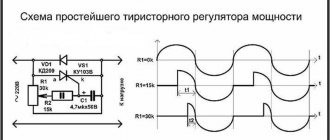
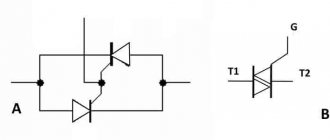
Author: Nemo
09 December 2022 09:05
Community: How it's made, how it works, how it works
Tags: algorithm how it works elevator
5963
5
You walk up to the elevator, press the arrow button, and the wait begins. Long wait. Very long...
0
See all photos in the gallery
In fact, there is a good reason why the elevator cars go up one after another without stopping at your floor. It's not because they don't love you. Every time we press a button, the elevator solves a difficult problem. The system must choose when and which cabin to send to our floor. We also need to decide whether the elevator should go up from the fifth floor and pick up passengers on the seventh before coming down to us on the first. You also need to consider who has already waited the longest and which route will be the most efficient. This system requires detailed development and fine tuning, and one cannot help but admire the painstaking work of the engineers who created it.
0
Source:
×
Production process
Steel is produced by smelting. The raw materials are cast iron, scrap steel or cast iron itself, pellets, fluxes and ferroalloys.
Cast iron itself, by nature, is not a sufficiently hard and brittle material, and therefore has limited use.
However, it is indispensable as a raw material for steel production. The essence of smelting is, in the case of using pig iron, to reduce the percentage of carbon in it to the required level.
Impurities not included in the final formulation are removed. The traditional composition of the charge is 55% cast iron and 45% steel scrap (scrap). There is also an ore process where ore material is added to components or a scrap process to recycle waste from engineering production.
To make it easier for impurities and carbon to be removed from the components during the smelting process, they are converted into gases and slag. First of all, when cast iron reacts with oxygen, iron is oxidized, forming iron oxide FeO.
At the same time, C, Si, Mn and P are oxidized, and oxygen is released from iron oxide to chemically active impurities. Flux is added to the charge mass to better dissolve the metal: limestone or lime, bauxite. Coal dust, liquid fuel oil, natural or coke oven gas are used as fuel.
Operating principle
The operating principle of a hair dryer is very similar to its household hair dryer. The material is heated to give it a certain shape and fix it in this position. The only difference lies in the power and object of heating, as in this case, soldering. To ensure proper soldering, the following tools are required:
The solder is always special rods made of the required material. The solder material is selected from a material similar to that of the welded object. These rods are installed in a hair dryer or in a special compartment on the nozzle, heat and weld parts, crevices, and so on. In addition, it would be a good idea to use clamps for reliability and files for quality processing.
Video on how to use a soldering gun and attachments
Process Features
The steel production process occurs sequentially in three stages.
The first stage is the melting of the rock. At the stage of its implementation, a melt is formed in the bath and the metal is oxidized, simultaneously giving oxygen to silicon, phosphorus and manganese.
One of the main tasks of this stage is phosphorus removal. Its implementation requires a relatively low temperature and the presence of a sufficient amount of FeO. When the ingredients interact, phosphorus anhydride forms an unstable compound (FeO)3 + P2O5 with iron oxide.
The presence of the more stable base CaO in the slag causes the replacement of FeO. As a result, it binds phosphorus anhydrite into another compound (CaO)4 x P2O5 + 4 Fe, which is what was required to be achieved.
Pure Fe was released in the melt, and phosphorus formed slag, which is removed from the metal surface and disposed of as unnecessary. Since phosphorus anhydride transforms the composition of the slag, the process must be continuous.
Therefore, FeO must be continuously replenished by loading new batches of iron ore and scale, which introduce ferrous slag into the melt.
How to solder with your own hands
It must be said that using a hot air gun for soldering plastic is not as easy to use as it might look from the outside, since polymers have different melting points. For polyvinyl chloride it is 150-220° C, for polypropylene – 160° C. Deviation to either side will result in poor welding of the butt joint or overheating, which will also have an unsatisfactory effect on the quality of the final result.
It is advisable for beginners to try soldering some rough material.
To solder thermoplastic polymer you will need:
- the hot air gun itself;
- a row of nozzles towards him;
- welding rod (tape).
Features of the second stage
The second stage of steel production technology is called steel boiling. The main purpose is to reduce the carbon content by percentage due to oxidation. FeO + C = CO + Fe.
The oxidation reaction occurs more intensely during boiling and is accompanied by heat absorption. Therefore, it is necessary to create a constant flow of heat into the bath, as well as to equalize the temperature in the melt.
During this oxidation reaction, carbon monoxide gas CO is intensively released, which causes rapid boiling in the liquid aggregate state, for this reason the process is called boiling. To ensure that excess carbon is more intensively converted into oxide, the production of high-quality steel involves injecting pure oxygen and adding scale to the molten structure. This is why the quality of raw materials for steel production is so important. All source materials undergo scrupulous testing.
It is important at this stage to remove sulfur, which improves the quality of the final steel. The sulfur used in the components is not present in direct form, but in the form of iron sulfide FeS.
At high temperatures, the component also reacts with CaO oxide, forming calcium sulfide CaS, which dissolves in the slag without combining with iron. This allows the sulfide to be easily removed outside the bath.
Converter steel production
What it is
A construction hair dryer is a fairly simple tool that is designed for working with polymers and other flexible materials. Using it, you can solder parts together. The tools themselves are divided into several varieties according to power and specifics of work, but the main element when soldering polymers is the nozzle for a hair dryer for soldering plastic.
This part also has a number of variations in shape and functional features. The nozzles are capable of changing the degree of heating jet and influencing other factors. To carry out such work, you need to understand the features of the main types and use them correctly.
Deoxidation
The third stage is metal deoxidation. After adding oxygen (at the previous stage), it is necessary to reduce its content in clean steel. Using O2, it was possible to achieve oxidation of impurities, but its residual presence in the final product reduces the quality characteristics of the metal. It is necessary to remove or convert FeO oxides by combining oxygen with other metals.
There are two deoxidation methods for this:
- diffusion;
- besieging.
With the diffusion method, additives are introduced into the molten composition: aluminum, ferromanganese and ferrosilicon. They reduce iron oxide and convert it into slag. In the slag, the oxide disintegrates and releases pure iron, which enters the melt. The second released element, oxygen, evaporates into the environment.
The precipitation method involves the introduction of additives that have a greater affinity for oxygen than Fe. These substances replace iron in the oxide. They, being less dense, float and are removed along with the slag.
The deoxidation process continues as the ingot solidifies, in the crystal structure of which iron oxide and carbon interact. As a result, it is removed along with nitrogen and hydrogen bubbles.
The more inclusions of various metals are removed during deoxidation, the higher the malleability of the resulting steel. To check, a hot piece of metal is forged; cracks should not form on it. This sample check indicates that the deoxidation process is being carried out correctly.
Depending on the degree of deoxidation, specialists can obtain:
- calm steel of complete deoxidation;
- boiling, not completely deoxidized steel, when the process of removing bubbles of carbon monoxide CO continues in the ladle and mold.
To obtain alloy steels with the addition of certain metals, ferroalloys or pure metals are added to the molten metal. If they do not oxidize (Ni, Co, Mo), then such additives can be introduced at any stage of smelting. Metals Si, Mn, Cr, Ti, which are more sensitive to oxidation, are added to the ladle or, as usually happens, to the mold for casting the metal.
There are basic methods for producing steel in steelmaking.
Open hearth method
This method is used to produce high-quality steels used in critical machine parts and precision mechanisms.
At one time, it replaced the labor-intensive and low-productivity crucible and pulding melts that had been used previously.
The loading capacity of one reverberatory furnace used in this method reaches 500 tons. A special feature of the open-hearth method is the ability to remelt not only pig iron, but also metallurgical waste and scrap metal.
The heating temperature of liquid steel reaches 2 thousand degrees. This result is achieved by the special design of the open hearth furnace:
- the use of additional heat from regenerators obtained by burning coke oven or blast furnace gas in a stream of hot air;
- reflections from the roof of the injected gas as a result of fuel combustion in it occurring above a bath of metal, which contributes to the rapid heating of the contents;
- using reversal of the heating flow.
An open hearth furnace consists of the following elements:
- working space with fire-resistant lining of walls and filling windows;
- hearths (bases) made of magnesite brick;
- furnace roof;
- furnace heads;
- slag for removing dust;
- regenerator with changeover valves.
The smelting process takes from 4 to 12 hours. In order to speed up the smelting process, the volume of pumped oxygen exceeds the requirements, which increases smelting productivity by 20–30%.
Converter method
Converters melt grades of steel for the production of automotive sheets, tool steel, welded structures and other steel blanks. They are inferior in quality to open-hearth ones and are used for the manufacture of less critical products.
They contain more impurities than in open-hearth production. Due to the high loading volume of one furnace, up to 900 tons, the method is considered the most productive, and therefore has become widespread.
The production of steel and other types of metal by this method is based on blowing liquid cast iron with air or oxygen under a pressure of 0.3–0.35 MPa, while the metal is heated to 1600 degrees. Melting is fleeting and lasts up to 20 minutes. During this time, oxidation occurs of carbon, silicon and manganese contained in the raw materials, which are extracted from the molten slag bath.
The converter is a retort-shaped (pear-shaped) vessel consisting of steel sheets with a lining on the inside. One hole is used to pour cast iron and release finished steel; cast iron and scrap are also loaded into it.
The Birth of Steel
Process Features
Together with them, slag-forming substances are loaded: lime and bauxite. The body is surrounded by a support ring attached to the pivot pins. With their help, the vessel is tilted and the finished steel is poured through this hole - the tap hole. Bottom blowing is carried out through through holes (tuyeres) made in the bottom of the furnace.
Historically, it has been the custom that the method used everywhere is called the Thomas or Bessemer method. In the last century, the open-hearth process became predominant. The regenerator is heated by purging furnace gases, after which it heats the cold air entering the melt.
In modern designs, the top method is more often used, in which blowing at high speed is carried out through nozzles lowered to the metal surface. In Russia, it is primarily the top blowing of furnaces that is used.
Being under a stream of air, cast iron intensively oxidizes in the contact zone. Since its concentration is much higher than other impurities, iron oxide is predominantly formed. But it dissolves in the slag. Therefore, the metal is enriched with the released oxygen.
C, Cr and Mn are oxidized, reducing the percentage in the metal structure. Oxidation is accompanied by the release of heat. Due to the presence of slags CaO and FeO before heating, phosphorus is removed at the very beginning of blowing.
The slag is merged with it and a new one is created. Steel production is accompanied by express analyzes and monitoring of current changes using control devices installed in the furnace. The phosphorus content in cast iron should not exceed 0.075%.
Terms of use
To improve quality and avoid mistakes, you need to follow certain rules of use. Compliance with the rules will protect you from problems with use and harm to health . These are the rules:
- During the process, you must maintain a safe distance between the nozzle and the object being processed, 25 cm or more. A shorter distance will reduce the coverage area and damage the coating.
- Before work, treat and clean the surface so that the solder lies more evenly. And after welding, remove defects; after hardening, this process can disrupt the integrity.
- A safe area from the air intake grille must always be maintained. Closing the grill can lead to critical overheating of the instrument, as well as its failure.
- During operation, the nozzle on the hair dryer for soldering plastic overheats greatly, so you can use the tool only with protective gloves that can withstand high temperatures.
Oxygen-converter method of steel production
Steel production today is carried out mainly in this way. BOF production recently accounted for up to 60% of global steel production.
However, this percentage is decreasing due to the advent of electric arc furnaces (EAFs). The furnaces are purged with pure oxygen (99.5%) under high pressure.
The product of an oxygen converter furnace is steel with specified chemical properties. It enters a continuous casting machine (CCM), where the material solidifies into a bloom or slab. To obtain certain stringent parameters, the metal is recycled.
Where is it used?
Today, hair dryers with attachments are used both at home and in large enterprises for a variety of tasks. The tool itself is not capable of performing many functions, but with a set of attachments the tool becomes universal and is used for:
- connections and processing of joints;
- repair of cracks, irregularities, deformations;
- soldering parts made of plastic, polymer film and other materials;
- roofing works;
- installation, repair, dismantling work in the automotive sector.
In addition to these tasks, a hair dryer with nozzles is capable of performing many other tasks where soft polymer materials are used and thermal effects are required.
Electric steelmaking method
Steel production by electric melting has a number of undeniable advantages. This method is considered the main one for the smelting of high-quality alloy steels.
The high temperature achieved in this case allows the smelting of steels containing refractory metals:
- molybdenum;
- tungsten;
- vanadium.
High quality is achieved by the virtual absence of phosphorus, sulfur and oxygen in steels. This method is also used to produce a wide range of construction steels.
The release of heat is not associated with the consumption of the oxidizer, but occurs as a result of the conversion of electrical energy into thermal energy. It is released during the passage of an electric arc or the induction of eddy currents. Depending on the principle of operation, furnaces are divided into electric arc and induction.
An electric arc furnace can simultaneously accept from 3.5 to 270 tons of raw materials:
- liquid steel from converters;
- scrap;
- iron ore.
It has several electrodes made of graphite-containing material, to which electrical voltage is applied. The melting time is up to 1.5 hours, while the arc temperature reaches 6 thousand degrees.
How to make a construction hair dryer and attachments for it with your own hands with drawings and videos
By choosing a kit with the additions that you need, you will really make full use of all the capabilities of your new gadget. Expensive professional kits with different types of attachments are recommended to be purchased either by those who work with hair, or by those who do not spare money on caring for their long hair.
- In the form of brushes
- Diffuser and its characteristics
- Types of diffuser
- Hub
Almost every girl has a hairdryer at home, which she uses to dry and style her hair. But not everyone knows that by adding attachments to this simple gadget, you can create many more interesting hairstyles and intricate curls. You will learn about what hair dryer attachments exist and how to use them correctly in this article.
- A pre-prepared rubber tube is placed on the handle of the hair dryer. This prevents hand burns from touching hot ceramics. For this purpose, you can use an old corrugation from a vacuum cleaner, rubberized on the inside and made of fabric on the outside. This material will reliably protect the worker.
Features of electric induction furnaces
In electric induction furnaces, steel is smelted in small volume (4.5–60 tons) containers called refractory crucibles. Around the crucible there is an inductor consisting of a large number of turns of wire.
When an alternating current passes inside, high-power eddy currents are induced, causing the contents of the crucible to melt. Electromagnetic forces simultaneously stir the molten steel. The duration of smelting in such furnaces does not exceed 45 minutes.
The electric steelmaking method produces little smoke, dust and emits less light energy. However, the high cost of electrical equipment with low capacity limits the use of this method.
Diagram of an electric furnace
In addition to the options discussed, there are not only basic methods of steel production. Modern steelmaking uses smelting in vacuum induction furnaces and enrichment of the percentage of iron in pellets by plasma-arc remelting.
Types of steel produced by chemical composition
The steel produced by these methods is divided, depending on the chemical composition, into two large groups:
- carbon;
- alloyed.
Percentage of elements in carbon steel:
| Name | Fe | WITH | Si | Mn | S | P |
| Content in percentage | up to 99.0 | 0,05–2,0 | 0,15–0,35 | 0,3–0,8 | up to 0.06 | up to 0.07 |
In carbon steels, strength is not sufficiently combined with ductility. The disadvantage is eliminated by introducing additives of other metals; such steel is called alloy steel.
According to GOST 5200, there are three groups of alloy steels with permissible impurity content:
- low alloy no more than 2.5%;
- medium alloyed in the range of 2.5–10%;
- highly alloyed over 10%.
Every year, smelting methods are improved thanks to the commissioning of new high-tech equipment. This allows the steel industry to produce high-quality steels with the optimal content of additives and metals.