Grinding wheel: scope of application
Despite its simple design, the grinding wheel is capable of performing many tasks, and the scope of application of this equipment is quite wide. This feature is responsible for such a variety of types and types of work items. It is recommended to buy a grinding wheel primarily for roughing or finishing processing of metals, plastic, wood and other materials. The specific purpose of the equipment is determined by its grain size , diameter and shape .
GOST describes the grinding wheel in great detail. There are a lot of requirements for equipment, which can be difficult to understand even for professionals.
The key characteristics that GOST describes are the following:
- abrasive material;
- type of grain bundle;
- grain level;
- degree of hardness of the circle;
- basis of the work element;
- diameter.
Most often, a grinding wheel is used on wood, but the equipment can also process other materials - stone, metal and even plastic. An abrasive surface can also remove old paint and rust.
Professionals prefer to buy a grinding wheel for the following types of work:
- clean the metal;
- sharpen cutting elements;
- carry out diamond finishing processing;
- perform finishing with hard alloys and non-metallic bases.
Grinding wheels differ in many characteristics, which are regulated by GOST. When choosing, it is recommended to pay special attention to the processing method (it can be straight or end-to-end), the color of the specific equipment and its characteristics.
Marking
The main parameters of the circle can be determined by its symbol, which is indicated in the product labeling. The symbol corresponds to GOST R 52781 and indicates:
- circle type;
- material;
- grain;
- geometric parameters (outer and inner diameters, height);
- type of ligament;
- structure and degree of hardness;
- the highest permissible processing speed.
The exception is wheels with individual markings, which have wheels from foreign manufacturers. When purchasing this product, you must study the information in the catalogs and on the packaging.
Type of grinding wheel bundle
The abrasive material is a key selection criterion.
A certain type of binder is used as a basis for the adhesion of grains bakelite, vulcanite or ceramic.
Each of them is designed to perform specific tasks.
A grinding wheel for an angle grinder
with a bakelite bond is used when working with metal.
This type of equipment is designed for carving or grinding at high speed. However, a grinding wheel with a bakelite bond quickly overheats. Therefore, it is recommended to use this nozzle only if the operating temperature does not exceed 300°C.
Working elements with
vulcanite bond are used for polishing and finishing.
This equipment also cannot withstand high temperatures and is used for cutting work at low temperatures.
An abrasive grinding wheel
with a ceramic bond is more resistant to high temperatures.
It is permissible to use various lubricants and coolants during operation. This equipment can withstand speeds of up to 65 m/s, however, thin circles are not resistant to lateral loads.
The type of abrasive compound is indicated by the following markings:
- V, ceramic;
- B, on synthetic resins;
- BF, glass fiber reinforced synthetic resins;
- B4, bakelite with graphite filler.
2 Normative references
This standard uses normative references to the following standards:
GOST 15.309 System for developing and launching products into production. Testing and acceptance of manufactured products. Basic provisions
GOST 577 Dial indicators with a division value of 0.01 mm. Specifications
GOST 801 Bearing steel. Specifications
GOST 1050 Metal products from unalloyed structural high-quality and special steels. General technical conditions
GOST 3060 Grinding wheels. Permissible unbalanced masses and method of their measurement
GOST 3647 Grinding materials. Classification. Grain size and grain composition. Control methods
GOST 4543 Metal products made from structural alloy steel. Specifications
GOST 14192 Marking of cargo
GOST 27595 Grinding materials and abrasive tools. Packaging, labeling, transportation and storage
GOST 30513 Abrasive and diamond tools. Safety test methods
GOST R 52381 (ISO 8486-1:1996, ISO 6344-2:1998, ISO 9138:1993, ISO 9284:1992) Abrasive materials. Grain size and grain composition of grinding powders. Control of grain composition
GOST R 52587 Abrasive tools. Symbols and methods for measuring hardness
GOST R 52588 Abrasive tools. Safety requirements
GOST R 52710 Abrasive tools. Acoustic method for determining hardness and sound indices by the speed of propagation of acoustic waves
Note - When using this standard, it is advisable to check the validity of the reference standards in the public information system - on the official website of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology on the Internet or using the annual information index "National Standards", which was published as of January 1 of the current year, and on issues of the monthly information index “National Standards” for the current year. If an undated reference standard is replaced, it is recommended that the current version of that standard be used, taking into account any changes made to that version. If a dated reference standard is replaced, it is recommended to use the version of that standard with the year of approval (adoption) indicated above. If, after the approval of this standard, a change is made to the referenced standard to which a dated reference is made that affects the provision referred to, it is recommended that that provision be applied without regard to that change. If the reference standard is canceled without replacement, then the provision in which a reference to it is given is recommended to be applied in the part that does not affect this reference.
Abrasive grinding wheel: grain marking
A grinding wheel for an angle grinder is made using abrasive materials. They are also divided into categories and labeled separately. There are two types of abrasives: natural
and
synthetic
.
The first category includes diamond, emery, corundum, chromium or iron oxide. The second type includes silicon carbides, boron carbides, zirconium carbides, borosilicarbide, cubic boron nitride, as well as electrocorundums - chromium, titanium, zirconium, etc.
The most common types of grains, indicated by markings:
- A, standard alumina;
- Z, zirconium;
- C, carborundum.
The designation may be preceded by numbers characterizing the special characteristics of the abrasive grain. For example, 54A is pink aluminum oxide, 53C is black silicon carbide, and so on.
The abrasive grinding wheel
under the brand “A” is used when working in difficult conditions with heavy loads.
Craftsmen often use such equipment when grinding materials with high strength, such as stainless or tool steel.
For roughing, where a large material removal is required, it is recommended to buy a grinding wheel
with the designation “Z” .
The grinding wheel for grinders
under the “C” brand is considered the hardest and very sharp.
This equipment is used both for grinding soft materials, products made of aluminum and cast iron, and for very hard ones.
The grain size of grinding wheels is marked with numbers, and the higher the value, the finer the particles:
- 3-24, coarse grain;
- 30-60, average;
- 70-220, fine.
The scope of application of the equipment depends on the particle size. For example, fine finishing, finishing of multi-edge tools and thread grinding require
coarse grinding wheels.
For these purposes, equipment marked 3, 6 or 12 is suitable.
To perform fine grinding of highly critical elements, craftsmen advise buying a grinding wheel
with a grit of 10 .
This type of equipment is also used when sharpening small tools. Semi-finish and fine grinding is performed using a working element with a grain size of 40 to 10.
An abrasive grinding wheel
with a grain size of 50 to 40 is used during rough finishing, pre-sharpening of tools, and processing of copper and brass.
To clean welds, smaller particles are required - from 125 to 80. Fibers of plexiglass, textolite and other non-metallic materials are ground with a wheel with the smallest grit - from 200 to 160.
ACCEPTANCE RULES
3.1. To monitor compliance of the wheels with the requirements of this standard, acceptance inspection and periodic testing are carried out.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 2).
3.2. Each circle is subjected to acceptance control for compliance with the requirements of clause 2.8, clauses 1.2, 2.5-2.7, 2.9-2.12 are subjected to circles with the following sample size:
0.5% of the lot, but not less than 10 pcs. for circles with a diameter of up to 63 mm;
1.0% of the lot, but not less than 10 pcs. for circles with a diameter over 63 mm to 125 mm;
10% of the lot, but not less than 10 pcs. for circles with a diameter of St. 125 mm to 250 mm;
15% of the lot, but not less than 10 pcs. for circles with a diameter of St. 250 mm.
According to clause 2.13, for wheels with operating speeds up to 80 m/s, wheels are subjected to the following sample volume:
0.2% of the lot, but not less than 10 pcs. for circles with a diameter of up to 200 mm;
0.5% of the lot, but not less than 10 pcs. for circles with a diameter of St. 200 mm to 500 mm;
1.0% of the lot, but not less than 5 pcs. for circles with a diameter of St. 500 mm to 750 mm;
1.5% of the lot, but not less than 5 pcs. for circles with a diameter of St. 750 mm;
for circles with an operating speed of 80 m/s and above, the sample volume should be doubled.
The batch must consist of circles of the same size, the same characteristics, simultaneously presented for acceptance using one document.
3.3. If during acceptance control it is determined that there is non-compliance with the requirements of the standard for more than one controlled indicator, then the batch is not accepted.
If non-compliance with the requirements of the standard is established for one of the controlled indicators, then repeated control is carried out on a double number of laps.
If there are defects in the re-sampling, the batch will not be accepted.
3.4. At least 5 wheels that have passed acceptance control at least once a year are subjected to periodic tests for compliance with the requirements of clause 2.14.
It is allowed to carry out tests at the consumer's site under production conditions.
3.3, 3.4. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 2).
3.5. (Deleted, Amendment No. 2).
How hard should a grinding wheel be?
The hardness of the wheel also has a great influence on the grinding process. This indicator is indicated by the following brands:
- F, G, very soft;
- H, I, J, soft;
- K, L, medium soft;
- M, N, medium;
- O, P, Q, medium hard;
- R, S, hard;
- T, very hard;
- V, extremely hard.
A soft
abrasive grinding wheel is used during finishing processing of hard materials. Equipment under the brands “M” and “N” are used during peeling work. A medium-hard and hard grinding wheel for an angle grinder handles fragile and soft materials well.
Polishing equipment comes in a variety of shapes.
Recently, Velcro grinding wheels have gained popularity.
The peculiarity of this working element lies in the fastening system. Such equipment is fixed on the support plate using special Velcro. This system allows you to quickly change consumables during operation, provides reliable grip and prevents the working element from moving.
Often, a Velcro grinding wheel is used to prepare the surface for finishing work and coating with a paint layer. Such equipment is also convenient for removing plaque, rust and old dust.
Diamond grinding wheels are still popular among professionals .
Such equipment is used for processing ceramics, marble, concrete, plastic and quartzite. It is also used in cases where the surface cannot be sanded using working elements with high grain hardness.
diamond wheel requires Velcro on the back side.
It is often made from velcro fabric.
This allows the equipment to maintain maximum flexibility and elasticity. The diamond grinding wheel is used in processing not only smooth planes, but also in finishing workpieces with smooth lines and bends. However, such equipment is susceptible to sharp objects and may lose its performance when working at sharp angles. Type of grinding wheel base
Like any other abrasive equipment, a Velcro grinding wheel can be made on the basis of:
- paper;
- fabrics;
- films.
A soft sanding wheel works best on wood.
Paper is used as a basis for processing non-solid materials .
Such equipment has high elasticity, but low strength.
A Velcro sanding wheel
with a fabric base is more stable and is not inferior in flexibility to paper counterparts.
Fiber
is pressed cardboard with an adhesive composition.
It is recommended to buy a grinding wheel with such a base for rough work during metal processing.
Film-based equipment has high performance characteristics.
This work element is designed for delicate work on paintwork, plastic or glass. The price of a grinding wheel with such a base is slightly higher, but the film has a high level of elasticity.
According to craftsmen, a grinding wheel on wood works best if it is made
of sandpaper on a hard base .
To give the workpiece a smooth surface, professionals use fine-grained equipment. In cases where it is necessary to remove only part of the layer, a wood grinding wheel is used with medium grit. Old paint layers are removed from the surface using equipment containing large particles.
TEST METHODS
4.1. Control of circle sizes is carried out using universal or special measures and measuring instruments.
Note. Dimensions are not controlled for reference.
4.2. Hardness control - according to GOST 18118, GOST 19202, GOST 21323, GOST 25961.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
4.3. Control of wheel imbalance - according to GOST 3060.
Note. Monitoring the imbalance of wheels with a diameter of up to 250 mm, types 6, 11, 2, 36, as well as wheels of all types operated at an operating speed of 15 m/s, may not be carried out.
4.1-4.3. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 2).
4.4. Testing of wheels for mechanical strength - according to GOST 12.3.028.
Note. Wheels of types 2 and 36 are not tested for mechanical strength.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 4).
Other types of grinding wheels
In wood and metal processing, a flap grinding wheel is often
used .
This type of equipment differs in design, in which the working surface is divided into segments. This allows for maximum efficiency in cleaning weld seams or edges, removing rust, scale and burrs, as well as during surface preparation for painting.
The flap grinding wheel has a long service life, and the surface wears evenly. This allows the equipment to be used until it is completely worn out. In addition, the flap grinding wheel maintains a constant rotation speed and operates without noise or vibration.
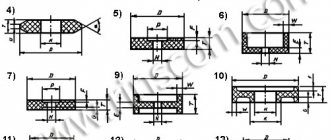
The grain size of grinding wheels and their dimensions are determined by GOST.
The choice of suitable equipment depends on the parameters of the angle grinder, machine and any other tool, as well as on the physical characteristics of the consumable.
The most widely used grinding wheels are the following
sizes : 115, 125, 180, 230 mm.
The 150 mm grinding wheel can be made of any abrasive and, as a rule, is used in the finishing of parts. In addition, this size of equipment is considered optimal for working at medium speed. Craftsmen consider the 150 mm grinding wheel convenient for processing the surfaces of round workpieces with a diameter of up to 1100 mm. Smaller equipment is used for working with small parts.
The 125 mm grinding wheel is suitable for finishing and profiling, sharpening cutting elements and working with thin-walled parts. Equipment of this size often features secure fastening and a solid base. In addition, a 125 mm grinding wheel is often used for processing wooden workpieces. Thanks to the holes, such a working element quickly removes dust.
Whatever the diameter of the wheel, it is important to pay attention to the characteristics of the grinding tool. Tooling must be compatible with the device to ensure surface treatment remains as efficient as possible.
Preface
1 PREPARED by the Federal State Unitary Enterprise "All-Russian Research Institute of Standardization and Certification in Mechanical Engineering" (VNIINMASH) based on its own translation into Russian of the English version of the standards specified in paragraph 4
2 INTRODUCED by the Technical Committee for Standardization TC 95 “Tool”
3 APPROVED AND ENTERED INTO EFFECT by Order of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology dated November 29, 2007 N 339-st**
4 This standard is modified from the following international standards:
ISO 525:1999* Bonded abrasive products. General requirements" (ISO 525:1999 "Bonded abrasive products - General requirements", MOD);
________________
* Access to international and foreign documents mentioned in the text can be obtained by contacting the User Support Service. — Note from the database manufacturer.
ISO 603-1:1999 Bonded abrasive products. Dimensions. Part 1. Grinding wheels for external cylindrical grinding" (ISO 603-1:1999 "Bonded abrasive products - Dimensions - Part 1: Grinding wheels for external cylindrical grinding between centres", MOD);
ISO 603-2:1999 Bonded abrasive products. Dimensions. Part 2. Grinding wheels for centerless external cylindrical grinding" (ISO 603-2:1999 "Bonded abrasive products - Dimensions - Part 2: Grinding wheels for centerless external cylindrical grinding", MOD);
ISO 603-3:1999 Bonded abrasive products. Dimensions. Part 3. Grinding wheels for internal cylindrical grinding" (ISO 603-3:1999 "Bonded abrasive products - Dimensions - Part 3: Grinding wheels for internal cylindrical grinding", MOD);
ISO 603-4:1999 Bonded abrasive products. Dimensions. Part 4. Grinding wheels for surface grinding" (ISO 603-4:1999 "Bonded abrasive products - Dimensions - Part 4: Grinding wheels for surface grinding/peripheral grinding", MOD);
ISO 603-5:1999 Bonded abrasive products. Dimensions. Part 5. Grinding wheels for face grinding" (ISO 603-5:1999 "Bonded abrasive products - Dimensions - Part 5: Grinding wheels for surface grinding/face grinding", MOD);
ISO 603-6:1999 Bonded abrasive products. Dimensions. Part 6. Wheels for sharpening cutting tools" (ISO 603-6:1999 "Bonded abrasive products - Dimensions - Part 6: Grinding wheels for tool and tool room grinding", MOD);
ISO 13942:2000 Bonded abrasive products. Limit deviations of dimensions and run-out tolerances" (ISO 13942:2000 "Bonded abrasive products - Limit deviations and run-out tolerances", MOD).
At the same time, additional provisions that take into account the needs of the national economy and the peculiarities of national standardization are highlighted in italics.
________________ * In the original document, the designations and numbers of standards and normative documents are in italics, with the exception of those marked in the “Preface” section with the sign “**”. — Note from the database manufacturer.
The name of this standard has been changed relative to the name of the specified international standards to bring it into compliance with GOST 1.5-2012* (clause 3.5)
________________
*Probably an error in the original. Should read: GOST R 1.5-2012. — Note from the database manufacturer.
5 INTRODUCED FOR THE FIRST TIME
6 REPUBLICATION. June 2022
The rules for the application of this standard are established in
Article 26 of the Federal Law of June 29, 2015 N 162-FZ “On standardization in the Russian Federation”
. Information about changes to this standard is published in the annual (as of January 1 of the current year) information index “National Standards”, and the official text of changes and amendments is published in the monthly information index “National Standards”. In case of revision (replacement) or cancellation of this standard, the corresponding notice will be published in the next issue of the monthly information index “National Standards”. Relevant information, notices and texts are also posted in the public information system - on the official website of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology on the Internet (www.gost.ru)