanity received large ships, airplanes, modern cars and bridges capable of withstanding multi-ton loads.
Automatic methods
Classification of welding methods using automation:
- Electric arc technology.
- A gas-electric arc is protected by gas, most often an inert gas such as argon or helium.
- Electroslag technology.
Tungsten welding - application diagrams.
Electric arc method: A close relative of the manual arc method, automatic submerged arc welding or AF is a type of arc method with excellent performance indicators. Here, too, a consumable electrode is used; all work is carried out under a special protective layer of flux. In the manual arc method, there is a serious risk of the arc itself burning in the air, so the strength of the supplied current is limited.
With AF, the arc is protected by a layer of flux, there is no risk of burning. The strength of the welding current is not limited in any way. This makes it possible to penetrate the metal deeply, resulting in a seam of excellent quality. The flux layer prevents metal splashing and loss during the process. Complete mechanization of the method allows less qualified welders to be admitted to AF. As a result, the productivity of the AF method is 5 to 10 times higher than that of manual arc AF. Let's be honest and present the shortcomings of AF, there are few of them:
- fluxes are not cheap;
- there is a harmful effect on the operator;
- You can only work in a limited space.
Electroslag technology, “heavy artillery” on the modern industrial front. This is a fundamentally new arcless method of melting. The source of thermal energy is not an arc, but an alternating current that passes through the molten slag. The metal surfaces are covered with slag, which is heated. This way you can weld metals of almost any thickness.
Advantages of arcless technology:
- high-quality tight seams;
- seams of complex shape;
- absence of deformations, especially angular ones;
- no need to process edges;
- ease of implementation
- labor automation, minimal human participation
The method is used mainly for large-sized structures.
Features of choosing the appropriate type and technique of welding
The classification of welding types is so broad that quite often specialists (especially beginners) wonder what types of welding exist with which even a non-professional could weld and obtain joints of impeccable quality.
If it is not difficult to list all types of welding, then it is impossible to definitively answer which one is the best. The fact is that each type of welding differs in the technique of execution and the equipment used. It is also necessary to consider what advantages and disadvantages specific types of welding have and their use has clear limitations.
Argon welding
The essence of the technique is the use of non-consumable electrodes. The advantages are:
- ideal fixation of thin elements;
- the ability to control the depth of metal heating;
- much less splashes from sparks when compared to other types of welding that exist and are actively used;
- an even, uniform, externally beautiful seam, which is especially important in cases where great importance is given to the aesthetic characteristics of the finished product.
Flaws:
- during manual welding, productivity is very low;
- automatic connection is contraindicated for joints with different directions or too short;
- expensive equipment.
Argon welding is used in the manufacture of metal structures from aluminum, copper, titanium, stainless and alloy steel, and non-ferrous metal alloys.
Arc welding
A fairly common classification of welding, which has a number of positive features:
- the ability to connect parts in any spatial positions;
- versatility of use in places with limited access;
- the working process is available on AC and DC;
- low cost.
As a continuation of the advantages, there are also disadvantages:
- the seams are not of the desired quality, they have lack of penetration and tubercles;
- very low efficiency due to the high amount of waste;
- not suitable for joining thin workpieces;
- low performance indicators.
Arc technology is used for the manufacture of stairs, canopies, fences, pipe joining, and installation of main pipelines. The seam does not have high aesthetic properties, but if you choose what types of welding exist to create products from thick metal, then arc is considered one of the best methods.
Gas flame technology
Comparing modern types of welding, which are suitable for welding assemblies and connections made from pipes, as well as for installing pipelines of medium and small diameters, here it is worth giving preference to the gas method.
Obvious advantages:
- complete independence from power supply;
- ease of transportation of equipment from one place to another;
- absence of overheating and metal burns;
- the ability to create internal seams in small diameter pipes.
But the technique also has some disadvantages. These are increased demands on the professionalism of the welder, a fairly large heating area, and low productivity coefficients.
Semi-automatic welding
The technology is similar to arc technology, but here the electrode is supplied automatically. Among the advantages it should be noted:
- ease and safety of the work process;
- efficiency;
- excellent accuracy and good performance;
- evenness of seams;
- ability to connect parts from 2 to 30 mm thick.
Negative points of the semi-automatic method:
- the inability to adjust the joint during the work process, since it cannot be seen;
- if the current is more than 200A, then the molten metal splashes heavily and it is necessary to remove all scale;
- The semi-automatic device can only be used indoors.
As for application, this technique is suitable for creating and installing metal fences, stairs, gates, garages and other structures.
To choose the most suitable method for joining elements for specific purposes, you need to know what types of welding there are, draw an analogy for each of them, and only after careful analysis give preference to a specific technology.
Arc methods
Above we dealt with the basic concepts and physics of the arc (the famous RDS - manual arc, the absolute champion in popularity).
But the classification of welding methods is a strict matter, so we present the types of arc welding as a separate family:
Structure and properties of the electric arc.
Manual arc:
- RAD – manual argon-arc non-consumable electrode;
- RADN – manual argon arc surfacing.
Automatic arc methods:
- AAD, AADN, ALSN, APPGN, etc. - an extensive family of methods using either electrodes (consumable and non-consumable), or wires, or flux-cored wires. You can cook with or without gas.
Submerged arc:
- the familiar AF, automatic submerged arc;
- various weldings, surfacing with strip or wire electrodes;
- mechanized arc.
Arc with coated electrodes:
- this is where the right place is for the people's champion of the RDS;
- manual arc surfacing;
Mechanized arc:
- MADP, MPGN, MSOD, etc. – a large “mechanical” family.
Mechanical class
All types mentioned above belong to the first thermal class. The main character in it is thermal energy with melting. The next class is mechanical. The main “mechanical” words in this context are pressure and plastic deformation.
It also has a neat classification of welding:
- Cold welding (forging)
- Friction welding
- Ultrasonic
- Explosion
Sometimes mechanical methods are combined under the name “pressure welding”; there is logic here, but we are talking about the same thing.
One of the promising mechanical technologies is friction welding. Heat is also present in it, but it is formed from the force of friction. The surfaces to be welded rotate and are compressed with force. Friction welding technology is especially effective when working with round parts - drills, cutters, reamers.
Table of welding types.
Types of friction welding:
- Friction stir welding.
- Radial friction welding.
- Friction pin welding.
- Linear.
- Inertial.
Let's take a closer look at these types of welding:
- Friction stir welding is a fairly new method, it requires special equipment for friction welding - a rotating tool with two elements - a base (shoulder) and a tip (pin). The seam is formed by two processes of extrusion and mixing.
- Radial friction welding is used in pipe work: it rotates a ring between the joints, which creates friction.
- Friction pin welding: a hole is drilled and a pin made of the same metal as the parts is inserted. The pin rotates, generates heat, and forms a connection in the form of metal threads. Excellent friction welding technology when “you need to fill a hole.”
- Linear method. There is no rotation here. The parts simply rub against each other until heat is released, plasticity increases, then the pressure is increased until an irreversible connection is achieved. With this method, an ideal, flat surface is formed; no other methods have this.
- Inertia welding. The movement of the surfaces occurs due to a massive rotating flywheel, which is accelerated by a special engine.
The mechanical class involves the use of pressure and mechanical action, energy.
Friction welding (friction)
This method differs from the others - the basis of its method is to obtain elevated temperatures by friction of metal workpieces. One of the parts rotates, then the workpieces are pressed against each other with a gradual increase in pressure.
Friction welding
Cold welding
Cold welding is performed using plastic deformation, which destroys the oxide film on surfaces and brings metal elements together until a bond is formed between them without the use of elevated temperatures. This method is applicable to those metals that have good plastic properties: aluminum, silver, idle, zinc, nickel, etc.
Explosion welding
This method is not very common due to the lack of accuracy of the technological process. The moving part is positioned at an angle to the main part, parallel, and with the help of a controlled part the parts are connected by joint plastic deformation.
Ultrasonic welding
The connection and fastening of parts occurs due to their squeezing together and the influence of ultrasonic vibrations. This method is applicable for spot and contour welding. Ultrasound heats the products and activates diffusion, then molecular bonds are formed and at the end the seam crystallizes, thus creating a strong connection.
Thermomechanical class
Third class from the point of view of physics: both types of influence on the surface are used here: heat and pressure. We present the types and methods of thermomechanical welding:
- Diffusion. The surfaces are compressed, then heated in a high vacuum, achieving mutual diffusion of atoms. It is effective when the metals to be welded do not fit well with each other or the materials are different in nature, for example, metal and ceramics. The method is not cheap, it is used mainly in the aerospace sector and other high-tech industries.
Types of pressure welding.
All the following points are types of resistance welding
- Contact electric. Everything is simple here: before pressing, you need to warm it up thoroughly. The surfaces are heated with current at the joints, then compressed or upset. An excellent, high-performance method that lends itself well to automation. Widely used in construction and mechanical engineering.
- Seam contact welding is a type of resistance welding: the seam is formed by overlapping electrodes.
- Point contact. Surfaces are placed between the two electrodes. The current is turned on after tight compression, resulting in a weld spot with a diameter equal to the diameter of the electrode surface. An extremely interesting variety is relief welding. The contact of the electrodes is carried out along protrusions determined in advance - reliefs, which are eventually deformed, the surface is leveled.
- Spot capacitor welding - “welding with stored energy in capacitors.” It features low power consumption and is used when working with small parts and when using optical instruments - watch mechanisms, aircraft instruments, etc.
The thermomechanical class is characterized by a combination of the use of elevated temperatures and mechanical products.
Forge welding
Forging welding and hand forging are some of the oldest welding methods. The metal is heated to the required temperature and its further connection occurs under the action of a forging hammer or a hydraulic press.
contact welding
Resistance welding uses electric current to join metals. This method involves the formation of an electric arc that melts the metal. Adjusting the current power allows you to process thicker metals.
Spot welding
The most common type is resistance spot welding, since this method can also be used at home. The parts are clamped in electrodes or special pliers, then a current is passed between the electrodes, the metal heats up, the electrodes are compressed more strongly and “forging” occurs, the metal crystallizes under pressure.
Relief welding
Metal workpieces have specially prepared convexities - reliefs, and the welding surfaces contact only in the zones of these reliefs, plastic deformation of these same reliefs occurs; in all other respects, the principle of the method is the same - current is passed through the parts under the compression force of the metals.
Diffusion welding
The basis of the method is the physical process of diffusion. As is known, metals pressed tightly against each other can merge at the molecular level.
Welding occurs in a protective environment - vacuum or special protective gases. The parts are treated to remove roughness, washed with acetone to degrease, then the metals are heated and compressed.
Welding with high frequency currents
When heated by high-frequency currents, the metal is placed in a magnetic field, during this process an electromotive force is induced in the metal, which causes a current in it, a surface effect (the current is distributed unevenly, it is greater at the surface, due to this the metal heats up faster) and the proximity effect (energy is more intensely concentrated near the surface due to the spread of the influence of its own alternating magnetic field and the field of other sources).
Advantages and disadvantages of metal welding as a joining method
In the age of technological progress, it is impossible to do without welding technologies not only in production, but also in everyday life. Every adult at least once in his life has had the need to reliably connect metal elements - change water pipes, repair a heating system, install metal gates, repair a car. Today, welding is a widely popular technology.
The welding method of connecting metal elements has many advantages:
- Metal saving.
Various types of metal welding ensure full use of the working sections of elements in connecting nodes. The structures are given the most optimal shape, designed for the required load. Welding technologies make it possible to significantly reduce the weight of connecting elements in welded assemblies, use thin-walled metal structures, eliminate waste of materials on gates and profits, reduce allowances for machining when replacing castings, and minimize even minor defects and rejects.If in riveted structures the rivets and gussets make up more than 4% of the total weight, then in welded metal structures the weight of the seams does not exceed 1-2%. Using various types of metal welding, you can save materials - in comparison with riveting by 25%, when replacing steel casting by 25-30%, when replacing cast iron - by 50-60%.
VT-metall offers services:
Various types of modern welding technologies are widely used in construction. They facilitate and speed up the process of assembling metal structures, increase the rigidity and strength of structures, and reduce the weight of steel elements by 15%. Connecting parts by welding instead of riveting allows you to save metal - when building blast furnaces by 12-15%, when constructing roof trusses - by 10-20%, when creating crane structures - by 15-20%.
- Reducing the labor intensity of work, reducing the production time of structures, reducing their cost.
All these advantages are made possible due to the economical consumption of metal materials. At metallurgical plants, when constructing large blast furnaces, the production of a steel casing is carried out using the electroslag method in 15 days. If the welding work was carried out manually, it would take more than 30 days, and the riveting process would take 7 to 9 months.Among the various types of metal welding, simple and inexpensive technologies with accessible technical equipment can be distinguished. This allows you to carry out welding work not only in construction and industrial production, but also in small enterprises, during individual work.
- Ability to assemble complex structures
. It is not always possible to make a product using forging or casting. In this case, the welding method will help. It is easier to assemble a stamped or welded metal structure from separately manufactured stamped or cast elements. This method of permanent connection is widely used in mechanical engineering, in the construction of ships, airplanes, and railway cars.Significant savings in material resources expand the scope of welding technologies. Using some types of welding, it is possible to connect elements that differ in the method of metalworking or in cases where rolled profiles, stamped, cast and forged parts are used to manufacture the structure. The welding method is well suited for the manufacture of complex structures from dissimilar metals and alloys, such as copper and steel.
It is difficult to dispute the economic benefits obtained when producing complex structures using new types of metal welding that have replaced traditional forging and casting. When producing similar forged and stamped parts, the service life will double. A ton of complex welded structures will cost the manufacturer 1.5–2 times less, and their cost due to weight reduction and material consumption is 1.3–1.6 times less than in foundry production. At the same time, such important characteristics as durability and wear resistance remain unchanged.
- Reducing the cost of technological equipment.
Equipment for welding work is relatively affordable, does not cause difficulties in operation, and is characterized by high productivity and reliability. This, in turn, has a positive effect on the work of metalworking enterprises and their production costs. - Integrated mechanization of mass production, continuous production of products.
The production of welded products of one type can be put on stream, while mechanization and automation of the technological cycle is ensured by 100%. As a rule, labor productivity and business profitability increase. - Widespread use of modern materials in welded structures
. The main types of metal welding used in industry make it possible to produce products from ultra-pure metals, high-strength steels, light alloys, lightweight bent sections, and multi-layer rolled sheets. - Manufacturing of small units and parts
. Semiconductor manufacturing requires micro parts. Modern welding technologies make it possible to produce reliable, highly functional elements for such devices. - Possibility of wide application of welding technologies.
Metalworking is a necessary component of most repair work. Modern types of welding fastening allow you to quickly, efficiently and economically perform surfacing, cutting, restore worn-out structures, and strengthen the structure. - Tightness, wear resistance and reliability of welded joints
. - Optimization of working conditions.
Modern welding technologies make it possible to ensure high production safety and low production noise levels.
Disadvantages of the main types of metal welding:
- Air pollution, high concentration of gases (products of melting electrodes) in the room during interior work.
- Possibility of cracks forming in the deposited weld. Due to the uneven distribution of harmful impurities in the ingot and rolled products, when welding low-carbon steel using a boiling melt, the seams sometimes crack.
- Shrinkage of welds can cause deformation of the metal and change the shape of the finished structure.
- If the joined elements are heated unevenly, residual welding stress is formed.
- Lack of a simple and reliable method for checking the quality of seams.
We recommend articles on metalworking
- Steel grades: classification and interpretation
- Aluminum grades and areas of their application
- Defects in metal products: causes and search methods
To minimize the negative impact of the welding process and ensure high quality work, a number of effective measures have been developed:
- production workshops are equipped with supply and exhaust ventilation;
- special-purpose structures are made of low-carbon steel of calm melting;
- when applying sutures, all rules are followed, technological operations are carried out in strict sequence;
- welding work is performed using rigid clamps; if this is not possible, each element is given an initial deformation opposite to subsequent changes;
- even before the start of work, a project is developed taking into account all possible deviations of the structure from the original form;
- the cross-sectional dimensions of the seams are strictly observed, deviations from the calculations are not allowed;
- special assembly devices are used.
The latest technologies provide high quality permanent connections. Automatic welding allows you to carry out the most critical work and is widely used in the construction of road and railway bridges and complex engineering structures.
Thermal class of welding
Using thermal energy, the surfaces of workpieces and parts are melted locally. Heat is obtained using various methods; they are discussed in detail below.
Arc welding
This type is the most popular. The welding arc uses direct, alternating or pulsating current. The arc is produced by a powerful discharge. The electrode comes into contact with the metal, a short circuit is produced, and the tool is withdrawn no more than 5 mm, due to this continuous action the metal is heated. The stability of the arc charge occurs due to the acceleration of the electrodes in the electromagnetic field, then ionization of the gas connection between the anode and the cathode occurs.
Gas welding
Gas welding is a type of fusion welding with the additional use of gases - oxygen, acetylene. The heat generated during the combustion of gases melts the surfaces along with the filler material, thereby forming a weld pool. The gas supply is regulated using a reducer on the cylinder.
Arc welding
The operating principle of electric arc welding is based on the melting of metals under the influence of an electric arc. An electric arc is formed by increasing the voltage between two electrodes, resulting in an electrical breakdown. The basis of the technological method of electric arc welding is a short circuit, or, more precisely, the saturation of the interatomic space with electrically charged particles. At the moment of contact between the electrode and the product, a current flows, the resulting electric arc, the temperature of which reaches 7000 ° C, melts the metal and forms a weld pool.
Manual arc welding
Devices for manual arc welding are widely used in everyday life due to the relative inexpensiveness of the devices. Also, this method does not require gas or flux, since their functions are performed by the electrode. The principle of arc welding is preserved: melting of surfaces occurs due to the contact of the electrode with the metal product, which forms a short circuit and the arc is ignited.
Non-consumable electrode welding (TIG)
This is a gas welding technology, its essence is as follows: an electric arc is ignited in an inert gas atmosphere between the electrode and the material, thus melting the metal and filler material. The electrode is made of refractory metals - tungsten, zirconium, hafnium. This technology requires highly qualified specialists.
Gas shielded welding
This type of welding can be performed with either a consumable electrode or a non-consumable one. For non-consumable electrodes, an additive is needed, and the consumable electrode itself participates in the process of creating a seam. Inert gases are used to ensure stable arc operation. The choice of gas determines the composition of the product being welded. Gas is supplied either centrally or from the side at higher capacities.
Submerged arc welding
The use of flux is necessary to maintain even burning of the arc and, when forming a weld, affects its chemical composition. Different flux compositions have different stabilizing properties. By varying the content of carbon, sulfur, manganese and others, strength and resistance to cold can be adjusted.
Hyperbaric welding
Hyperbaric welding is welding under conditions of high pressure, for example, in water or a specially created dry environment. Underwater welding uses a waterproof electrode that melts and hits the metal with a gas bubble. Underwater welding is one of the most difficult types of work, which, among other things, has an increased risk of electric shock.
How to ignite an electrode
There are two ways. Option one: ignite the electrode - end-to-end (by touching). Option two: strike. The methods are clear from the photo below.
The second method is similar to lighting a match on a matchbox. The first method is sometimes replaced by lightly tapping the workpiece. When the electrode is new and the metal of the rod is visible at the tip, ignition of the arc occurs easily.
If the electrode has been in use, a coating may appear around the rod. The protective coating of the electrode does not conduct electric current. Therefore, it needs to be knocked off by tapping the tip of the electrode on the part to be welded several times. Easy ignition of the electrode is a skill that has been brought to automaticity.
And for dessert
Special types of welding are a vague concept, given the huge number of technical options, groups, types, subtypes. Everyone sees this list differently.
In our list, the classification of welding is determined by manufacturability. These are unique methods that rightfully belong to aerobatics technologies.
Electron beam and plasma welding:
- Electron beam welding. Here an electron gun and a beam of accelerated electrons from this gun are used. The work is carried out in large vacuum chambers. The energy concentration and heat output are fantastic. The seams are narrow and deep. It is used for the production of high-precision parts from special alloys - not a cheap pleasure.
- Plasma welding. One of the most high-tech types - the name speaks for itself. Plasma is a stream of ionized gas (argon, helium, hydrogen) of the highest temperature. This jet cooks everything - from the most refractory metals to non-metallic surfaces. Outstanding performance with fantastic seam and surface quality.
Let's generalize and loop
Welding is the process of forming inseparable joints between surfaces of different structures.
First, all types and methods of welding are divided into three powerful classes from the point of view of physics:
- Thermal (heat and melt)
- Mechanical (three, push, push, etc.)
- Thermomechanical (heat and press at the same time)
Tig welding of aluminum.
Within these classes, methods can be grouped as desired:
- with or without arc;
- with or without gas, possible with arc and gas together;
- manual or automatic. Or semi-automatic;
- what types of welding electrodes do you use;
- all types of resistance welding;
- types of welding of metal or, conversely, polymers;
- and so on, the list of options is long.
The main thing is to find out, try, learn and move forward to professional heights. Don't forget to read the reviews, you need to stay informed. We cannot stand still. We wish you pure metal, good orders and a working mood.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ocJFw1HwOpw