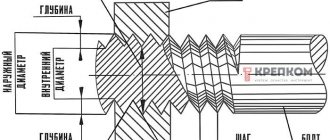
82. Main dimensions of metric threads, mm (according to GOST 9150-81, GOST 8724-81, GOST 24705-81)
d, D are the outer diameters of the external thread (bolt) and internal thread (nut), respectively;
d2, D2 are the average diameters of the bolt and nut, respectively;
d1, D1 are the internal diameters of the bolt and nut, respectively;
d3 is the internal diameter of the bolt along the bottom of the cavity;
P - thread pitch;
H is the height of the original triangle.
The nominal values of the thread diameters must correspond to those indicated in the drawing and in the table. Diameter values are calculated using the following formulas:
H = 0.866025R.
D2 = D – 2(3/8)H = D – 0.649519053P
d2 = d -2(3/8) = d - 0.649519053Р;
D1 = D – 2(5/8)H = D – 1.082531755P;
d1 = d - 2(5/8)H = d - 1.082531755P;
d3 = d - 2(17/24)H = d - 1.226869322P.
| Thread pitch P | Thread diameter | |||
| outer | average | interior | Internal along the bottom of the depression | |
| In a slow step | ||||
| 0,40 | 2,0 | 1,740 | 1,567 | 1,509 |
| 0,45 | (2,2) | 1,908 | 1,713 | 1,648 |
| 0,45 | 2,5 | 2,208 | 2,013 | 1,948 |
| 0,50 | 3,0 | 2,675 | 2,459 | 2,387 |
| 0,60 | (3,5) | 3,110 | 2,850 | 2,764 |
| 0,70 | 4 | 3,546 | 3,242 | 3,141 |
| 0J5 | (4,5) | 4,013 | 3,688 | 3,580 |
| 0,80 | 5 | 4,480 | 4,134 | 4,019 |
| 1 | 6 | 5,350 | 4,918 | 4,773 |
| 1,25 | 8 | 7,188 | 6,647 | 6,466 |
| 1,50 | 10 | 9,026 | 8,376 | 8,160 |
| 1,75 | 12 | 10,863 | 10,106 | 9,853 |
| 2 | (14) | 12,701 | 11,835 | 11,546 |
| 2 | 16 | 14,701 | 13,835 | 13,546 |
| 2,5 | (18) | 16,376 | 15,294 | 14,933 |
| 2,5 | 20 | 18,376 | 17,294 | 16,933 |
| 2,5 | (22) | 20,376 | 19,294 | 18,933 |
| 3 | 24 | 22,051 | 20,752 | 20,319 |
| 3 | (27) | 25,051 | 23,752 | 23,319 |
| 3,5 | 30 | 27,727 | 26,211 | 25,706 |
| 3,5 | (33) | 30J27 | 29,211 | 28,706 |
| 4 | 36 | 33,402 | 31,670 | 31,093 |
| 4 | (39) | 36,402 | 34,670 | 34,093 |
| 4,5 | 42 | 39,077 | 37,129 | 36.479 |
| 4.5 | (45) | 42,077 | 40,129 | 39,479 |
| 5 | 48 | 44,752 | 42,587 | 41,866 |
| 5 | (52) | 48,752 | 46.587 | 45,866 |
| 5,5 | 56 | 52,428 | 50,046 | 49,252 |
| 5,5 | (60) | 56,428 | 54,046 | 53.252 |
| 6 | 64 | 60,103 | 57,505 | 56.639 |
| 6 | (68) | 64,103 | 61,505 | 60.639 |
| With small steps | ||||
| 0,25 | 2,0 | 1,838 | 1,729 | 1,693 |
| 2,2 | 2,038 | 1,929 | 1,893 | |
| 0,35 | 2,5 | 2,273 | 2,121 | 2,071 |
| 3 | 2.773 | 2,621 | 2,571 | |
| (3,5) | 3,273 | 3,121 | 3,071 | |
| 0,5 | 4 | 3,675 | 3,459 | 3,387 |
| (4,5) | 4,175 | 3,959 | 3,887 | |
| 5 | 4,675 | 4,459 | 4,387 | |
| 6 | 5,675 | 5,459 | 5,387 | |
| 8 | 7,675 | 7,459 | 7,387 | |
| 10 | 9,675 | 9,459 | 9,387 | |
| 12 | 11,675 | 11,459 | 11,387 | |
| (14) | 13,675 | 13,459 | 13,387 | |
| 16 | 15,675 | 15,459 | 15,387 | |
| (18) | 17,675 | 17,459 | 17,387 | |
| 20 | 19,675 | 19,459 | 19,387 | |
| (22) | 21,675 | 21,459 | 21,387 | |
| 0,75 | 6 | 5,513 | 5,188 | 5,080 |
| 8 | 7,513 | 7,188 | 7,080 | |
| 10 | 9,513 | 9,188 | 9,080 | |
| 12 | 11,513 | 11,188 | 11,080 | |
| (14) | 13,513 | 13,188 | 13,080 | |
| 16 | 15,513 | 15,188 | 15,080 | |
| (18) | 17,513 | 17,188 | 17,080 | |
| 20 | 19,513 | 19,188 | 19,080 | |
| (22) | 21,513 | 21,188 | 21,080 | |
| 24 | 23,513 | 23,188 | 23,080 | |
| (27) | 26,513 | 26,188 | 26,080 | |
| 30 | 29,513 | 29,188 | 29,080 | |
| (33) | 32,513 | 32,188 | 32,080 | |
| 1,0 | 8 | 7,350 | 6,917 | 6,773 |
| 10 | 9,350 | 8,917 | 8,773 | |
| 12 | 11,350 | 10,917 | 10,773 | |
| (14) | 13,350 | 12,917 | 12,773 | |
| 16 | 15,350 | 14,917 | 14,773 | |
| (18) | 17.350 | 16,917 | 16,773 | |
| 20 | 19,350 | 18,917 | 18,773 | |
| (22) | 21,350 | 20.917 | 20.773 | |
| 24 | 23,350 | 22,917 | 22.773 | |
| (27) | 26,350 | 25,917 | 25.773 | |
| 30 | 29,350 | 28,917 | 28.773 | |
| 36 | 35,350 | 34,917 | 34,773 | |
| (39) | 38,350 | 37,917 | 37.773 | |
| 42 | 41,350 | 40,917 | 40,773 | |
| (45) | 44,350 | 43,917 | 43.773 | |
| 48 | 47,350 | 46,917 | 46,773 | |
| (52) | 51,350 | 50,917 | 50,773 | |
| 56 | 55,350 | 54,917 | 54,773 | |
| (60) | 59,350 | 58,917 | 58,773 | |
| 64 | 63,350 | 62,917 | 62,773 | |
| (68) | 67,350 | 66,917 | 66,773 | |
| 72 | 71,350 | 70,917 | 70,773 | |
| (76) | 75,350 | 74,917 | 74,773 | |
| 80 | 79,350 | 78,917 | 78,773 | |
| 1,25 | 10 | 9,188 | 8,647 | 8,466 |
| 12 | 11,188 | 10,647 | 10,467 | |
| (14) | 13,188 | 12,647 | 12,466 | |
| 1,5 | 12 | 11,026 | 10,376 | 10,160 |
| (14) | 13,026 | 12,376 | 12,160 | |
| 16 | 15,026 | 14,376 | 14,160 | |
| (18) | 17,026 | 16,376 | 16,160 | |
| 20 | 19,026 | 18,376 | 18,160 | |
| (22) | 21,026 | 20,376 | 20,160 | |
| 24 | 23,026 | 22,376 | 22,160 | |
| (27) | 26,026 | 25,376 | 25,160 | |
| 30 | 29,026 | 28,376 | 28,160 | |
| (33) | 32,026 | 31,376 | 31,160 | |
| 36 | 35,026 | 34,376 | 34,160 | |
| (39) | 38,026 | 37,376 | 37,160 | |
| 42 | 41,026 | 40,376 | 40,160 | |
| (45) | 44,026 | 43,376 | 43,160 | |
| 48 | 47,026 | 46,376 | 46,160 | |
| (52) | 51,026 | 50,376 | 50,160 | |
| 56 | 55,026 | 54,376 | 54,160 | |
| (60) | 59,026 | 58,376 | 58,160 | |
| 64 | 63,026 | 62,376 | 62,160 | |
| (68) | 67,026 | 66,376 | 66,160 | |
| 72 | 71,026 | 70,376 | 70,160 | |
| (76) | 75,026 | 74,376 | 74,160 | |
| 80 | 79,026 | 78,376 | 78,160 | |
| (85) | 84,026 | 83,376 | 83,160 | |
| 90 | 89,026 | 88,376 | 88,160 | |
| (95) | 94,026 | 93,376 | 93,160 | |
| 100 | 99,026 | 98,376 | 98,160 | |
| (105) | 104.026 | 103,376 | 103,160 | |
| 110 | 109,026 | 108,376 | 108,160 | |
| (115) | 114,026 | And 3.376 | 113,160 | |
| (120) | 119,026 | 118,376 | 118,160 | |
| 125 | 124,026 | 123,376 | 123,160 | |
| (130) | 129,026 | L28.376 | 128,160 | |
| 140 | 139,026 | 138,376 | 138,160 | |
| (150) | 149,026 | 148,376 | 148,160 | |
| 2,0 | (18) | 16,701 | 15,835 | 15,546 |
| 20 | 18,701 | 17,835 | 17,546 | |
| (22) | 20,701 | 19,835 | 19,546 | |
| 24 | 22,701 | 21,835 | 21,546 | |
| (27) | 25,701 | 24,835 | 24,546 | |
| 30 | 28,701 | 27,835 | 27,546 | |
| (33) | 31,701 | 30,835 | 30,546 | |
| 36 | 33,701 | 32,835 | 32,546 | |
| (39) | 37,701 | 36,835 | 36,546 | |
| 42 | 40,701 | 39,835 | 39,546 | |
| (45) | 43,701 | 42,835 | 42,546 | |
| 48 | 46,701 | 45,835 | 45,546 | |
| (52) | 50,701 | 49,835 | 49,546 | |
| 56 | 54,701 | 53,835 | 53,546 | |
| (60) | 58,701 | 57,835 | 57,546 | |
| 64 | 62,701 | 61,835 | 61,546 | |
| (68) | 66,701 | 65,835 | 65,546 | |
| 72 | 70,701 | 69,835 | 69,546 | |
| (76) | 74,701 | 73,835 | 73,546 | |
| 80 | 78,701 | 77,835 | 77,546 | |
| (85) | 83,701 | 82,835 | 82,546 | |
| 90 | 88,701 | 87,835 | 87,546 | |
| (95) | 93,701 | 92,835 | 92,546 | |
| 100 | 98,701 | 97,835 | 97,546 | |
| (105) | 103,701 | 102,835 | 102,546 | |
| BY | 108,701 | 107,835 | 107,546 | |
| (115) | 113,701 | 112,835 | 112,546 | |
| (120) | 118,701 | 117,835 | 117,546 | |
| 125 | 123,701 | 122,835 | 122,546 | |
| (130) | 128,701 | 127,835 | 127,546 | |
| 140 | 138,701 | 137,835 | 137,546 | |
| (150) | 148,701 | 147,835 | 147.546 | |
| 160 | 158,701 | 157,835 | 157,546 | |
| (170) | 168,701 | 167,835 | 167,546 | |
| 180 | 178,701 | 177,835 | 177.546 | |
| (190) | 188,701 | 187,835 | 187,546 | |
| 200 | 198,701 | 197,835 | 197,546 | |
| 3,0 | 30 | 28,051 | 26,752 | 26,319 |
| (33) | 31,051 | 29,752 | 29,319 | |
| 36 | 34,051 | 32,752 | 32,319 | |
| (39) | 37,051 | 35,752 | 35.319 | |
| 42 | 40,051 | 38,752 | 38.319 | |
| (45) | 43,051 | 41,752 | 41,319 | |
| 48 | 46.051 | 44,752 | 44.319 | |
| (52) | 50,051 | 48,752 | 48,319 | |
| 56 | 54,051 | 52,752 | 52,319 | |
| (60) | 58,051 | 56,752 | 56,319 | |
| 64 | 62,051 | 60,752 | 60,319 | |
| (68) | 66,051 | 64,752 | 64,319 | |
| 72 | 70,051 | 68,752 | 68,319 | |
| (76) | 74,051 | 72,752 | 72,319 | |
| 80 | 78,051 | 76,752 | 76,319 | |
| (85) | 83,051 | 81,752 | 81,319 | |
| 90 | 88,051 | 86,752 | 86,319 | |
| (95) | 93,051 | 91,752 | 91,319 | |
| 100 | 98,051 | 96,752 | 96,319 | |
| (105) | 103,051 | 101,752 | 101,319 | |
| 110 | 108,051 | 106,752 | 106,319 | |
| (115) | 113,051 | 111,752 | 111,319 | |
| (120) | 118,051 | 116,752 | 116,319 | |
| 125 | 123,051 | 121,752 | 121,319 | |
| (130) | 128,051 | 126,752 | 126,319 | |
| 140 | 138,051 | 136,752 | 136,319 | |
| (150) | 148,051 | 146,752 | 146,319 | |
| 160 | 158,051 | 156,752 | 156,319 | |
| (170) | 168,051 | 166,752 | 166,319 | |
| 180 | 178,051 | 176,752 | 176,319 | |
| (190) | 188,051 | 186,752 | 186,319 | |
| 200 | 198,051 | 196,752 | 196,319 | |
| (210) | 208,051 | 206,752 | 206,319 | |
| 220 | 218,051 | 216,752 | 216,319 | |
| (240) | 238,051 | 236,752 | 236,319 | |
| 250 | 248,051 | 246,752 | 246,319 | |
| (260) | 258,051 | 256,752 | 256,319 | |
| 280 | 278,051 | 276,752 | 276,319 | |
| (300) | 298,051 | 296,752 | 296,319 | |
| 4,0 | 42 | 39,402 | 37,670 | 37,093 |
| (45) | 42,402 | 40,670 | 40,093 | |
| 48 | 45,402 | 43,670 | 43,093 | |
| (52) | 49,402 | 47,670 | 47,093 | |
| 56 | 53,402 | 51,670 | 51,093 | |
| 60 | 57,402 | 55,670 | 55.093 | |
| 64 | 61,402 | 59,670 | 59,093 | |
| 72 | 69,402 | 67,670 | 67,093 | |
| (76) | 73.402 | 71,670 | 71,093 | |
| 80 | 77,402 | 75,670 | 75,093 | |
| (85) | 82,402 | 84,670 | 80,093 | |
| 90 | 87,402 | 85,670 | 85.093 | |
| (95) | 92.402 | 90,670 | 90,093 | |
| 100 | 97,402 | 95,670 | 95,093 | |
| (105) | 102,402 | 100,670 | 100,093 | |
| 110 | 107,402 | 105,670 | 105,093 | |
| (115) | 112,402 | 110,670 | 110,093 | |
| (120) | 117,402 | 115,670 | 115,093 | |
| 125 | 122,402 | 120,670 | 120,093 | |
| (130) | 127,402 | 125,670 | 125,093 | |
| 140 | 137,402 | 135,670 | 135,093 | |
| (150) | 147,402 | 145,670 | 145,093 | |
| 160 | 157,402 | 155,670 | 155,093 | |
| (170) | 167,402 | 165,670 | 165,093 | |
| 180 | 177,402 | 175,670 | 175,093 | |
| (190) | 187,402 | 185,670 | 185,093 | |
| 200 | 197,402 | 195,670 | 195,093 | |
| (210) | 207,402 | 205,670 | 205,093 | |
| 220 | 217,402 | 215,670 | 215,093 | |
| (240) | 237,402 | 235,670 | 235,093 | |
| (260) | 257,402 | 255,670 | 255,093 | |
| 280 | 277,402 | 275,670 | 275,093 | |
| 300 | 297,402 | 295,670 | 295,093 | |
Tolerances of metric threads (GOST 16093-81)
The standard applies to metric threads with a profile in accordance with GOST 9150-81, diameters from 1 to 600 mm in accordance with GOST 8724-81 and GOST 16967-81, main dimensions in accordance with GOST 24705-81 and GOST 24706-81 and establishes a system of tolerances and clearance fits.
The positions of the tolerance fields of external and internal threads are shown in Fig. 2, 3.
Deviations are measured from the nominal thread profile in the direction perpendicular to the thread axis.
Tolerances of thread diameters are established according to degrees of accuracy, indicated by numbers.
The degrees of accuracy and main deviations of diameters are given in table. 83, thread diameter tolerances - in table. 84.
Rice. 2 Positions of external thread tolerance fields:
a - with main deviations d, e, f, R; b - with main deviations h
Diameter tolerances d1 and D are not established.
Tolerances for the average thread diameter are cumulative.
The position of the thread diameter tolerance field is determined by the main deviations (upper es for external threads and lower EI for internal threads) and is designated by a letter of the Latin alphabet, lowercase for external threads and uppercase for internal threads.
The tolerance field of the thread diameter is formed by a combination of tolerance and basic deviation.
The thread tolerance field is formed by combining the average diameter field with the tolerance field of the diameter of the protrusions (diameters d or D\).
Designation of the thread diameter tolerance zone
consists of a number indicating the degree of accuracy and a letter indicating the main deviation.
For example, 4h; 6g; 6H.
The designation of the thread tolerance field consists of the designation of the tolerance field of the average diameter, placed in the first place, and the designation of the tolerance field of the diameter of the protrusions.
Structural elements of pipe threads
The main structural elements of pipe threads are:
- Run-off is a section with an incomplete thread profile at the transition from the thread to the smooth surface of the part.
- An undercut is a section without a thread or with an incomplete thread profile due to the thread manufacturing technology.
- Groove is an element that allows you to eliminate thread undercut by reducing the outer diameter of the cylindrical surface located behind the external thread, or by increasing the internal diameter of the cylindrical surface located behind the internal thread.
- Chamfer is a bevel on the end surface of a part that simplifies the assembly of a threaded connection.
Dimensions of runs, undercuts, grooves for external pipe threads
The figure shows the structural elements of external pipe threads.
The dimensions of structural elements - runs, undercuts, grooves - are presented in the table.
Dimensions of structural elements of internal pipe threads
The main elements of internal pipe threads are shown in the figure.
The dimensions of the internal thread structural elements are presented in the table.
Thread errors
The main thread errors are pitch incursion and profile angle distortion.
The error (deviation) of the DP step is the difference between the actual and nominal step sizes.
The pitch error consists of local and progressive pitch errors.
Local errors do not depend on the make-up length.
Progressive errors in the pitch of the cut thread arise in proportion to the number of turns along the make-up length.
The error (deviation) of half the thread profile angle Da/2 of a bolt or nut is the difference between the actual and nominal values Da/2.
The influence of deviations in diameters, pitches, and angle of inclination of the side of the profile on the strength of the thread and make-up.
In case of diameter deviations, the bolt and nut may not be screwed together. Deviation of the pitch in any direction worsens the make-up.
Cyclic strength depends on the uniform distribution of forces between turns. The presence of gaps along d2, d1 and d eliminates jamming of the turns, reduces friction between them and increases the compliance of the thread, compensating for manufacturing errors and evenly distributing the load between the turns.
With a progressive error and deviation of half the profile angle, the static strength of the thread decreases. Deviations of the pitch reduce the cyclic strength of the threaded connection, and deviations of the half angle of the profile increase it.
This is the result of the fact that a step error is rarely local. It is usually progressive, increasing in proportion to the number of complete steps along the make-up length (ΔPn).
An accumulated step error occurs:
- due to copying tap or die pitch errors;
- due to errors in the kinematics of the machine when cutting threads with a cutter using the machine feed box;
- due to wear of the lead screw and its temperature and force deformations;
- heterogeneity of the workpiece material and other reasons.
When manufacturing threaded parts, errors in the thread profile and its dimensions are inevitable, which can interfere with make-up and deteriorate the quality of the connections. To ensure make-up and quality of connections, the actual contours of the parts being made up should not exceed the limit contours along the entire make-up length.
The reduced average thread diameter is the average diameter of an imaginary ideal thread, which has the same pitch and flank angle as the main or nominal thread profile, and a length equal to the specified make-up length, which is in close contact (without mutual displacement or interference) with the real one. carvings on the sides of the threads.
How to cut threads - thread-cutting equipment and tools
The choice of thread-cutting equipment depends on the type and scale of production, material and size of pipes, requirements for thread accuracy and other factors.
Threads can be obtained by rolling or cutting.
Rolling threads are produced using special thread-cutting rollers. To do this, the workpiece is placed between rollers with the required thread contour and thread turns are rolled on automatic and semi-automatic thread rolling machines, and sometimes on lathes and turret machines. Due to the smooth distribution of stress waves between turns due to metal deformation, such threads are distinguished by high mechanical characteristics and high performance. However, the accuracy of the rollers used must be at a very high level, and the manufacturing material must have improved mechanical properties - most often high-alloy stamped steel is used.
Cut threads are easier to manufacture, but in terms of mechanical properties and endurance limit they are inferior to rolled threads. This is due to the presence of sharper profile edges and a higher stress factor.
According to the method of thread cutting, it is divided into manual and using a special machine.
When manually cutting, special devices are used: a tap (for internal pipe threads) and dies (for external pipe threads), or a special thread-cutting hand tool - a die, which carries out cutting using movable adjustable comb cutters. Manual cutting is recommended for pipe diameters up to 1 inch, since larger diameters require significantly more physical effort.
For large loads and volumes of work, today there is a huge selection of reliable threading tools: from portable electric threading tools to special machines that can cope with cutting threads of any type on pipes of various diameters from any materials.
Our company ITC (ITC) offers a wide range of Ridgid and Rex thread-cutting tools. We are the official dealers of these brands in Russia, so we can offer not only the best prices, but also warranty and post-warranty service.
Sources
- https://stroychik.ru/strojmaterialy-i-tehnologii/rezba-trubnaya
- https://itc-russia.ru/blog/sovety-pokupatelyam/trubnaya-rezba-vidy-razmery-gosty/
- https://www.prof-inst.by/poleznoe/opisanie-tipov-trubnoj-rezbyi
- https://master-pmg.ru/dlya-vody/oboznachenie-trubnoj-rezby-gost.html
- https://www.hydro-pnevmo.ru/topic.php?ID=92
Pipe threads differ in the following parameters:
- Diameter measuring system: metric and inch thread
- Thread direction: right, left
- Thread location: external, internal
- Number of passes: single-pass, multi-pass
- Purpose: fastening, fastening and sealing, running, special, etc.
The main characteristics of pipe threads are:
- External diameter
- Inner diameter
- Pitch - the distance between adjacent turns
- Stroke is the distance that the fastener moves in the longitudinal direction in one full revolution. With single-pass knurling, the stroke is equal to the step, with multi-pass knurling - the step multiplied by the number of passes.
Metric thread
Metric thread is characterized by measuring the main parameters in millimeters; according to GOST, it corresponds to the marking “M”. Widely used in diameters from 1 to 600 mm and pitches of 0.25 to 6 mm. The metric thread profile is an equilateral triangle with an apex angle of 60° and a theoretical height of H-0.866025404. The main dimensions of metric threads are currently determined according to the current GOST 24705-2004, adopted by the Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification, as well as national standardization bodies of the Russian Federation, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Belarus, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Ukraine.
Inch thread
With inch threads, all parameters are expressed in inches, according to GOST it is designated “Tr”. Inch threads are based on the British standard Whitworth (BSW), patented by the English engineer Whitworth back in 1841, and correspond to the BSPT (British standard pipe thread) standard. One inch is equal to 2.54 cm, and the graphic symbol for an inch is a double stroke to the right and above the number (1″ = 1 inch). With inch pipe threads, the size refers to the inner diameter of the pipe, not the outer diameter. There are four pitch options: 28, 19, 14 and 11 threads per inch. Inch profiles are distinguished by sharper crests and valleys with angles of 55° and a theoretical height of H = 0.960491, while the tops of the teeth are rounded. It is impossible to combine metric and inch threads in one connection; a special adapter is required for this. The size of the pipe inch thread is determined according to the current GOST 6357-81 “Basic standards of interchangeability”.
Basic Concepts
Source : GOST 11 708 - 66
Make-up length is the length of contact of the screw surfaces of the external and internal threads in the axial direction.
Thread length - the length of the surface area on which the thread is formed, including the run-out and chamfer.
| Thread diameter intervals, d | Pitch ,P, mm | Maximum make-up length |
| 10-14 | 3 | 30 |
| 30-44 | 35 | |
| 22-28 | 5 | 50 |
| 30-42 | 6 | 55 |
| 22-28 | 8 | 65 |
| 44-60 | 90 | |
| 30-42 | 10 | 90 |