Welding in a neutral gas environment is a reliable and durable connection of workpieces into one whole. The cost of carbon dioxide in relation to argon and helium is much lower and this improves the ratio of price and quality of work. You need to know how to properly weld using a semi-automatic machine with carbon dioxide, while achieving good seam quality. You can cook using mixtures of gases when increased quality is needed, or you can learn to weld in a carbon dioxide environment using a semi-automatic machine and an adjustable feed of welding wire. We will tell you in detail about this process, which allows you to save considerable money and achieve the desired result.
Specifics of technology
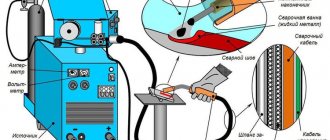
Welding in a carbon dioxide atmosphere is a type of electric arc .
The constant discharge of the electric arc releases a large amount of thermal energy, which heats and melts the metal of the workpiece. The current flows through the workpiece, the air gap and the infusible tungsten electrode. The welding material in the form of wire is fed into the working area separately; it does not serve as a conductor. Feeding is carried out at a constant speed by a feed mechanism built into the semi-automatic welding machine.
In order to protect the weld pool from the effects of oxygen and hydrogen in the air, as well as water vapor, a protective atmosphere consisting of carbon dioxide is supplied to the working area. Its cloud displaces air and prevents unwanted chemical reactions
Welding with coated electrodes
This is the most common technology for welding stainless steel at home. The method allows you to obtain good quality welding with minimal practical experience. The advantage of this method is its simplicity. The downside is that it does not allow you to obtain high-quality welds.
To use this method at home, you need a special device called a welding inverter. Special electrodes are also needed.
Coated metal electrodes are the following brands: OZL-8, TsL-11, NIAT-1. These electrodes make it possible to obtain a weld with high heat resistance, corrosion resistance and high strength.
Welding work is carried out with direct current of reverse polarity. It is necessary to achieve less weld penetration. This can be done using small diameter electrodes . The current strength is approximately 15−30% less than for conventional steel.
These electrodes are characterized by high electrical resistance and low thermal conductivity. Taken together, this can lead to overheating and rapid melting of the electrode during operation.
Read also: Three-phase welding machine diagram
At the very beginning, the parts to be welded are heated at the site of the future seam to a temperature of 100 degrees. This is done in order to remove residual moisture from the welding zone. Under no circumstances should the workpiece be overheated above 150 degrees. The work itself is performed at high speed, without transverse oscillatory movements, with a short arc, using low currents. As a heat sink, in order to prevent overheating, copper plates are placed under the workpieces.
After the process is completed, the seam is cleaned of slag using a metal brush. Then it is treated with a special etching paste for 30 minutes. This is done to restore the anti-corrosion properties of the metal at the site of penetration. Subsequently, the remaining paste is washed off with water.
You need to keep in mind that thick-walled stainless steel is much easier to work with than thin-walled stainless steel.
What is carbon dioxide?
The CO2 carbon dioxide molecule consists of a carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. Under normal conditions, carbon monoxide is a gaseous substance, heavier than air, colorless and odorless.
Carbon monoxide has low chemical reactivity, making it an excellent candidate for creating a protective atmosphere around the welding zone . The same property is used when operating carbon dioxide fire extinguishers, which stop the access of air oxygen to the source of fire.
At atmospheric pressure it cannot exist in a liquid state. When cooled to -78°C, it hardens, forming a loose mass reminiscent of snow. This is the so-called “dry ice” used for cooling products in the food industry and trade.
The substance is released during the oxidation of organic substances - during combustion, decay, and respiration of living organisms.
Technical conditions for industrial CO2 are regulated by GOST 8050-85.
The substance is transported in a gaseous state, in containers under pressure.
Scope of application
Carbon dioxide is significantly cheaper to produce than argon, helium and others, but is inferior to them in its protective properties. Welding in a CO2 atmosphere is used for ordinary joints made of ordinary structural steels .
For more critical structures, special steels, and highly loaded components, more expensive inert gases are used, which are difficult to store and use.
In the mass production of standard metal structures, the use of carbon dioxide to protect the welding zone makes a noticeable difference in cost.
Organizing CO2 storage is also cheaper.
Types of steel
Conventional welding techniques are used to join non-ferrous metals and stainless steel, provided the appropriate gas is used to reduce corrosion resistance.
Ferritic stainless steel can be welded using TIG or MIG/MAG submerged arc electrodes. In order to avoid hyperplasia of metal grains and the formation of cold cracks, a low current should be used. Argon, helium, or a mixture free of nitrogen dioxide and hydrogen should be used as a shielding gas. Electrodes must be alkaline.
Martensitic stainless steel is difficult to fuse. As a rule, it is welded only when the carbon content is less than 0.15% due to the fact that with increased carbon content it is subject to cracking.
Austenitic steel can be welded by all commonly known and used methods. It is recommended to avoid strong heating to reduce the risk of cracking, grain growth, and intercrystalline corrosion. Argon, argon-helium mixture, or argon-hydrogen mixture is recommended.
Shut-off and control equipment for cylinders
When working with nitrogen oxide, special shut-off and distribution valves are used .
The reducer reduces the input pressure from 100 atm. up to a working value of 3 atm. It is equipped with two pressure gauges: at the outlet and at the inlet, by which the welder monitors the pressure value.
The gearbox is equipped with two filters that retain impurities.
The required operating pressure is set by rotating the regulator handle.
Using union nuts, the device is connected to the cylinder and to the hose supplying the consumer.
In the event of an emergency, the safety valve releases excess pressure into the atmosphere.
All devices associated with carbon dioxide - cylinders, reducers, hoses - are marked in black.
Start of the welding process
Before starting, it is necessary to process the edges of the parts to be welded.
- The joint between the edges of the parts being welded should have a gap of 2-3 mm to ensure free shrinkage of the seams.
- The surfaces of the edges are cleaned to a shine using a special metal brush or grinder.
- Then the surfaces are treated with a solvent, which is acetone or aviation kerosene. The solvent will ensure the removal of fat from the future welding site. Which, in turn, will prevent the further formation of pores in the weld seam.
Refill features
A carbon dioxide cylinder for a semi-automatic machine is charged using two methods:
- bypassing from the storage tank through the reducer and flow meter into the refilled cylinder;
- pumping into a refillable cylinder using a compressor.
Regardless of the filling method, it is important to accurately determine the empty weight of the cylinder . By weighing the cylinder after filling, you can accurately determine the amount of CO2 injected.
Filling cylinders with carbon monoxide, unlike acetylene or oxygen, does not require extraordinary precautions. However, one cannot relax: in the event of a massive leak, carbon dioxide forms an atmosphere unsuitable for breathing. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully check the condition of cylinders, fittings and hoses for mechanical damage.
When refueling using the “cylinder to cylinder” method, it is recommended to turn the cylinder from which you refuel upside down and monitor its temperature.
Technical requirements
Steel pressure vessels with a volume of 0.4–50 l are used almost forever .
Domestic GOST 949-73 applies to containers for transportation of intermediate storage and technological distribution to consumers. Solid-drawn seamless cylinders of small and medium volume made of structural steel 45D and alloyed 40KhGSA are designed for a working pressure of 15 and 20 MPa for vessels of 50–20 l and 15 MPa for smaller ones, which can be produced with a flat bottom.
Distinctive marking is a yellow enamel inscription “carbon dioxide”, “CO2”, “carbon dioxide” on a black field . The main physical parameters and standard sizes are presented in the table:
| Pressure, MPa | 50 l, Steel 45D/30HGSA | 40l Steel 45D/30HGSA | 20 l Steel 45D | ||||||
| Ø, mm | L, mm | M, kg | Ø, mm | L, mm | M, kg | Ø, mm | L, mm | M, kg | |
| 15 | 219 | 1685/1660 | 71,3/62,5 | 219 | 1370/1350 | 58,5/51,5 | 219 | 740 | 32,3 |
| 20 | 1755/1650 | 93,0/62,5 | 1430/1350 | 76,5/51,5 | 770 | 42,0 | |||
Vessels of smaller volumes are made of steel 45D, operating pressure 15 MPa
| Ø, mm | 12 l | 10 l | 8 l | 5 l | 4 l | 2 l | ||||||
| L, mm | M, kg | L, mm | M, kg | L, mm | M, kg | L, mm | M, kg | L, mm | M, kg | Ø, L, mm | M, kg | |
| 140 | 1020 | 17,6 | 865 | 13,0 | 710 | 12,4 | 475 | 8,5 | 400 | 7,3 | 108/330 | 3,7 |
The package includes:
- oxygen shut-off valve with right-hand thread, brass;
- rubber safety rings for the cylindrical part;
- rectangular support shoe for stability;
- safety cap made of steel or molded from non-metals.
Cylinders in use undergo periodic re-certification after 5 years , including technical inspection and testing with excess pressure exceeding the working pressure by 50%. Information with the date of inspection is applied with impact stamps to the cleaned neck, framed by a yellow stripe around the perimeter.
This is a “carbon dioxide cylinder passport” with a complete list of information:
- date of issue, recertification;
- Cylinder number assigned by the manufacturer;
- filling capacity;
- process hydraulic pressure;
- steel grade and physical quantities of weight and dimensions.
Consumption
The carbon dioxide consumption for semi-automatic welding is determined by a combination of a number of factors.
- weather conditions (temperature, wind, humidity);
- quality of welding materials;
- qualification and experience of the welder.
It can vary from 3 to 60 liters per minute.
When calculating the planned consumption, such characteristics as the diameter of the welding wire and the thickness of the workpieces are taken into account. To the calculated value equal to the product of the specific consumption and the length of the seam, a margin of 10% is added for preparatory operations.
From a standard cylinder containing 25 kg of CO2, after reducing the pressure to working pressure, approximately 500-510 liters of gas are formed. At maximum consumption, this amount will be enough for 8 hours of operation of a semi-automatic carbon dioxide welding machine. On average, a bottle lasts for 15-20 hours.
Advantages and disadvantages
Working in a CO2 atmosphere has the following advantages over other types of welding:
- reliable protection of the welded zone from chemically active substances;
- cheapness;
- the ability to cook “by weight”, without the use of backing plates;
- stable arc on thin-walled workpieces;
- rational use of thermal energy of the electric arc.
In addition to its advantages, the method also has a number of disadvantages:
- low suitability for working with high-alloy alloys and non-ferrous metals;
- complexity of multilayer welding;
- danger of suffocation when working in unventilated areas.
The long preparation and startup time of the process makes it unsuitable for small volumes of welding work that need to be completed quickly.
Wire for welding stainless steel
The first thing you need to start with is welding wire. The material must be identical to the metal being welded, so ordinary wire for a semi-automatic machine will not work for us. It can be used, but such a connection will be of poor quality and easily corroded. There are two main types of material for working with an alloy of steel and chromium:
- solid welding wire, stainless;
- flux cored, self-shielding wire.
Wire for welding stainless steel semi-automatically without powder, used in a standard set: wire + gas. To work with such material, you can use ordinary carbon dioxide or a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide. We'll talk about gas next.
The second option is a more expensive material, the main advantage of which is the presence of a protective layer. This means that you do not need to use shielding gas when welding parts. The powder layer creates a barrier that prevents air from entering the welded area. The material is used most often at home on an industrial scale. Due to the high cost of the material, a wire + gas combination is preferred.
Wire sizes range from 0.13 to 6 mm, while for manual or home welding, wire about 1 millimeter thick is used. Thicker wire is intended for industrial work using powerful semi-automatic welding systems.
Safety precautions.
Carbon dioxide has two potentially dangerous exposure factors:
- balloon explosion when heated;
- suffocation when working in a closed, unventilated space when the concentration level exceeds 5%.
Based on these risks, safety requirements for carrying out work with CO2 are formed.
During the transportation:
- all cylinders must be transported in a special pallet, in a vertical position;
- Each cylinder must have rubber safety rings.
During storage and refueling:
- all premises must be equipped with gas analyzing equipment;
- when filling the cylinder, it is necessary to control its temperature;
- it is not allowed to refill the cylinder above the standard value;
- Do not touch pipelines, hoses and fittings without protective gloves.
During operation:
- when working in a confined space, organize constant monitoring of CO2 content in the air;
- provide ventilation or provide the welder with an insulating mask with an air supply;
- work together, and one person should be outside the volume and monitor the condition of the welder.
If safety requirements are met, carbon dioxide does not pose a health threat.
Danger of carbon monoxide CO.
Carbon monoxide is a highly toxic substance . If inhaled, it leads to a general depression of body functions and severe poisoning. Death is also possible. It is allowed to work in a carbon monoxide atmosphere only in self-contained breathing equipment.
Polarity
The polarity when welding semi-automatically in a carbon dioxide environment is reversed, that is, “plus” is connected to the workpiece, and “minus” is connected to the electrode. When working with straight polarity in a CO2 environment, it will be difficult to ensure the stability of the electric arc . An unstable arc with such a connection scheme leads to weld defects.
Welding with stainless wire using a semi-automatic machine
The use of a semi-automatic machine allows you to implement several technological tasks at once: cooling the torch, increasing the feed speed of stainless filler wire, welding in hard-to-reach places. All this together leads to the fact that a semi-automatic welding machine can dramatically improve the quality of the weld and at the same time increase the speed of the process.
Semi-automatic welding of stainless steel is impossible without gas. As a rule, either carbon dioxide or a mixture of carbon dioxide and argon is used as a gas medium. The use of pure carbon dioxide is justified from an economic point of view. This is a very cheap and accessible gas. But it is not entirely justified from the point of view of the quality of the resulting weld. In this case, severe spattering of the metal occurs, which ultimately leads to the formation of a clumsy seam and a decrease in the quality of welding.
Therefore, a mixture of carbon dioxide and argon is often used. As a rule, 98% argon and 2% carbon dioxide are used. Sometimes, in order to reduce the cost of work, a cheaper mixture is used: 70% argon and 30% carbon dioxide.
All semi-automatic machines have two adjustments on their front surface: welding voltage and wire feed speed.
In order to change the level of arc rigidity, penetration depth and weld shape, it is necessary to change the welding voltage or the inductance value. At low inductance the arc is cold. As a result, we get a thin seam with deep penetration. With high inductance, the arc, on the contrary, becomes hot. The result is a wide weld with shallow penetration.
The burner is held at an angle of 25-65 degrees. The distance between the torch nozzle and the weld pool is 15-25 mm. Welding is carried out with short, gripping movements.
The stainless filler wire must be more highly alloyed than the metal being welded. This is necessary in order to prevent the burnout of all alloying elements from the wire during the process of its melting, that is, to maintain the balance of alloying additives in the weld. The filler wire melts during the burning of the electric arc and is then fed in small drops into the weld pool area.
The gas supplied to the welding zone must first be passed through a drying agent, which is usually copper sulfate.
In order to prevent splashing of molten metal during the electric welding process, the metal edges being welded are pre-treated with an aqueous solution of chalk.
To obtain a high-quality and beautiful seam, welding should not begin and end at the edge of the parts being welded. You should always step back a few millimeters from the edge.
During the welding process, stainless steel is always subject to thermal deformation. Therefore, after completing the welding work, it is necessary to eliminate its consequences. For these purposes, processing is carried out using a hammer and a special trowel. The so-called “bubble” that appears on the surface of the metal is tapped. Simultaneously with tapping, the metal surface is slightly heated using a conventional gas burner. Finally, the welding area is polished and polished using a special paste.
Books can be written about welding methods, this process of joining metals is so popular. The easiest way to weld ferrous metal. Stainless steel welding technology has its own characteristics. In order to properly master the process of welding stainless steel at home, you need to purchase a welding machine and electrodes. Electric welding technology is constantly being improved, and new generation devices are being produced, for example, welding inverters.
Read also: Feron sen26 connection diagram