Among non-destructive methods for checking the reliability of welded joints, magnetic particle testing occupies a leading position. This is due to the fact that magnetic particle flaw detection does not require expensive and complex equipment, which requires serious training to operate. This inspection method detects surface and hidden defects. Using a flaw detector, the condition of seams in hard-to-reach places and at heights is assessed. The prevalence of magnetic particle testing of joints formed by welding is explained by the clarity of the results. Flaw detectors have a high degree of detection of defects that reduce the strength of supporting metal structures, high-pressure vessels, process tanks, and pipelines.
Definition and features of the method
Knowing the school physics course, it is easy to imagine the essence of determining defects. All materials are divided into two groups: conducting electrons and dielectrics. The principle of the magnetic particle non-destructive testing method is based on the distortion of the pattern of magnetic lines around discontinuities that arise during welding. If fistulas or cracks form in the diffuse layer or thermally affected zone, the lines of force change direction and bend around obstacles.
In areas with defects, the lines form a peak that extends beyond the part. If small particles of ferromagnetic materials are present at the distortion sites, they will change their spatial position and be oriented in the direction of the magnetic field lines.
The greater the inhomogeneity of the field above the defect, the stronger the resulting electromagnetic force that moves the magnetized particles. Chains of particles are formed in the defect area. Only if the discontinuity is located at right angles to the field direction will it not be visible from the position of the particles.
Other methods of acoustic flaw detection:
— An acoustic emission flaw detector is based on the reception and analysis of acoustic emission waves that arise in a product when cracks develop during loading. — A velocimetric flaw detector is based on measuring changes in the speed of propagation of elastic waves in the area where defects are located in multilayer structures, and is used to detect areas of adhesion between metal layers. — An acoustic-topographic flaw detector is based on excitation of powerful bending vibrations of a given (in the first version of the method) or continuously changing (in the second version) frequency in the controlled product with simultaneous visualization of the vibration pattern of the surface of the product, for example. by applying a fine powder to this surface. With sufficiently strong vibrations of the surface of the product with a given frequency, powder particles from places that do not belong to the nodes gradually shift to the vibration nodes, drawing a picture of the distribution of nodal lines on the surface. For a defect-free isotropic material, this picture is clear and continuous. In the defect zone, the picture changes: nodal lines are distorted in the place where inclusions are present, as well as in areas characterized by mechanical anisotropy. properties, or are interrupted in the presence of delamination. If the second version of the method is used, then in the presence of delamination, the section of the upper layer of the product located above it is considered as an oscillating diaphragm fixed at the edge; at the moment of resonance, the amplitude of its oscillations increases sharply, and the powder particles move to the boundaries of the defective zone, outlining it with great accuracy. The flaw detector operates at frequencies of 30–200 kHz. The sensitivity of the method is very high: in a multilayer product with a top sheet thickness of 0.25 mm, defects with a length of 1-1.5 mm are detected. There is no dead zone, scanning is not required - the emitter is pressed against the surface of the product at one point.
Magnetic particle testing technology
The sequence of operations for all welded joints is the same. The magnetic particle method is regulated by the standard. Sequencing:
- Surface preparation consists of cleaning the seam and heat-affected zone from scale, traces of rust, dirt, and traces of lubricants. To ensure clarity of the control pattern, dark metals are coated with white water-based paint, and the layer is made thin.
- To carry out magnetic powder flaw detection, the workpieces are magnetized (methods are listed in a separate section). The sensitivity of testing depends on magnetization in flaw detection.
- An indicator with ferromagnetic particles is applied in a way that depends on the type of flaw detection devices.
- Inspection of the controlled area, if necessary, is carried out using optics and devices required by regulations.
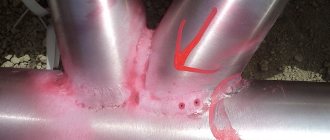
- Interpretation of the indicator pattern obtained during magnetic particle flaw detection is carried out with the fixation of defects after the unchanged position of the indicator particles. The inspector deciphers the drawing, comparing it with photographs from the atlas of defects. The data is entered into a log.
- Demagnetization is the final operation. The parts are exposed to a magnetic field with a damped amplitude or heated to the Curie point. Demagnetization control is mandatory during flaw detection.
- Remains of the magnetic particle indicator are removed manually or using wiping compounds.
Methods of applying the indicator
For magnetic powder testing, dry, wet, and paste-like indicators are used. Dry is a mixture of fine metal filings; it is applied to the surface in its natural state, without adding liquids.
The dry flaw detection method is effective for detecting discontinuities, slag inclusions on the surface or subsurface type defects. For the manufacture of magnetic particle indicators, iron scale, babbitt, magnetite, and other highly magnetizable materials are used. The field in the welded workpiece is created by a U-shaped electromagnet connected to a source of direct or alternating current with a power of 300 to 600 amperes. The ferromagnetic mixture is applied from an aerosol package, dispersed by a sieve, and directed by a bulb.
In wet indicators, magnetizable particles are suspended. They are added:
- in water with anti-corrosion substances;
- liquid soap solution;
- kerosene;
- transformer oil;
- special concentrate based on polymers.
For flaw detection, compounds are applied using several methods:
- using a brush;
- immersing in suspension;
- pouring liquid over the surface being examined.
The wet flaw detection method is used to identify surface discontinuities in welds.
Verification and calibration of magnetic particle flaw detectors
non-destructive testing equipment
- maximum value of pulse current, duration and pulse repetition rate;
- errors in current measurement by the device itself;
- determination of the mechanical properties and microstructure of sheet, section, shaped, and strip metal products, including sheets with non-magnetic coatings and pipes made of electrical, alloy, and carbon steel. The magnetic control method as one of the areas of structuroscopy is regulated by GOST 30415-96;
- duration of current flow in the solenoid in a state of residual magnetization and holding force. This effect occurs due to the so-called self-induction, when even after turning off the power, a damped current flows in the coil;
- duration of demagnetization;
- duration of current and pause in the “current-pause” mode;
- detecting ability - the ability to identify discontinuities when using magnetic suspensions of appropriate quality.
laboratories
Types of magnetization
With the magnetic particle testing method, types of magnetization that are applicable to parts of simple shape are more often used:
- circular creates a uniform magnetic field inside the part, there are no magnetic poles at the ends;
- longitudinal is called pole: a plus is formed at one end of the workpiece, a minus at the other, the field is directed along the part;
- combined involves the simultaneous influence of several multidirectional magnetic fields (in two mutually perpendicular directions, three or more).
In production, a type of magnetization of welds in a rotating magnetic field is used.
Various types of electric currents are used for magnetization:
- constant creates uniform induction;
- variable is applicable for less sensitive control methods;
- Pulse characteristics are close to constant.
Single-cycle and rectified current generators are built into flaw detection devices.
The legislative framework
Basic documents regulating the conduct of MTD
| Name | Description |
| GOST R 56512-2015 | Non-destructive testing. Magnetic particle method. Typical technological processes |
| GOST R ISO 9934-1-2011 | Non-destructive testing. Magnetic particle method. Part 1 |
| GOST R ISO 9934-2-2011 | Non-destructive testing. Magnetic particle method. Part 2. |
| GOST R 53700-2009 (ISO 9934-3:2002) | Non-destructive testing. Magnetic particle method. Part 3 |
| GOST R 55612-2013 | Non-destructive magnetic testing. Terms and Definitions |
Why is it worth ordering magnetic particle testing from REP LLC?
- certified laboratory and personnel . Our specialists are certified in accordance with PB 03-440-02 and ISO 9712 for magnetic and other testing methods. This allows us to work with all objects specified in the list of control objects approved by Rostechnadzor. We also work with objects of the Russian Maritime Register of Shipping.
- full-fledged material and technical base . We use equipment and consumables from world brands.
- versatility _ We use a magnetizing device with permanent magnets, which allows us to work in places where there is no current source. Our team includes industrial climbers, thanks to which we work at heights.
Want to order but still have questions?
Check the condition of pipelines or metal structures in production with a minimum of investment - call or contact us via the feedback form. We will advise you!
Sensitivity of magnetic particle flaw detection
Flaw detection is carried out on materials with a relative magnetic permeability of at least 40, the sensitivity of the MTD depends on:
- on the electromagnetic properties of the material used for research (mobility of indicator particles);
- magnetic characteristics of workpieces (ability to be magnetized);
- type of current, at constant a stable magnetic field is formed
- smoothness of the surface of the part, roughness is graded from 2.5 to 40 microns, the lower the roughness, the more accurate the control;
- magnetizing field strength;
- the position of discontinuities and other defects relative to the induction lines;
- method of applying an indicator to the surface of a part;
- testing conditions (the “dry” method of testing welded joints has higher accuracy);
- method of registering an indicator pattern over defects.
Method - magnetic flaw detection
Magnetic flaw detection methods can be used to detect iron-oxide deposits in pipes made of austenitic steels. The use of such methods for inspecting pipes made of magnetic materials is practically excluded due to the need to have a magnetizing current of hundreds of amperes, which cannot be obtained with a battery-powered flaw detector.
Magnetic flaw detection methods can be used to detect iron oxide deposits in austenitic pipes. The use of these methods for testing pipes made of magnetic materials is practically eliminated due to the need for a magnetizing current of hundreds of amperes, which cannot be obtained with battery power.
Methods of magnetic flaw detection of welded joints are based on the magnetization of products and the formation of stray fields in welds with defects. There are two methods of magnetic flaw detection: magnetic powder and induction. The magnetic powder method is that if there is a defect in the welded joint, then the magnetic lines of force, trying to bypass it, reach the surface of the seam, and the defect is detected by the accumulation of magnetic powder. This method reveals defects located at a depth of up to 5 mm, with a width of more than 0 03 mm. The induction method allows you to identify defects located at a depth of up to 15 mm. The induction method is used to control butt welded joints up to 30 mm thick.
Methods of magnetic flaw detection of welded joints are based on the magnetization of products and the formation of stray fields in welds with defects.
| The presence of stray fields when the defect is oriented perpendicular to the magnetic field lines ( a and along the magnetic field lines ( b. | Diagram of distortion of the magnetic field lines at the point of metal discontinuity. |
Inspection using magnetic flaw detection methods involves creating a magnetic stray field over a defect and its subsequent detection.
The corrosion state is monitored using magnetic flaw detection, radiographic, ultrasonic listening or television cameras passed inside the pipe. The study of stresses and deformations is carried out by mechanical devices launched through the pipeline at the end of construction, by the strain gauge method, etc. To detect leaks, visual inspection is used during detours or overflights of the route, gas analytical, acoustic emission and other methods.
Magnetic flaw detection methods are based on the registration of the latter.
We advise you to study - The use of asynchronous motors with a wound rotor as part of a variable-frequency electric drive
Each connecting rod bolt is subjected to testing using magnetic flaw detection methods to identify external defects and ultrasound to identify internal defects.
Ultrasonic, color and magnetic flaw detection methods are used to carry out inspections of equipment, machines and communications; in some cases, the audit is carried out during the overhaul period, which makes it possible to reduce equipment downtime during the audit to zero.
| Halogen leak detector. |
Depending on the method of detecting magnetic leakage fluxes, there are two main methods of magnetic flaw detection: magnetic powder and induction. With each method, the controlled area is magnetized.
To check the suspension devices of lifting machines with a belt traction element, it is advisable to use magnetic flaw detection methods. For this purpose, the tested parts are magnetized by directly passing an electric current through them or indirectly by winding several turns of insulated copper wire around the tested part and passing a current of the required magnitude through them. After this, small parts are immersed directly in oil, in which magnetic particles are suspended. Large parts are sprayed with a similar solution or a layer of magnetic powder and oil is applied to them.
| Formation of magnetic flux leakage fields. |
Depending on the method of recording (fixing) magnetic stray fields, magnetic particle, induction and magnetographic methods of magnetic flaw detection are distinguished.