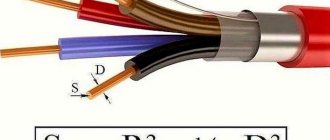
On the one hand, there is nothing simpler than calculating the area of any surface (vertical, horizontal). However, here you can find several nuances and some of them can lead to difficulties. Let's look at what's special about area calculations and look at a few examples. After reading this material, you will no longer float on this issue. At the same time, remember the school curriculum with its formulas.
It would seem that it could be simpler Source ar.aviarydecor.com
Why is it not so simple
So the question of how to calculate the area of any surface may seem funny, because we all went to school. But let's not be so categorical. Firstly, many of us left school a long time ago. Secondly, not every time in everyday life you have to deal with the need for geometric calculations. And some things have already been forgotten.
And thirdly, the surface does not always have the correct shape. Then you have to dodge, using more complex calculation techniques. It’s all simple with squares and rectangles, but what about trapezoids, triangles and other complex geometric shapes?
Types and technical properties of rolled sheets
1. Rolled metal thin sheets:
Interesting read: Homemade cutters for a metal lathe
2. Sheet metal in rolls:
3. Metal sheet with polymer coating (RAL).
For the production of iron sheets, depending on the rolling method in production, the following steel grades are used:
- Hot rolled iron sheets (GOST 19903-90):
- steel of normal properties: 3 sp/ps, 2 ps
- low alloy steel: 09G2S, 17G1S
- structural steel: 10, 20, 35, 40Х, 45, 65Г
- high-quality carbon steel, structural (08 kp/ps, 15 kp/ps, 25, 35, 45; 10 kp/ps, 20 kp/ps, 30, 40).
Necessity of calculations
Someone may ask the following question: “Actually, why do you need to calculate the area?” There are certain reasons for this:
- The data obtained will allow you to select the right amount of building materials so as not to overpay.
- By calculating the area, you can determine the volume of the room. And this is the main characteristic that cannot be avoided when choosing climate control equipment, heating devices or a ventilation system.
- Some utilities take into account the area of the premises.
- The choice of lighting fixtures, or rather their number, also depends on this calculated parameter.
For example, the amount of purchased laminate can be calculated only by knowing the area of the room Source bazazakonov.ru
Which measuring tools make calculations easier?
The following tools will be excellent helpers in calculations:
- piece of paper;
- pencil;
- roulette;
- square;
- building level (to determine height differences, evenness of walls);
- regular calculator.
It is better to take a tape measure with divisions in centimeters or meters. This will make it easier to find out the area. You don’t have to convert one unit of measurement to another several times.
A diagram of the room is drawn on a sheet of paper, the location of doors, windows, various ledges, a fireplace or stove (if any) is indicated, and the results of the measurements taken are noted.
An alternative to a building level will be a modern laser level, which can immediately mark the level of several walls and simultaneously show the overall picture.
If creating a drawing manually seems complicated, you can use 3D computer editors. To do this, the program must be installed on your computer. Great examples of such editors are SketchUp or AutoCAD. The first program is well suited for beginners, as it has simpler functionality and standard templates for popular shapes and objects. The program will help you perform the necessary calculations and give a visual picture of the room. This is an excellent option for buildings with complex geometry.
Where to start
It's time to remember school mathematics - to calculate the area, three parameters are needed:
- Length - usually it is 4 or 4.5 meters.
- Width – the standard value for most houses is 3 or 3.5 meters.
- Height - in new buildings it is usually 2.5 meters. But in buildings of the Stalin era it can be up to 3 meters.
In solving the problem of how to calculate the area, you cannot do without the appropriate tools :
- roulette;
- construction square;
- pencil;
- calculator;
- building level.
If you plan to write a lot, then instead of a piece of paper it is better to take a notepad or notebook. Leaves tend to get lost, and when you need them you don’t always find them later. The tape measure must have a lock, otherwise difficulties will arise and the calculation procedure will turn into real torture.
Accuracy
| Sample area | ||||
| Permission | 10 cm 2 | 3 cm 2 | 1 cm 2 | 0.3 cm 2 |
| 1 mm 2 | ± 2.0% | ± 3.0% | ± 6.0% | ± 10.0% |
| 0.1 mm 2 | ± 1.0% | ± 1.5% | ± 3.0% | ± 5.0% |
The design features of the device make it possible to achieve 99% reliability of results when calibrated on standard-shaped samples. Higher accuracy can be achieved by calibrating the Li-3100C and/or by positioning the sheet to be measured on the middle portion of the moving belt. When measuring the area of conifer needles, plant roots and other similar objects, set the device to a resolution of 0.1 mm 2. For this type of object, the measurement accuracy will be approximately 5% lower than when measuring the area of normal leaves.
Calculation algorithm
If everything is prepared, then you can proceed to the calculations themselves. If you need to calculate the surface area of the correct shape, then there is nothing complicated here - no one will forget these formulas.
No way without a tape measure Source sv.decorexpro.com
See also: Catalog of rectangular house projects
It's another matter when the wall, floor, ceiling have complex outlines. Here you will have to combine various techniques. That is, divide the room into several blocks, and then calculate the area of each of them. And then subtract or add them from the total area.
It is not at all necessary to measure the length of the walls strictly along the baseboards - the measurement can be carried out in any convenient place if, say, furniture is in the way. That is, higher, lower, in the middle, the main thing is to maintain a strict parallel to the floor and ceiling. No diagonals or slopes! Otherwise, the calculations will be incorrect.
If difficulties arise, you can always enlist the support of someone at home.
Correct geometry
There are no difficulties regarding how to calculate the area. In the case of a simple rectangle, it is enough to measure only two sides and the height, because in such a figure the opposite sides are equal. To make sure that the room has the correct outlines, it is enough to apply a construction square to the corners, although it is not always possible to get a clear picture.
The formula for calculating a rectangle is known to everyone:
S=a⋅b, where:
- S – calculated area;
- a – length;
- b – width.
It seems that it is impossible to forget the formula for the area of a rectangle, although some people succeed in this Source wezanu.ritobypus.ru.net
This formula is relevant for walls, ceilings, floors, doors, windows and other rectangular surfaces. In the case of planned repairs, it is important to obtain clean values. To do this, subtract the area of doors and windows from the area of the wall. The total area of the entire room can be calculated using the following formula - h(a⋅2+b⋅2). Where h is the height of the room.
With a square it’s even simpler - just measure one side and square its value.
Rooms with irregular outlines
But how to calculate the area of a room if it has irregularly shaped surfaces? There are some nuances here:
- Walls . In the attic room, the wall can be in the shape of a trapezoid or triangle.
- Ceiling . In the same attic rooms, this plane can be at a certain angle. There are also options with a broken surface, when several planes intersect with each other.
But there is nothing scary here and there is no need to delve into trigonometry. It is enough to visually divide any complex surface of walls or ceilings into several simple planes. After this, all that remains is to calculate the area of each figure and add them together.
The case is a little more complicated - but not much Source wezanu.ritobypus.ru.net
Mathematical methods for determining plant leaf area
MATHEMATICAL METHODS FOR DETERMINING AREA
PLANT LEAVES.
INTRODUCTION
The study of the vital processes of plant organisms involves measuring a large number of different indicators. Due to the need and possibility of a quantitative description of individual dependencies as components of a more complex system of connections, the interest of researchers in mathematical methods for calculating the values of various indicators, in particular the size of the assimilating system of plants (leaf surface area), has increased.
The leaf is the main assimilating organ of the plant, in which the bulk of organic substances are formed, serving as structural and energetic material for the entire organism. The area of an individual leaf and the total leaf surface of the plant make it possible to assess the photosynthetic potential and the intensity of its work.
Currently, much experience has been accumulated in determining the leaf area of various plant species using mathematical methods. Instruments (planimeters) have been developed to automatically determine leaf area, but the possibilities for their use are limited. Currently, a mathematical method based on measuring individual linear dimensions of leaves is becoming increasingly popular. In 1911, G. Montgomery proposed calculating the area of a sheet based on its linear dimensions.
The purpose of our work:
determining the leaf area of different amaranth varieties using simple mathematical calculations.
Research objectives
:
— review known methods for determining leaf area;
— master the method of determining leaf area using calculated coefficients;
— give specific practical recommendations for determining the leaf area of a non-traditional crop - amaranth.
The study of the vital processes of plant organisms involves measuring a large number of different indicators. Due to the need and possibility of a quantitative description of individual dependencies as components of a more complex system of connections, the interest of researchers in mathematical methods for calculating the values of various indicators, in particular the size of the assimilating system of plants (leaf surface area), has increased.
The leaf is the main assimilating organ of the plant, in which the bulk of organic substances are formed, serving as structural and energetic material for the entire organism. The area of an individual leaf and the total leaf surface of the plant make it possible to assess the photosynthetic potential and the intensity of its work.
Currently, much experience has been accumulated in determining the leaf area of various plant species using mathematical methods. Instruments (planimeters) have been developed to automatically determine leaf area, but the possibilities for their use are limited. Currently, a mathematical method based on measuring individual linear dimensions of leaves is becoming increasingly popular. In 1911, G. Montgomery proposed calculating the area of a sheet based on its linear dimensions.
The purpose of our work:
determining the leaf area of different amaranth varieties using simple mathematical calculations.
Research objectives
:
— review known methods for determining leaf area;
— master the method of determining leaf area using calculated coefficients;
— give specific practical recommendations for determining the leaf area of a non-traditional crop - amaranth.
1. METHODS FOR MEASURING LEAF AREA
1.1 Review of methods for determining sheet area
The scientific literature contains a large number of methods that, with varying degrees of accuracy, make it possible to determine the area of leaves: weight, planimetric, standard method, determination of area by the specific gravity of leaf cuttings, electrographic powder method.
The most widely used methods include gravimetric and planimetric. The use of a planimeter and the method for calculating leaf area with its help is carried out in strict accordance with the instructions supplied with the planimeter. When using the weight method to determine the area of a sheet, its outline is transferred to tracing paper, cut out and weighed. Then, knowing the mass of a square decimeter of tracing paper, the area of the sheet under study is calculated using the proportion.
Such numerous developments have several significant drawbacks - they are either labor-intensive and low-productivity, or their use is associated with the separation of leaves from the plant and the impossibility of further observation of them. Therefore, in addition to these methods, the mathematical method of calculating sheet area based on linear dimensions is gaining more and more attention. Two methods of such calculation are discussed in the literature: 1 - based on a conversion factor, 2 - through regression equations relating the leaf area to its linear dimensions (Markovskaya et al., 1988).
1.2. Determining sheet area using a conversion factor
The method is based on the correspondence between the shape of the leaf under study and the simplest geometric figure describing the leaf. The entire variety of leaves can be compared with four geometric figures (circle, ellipse, triangle and rectangle) to determine the areas of which well-known geometric formulas are used (Fig. 1).
Fig.1
Having determined the type of figure into which the sheet fits, you can calculate the proportionality coefficient between the actual area of the sheet, measured by one of the direct methods (planimetric or weight), and the area of this figure.
The rectangle is the most commonly used geometric shape, and the conversion factor is defined as the ratio of the actual area to the area of a rectangle with sides x, y:
K=S/L*W, (1)
where K is the coefficient; D – leaf length; W – sheet width; S – leaf area determined by one of the direct methods.
The variety of shapes of leaf blades suggests a wide variation in the choice of linear dimensions. In most cases, two indicators are used - length and width, which have a high correlation with leaf surface area. Some researchers have decided to further simplify the calculation of the calculated coefficient; I calculate it using one of the leaf parameters (length or width):
K=S/D2 (2)
К=S/Ш2 (3)
The size of the leaf sample, which varies from 20 to 100 or more, is of great importance for the accuracy of calculating the coefficient.
Currently, conversion factors have been determined for most agricultural crops; their values vary from 0.6 to 0.85 (Table 1).
Table 1. Examples of calculated coefficients for determining the leaf area of different plant species (according to literary sources)
| View | Coefficient (K) |
| Cowberry | 0,77 |
| Cabbage | 0,85 |
| Sunflower | 0,7 |
| Wheat (different varieties) | 0,57-0,82 |
| Beans | 0,68 |
The conversion factor method does not require complex computer technology. It is simple to use, making it easy to use in the field. And most importantly, when using this method, it is not necessary to destroy the leaves, which allows long-term observations of them, for example, to determine the change in leaf area during the development of the plant from the initial stages of development to death.
2. DETERMINATION OF CALCULATION COEFFICIENTS FOR DIFFERENT VARIETIES OF AMARANTH
2.1. Object and methodology of research.
The object of our research was amaranth plants, a non-traditional (new) agricultural crop (Fig. 2). Amaranth is often called the culture of the 21st century, as it has unique characteristics. This is an annual plant, capable of forming large biomass (up to 1000 c/ha) in a short time (2-2.5 months). Giant plants, reaching a height of 2-2.2 m, accumulate a lot of protein and biologically active substances in their organs (primarily leaves), which allows them to be used as valuable raw materials (feed, food and medicinal).
The Siberian Botanical Garden of Tomsk State University is introducing various varieties of amaranth into cultivation. In botanical research, it is necessary to know how new plant species develop in unusual conditions, how they react to various environmental factors (temperature, fertilizers, etc.). One of the most important indicators of the development of amaranth plants is the change in leaf surface area. Typically, three measurements of this parameter are carried out during the growing season (spring - autumn). Moreover, the determination of leaf area should be carried out without destroying them.
We tested the method for determining leaf area using a calculated coefficient on scarlet amaranth (variety Cherginsky). The sample of cut leaves was 100 pieces. For each sheet, the actual area was determined, and the length and width of the sheet were measured. The actual area was determined by the gravimetric method. We cut out the outline of the sheet on tracing paper and weigh it, calculate the mass of 1 dm2 of paper, then draw up the proportion and determine the actual area. Using well-known formulas (1, 2, 3), three variants of the calculated coefficient were determined - K1, K2, K3. For each coefficient, three samples of 100 values were obtained. The samples were subjected to statistical processing with the calculation of the average value (X) and the coefficient of variation (V, %). The obtained average values of various coefficients and the degree of their variation are given in Table 2.
Table 2. Options for calculation coefficients
| Odds options | X | V, % |
| K1 | 0,62 | 4,8 |
| K2 | 0,31 | 16,1 |
| K3 | 1,28 | 12,0 |
The accuracy of the experiment is assessed using the coefficient of variation (V), which in our experiment varies from 4.8 (for K1) to 16.1 (for K2). The smaller the coefficient of variation, the smaller the deviation of each sample value from the calculated mean (X).
Thus, the most accurate way to determine the area of amaranth leaves using design coefficients is to calculate the product of the length and width of the leaf using the following formula:
S= 0.62. (D.Sh)
This formula can be used to quickly and accurately determine the area of amaranth leaves without destroying them.
conclusions
Using this method allows you to observe changes in leaf area over a long period of time and determine an important physiological parameter - the rate of photosynthesis (the amount of organic matter accumulated by leaves over a certain period of time).
LITERATURE
, , Kurets methods for determining some biometric indicators in plants. – Petrozavodsk, 1988. – 35 p.
, , On determining the area of leaves of various types of wheat // Scientific reports of higher school. Biological Sciences. – 1985. – No. 5. – P. 105-108.
A simple solution to the issue
How to calculate a square meter of walls, ceiling or floor if you have no free time, especially when you are dealing with complex figures, but have the Internet? In this case, the task is significantly simplified. On the Internet you can find a bunch of online calculators that will carry out all the calculations in a few seconds. All you need to do is set the required parameters.
With an online calculator, calculating area is much easier Source doverie-mo.ru
For convenience, all measurements are indicated in different units of measurement, based on specific needs. With their help, any such calculator can easily calculate not only the area of premises, but also land plots. In addition, the obtained result can be converted to any other desired unit of measurement.
Areas of application
The area of a square with a side length of one meter is equal to a meter squared.
The Russian designation for a square meter is m², in the international system it is m². Used in the international systems of units SI, MTS, MKGSS.
The square meter as the basic unit of measurement is used in the following areas:
- construction and repair;
- interior design;
- sale/purchase of real estate;
- purchase/sale/rent of land plots.
In addition, it is found in the school curriculum in mathematics and physics.
Quadrature calculation is needed in the following cases:
- find out how much corrugated sheeting is needed to cover a garage or fence;
- determine the total consumption of building materials during the construction of a house, bathhouse or other building;
- calculate the number of paving slabs for flooring in the local area, alley;
- calculate the amount of wallpaper to decorate a room or an entire apartment;
- to simplify the determination of the consumption of roofing materials for roof decking;
- to understand how much plaster or putty will be needed for certain jobs.
The list is far from complete, since in the construction industry, many materials are usually measured in square meters.
It is also permissible to calculate the area of land that is in use in square meters. Sometimes you can find measurements in hundreds, acres. For large areas of land, it is more convenient to use square kilometers or hectares.