“ANO-4” electrodes are very popular among both professionals and novice welders. As a basis for them, welding wire SV-08 (A) is used. It has carbon in its composition and provides excellent welding properties.
This type of electrodes is produced by many enterprises, including SZSM, Paton, Kirov Plant, etc. Most of these manufacturers have extensive dealer networks. This means that their products can be found in almost every corner of the country.
“ANO-4” has all the necessary quality certificates. They are tested and run on test benches. This makes it possible to constantly improve their quality and properties.
Marking, decoding, UD
ANO-4 electrodes have the following designation (marking) – E46-ANO-4-Ø-UD E 43 0(2)-P25, where:
- E46 – type of electrode for arc welding of steels with tensile strength up to 46 kgf/mm2;
- ANO-4 – electrode brand;
- Ø – rod diameter in mm;
- purpose – U – for welding carbon and low-alloy steels with tensile strength up to 451 MPa;
- coating thickness – D – thick coating;
- E – international designation of a consumable coated electrode;
- tensile strength – 43 – 430 MPa;
- relative elongation – 0 – less than 20%;
- minimum temperature at which the impact strength of the weld metal is at least 34 J/cm2 – 2 – 0°C;
- type of coating – R – rutile;
- spatial positions of the electrode at which welding is carried out - 2 - everything except vertical top-down;
- welding current and no-load voltage – 5 – direct or alternating current of any polarity, no-load voltage 70V.
Peculiarities
The surface of AHO-4 electrodes is coated with rutile. Its main component is titanium dioxide (TiO2). This composition:
- provides the opportunity to obtain a high-quality weld;
- does not produce harmful substances during combustion. Thanks to this, AHO-4 electrodes are one of the safest for the health of the welder.
In addition, the composition of the coating ensures easy initial and re-ignition of the electric arc. The weld metal is characterized by high resistance to pore formation. And the resulting slag crust is simply separated. Consumables of the AHO-4 brand weld metal on the surface of which there is rust, slight dirt and moisture.
Packaging, how many pieces, weight and length of rods
ANO-4 electrodes are produced in cardboard packs, the weight of which is 1; 2.5 and 5 kg.
Average number of electrodes per 1 kg. varies depending on the diameter of the rods and is:
- 3.0 mm. – 39 pieces;
- 4,0 – 16;
- 5,0 – 11.
Depending on the diameter of the rod, the weight and length of the rod .
| Diameter, mm. | Length, mm. | Weight, g. |
| 2,5 | 350 | 18-19 |
| 3,0 | 350 | 25-26 |
| 4,0 | 450 | 58-59 |
| 5,0 | 450 | 91-92 |
| 6,0 | 450 | 137-138 |
Characteristics
Welding with AHO-4 electrodes can be carried out using any current - both alternating and direct - with direct and reverse polarity. These products have the following characteristics:
- deposition coefficient value – 8.30 grams/Ampere-hour;
- good deposition performance. The value of this parameter directly depends on the diameter (designation Ø) of the electrode. For the most popular product with Ø=4.0 mm, the surfacing productivity is 1.4 kg/hour;
- to fuse one kilogram of metal, 1.7 kilograms of consumables are required.
The weld formed by AHO-4 electrodes has the mechanical properties presented below.
- Impact strength value: α=140 Joule/sq. cm.
- Elongation value: δ=25%.
- Indicator of temporary resistance of the metal of the formed weld: γ = 490.0 MPa.
The chemical composition (typical) of the metal deposited with AHO-4 electrodes looks like this: element
- P (phosphorus) – 0.033%;
- S (sulfur) – 0.025%;
- Si (silicon) – 0.15%;
- Mn (manganese) – 0.52%;
- C (carbon) – 0.1%.
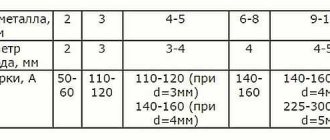
The current strength (designation It.) when carrying out welding work with AHO-4 electrodes depends on their diameter (designation De.) and length (Le.). So, with:
- De.=5.0 mm and Le.=450.0 mm, the current strength takes values within the limits of 150.0 A≤It.≤230.0 A. One kilogram contains on average 11 pieces of products with these dimensions;
- De.=4.0 mm and Le.=450.0 mm, the current strength can vary in the range of 120.0 A≤It.≤180.0 A; The average number of electrodes of this size in one kilogram is 16 pieces.
- De.=3.0 mm and Le.=350.0 mm, the current strength fluctuates within 80.0 A≤It.≤150.0 A. On average, the number of products of this standard size in one kilogram is 39 pieces.
Consumption, consumption rates
Electrode consumption is provided in reference format. For ANO-4 brand rods, consumption per 1 kg. deposited metal is 1.6-1.7 kg.
Official documents VSN 452-84 or VSN 416-81 (“Departmental Construction Standards”) also indicate production standards per 1 joint and per 1 meter of seam . These indicators are shown in the form of tables.
It is also possible to calculate the norm yourself. Consumption consists of the mass of deposited metal and losses. First you need to calculate the mass of deposited metal using the formula:
Mass = weld cross-sectional area x metal density x weld length
Density values can be found in reference literature. Then, using the second formula, the total consumption of electrodes during welding is calculated:
Consumption rate = mass of deposited metal x consumption coefficient
The consumption coefficient depends on the specific brand of electrode; for ANO-4 it is 1.7.
These data are provided in regulatory documents such as VSN 452-84. Reference. There are also other methods for calculating the consumption rate.
How to properly weld with AHO-4 electrodes
AHO-4 electrodes, on the surface of which a rutile-carbonate coating is applied, allow welding work at high conditions. Professionals recommend welding with a short or medium arc. When performing this procedure, the following points must be taken into account:
- if the coating is moistened, the electrodes must be dried at a temperature (designation T) varying within 160℃≤T≤180℃;
- to guarantee a high-quality result, all contamination must be removed from the edges of the mating plates before welding;
- welding of the root of the seam must be performed with electrodes with d=3.0 mm and d=2.5 mm. Upon completion of this operation, it is recommended to remove the solidified slag as thoroughly as possible, as well as part of the deposited metal. You can use a grinding wheel for this. Thanks to this, it will be easier in the future to monitor the correct formation of filling joints, which will eliminate their slagging. To increase the ability to control the weld pool, the part being welded must be given as small an inclination as possible (about 5°-7°) in the direction of movement of the electrode;
- You need to weld the filling layers with consumables with d=4.0 mm and d=3.0 mm. In this case, it is necessary to avoid cutting the edges of the mating parts; the formation of narrow grooves-slots between the edges of the plates and rollers.
This approach will prevent the formation of slag pockets.
A few words about the features of groove welding with AHO-4 electrodes. During this operation, the following points must be taken into account:
Welding with a medium arc in its afterburner mode will allow you to avoid slagging. Modern welding inverters have an “Arc force” regulator for this purpose.
If slag inclusions do appear, they must be removed before surfacing the next weld;
When T-type connections are welded, the welding current must not be allowed to exceed the values recommended by the electrode manufacturer. This is accompanied by:
- strong splashing of molten metal;
- formation of undercuts;
In addition, it will be difficult to remove the resulting slag crust;
When welding with direct current, AHO-4 electrodes exhibit increased sensitivity to a phenomenon known as “Magnetic Blast”. Its main features are as follows:
- strong splashing;
- formation of a kind of visor on the consumable welding element;
- spontaneous deflection of the electric arc, preventing the formation of a weld pool.
To level out this phenomenon, professionals recommend securing the return wire as close as possible to the place where welding is being carried out; form more potholders; weld with alternating current.
Advantages of the elements
Electrodes of the TsCh-4 brand have a number of functional advantages, among which the following can be distinguished:
- They allow you to weld objects/structures made of cast iron, as well as together – from cast iron and steel, which is impossible with the help of many other brands of electrodes.
- They are characterized by simplified ignition and stable combustion of the welding arc, which results in a uniform, strong connection of the parts being welded.
- The chemical composition is selected in such a way that it is possible to work with different types of cast iron.
- Versatile. They are used equally effectively in both the down and corner positions, both for cold welding (without heating) and for hot welding (at temperatures above 250°C).
- They perfectly eliminate defects and do an excellent job with preparatory deposition on parts from the 1st to the 2nd layer.
- During the welding process, metal is formed in the seam with virtually no metal spattering.
- Available for purchase.
When used correctly, these electrodes guarantee a strong welded connection with an even and durable seam. Moreover, they are suitable for both industrial use and home use.
Electrodes of this brand perform well in combination with modern welding machines.
Storage rules
Electrodes are supplied to customers in packages with film thermal protection. Inadequate storage can minimize this security. Therefore, these products must be stored in rooms with a temperature not lower than +15°C and a minimum level of humidity.
It is necessary to provide reliable protection against accidental falls of other objects onto stored rods or from falling off warehouse shelves. Mechanical damage compromises the integrity of the coating, which can negatively affect the quality of welding.
Types and purpose of welding electrodes
With welding you can:
- connect metal parts;
- manufacture metal structures of any size;
- cut metal;
- eliminate cracks;
- cut round and shaped holes;
- weld metal to restore wear areas;
- carry out repairs and other types of work.
The industry produces many types of electrodes, about two hundred of them. Each of them is most effective within the limited characteristics of these works, so the choice of electrodes for welding is a very important step. It should be done after thoroughly studying the topic or with the help of specialists.
The criteria for selecting electrodes are the design parameters, characteristics and purpose specified by the product manufacturer. The main ones are:
- electrode brand;
- appointment;
- core diameter;
- type of electrode coating;
- electrode length;
- the magnitude of the working current;
- type of current and polarity of connection;
- composition of the central rod;
- welding position;
- special technological characteristics of the welding process.
Dependence of electrode metal transfer on coating thickness
The mechanical characteristics of the deposited metal and its chemical composition are significantly influenced by the thickness of the coating. A somewhat different situation is observed with the welding and technological properties of electrodes. They are largely determined by the Rod Metal Transfer Indicators (hereinafter abbreviated as PPMS) of the consumable elements themselves. Below are the results of research related to this technical attack, posted on the World Wide Web in free access.
To study the degree of influence of the thickness of the coating on the PPMS when performing welding work with electrodes, including AHO-4, high-speed X-ray filming was used.
The experimental conditions were as follows:
- the samples under study were electrodes with rods with a diameter of d=4.0 mm, made from welding wire of the Sv-08 grade;
- the coating mass coefficient (designation Km.p.) was regulated by changing the diameter of the calibrating sleeve/bushing;
- upon completion of crimping followed by drying in open atmospheric air, the electrodes were calcined at a temperature of T = 200℃;
- welding was carried out using constant reverse current. The value of this parameter was selected so that droplet transfer of metal was carried out;
One peculiarity was observed in the AHO-4 electrodes. “Fog-like” metal transfer (meaning tiny drops) was achieved when the current strength (It) exceeded 220A-230A. For comparison: for products of the TsM-7 brand with d=4.0 mm, this phenomenon was observed at 116 A≤It≤170 A.
The results of processing X-ray films regarding the metal transfer parameters of AHO-4 electrodes are presented in the table.
| Reverse current welding mode | Km.p. | PPMS parameter | |||||
| U | It. | Θch.p., sec-1 | μ | Vk.n.p., g | Vp.f.k, g | In, g | |
| 24,0 | 195,0 | 64,2 | 3,22 | 0,42 | 0,26 | 0,15 | 0,11 |
| 25,5 | 200,0 | 53,0 | 4,54 | 0,39 | 0,21 | 0,13 | 0,08 |
| 36,2 | 4,9 | 0,42 | 0,2 | 0,12 | |||
| 26,0 | 190,0 | 19,6 | 4,08 | 0,43 | 0,22 | 0,13 | 0,09 |
| 24,5 | 195,0 | 4,5 | 3,68 | —— | —— | —— | 0,06 |
| 26,5 | 135,0 | 0 | 1,8 | 0,17 | 0,49 | 0,41 | 0,08 |
The following designations are used in the table:
- U – electric arc voltage;
- W is the weight of the droplet residue located at the end of the electrode in a liquid state of aggregation;
- Vp.f.k – weight of the transferred fragment of a drop;
- Vk.n.p.p. is the weight of the drop immediately before the transition;
- μ – part of the liquid residue. Calculated by the formula μ= Во/ Вк.н.п.п.;
- Θch.p. – transition frequency.
In drops of metal from AHO-4 electrodes, as the thickness of the coating increases, the content of the element O2 (oxygen) decreases. And, conversely, under this condition, the parameter Vk.n.p.p. increases. Moreover, on forward current it increases faster compared to reverse current. Experts interpret this phenomenon as follows: the weight of a drop retained at the end of the rod of the consumable element is a parameter derived from the influence of many forces, the main of which are surface tension and electrodynamic forces.