10/14/2021 In the modern world, it is difficult to imagine a mechanism consisting of many parts that does not have threaded connections. This ingenious invention of mankind has gained such popularity due to its reliability, versatility, and the ability to quickly combine and separate assembled elements.
Threaded connection technology involves the use of screws, nuts, bolts, studs and other fasteners. Manufacturers apply right-handed or left-handed threads to the working part of these products. Most often, fasteners with right-hand threads are used. The non-standard left option is used in cases of high probability of spontaneous separation, for example, when combining rotating mechanisms.
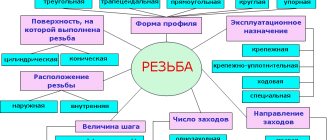
How are threads marked on the drawing?
carving
depicted: a) on the rod - with solid main lines along the outer diameter
of the thread
and solid thin lines - along the inner diameter.
b) in holes - with solid main lines along the internal diameter of the thread
and solid thin lines - along the outer diameter.
Interesting materials:
How to set up a mouse on a Windows 10 laptop? How to customize the Windows 10 Start screen? How to set up a shared folder in Windows 10? How to set up a shared network in Windows 10? How to set the screen to turn off in Windows 10? How to set up keyboard switching in Windows 10? How to set up a signature in Windows Live? How to set up administrator rights in Windows 10? How to set up photo viewing in Windows 10? How to adjust window transparency in Windows 10?
Types of threaded connections
pkmetiz.ru
The most common method of joining elements of various structures is a threaded connection. It is widely used in construction, pipeline installation, mechanical engineering and many other industries. The popularity of this method is due to the following advantages:
- high reliability and long service life;
- creation of detachable connections, ease of installation and dismantling using publicly available tools;
- control of tightening force during assembly;
- low weight and dimensions of fasteners compared to the structural elements being connected;
- wide availability, large selection of fastener sizes.
Metric and imperial
Metric threads are manufactured based on the standards prescribed in GOST 8724–2002. Often this type is used to create fasteners. This type can be used as a chassis if certain conditions have been met.
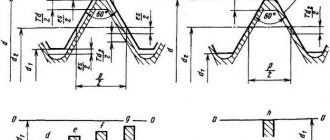
The basis for the metric type is an equilateral triangle, the angle of which at the base is 60 degrees. The manufactured thread can have from one to several starts. The second option is used when it is necessary to increase the strength of the joint.
Now they produce products with a cross-section of up to 600 mm and a pitch of turns up to 6 mm. Small ones are used in cases where you need to make a detachable mount on the thin walls of the device. This type is very common in the automotive industry.
The thread can be left or right. First, the letter M is indicated, which indicates that the product is made in accordance with the metric system. After this, the size and pitch in millimeters are indicated.
The inch system is mainly used in the manufacture of pipeline fittings and fittings. Marking is applied to both plastic and metal products. All requirements are specified in GOST 6111–52. This regulatory document contains tables with dimensions and pitch for a specific type. All designations are in inches.
TOLERANCES
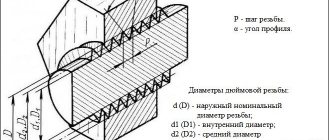
3.1. The axial displacement of the main plane of the external and internal threads (Fig. 4) relative to the nominal location should not exceed the values specified in Table 3.
Damn.4. Axial displacement of the main plane of external and internal threads
Note. In the main plane, the average diameter has a nominal value.
The displacement of the main plane is total, including deviations of the average diameter, pitch, angle of inclination of the side of the profile and cone angle.
3.2. The maximum deviations of the average diameter of the internal cylindrical thread must correspond to those indicated in Table 3.
3.3. It is allowed to connect an external conical thread with an internal cylindrical thread of accuracy class A according to GOST 6357.
3.4. Recommended maximum deviations of individual thread parameters are given in the reference appendix.
Slicing principles
When slicing, you need to take into account a number of features:
- cutting accuracy is determined by the parameters of the holes: diameter, perpendicularity of the center line to the surface of the workpiece, length;
- inch is cut with a profile angle of 60 degrees, and metric - 55;
- the tops and bottoms of inch threads, unlike metric threads, have more bluntness and have better tightness;
- to simplify the process, drilling a hole with a cylindrical drill is required; it is selected according to the smallest diameter;
- chamfering is required;
- When working, the tool must be lubricated to prevent overheating;
- when cutting, 2 turns are made forward, and then 1 turn back;
- the force on the cutting tool can be weakened after driving to the middle of the calculated length;
- Once the desired length is reached, the die can be removed by rotating in the opposite direction;
- Before finishing cutting, you need to do a rough cut.
Conical taps are distinguished by an elongated shape of the intake part and an incomplete thread, which additionally plays a calibrating role. In the upper part they have a square cross-section; longitudinal grooves are made on the cutting part to remove chips.
Cutting:
- The workpiece is vertically fixed in a vice.
- Lubricant is applied to the tool.
- The tool is applied perpendicular to the center line for cutting threads, that is, strictly in a horizontal plane.
- Several turns are cut.
- The correctness of the work is checked. In case of misalignment, you need to remove the cutting tool, tap the part and repeat steps 3–4.
- Further cutting is carried out provided that the first turns are correctly positioned. You can check with a regular level.
- A thread is formed to the required length.
- At the end of the work, remove the chips and clean the tool from lubricant.
For cutting on lathes, heads with thread-cutting dies are used. A special design feature of the tool is the automatic spreading of the dies during operation. This ensures high machining precision and optimal productivity.
In some cases, knurling rollers are used. The cutting accuracy is lower than when using heads, and the complexity of the work is higher.
To set up a lathe, it is enough to set the spindle rotation speed to low and associate the caliper offset with it. Setting rule: one revolution of the spindle must correspond to the movement of the caliper by the distance of the thread pitch.
On lathes, adjustments are easy because there are many clutch combinations available on the gearbox. If necessary, it is possible to cut threaded grooves of non-standard sizes.
In branding
To protect against the use of counterfeit parts in the automotive industry, manufacturers resort for commercial purposes to the marketing ploy of using left-hand cutting, from which their products acquire uniqueness and individuality.
This idea ensures that customers will only buy spare parts for repair or replacement from the official manufacturer.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Sizes of grinders
A grinder is an angle grinder used for processing and cutting durable materials. It is used in construction, dismantling and repair work. The popularity of the tool is due to its relatively low cost and wide capabilities. The grinder is considered one of the most popular tools due to its versatility. It is popular among both professional builders and ordinary users. This instrument received recognition due to the huge variety of types, sizes and their price category.
- protection from standard operations
0
Often, fasteners with left-hand threads are used on similar equipment that poses an increased danger. If there is a possibility of a mistake in connecting the products, then one of them is made with a right-hand thread, and the other with a left-hand thread. The connecting threads for the compressed gas cylinder reducer are designed using this principle. The propane tank has a left-hand thread, the oxygen tank has a right-hand thread. Thus, it is impossible to attach a reducer from a flammable gas cylinder to an oxygen cylinder.
Left and right hand thread. Differentiating, application
There are two types of fasteners, divided according to the direction of rotation of the profile: with a right-hand thread and a left-hand thread. The most widely used products are those with screws directed clockwise, that is, with right-hand threads. But there are a number of elements and parts that are equipped with threads in the opposite direction.
How to distinguish right-handed from left-handed threads
There are several methods that can help in solving this problem, but the simplest, “everyday” one that most modern craftsmen use is the following:
Place the product whose thread direction you want to determine on your palm with the chamfer facing up (thread facing you) and pay attention to the end of the spiral. If you trace the rotation of the thread from its base to the “tail”, and this “tail” will be directed to the right, then you have a right-hand thread (clockwise)
Accordingly, if it’s the other way around, then it’s left.
Right-hand threads are most often found in the industrial sector, however, it is not always advisable to use it. Let's consider several options when a right-handed thread cannot satisfy all design requirements, and it would be more rational to use a left-handed thread.
Preventing self-unscrewing and loosening of connections
The rotating shaft or any other rod on which nuts and bolts are screwed determines the direction of rotation of the hardware used: the screws or nuts must be tightened according to the direction of movement of the shaft. This is done so that during operation the fastening does not weaken or unwind.
Screed
There are a number of tightening devices, such as lanyards, the design of which implies the presence of a part with a right-hand thread and a part with a left-hand thread. Rotation of the element body allows you to loosen the tie or, on the contrary, load it, depending on the direction of rotation.
As a way to protect against dangerous operations
In some of the most critical operations, the incorrect implementation of which can result in casualties or pose a threat to health, it is recommended to use left-handed threads. Thus, the likelihood of dangerous actions is reduced. For example, working with cylinder equipment requires careful monitoring of the gas in the container. Therefore, propane cylinders are produced with a left-hand thread, and oxygen cylinders with a right-hand thread, in order to prevent emergency situations of improper use of this cylinder.
Branding
Some manufacturers produce products with counterclockwise threads in order to uniqueize their product and protect the buyer from purchasing non-original products.
- to prevent self-unscrewing
0
The nut or screw that secures a part to a rotating shaft must be tightened in the direction of rotation of the shaft. Otherwise, the likelihood of self-unscrewing of the fasteners increases sharply. Therefore, threaded fasteners with left-hand threads are often in demand for completing such products or equipment. Examples include mounting bicycle pedals, fan blades, angle grinder discs (some models), wheels of some bus models, trucks, and many other devices.
- when screeding
0
In coupling structures, multidirectional threads are provided on the rotating part. On one side is left, and on the other is right. By rotating such a device, the attached parts will either move closer or move away. A striking example of such a device is TALREP. The lanyard body (it can be open or closed) has a left-hand thread on one side and a right-hand thread on the other. As it rotates, the mating parts—this could be a screw with a hook, ring, or eye—either move closer together or move away. So, with the help of a left-hand thread, cables are tensioned, masts or canopies are installed, and equipment or equipment is secured to the platform. Another example is a nipple for a sectional radiator. Having multi-directional threads on both sides, they use a special wrench to tighten sections of aluminum, bimetallic, and cast iron radiators.
0
Cutting tools
A tap is used to cut internal threads. This is a special screw that has hard cutting edges. This tool consists of a working part and a shank designed for fixation in the driver. The device can be manual or machine.
Locksmith kit contents:
- Tap. Its diameter can vary and reaches 18 mm.
- Two rough working parts.
- Rough tap of a different diameter, medium and finishing.
Before you start cutting, you must first make a hole that will have a slightly smaller diameter. During operation, the tool must be held perpendicular and lubricant added to the cutting area. The tap should be unscrewed every few turns to remove accumulated metal shavings. This is very convenient to do with a small special brush.
On an industrial scale, external threads are made on a machine. For household needs, dies are used, which are:
- Split. The tool is made of two halves, which is why it is not as rigid as other types. Can be used for undemanding connections.
- Whole round. With this die you can cut high-quality threads.
- Sliding. Used in clamps. You can make pipe threads.
The die itself looks very similar to a regular nut, inside of which there are cutting edges. The tool can be designed for cutting metric or inch threads.