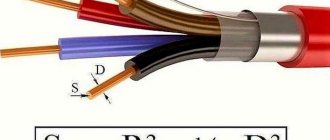
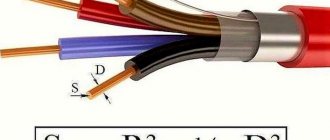
Any body through which electric current flows exhibits a certain resistance to it. The property of a conductor material to prevent electric current from passing through it is called electrical resistance.
The electronic theory explains the essence of the electrical resistance of metal conductors. Free electrons, when moving along a conductor, encounter atoms and other electrons on their way countless times and, interacting with them, inevitably lose part of their energy.
Electrons experience a kind of resistance to their movement. Different metal conductors, having different atomic structures, offer different resistance to electric current.
The same thing explains the resistance of liquid conductors and gases to the passage of electric current. However, we should not forget that in these substances it is not electrons, but charged particles of molecules that encounter resistance during their movement.
Resistance is denoted by the Latin letters R or r.
Ohm is the resistance of a column of mercury 106.3 cm high with a cross section of 1 mm 2 at a temperature of 0 ° C.
If, for example, the electrical resistance of a conductor is 4 ohms, then it is written like this: R = 4 ohms or r = 4 ohms.
To measure large resistances, a unit called megohm is used.
What kind of lighting do you prefer?
Built-in Chandelier
The greater the resistance of a conductor, the worse it conducts electric current, and, conversely, the lower the resistance of the conductor, the easier it is for electric current to pass through this conductor.
Consequently, to characterize a conductor (from the point of view of the passage of electric current through it), one can consider not only its resistance, but also the reciprocal of the resistance and called conductivity.
Electrical conductivity is the ability of a material to pass electric current through itself.
Since conductivity is the reciprocal of resistance, it is expressed as 1/ R, conductivity is denoted by the Latin letter g.
The influence of conductor material, its dimensions and ambient temperature on the value of electrical resistance
The resistance of various conductors depends on the material from which they are made. To characterize the electrical resistance of various materials, the concept of so-called resistivity has been introduced.
Specific resistance is the resistance of a conductor with a length of 1 m and a cross-sectional area of 1 mm 2. Resistivity is denoted by the letter p of the Greek alphabet. Each material from which a conductor is made has its own resistivity.
Expert opinion
It-Technology, Electrical power and electronics specialist
Ask questions to the “Specialist for modernization of energy generation systems”
Conductor cross-section as the most important criterion for choosing a wire In order to independently correctly calculate the cross-section or area of stranded wires, you must initially calculate the cross-section of each wire in the bundle, and then multiply the result by their total number. Ask, I'm in touch!
Cone sections
A cone is a figure of rotation of a right triangle around one of its legs. The cone has one top and a round base. Its parameters are also radius r and height h. An example of a cone made from paper is shown below.
There are several types of conic sections. Let's list them:
They replace each other if you increase the angle of inclination of the cutting plane relative to the circular base. The easiest way to write down the formulas for the cross-sectional area of a circular and triangular one.
A circular section is formed as a result of the intersection of a conical surface with a plane that is parallel to the base. The following formula is valid for its area:
Here z is the distance from the top of the figure to the formed section. It can be seen that if z = 0, then the plane passes only through the vertex, so the area S1 will be zero. Since z
Triangular is obtained when the plane intersects the figure along its axis of rotation. The shape of the resulting section will be an isosceles triangle, the sides of which are the diameter of the base and two generatrices of the cone. How to find the cross-sectional area of a triangular? The answer to this question will be the following formula:
This equality is obtained if we apply the formula for the area of an arbitrary triangle through the length of its base and height.
Electrical resistance of conductors » School for an electrician: electrical engineering and electronics
The resistance of a conductor is directly proportional to its length, i.e. the longer the conductor, the greater its electrical resistance.
Expert opinion
It-Technology, Electrical power and electronics specialist
Ask questions to the “Specialist for modernization of energy generation systems”
Cross-sectional area of a conductor: how to find the area using the formula This formula makes it possible to determine the length of the conductor, its cross-section and resistivity if the other quantities included in the formula are known. Ask, I'm in touch!
Calculation formulas
When carrying out calculations, it must be taken into account that the pipes are essentially cylindrical. Therefore, to find their cross-sectional area, you can use the geometric formula for the area of a circle. Knowing the outer diameter of the pipe and the thickness of its walls, you can find the internal diameter indicator that will be needed for calculations.
The standard formula for the area of a circle is:
S=π×R2, where
π – constant number equal to 3.14;
R – radius value;
S is the cross-sectional area of the pipe, calculated for the internal diameter.
Selection by table
Knowing the diameter of the wire, you can determine its cross-section using a ready-made dependence table. The table for calculating the cable cross-section by core diameter looks like this:
| Conductor diameter, mm | Conductor cross-section, mm2 |
| 0.8 | 0.5 |
| 1 | 0.75 |
| 1.1 | 1 |
| 1.2 | 1.2 |
| 1.4 | 1.5 |
| 1.6 | 2 |
| 1.8 | 2.5 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 2.3 | 4 |
| 2.5 | 5 |
| 2.8 | 6 |
| 3.2 | 8 |
| 3.6 | 10 |
| 4.5 | 16 |
When the cross-section is known, it is possible to determine the permissible power and current values for copper or aluminum wire. In this way, it will be possible to find out what load parameters the current-carrying core is designed for. To do this, you will need a table of the dependence of the cross section on the maximum current and power.
Converting watts to kilowatts
In order to correctly use the table of wire cross-section versus power, it is important to correctly convert watts to kilowatts.
1 kilowatt = 1000 watts. Accordingly, to obtain the value in kilowatts, the power in watts must be divided by 1000. For example, 4300 W = 4.3 kW.
Some special cases of simplifications
If the drawing shows sections, sections, views for regularly changing surfaces, they can be broken. This is done in a certain way. There are three restriction options.
The first type involves using a solid thin broken line. It can extend beyond the image border by 2-4 mm. Also, the outline of parts of a part can be connected by a solid wavy line or hatching.
To simplify the drawing, it is allowed to cut with a dotted line between the cutting plane and the observer. Complex slices are also used to improve understanding of graphics.
When depicting the holes of some parts (gear hubs, keyways, pulleys), only their outline is given. If the recess located on the round flange does not fall into the cutting plane, it is depicted in a section.
If there is an ornament or a continuous mesh on a part, it is allowed to depict only a small part of it or to simplify the elements of the design.
Such methods allow you to achieve purity of the drawing and make it easier to understand. After all, the use of engineering graphics to create all kinds of objects implies the use of a single symbolic language. Every specialist whose work involves this type of image should know it. The quality of the final result depends on this.
Having studied the types of sections, you can understand the basic principles of their implementation and understanding. By applying the recommendations of the standards, you can achieve good cleanliness of the drawing. This makes the process of its interpretation easier. Understanding the difference between view, section and section, knowing their classifications and the technology for correct drawing, a specialist can create the correct image. It can be easily understood by the technician who produces the workpiece or finished product, and will be able to create units and parts that meet all the requirements. The quality of the entire production depends on this process.
Diameter and cross-section of wires in the table
At first glance, the use of such tables is not advisable, since the conductor tag indicates its main parameters, however, there are certain subtleties here too. The fact is that the parameters declared by the manufacturer do not always correspond to reality, but the parameters given in the table are absolutely objective.
If, when measuring the diameter, the result given in the table does not differ significantly from the declared one, then you are dealing with a high-quality wire, but there are cases when the cross-sectional area does not correspond to the measured diameter of the wire, in this case, using the table will allow you to avoid purchasing a low-quality cable.
Expert opinion
It-Technology, Electrical power and electronics specialist
Ask questions to the “Specialist for modernization of energy generation systems”
Wire cross-section and diameter: table | Advice from experts In order to avoid such unpleasant situations, it would be a good idea to measure the diameter of the core yourself before purchasing a wire and make sure that the declared characteristics correspond to the actual ones. Ask, I'm in touch!
Designation options
The concept is used not only in mathematics. It is also relevant for physics.
Due to the versatility of the application, the question arises as to which letter denotes the area.
Depending on the discipline within which the concept being studied is applied, the answer becomes obvious which letter of the alphabet denotes this value.
In sciences such as physics and mathematics, the Latin alphabet sign S is used. This letter is pronounced {es}.
Note! The sign S denotes the area of such figures as a square, triangle, rhombus, rectangle, circle.
Among the questions occupying the minds of students of higher educational institutions, there is a topic: how to designate a given value of several geometric objects. In this case, in the written version, subscripts are used. Among the values used in the index notation system are numbers.
An example is the designation S1, S2, S3. It is also considered acceptable to use abbreviated names of geometric objects in relation to which numerical measurements are made. Thus, when studying triangles, the names of the vertices, indicated in Latin letters, are used for the abbreviated name. Examples would be SAOB, SCLE, SOME.
Interesting! What does vertical mean and what does a vertical line look like?
A relevant question for students is how area is written in physics. It should be noted that this concept characterizes a cross section. It is considered acceptable to use a subscript for a more precise designation. It is still possible to write prime numbers in the index system.
The question of how this quantity is written in structural mechanics and strength of materials makes students think. In these disciplines, the letter S of the Latin alphabet means a designation of static moment. This is how the area is expressed relative to the axis under consideration. The symbol denoting this indicator is a letter of the Latin alphabet A or F.
Tensile strength and tensile elongation
When choosing wires, in addition to the cross-section, wire material, and insulation, it is necessary to take into account their mechanical strength. This is especially true for overhead power lines. The wires are stretched. Under the influence of force applied to the material, the latter elongates. If we denote the initial length as l1 and the final length as l2, then the difference l1 – l2 = Δl will be the absolute elongation.
Attitude
called relative elongation.
The force that produces a rupture of a material is called the breaking load, and the ratio of this load to the cross-sectional area of the material at the moment of destruction is called the temporary tensile strength and is denoted
Data on tensile strengths for various materials are given below.
Tensile strength value for various metals
| Name of metal | Tensile strength, kg/mm² |
| Aluminum Aldrey Bronze Tungsten Gold Brass Copper Molybdenum Nickel Tin Platinum Mercury Steel Silver Lead Zinc Cast Iron | 8 – 25 30 – 38 31 – 135 100 – 300 – 30 – 70 27 – 44,9 80 – 250 40 – 70 2 – 5 15 – 35 – 70 – 75 15 – 30 0,95 – 2,0 14 – 29 12 – 32 |
General information
Area is the size of a geometric figure in two-dimensional space. It is used in mathematics, medicine, engineering and other sciences, for example in calculating the cross-section of cells, atoms, or pipes such as blood vessels or water pipes. In geography, area is used to compare the sizes of cities, lakes, countries, and other geographic features. Population density calculations also use area. Population density is defined as the number of people per unit area.
Read also: Calculation of the gear ratio of a planetary gearbox
Interesting facts about the square
Theorem on properties of areas
According to the isoperimetric theorem, of all figures with the same perimeter, the circle has the largest area. If, on the contrary, we compare figures with the same area, then the circle has the smallest perimeter. The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of the sides of a geometric figure, or the line that marks the boundaries of this figure.
Geographical features with the largest area
Country: Russia, 17,098,242 square kilometers, including land and water. The second and third largest countries by area are Canada and China.
City: New York is the city with the largest area of 8683 square kilometers. The second largest city by area is Tokyo, occupying 6,993 square kilometers. The third is Chicago, with an area of 5,498 square kilometers.
City Square: The largest square, covering 1 square kilometer, is located in the capital of Indonesia, Jakarta. This is Medan Merdeka Square. The second largest area, at 0.57 square kilometers, is Praça doz Girascoes in the city of Palmas, Brazil. The third largest is Tiananmen Square in China, 0.44 square kilometers.
Lake: Geographers debate whether the Caspian Sea is a lake, but if so, it is the largest lake in the world with an area of 371,000 square kilometers. The second largest lake by area is Lake Superior in North America. It is one of the lakes of the Great Lakes system; its area is 82,414 square kilometers. The third largest lake by area is Lake Victoria in Africa. It covers an area of 69,485 square kilometers.
You can hide articles if you use the converter frequently. Cookies must be allowed in the browser.
You may also be interested in other converters from the “Popular unit converters” group:
Do you find it difficult to translate units of measurement from one language to another? Colleagues are ready to help you. Post a question in TCTerms
and within a few minutes you will receive an answer.
Popular unit converters
Area converter
Square
- a numerical characteristic of a two-dimensional flat or curved geometric figure, showing the size of this figure. Units of length are used to measure area. Thus, area can be measured in square meters, square centimeters, square millimeters, square kilometers, square feet, square inches, square miles, square versts, tithes and square fathoms.
Read also: How to coat metal against corrosion
Features of electrical wires
The most widely used brands of wires are PUNP and PUGNP, as well as VPP, PHCB and PKGM, which have the following basic technical characteristics that are very important for obtaining a safe connection:
- PUNP is a flat wire product of the installation or so-called installation type, with single-wire copper conductors in PVC insulation. This type is distinguished by the number of cores, as well as a rated voltage within 250 V with a frequency of 50 Hz and an operating temperature from minus 15 °C to plus 50 °C;
- PUGNP is a flexible type with multi-wire conductors. The main indicators, which are represented by the nominal voltage level, frequency and temperature operating conditions, do not differ from similar data from PUNP;
- APB is an aluminum single-core variety, a round wire with protective PVC insulation and a single-wire or multi-wire core. The difference between this type is its resistance to mechanical damage, vibration and chemical compounds. The operating temperature ranges from minus 50 °C to plus 70 °C;
- PBC is a stranded copper variety with PBX insulation, which gives the wire high density and a traditional round shape. The heat-resistant core is designed for a nominal level of 380 V at a frequency of 50 Hz;
- PKGM is a power mounting type, represented by a single-core copper wire with silicone rubber or fiberglass insulation impregnated with a heat-resistant compound. The operating temperature ranges from minus 60 °C to plus 180 °C;
- PHCB is a single-core heating type in the form of a single-wire wire based on galvanized or blued steel. Operating temperature ranges from minus 50 °C to plus 80 °C;
- The runway is a single-core copper variety with a stranded core and PBX or polyethylene insulation. The operating temperature ranges from minus 40 °C to plus 80 °C.
In conditions of low power, copper wire ШВП with protective external PBX insulation is used. The stranded core has excellent flexibility, and the wire product itself is designed for a maximum of 380 V, with a frequency within 50 Hz.
Wire products of the most common types are sold in coils, and most often have white insulation.
Area calculation
The area of the simplest geometric figures is found by comparing them with the square of a known area. This is convenient because the area of the square is easy to calculate. Some formulas for calculating the area of geometric figures given below were obtained in this way. Also, to calculate the area, especially of a polygon, the figure is divided into triangles, the area of each triangle is calculated using the formula, and then added. The area of more complex figures is calculated using mathematical analysis.
Formulas for calculating area
- Square:
side in a square. - Rectangle:
product of sides. - Triangle (side and height known):
the product of the side and the height (the distance from that side to the edge), divided in half.
Formula: A = ½ah
, where
A
is area,
a
is side, and
h
is height. - Triangle (two sides and the angle between them are known):
the product of the sides and the sine of the angle between them, divided in half.
Formula: A = ½ab
sin(α), where
A
is the area,
a
and
b
are the sides, and α is the angle between them. - Equilateral triangle:
side squared divided by 4 and multiplied by the square root of three. - Parallelogram:
the product of a side and the height measured from that side to the opposite side. - Trapezoid:
The sum of two parallel sides multiplied by the height and divided by two. The height is measured between these two sides. - Circle:
product of the square of the radius and π. - Ellipse:
product of semi-axes and π.
Read also: Double-sided automatic submerged arc welding
Surface Area Calculation
You can find the surface area of simple volumetric figures, such as prisms, by unfolding this figure on a plane. It is impossible to obtain a development of the ball in this way. The surface area of a sphere is found using the formula by multiplying the square of the radius by 4π. From this formula it follows that the area of a circle is four times less than the surface area of a ball with the same radius.
Surface areas of some astronomical objects: Sun - 6,088 x 10¹² square kilometers; Earth - 5.1 x 10⁸; thus, the surface area of the Earth is approximately 12 times smaller than the surface area of the Sun. The Moon's surface area is approximately 3.793 x 10⁷ square kilometers, which is about 13 times smaller than the Earth's surface area.
Planimeter
The area can also be calculated using a special device - a planimeter. There are several types of this device, for example polar and linear. Also, planimeters can be analog and digital. In addition to other functions, digital planimeters can be scaled, making it easier to measure features on a map. The planimeter measures the distance traveled around the perimeter of the object being measured, as well as the direction. The distance traveled by the planimeter parallel to its axis is not measured. These devices are used in medicine, biology, technology, and agriculture.
Simplifications
Images (types, sections, sections) can be simplified to make them easier to understand. Standards and norms regulate this process.
For symmetrical figures, it is allowed to draw only one half of the cut or most of it, drawing a break line. When an object has several identical elements, only one of them is drawn. The remaining identical parts are drawn schematically.
Projections of intersection lines may be depicted in a simplified manner. But only if their detailed image is not required.
When drawing simple figures, for example, if you need to consider the types of sections of a cone, you use a certain approach to graphics. This makes the drawings easier to understand. When one surface changes in a particular pattern, it can be interrupted.
If one surface smoothly passes into another, their boundary is not indicated or is indicated conditionally.
Non-hollow symmetrical parts and products in the drawing are shown uncut in a longitudinal section. And if the size of a part of the product in the drawing is less than 2 mm, it is depicted with a deviation from the main scale.
To indicate flat surfaces, diagonals can be drawn with solid lines.
It should also be taken into account that permanent connections of electrical or radio devices are simplified by standards corresponding to the type of product. These are the main simplifications that are regulated by the Unified System of Design Documentation. They are most often used to create drawings in large industries, where it is necessary to depict complex parts, assemblies or mechanisms.