Feature of ZV Pu-Zinc system:
1. Application up to 98% humidity.
2. Drying time for ZV zinc paints to “touch” is 30 minutes.
3. Instant resistance to fresh and sea water.
4. Long service life of the zinc anti-corrosion “working” film.
5. Can be applied to an unprepared surface.
6. Extreme adhesive performance of ZV zinc paint.
7. Provides cathodic protection of the metal.
8. Our zinc paints are oil and grease resistant.
9. It is recommended to apply ZV zinc compounds at temperatures from -5°C to +50°C.
10. ZV is compatible with other polyurethane and epoxy compounds.
Purpose
Zinc-containing paint is most often used for painting ferrous metals that are used in difficult weather conditions. These compositions cover:
- building structures;
- bridge structures;
- ships;
- metal tanks;
- metal pipes;
- gas pipelines;
- agricultural machinery;
- metal pillars;
- tunnels;
- port facilities.
It is not prohibited to use paint with zinc in everyday life. It can be used to paint water pipes or heating radiators. If the paint functions as a primer, it is applied in 1-2 layers, and if as a coating - in 2-3.
Areas of application
The cold galvanizing method is used for painting:
- metal objects used outdoors;
- metal bridges, hydraulic structures, power line supports, road fences;
- radiators, batteries;
- pipes, rolled metal, containers, tanks;
- vehicle bodies, ship hulls;
- building metal structures;
- gates, fences, doors, metal elements;
- to restore a previously galvanized surface;
- water, gas pipes and heating mains.
Types of body galvanization
Specialists use several technological options for galvanizing of varying complexity of processing, cost and durability:
- Hot (thermal). The operation is not available for garage repairs. The entire car body or only a certain part is lowered into a tank with a zinc alloy; during rental, a protective layer is applied on top. The most effective method of protection.
- Cold galvanized. A budget and easy to implement option, but the least effective. It takes place in two stages: applying a chemical layer; coating with a composition that contains tiny particles of zinc.
- Galvanic. The most common option. You can carry out the process yourself. A car part is lowered into a container with a special composition containing zinc. Under the influence of an electric discharge, the protective layer is fixed. An example is galvanized body washers.
- Zinc metal. The sheet metal is treated with a coat of zinc-based epoxy paint with a secondary coating of rust inhibitor. The main advantage of this option is that the anti-corrosion properties are not lost during mechanical processing.
Types of body galvanization depend on the degree of processing of the machine:
- full – the whole machine is galvanized;
- partial - only some parts were galvanized.
How to choose a composition?
Before deciding to purchase a specific composition for cold galvanizing, it is necessary to study its content and product quality. There is practically no possibility to choose by color; it is mostly a gray-matte shade. The material consumption does not differ much from the type of paint and the type of its application; on average, it amounts to 300 grams per square meter.
To choose a high-quality composition for galvanizing, you need to pay attention to the following:
- product cost;
- shelf life of the product;
- time for complete drying of 1 layer;
- amount of zinc in the composition;
- conditions under which the surface is processed;
- service life of the protective coating.
Cold galvanizing is a popular method among specialists for protecting metal products, which can be done at home with your own hands. With proper surface preparation, high-quality finishing materials and following the advice of the experts, metal galvanization will take place without problems.
Cold galvanizing technology with Galvanol composition (1 video)
Zinc-based paint of different brands (20 photos)
Cold galvanizing method
It is not difficult to paint with paint containing zinc on your own, the main thing is to adhere to consistency in the process. Painting is no different from painting with conventional paints and consists of the following steps:
1. It is necessary to clean the surface of old finish, rust and other dirt. You can use regular sandpaper or a wire brush to complete this task. The coating must be clean after cleaning.
2. Prepare the coloring composition by stirring it thoroughly until a homogeneous structure is formed. If you need to thin the paint, you need to use a solvent, the type of which is indicated on its packaging.
3. The material is applied in a thin layer using a painting tool (brush, roller, spray gun). There is also paint on sale in aerosol form, which is applied evenly without forming smudges or streaks.
4. Re-application of the coloring composition is carried out after the previous layer has completely dried.
5. The final finishing process can be coating with decorative paint.
As a result of painting, the surface becomes 95% covered with zinc.
On video: preparing metal for galvanizing.
How much does the procedure cost?
According to the latest data, complete hot galvanization in a service center costs from 25,000 rubles. The difficulty is that only 5% of service stations carry out complex galvanizing with complete removal of the body, cleaning, priming and subsequent application of paintwork.
Partial galvanizing of small parts or body parts will cost from 5,000 rubles. The cost of the kit for use in the garage and independent work is 800 rubles. and more.
Do-it-yourself galvanizing of metal protects your car from corrosion by 98%. When self-galvanizing component parts, this is the only reliable and longest-lasting method of protecting the part, which can be used at any time. It is enough to carry out a full inspection twice a year and update the partial cold galvanization of the body and galvanization for removable parts.
If noticeable pockets of corrosion have formed on the body of your truck or car, but they are still not through, you need to take immediate action. As practice shows, if you do not stop body corrosion in time, the cost of subsequent repairs to your car will be many times higher. For this reason, you can’t hesitate!
In recent years, many motorists have noticed: even in large densely populated cities, road services mercilessly use salt. As a result, the bodies rot to holes in literally two to three years. To resist the rusting process and the aggressive effects of road reagents, there is a very simple but effective way - do-it-yourself galvanizing of the body.
Galvanizing a car is carried out in order to protect the body once and for all from the formation of annoying “saffron caps”, as well as to prevent the further spread of corrosion throughout the body.
The zinc “crust” on the surface of the metal creates a kind of barrier that protects the steel from negative factors and the destructive effects of an aggressive environment. The zinc-based coating effectively resists the effects of salts, chemicals and moisture.
Please note that you can galvanize both a part of the car body (fender, trunk, hood, etc.) and any individual part. And this will require direct hands, certain knowledge, a specific set of materials and tools, as well as the desire to give your car additional strength.
The “home” method of galvanizing metal allows you to prevent the formation of corrosion on the car body and thereby reduce service costs. Liquid galvanizing can also be used for various metal products to further protect them from rust.
It must be said right away that this method is very simple and does not require large financial costs. In fact, this is the well-known Zinkor car, but with your own hands. This miracle remedy will be written in detail below, as the article progresses.
Preparatory work
This method involves the use of phosphoric acid with zinc dissolved in it, and will also require zinc (salt) batteries. You can use both small finger batteries and large batteries - in this case it all depends on the amount of work being done.
If you need to galvanize a large surface area on your car, then it is better to take large zinc batteries. First, you need to “print” them all and remove all the excess braiding.
If you wish, you can also use only the casing of a salt battery, after removing the graphite core and soot, but in principle you can leave all the “internals” in place.
On the body of the “bare” galvanized battery, on one side you need to secure a cotton pad with an elastic band, and on the other side (also using a regular rubber band) - the power wire. You can use a car battery or a suitable power supply as a power source.
How does galvanizing of a surface occur?
If you don't know how to galvanize correctly, read the short instructions first.
The “minus” from the car battery must be connected directly to the part of the body (or part) that you are going to galvanize with the battery - that is, using the battery.
We connect the wire that goes to the zinc body of the battery to the positive terminal of the battery. Please note that the negative terminal should never be disconnected, because the desired effect will not be obtained.
Before starting galvanizing, it is advisable to clean the surface to be treated from traces of rust, if any. You need to take orthophosphoric acid with zinc dissolved in it into a syringe and soak a cotton pad that is placed on the body of the salt battery. After this, you just need to move the “nozzle” over the entire area of the surface being treated.
The most important thing is not to stop. If you keep the battery in one place for a long time, then burns appear, and if you move continuously over the surface, you get a neat and even layer of zinc. You will see the result almost from the first seconds.
Although some people call this method of galvanizing a car “artisanal,” it is truly a proven, simplest and, most importantly, effective way to combat corrosion. And, as an option, you can use a ready-made camping kit - a car kit for galvanizing Zinkor auto.
Using this product, you can quickly localize particularly advanced areas of rust, as well as remove all traces of corrosion on the car body. Galvanic galvanization allows you to reliably protect the metal surface from the reappearance of “saffron caps”.
Method of galvanizing metal using “white powder”
Typically, for galvanizing small areas of metal surfaces, phosphoric acid and a galvanized battery casing are most often used. However, for better processing, it is better to use soldering acid instead of phosphoric acid. It is hydrochloric acid in which zinc is dissolved. It is believed that the galvanization of the body in this case will be deeper and more durable.
You can purchase soldering acid at almost any radio electronics store. But it’s not entirely convenient that soldering acid for soldering at home is sold only in small bottles.
Therefore, if you need large volumes of soldering acid for galvanizing, it can be made at home from “white powder” - zinc chloride, which is sold by weight.
Main stages of work
Pour zinc chloride into a suitable container, then add distilled water and mix until a clear liquid consistency is formed (note that you need to wear rubber gloves when working with chemicals). From 1 kg of zinc chloride, approximately 3.5 liters of finished soldering acid are obtained.
The result is a galvanic bath, in which, if necessary, pieces of sheet steel and entire metal parts can be galvanized.
For further work, you will need a galvanized battery case and an iron bolt, at the ends of which cotton fabric must be secured with rubber bands.
The part that needs to be galvanized must first be thoroughly cleaned of rust with a grinder, using a cleaning disc with a metal brush. Before galvanizing, the metal must be “activated” - the oxide film must be removed from the surface using electricity.
Types of zinc paint
Protective agents against metal corrosion containing zinc are presented on the market in two versions, which differ in the binding components:
- with organic binders;
- with inorganic binders.
Zinc coatings with binders of organic origin are:
- epoxy;
- alkyd;
- urethane;
- chlorinated rubber.
Compositions with inorganic substances are presented in the form of silicate materials that contain zinc.
Varieties
Zinc-containing coatings, in addition to zinc, contain resins: organic (epoxy, alkyd, chlorinated rubber, urethane) or inorganic (silicate). Paints and varnishes for cold galvanizing can be one-component or two-component. Compositions consisting of two semi-finished products are combined with each other and mixed before use.
Epoxy
Epoxy resin-based coatings are considered the most durable. Zinc-containing compounds containing at least 85 percent zinc powder are used to protect objects in the oil, gas, energy industries, and waterfowl from corrosion.
form an anti-corrosion coating of increased strength;
have a long service life.
toxic composition;
high consumption.
Alkyd
The most common coatings containing zinc. Available in the form of a spray or liquid paint in cans. Used to protect metal elements and structures from rust.
the coating is resistant to adverse weather conditions and moisture;
Coatings with zinc can be applied over a painted base.
toxic composition;
relatively high consumption;
Urethane
Zinc-rich urethane or polyurethane coatings are used to protect metal objects from rust. May contain up to 96 percent zinc. Suitable for cold galvanizing.
creates a durable anti-corrosion film;
has a long service life.
toxic composition;
high consumption.
Chlorinated rubber
This is a zinc-containing primer based on chlorinated rubber. Creates a coating that is resistant to moisture, acids, and petroleum products.
forms a durable anti-corrosion film;
protects metal objects from adverse weather conditions.
the coating is not resistant to organic solvents;
the paintwork itself has a toxic composition.
Silicate
Typically these are two-component heat-resistant compounds. They are used to protect metal objects that heat up during operation from rust.
durable anti-corrosion film;
durability of operation regardless of the thickness of the coating;
toxic composition;
surface preparation for painting is necessary.
Comparison of Tsinkoshov coating with other coatings
- home
- More about Tsinkoshov
- Comparison with other coatings
Tsinkoshov
is the first and unique composition for protecting welds, which has no analogues on the market. However, according to its characteristics, it is a powerful protection against metal corrosion, competing with other methods of protection. We will compare the qualities of Zinkoshov with other anti-corrosion coatings, as well as with the traditional hot-dip galvanizing method.
What are the methods of corrosion protection?
- Paints with anti-corrosion additives
based on alkyd, acrylic, epoxy or polyurethane create a coating that lasts 3-5 years. However, they are not able to provide complete protection against corrosion. Under the film of paint, corrosion can develop with might and main, destroying the metal. Even when the appearance of the coating remains unchanged. - Zinc-containing paints
fight corrosion more effectively due to the zinc in the composition, which corrodes more slowly than all metals. But simply containing zinc powder in paint is not capable of providing reliable protection against corrosion for 25-50 years. Only cold galvanizing compounds can do this.
In the photo: Salt fog chamber (test of protection duration). Test - 1200 hours 3% NaCl. On the left is zinc-containing paint, on the right is a composition for cold galvanizing (96% zinc).
Tsinkoshov is not only a special composition for protecting welds, but also a complete composition for cold galvanizing. Cold galvanizing can also be classified as coating materials. However, compared to other paints and enamels, they provide different levels of protection and provide coatings with different service life.
Conventional metal paints can last about 2 years without touch-ups, and cold galvanizing with Tsinkoshov can last up to 50 years.
The principle of operation of anti-corrosion paints
Oil- and alkyd-based paints create a weak barrier between metals and the environment, cannot withstand temperatures above 70-80 °C, quickly fade, peel, crack, and offer almost no protection against rust. Enamels based on acrylic, epoxy resin and water-based paints provide visual appeal and last 2-3 years without cracking under favorable operating conditions. They also do not withstand temperature changes, chemicals and mechanical damage. They protect against corrosion until the first crack in the coating, then environmental influences get under the film and the corrosion process starts.
The above types of enamels protect metals from above, and corrosion can develop under the paint film. Since the appearance remains attractive, you will not immediately notice the formation of rust and will not be able to quickly take the necessary measures to eliminate it.
How do zinc and aluminum paints work?
There are two types of zinc paints. These are zinc-containing paints, which contain from 10 to 85% zinc in the composition and zinc-rich compositions, where zinc is the main component and is contained in an amount of 95% or more. Only such compositions create a galvanizing effect that can protect metals for several decades. Tsinkoshov is just such a composition for cold galvanizing.
Zinc-containing paints can protect metals from corrosion for a period of 10 years. This opportunity is given to them by zinc, which, according to studies, corrodes 3 times slower than other metals. That is, 1 zinc layer on top of another metal will slow down corrosion as much as possible for about 10 years, depending on operating conditions.
The zinc-rich composition of Tsinkoshov is characterized by a high zinc content of 96%. In addition, the zinc in the dry coating film is 98-99.99% pure. In addition, the composition contains a special polymer binder and neutral resins, which allow zinc to freely move electrons and actively act in the fight against corrosion. Only such anti-corrosion paints can protect metals from corrosion in the same way as with the “hot” galvanizing method. That's why they are called cold galvanizing.
Aluminum is also a slowly corroding metal that is used to protect metals from corrosion. In addition to protection, it gives metals an attractive silver color and shine. The Alyumoshov coating contains aluminum powder and protects metals from corrosion for up to 10 years. However, without primer, such a coating will last only 2-3 years. It is recommended to use Alyumoshov as a topcoat for Tsinkoshov. Then the protection period will increase by an additional 10 years to the declared service life of Tsinkoshov. The aluminum coating will additionally protect the metal from corrosion, and will also protect the zinc coating from environmental influences: moisture, air, sea and fresh water, chemicals, oil products and other things.
How does Tsinkoshov protect from 10 to 50 years?
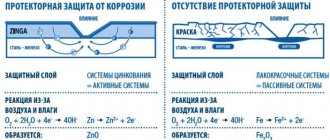
This is achieved through tread protection. Enamels without zinc do not have such protection and are protected only by the barrier method. Tsinkoshov, in contrast, protects in two ways at once: barrier and protector. The tread method is also called active or cathodic.
Sacrificial protection means that zinc protects the metal it coats and donates its electrons to it to fight corrosion. Zinc acts actively, even if the integrity of the coating has been damaged, in case of scratches and mechanical damage to the layer. Corrosion does not reach the metal surface until the entire zinc layer is depleted. Therefore, such protection is called active.
Comparison of Tsinkoshov and conventional paint
| Indicators | Tsinkoshov (cold galvanizing) | Regular metal paint (alkyd) |
| Drying time | 20 minutes | 24 hours |
| Life time | From 10 years (1 layer) | Maximum 2-3 years |
| Corrosion protection | Completely prevents corrosion for the stated period | Slows down corrosion, hides hot spots under film |
| Base for painting | No soil needed | Need soil |
| Color | Gray matte | According to the RAL catalog |
| Number of layers | 1 layer is enough | 2-3 layers |
How long does Zinkoshov coating protect?
Calculation of the cost of covering Tsinkoshov
Comparison of Zinkoshov and hot-dip galvanizing
We have already seen that LKM is inferior compared to Tsinkoshov in many respects. However, this composition also has advantages compared to the traditional, popular method of protecting metals from corrosion - hot galvanizing. If we compare the two methods, we get the following data:
| Cold galvanizing (Tsinkoshov) | Hot galvanizing |
| Advantages | |
| — Dries in 20 minutes — Compatible with almost any paintwork — Regular solvent is suitable — Protective properties are higher with equal coating thickness — Corrosion cannot form under the coating — Protects seams after welding — Welding after application is allowed — Structures do not need to be transported — no transportation costs — Adhesion – 1 point – Does not rust in areas of damage – Easy to restore damaged areas – Can be applied locally, to small areas, seams and joints | — Small products are dipped easily and quickly — 100% penetration into hard-to-reach places — The price is calculated based on the weight of the structure — The quality of the coating does not depend on who is applying it — Forms a continuous coating, without joints or boundaries — Gives metals visual appeal — Everything will be done for you specialists - less of your time and effort |
| Flaws | |
| — Strict adherence to the technological process — It is difficult to coat internal cavities and hard-to-reach places — Careful surface preparation is required | — Dipping baths are limited in size - not suitable for very large structures — Does not work with some grades of metals — Deformation of thin structures when heated — Welding parts after hot-dip galvanizing destroys the protection — Damaged coating cannot be repaired, only galvanize the entire structure again — For dipping and hanging to the structure, special “ears” are welded, from which traces then remain - When assembling the structure after galvanizing, the joints and assembly points must be additionally protected from corrosion - It is necessary to bring the structures to the place of galvanizing and back - additional transportation costs - During transportation, areas destroyed which then need additional protection - After galvanizing, unsightly streaks of “liquid” zinc may remain |
Based on the above, we can see that traditional and proven methods of galvanizing, such as hot galvanizing, although they have been used for decades, still have a lot of disadvantages compared to modern methods.
Cold galvanizing using the Zinkoshov composition is conveniently and quickly applied to small areas, seams and joints anywhere in the structure, for example, right at the site of its operation. You don’t need to transport anything anywhere and can be used for structures and seams of any size and complexity.
For clarity, we present you with a comparative table of different methods of corrosion protection and their advantages.
Pros and cons of galvanizing methods (in comparison with Tsinkoshov)
| Characteristics | Cold galvanizing (Tsinkoshov) | Hot galvanizing | Dye |
| Active cathodic protection | + | + | — |
| Easy on-site application | + | — | + |
| Repeated application | + | + | — |
| Finish coating possible | + | +/- | + |
| Application under extreme conditions (high humidity and low temperature) | + | — | — |
| Unlimited shelf life | + | — | — |
| Contact with drinking water | + | + | — |
| Temperature and mechanical stability | + | — | — |
| Welding on coating | + | +/- | — |
| Coating restoration | + | — | — |
| Application at negative temperatures (-35) | + | — | — |
CONTACT US RIGHT NOW AND GET 5% DISCOUNT ON YOUR FIRST PURCHASE
Telephone:
Email:
[email protected]