Welding duty cycle and turn-on period (PV) of the welding machine
Welding duty cycle and turn-on period (PV) of the welding machine
Those purchasing a welding machine for arc welding for the first time will most likely pay special attention to its cost, dimensions, weight and permissible diameter of electrodes or wire. Those who have at least a little experience in welding will probably be interested in the availability of additional functions that facilitate the process and the switching period (load). In addition to all this, professionals will check what general welding cycle is indicated in the specification and at what welding current the power source can operate without interruption.
What is the on (load) period or duty cycle?
The on period (PV), also known as the load period (LP) or DC (duty cycle) - all this is the same parameter of the welding machine, which is one of the main ones. It is he who directly determines the performance, and indirectly also the service life of the device. It is indicated as a percentage, indicating that part (time period) of the total welding cycle during which the device can operate continuously. That is, if PV = 100%, then there is no need to pause in work. If PV=50%, then the welding duration is equal to the “rest” duration.
Pauses are necessary for the apparatus to cool to the permissible temperature, which rises sharply during the arcing period. The better the design and the more powerful the cooling system, the higher the PV, which means that in a shorter period of time, with proper qualifications, a larger amount of work can be done. At the same time, devices with high duty cycle usually last longer, since their components operate less often under extreme temperature conditions.
What is the welding cycle time?
This question cannot be answered unambiguously. The fact is that different manufacturers take this period to be 5 or 10 minutes. It is generally accepted that in Russia the general welding cycle is five minutes, and in Europe it is ten minutes. However, even if you purchase a device from a European brand, it is advisable to find the corresponding clarification in the specification. If it is not there, then you need to be prepared for the cycle to be five minutes long.
At first glance, it seems that the difference is small, because the parameter is indicated as a percentage and the total working time of the device will not change. However, in practice, a longer operating cycle is much more convenient. For example, with the same PV = 60%, with a ten-minute cycle you can cook for 6 minutes without a break, and with a five-minute cycle only 3. In the latter case, it is not always possible to complete the operation completely.
PV, welding current and ambient temperature
The specifications for welding machines indicate the switching period not only for the maximum, but also for the intermediate current. The higher the welding current, the lower the duty cycle, but at some current it will in any case be equal to 100%. If you plan to use the device for short-term work at maximum current, or for intense work at low currents, then purchasing expensive devices with a high duty cycle does not make much sense. If maximum continuous load is expected, then this parameter should be as high as possible. An alternative option is to purchase a welding machine designed for a higher maximum current. For example, if you plan to cook at 100-120 A, buy a device that produces a current of 180-200 A.
When choosing a device, it is worth considering one more nuance. PV is indicated for a temperature of 40º C. If it is higher, the duration of continuous operation will decrease proportionally with each “extra” degree. If the air temperature is below forty degrees (which most often happens), you will be able to work without a pause a little longer.
Welding machine load percentage PN
Many novice welders, when choosing the most suitable welder model, pay special attention to the current strength of the device, rightly believing that the more powerful the device, the better it is. However, there are other important parameters that should be taken into account when purchasing. For example, the concept of duty cycle or load duration (LOD) is very important. We can say that this concept is decisive when talking about the reliability of a welder. This indicator is described using percentages. A device whose indicator is 100% is able to work without turning off for days on end. You will only have to stop to replace the electrode. This value is based on a 10-minute operating time of the device. This means that with a work cycle of 60% of 10 minutes, the master can cook for 6 minutes, and 4 minutes are required for a break. With a PN rate of 50%, the periods of work and rest will be equal to every five minutes. Beginners often interpret this indicator not entirely correctly when purchasing their first welding device. You should pay attention to the fact that at different currents this indicator may well vary. If the device has an adjustment of 10 - 200 amperes, the load duration indicator when operating at maximum and at a power of 150 amperes will be different. The thicker the metal that needs to be welded, the higher the power of the machine will be required. This means that the welder will heat up faster and the resulting work time will be shorter than when welding thinner metal. Today, even modern professional welding machines, which are designed for intensive long-term use, do not have 100% operating time. Almost always, enterprises prefer to purchase devices with some reserve. For example, if the duty cycle involves welding at 300 amps, then devices with a power limit of 300 amps will be able to produce, at best, 60% of the required power. For most modern enterprises, this option is completely unacceptable. Therefore, it is necessary to use welding machines with a power of 500 amperes. At the same 60% PN, subject to welding at 300 amperes, it will just reach the required 100%. It is for this reason that before purchasing a welder, you should clarify which current will most often be used in your work. It is important to consult in advance what exactly the duration of the load at these currents is typical for the device you have chosen. For domestic use, welding is most often required at currents from 90 to 120 amperes. At this current, to work with a coefficient of 100%, a device with a power limit of 160 amperes or higher will be sufficient. In this case, it is worth taking into account the intensity of the upcoming welding work, the thickness of the materials to be welded and, of course, the duration of the welding. In most cases, for private use in the country or in the garage, a small 120 ampere welding machine with a load duration of 40% at maximum current is sufficient. At the same time, the price of slightly more powerful devices is not much higher. That is why it is better to purchase a more powerful device than required. After all, if you need to use it more intensively, then the second option will be much preferable. When choosing a specific welder, the main thing to take into account is that the voltage decreases the more, the closer the operating current is to the maximum.
- About company
- News
- Certificates
- Contacts
- Personal Information
- Payment and delivery
- Details (download)
- Organizations
- Guarantee
- Leasing
- Buy in credit
- Catalog
- Special offers
- Service
- Cases
- Reviews and articles
- Commissioning
- Demonstration
Principle of operation
Inverter welding machine: what does it mean? A welding inverter is a converter of alternating current 220 volts to direct current 70-120 volts . An outdated welding rectifier does the same thing. The quality of the weld made using a transformer-rectifier strongly depends on the stability of the characteristics in the electrical network. The operation of the device itself can greatly influence the stability of the network parameters; when the arc is ignited, voltage surges begin. What is inverter welding? The welding inverter also outputs 70-90 volts, but the conversion is carried out as follows.
- alternating current 220 volts 50 hertz is rectified and supplied to the input of the high-frequency generator;
- the generator creates a high-frequency (20-50 kilohertz) signal;
- it is fed to a transformer, which reduces the voltage to 70-90 volts;
- the current is rectified by the second rectifier and direct current is supplied to the electrode and the workpiece;
- the electric arc is ignited, the edges of the workpiece are melted, the electrode also melts, forming a cloud of protective gases and replenishing the weld pool;
- after cooling of the seam material, a permanent connection of high strength and durability is formed.
Now it becomes clear what inverter means: it is a converter with double inversion (from the Latin inversio, turning over, rearranging) voltage from alternating to direct and back.
Converting current at high frequencies made it possible to reduce the weight and dimensions of the transformer many times . Controlling the process at each stage using electronic circuits made it possible to ensure high stability of the output voltage, its independence from fluctuations in the supply network (within certain limits) and eliminated the negative impact of the inverter itself on jumps in the parameters of this network. In addition, welding inverters provide high stability of the arc, facilitate its ignition and prevent the electrode from sticking.
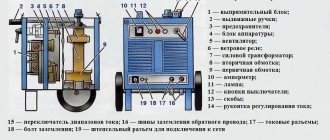
Welding rectifier device. The low-frequency transformer accounts for the bulky dimensions and heavy weight of the device.
These are the main differences between an inverter and welding rectifiers. Semi-automatic welding machines are also built on the basis of an inverter current source , supplying welding wire to the working area instead of a rod electrode.
If the parameters of the electrical network are significantly lower than 180-190 volts, then a conventional inverter can no longer compensate for such a voltage drop. Often in remote areas it drops to 150 volts.
In this case, inverters that can operate at reduced voltage come to the rescue . in their design there are two blocks designed to correct the situation:
- stabilizer with an extended range; it maintains the specified output voltage, despite fluctuations at the input;
- power factor corrector: an electronic circuit that adapts the operation of the entire device to changing power supply conditions.
These blocks do not perform miracles and do not violate the law of conservation of energy. If the input is below 135 volts, the welding machine will not work .
In addition, only the thinnest electrodes or wire can be used.
The corrector will try to keep the power delivered to the arc at the same level.
Such a unit is also very useful when operating from a household generator or through an extension cord over 40 meters long, on which large losses are observed.
Load duration (LOD) of the welding inverter. What is it and why should you know it?
Why do you need to know and observe PN - the load duration of the welding machine? How to prevent overloading of the inverter and its breakdown? How to operate an inverter taking into account the PN?
As a rule, in the descriptions of the welding inverter (passports, instructions, advertising brochures) the rated welding current in amperes is indicated with the corresponding value of the load duration (load duration) in percent. The rated welding current is the current at which the inverter will operate without overload and will not overheat, taking into account compliance with the PN (%), i.e. in intermittent mode.
■ Load duration - PN (%) of the welding inverter or switching duration - PV: Most welding sources - rectifiers and inverters in particular, operate in intermittent mode . This means that the period of operation under load (welding) alternates with a period of operation without load (idling, pause mode). These periods are repeated and form a welding cycle. The intermittent mode is characterized by Load Duration PN (%). The PN value is determined by dividing the operating time of the inverter under load (welding time - Tw.) by the total welding cycle time (welding time Tw. + pause time Tpause), as a percentage.
The welding cycle time is usually 5 minutes, for industrial rectifiers or inverters - 10 minutes.
The PN of the inverter can be 20, 30, 40, 60 or 100%, taking into account this value the rated welding current .
The manufacturer can indicate several values of the rated current at the corresponding values of PN%, for example, for the Forsazh-200 inverter: 200A - 40% 160A - 80% 140A - 100% Example : The popular inverter BARS Profi ARC-207D will have a rated current at PN = 60% 200A, at PN=100% – current 160A. (with a welding cycle of 5 minutes). You can work at a rated welding current of 200A for 3 minutes with 5mm electrodes, and the pause time should be at least 2 minutes (PN=60%). At a welding current of 160A, the inverter can operate in long-term (continuous) mode (PN=100%) with 4mm electrodes. As a rule, for Russian-made equipment, PN is calculated at an ambient temperature of 25°C, for Asian and European equipment - at a temperature of 40°C. It is believed that in practice it is impossible to work in the PN=100% mode, because technological time is always required to change the electrode, inspect the seam, remove slag, position parts, physiological breaks, rest, etc. Scientifically based PN, at which the welder is physically able to work during the shift - no more than 60%. Therefore, for professional devices, PN = 60% at rated current is more than sufficient,
For most European-made models, PN = 30% is the norm, because equipment is rarely used at full power for long periods of time. The PN value = 30-40% at maximum current should not confuse anyone.
For example , for the BARS MiniARC-200D inverter, PN=35% at a current of 200A. At the same time, with a decrease in air temperature, the PN of the source increases, as its cooling improves. At a temperature of 15º C, the load duration of this inverter will be approximately 50%, and at a current of 160A - about 60%. The inverter can operate with a 4mm electrode in the following mode: 3 minutes – welding, 2 minutes – pause, provided that the length of the welding cables does not exceed 3-5m. This is quite enough for work in domestic conditions. Therefore, when choosing an inexpensive household inverter, you can focus on the PN = 30% indicator, if the model, manufacturer and brand are trustworthy.
A number of unscrupulous manufacturers overestimate the rating data for current and PN%, as a result of which the inverter either does not provide the required current or operates with overload, overheats and fails. This is typical for cheap household appliances. Be careful! In addition to advertising materials, we recommend that you read passports, nameplates on the device body , and also study reviews about the operation of inverters.
How to choose a welding inverter manufacturer
Now you know how to choose a welding inverter based on technical characteristics. The most difficult task remains: choosing the brand of the device, or rather, the manufacturer.
Chinese welding machines or?
In the category of household welding inverters, almost all units come from China. There are brands that are completely unknown to anyone, and there are brands that have been working for years and have earned a certain authority. Well-known Chinese brands are, as a rule, equipment produced by reputable factories equipped with modern equipment.
The “owners” of the brand are Europeans, Americans and even Russians, and production facilities are located in China. This scheme has long been worked out and is well known. That’s why recently even two lines have appeared in the descriptions of devices: “homeland of the brand” and “country of manufacture.” To call these inverters “Chinese” is not entirely correct, but they were manufactured there. In general, it's up to you.
Chinese inverter welding machines known on the market do not have the lowest prices. But they have been tested, and most of them have a network of service workshops or a repair contract with one of the similar services. Here are a few brands that have mostly good reviews:
- Welding inverters Resanta. The homeland of the brand is Latvia, the manufacturer is China. There are three lines: SAI - models with a maximum welding current from 140 A to 250 A, supply voltage from 170 V to 250 V. Price from 6.5 thousand rubles for SAI 140, up to 14 thousand rubles. for the 250 amp model.
- SAI PN - models operating at reduced voltage - from 150 V. Price from 11 thousand rubles. for a 160-amp unit, up to 18-19 thousand rubles for a power of 250 amperes.
- SAI K are compact models that have less weight and dimensions, and have the same characteristics as SAI. Priced from 7.3 thousand rubles for a 160-amp device, up to 12 thousand rubles for 250 A. Resanta welding inverters of the SAI, PN (reduced voltage) and K (compact) lines (To increase the size of the picture, right-click on it )
- Household models ARS 165, ARS 205;
- Welding inverters Fubag (Fubag), the homeland of the brand is Germany, the manufacturer is China or France. The IN series is assembled in France, and the IR series in China. Permissible deviation in supply voltage 220 V +/- 15% (190 - 250 V). The Fubag IN series of welders can operate in MMA and TIG modes (welding in an argon environment; the TIG mode requires a special set of equipment - purchased additionally). Price from 11.8 thousand rubles for a device with a capacity of 16 Amperes, up to 18 thousand rubles. for a power of 220 amperes.
- The IR series of inverter welding machines is MMA welding only and has anti-stick and hot start functions. Price from 7 thousand rubles. for 160 ampere and up to 9.5 thousand rubles for 220 ampere.
- Another representative of Russian inverters produced in China is the Kedr inverter welding machines. “Cedar MMA” series - work only with consumable electrodes. There is a “hot start” and “anti-stick” function. Prices from 7.5 thousand rubles. for the lowest power (170 Amperes) and up to 9.5 thousand rubles. for a 220 Ampere unit.
- The “Cedar ARC” series is a professional series of units, they also have an arc stabilization function, the price starts from 10.5 thousand rubles for a unit with a capacity of 160 amperes, and up to 28 thousand rubles for a 400 ampere unit.
- Interskol inverter welding machines. This is another brand originally from Russia that produces equipment in China. Feature of the package: the power plug is not included in the package. It is stated that the device operates with a power supply from 140 to 240 V. There are two lines: “Interskol ISA, for MMA (manual electric arc welding with a consumable electrode). Prices from 6.5 thousand rubles. for a device delivering 160 amperes, up to 10 thousand rubles. for a power of 250 amperes.
- Intersokl ISP series - in addition to MMA welding, it can work in MIG/MAG mode (in an environment of inert or shielding gases). The price for ISP 160 amperes is 19 thousand rubles, for ISP 200 amperes - 21 thousand rubles.
- FoxWeld welding inverters are made in China. Good characteristics, wide choice. There are several lines of budget welders for dachas that operate at reduced voltage. FoxWeld Summer resident - price from 7.2 thousand rubles for a 160 A unit. A digital display with large numbers makes it easier to perceive information. Supply voltage is 180-240 V, although not the best performance at maximum current: PV 40%. Open circuit voltage 56 V.
- FoxWeld Corundum - With generally similar characteristics, it has the best current-voltage characteristic: open circuit voltage 78 V.
- FoxWeld Master can work with a argon arc welding kit. PV at maximum current is even lower: 35%. There are functions of “hot start” and “anti-sticking”, arc forced.
What is PV?
The abbreviation PV stands for duration of switching on, and PN, respectively, for duration of load. Measurements are made according to different standards, which significantly affects the results. In Europe, welders are evaluated at a temperature of 40 degrees and for a 5-minute interval. But in the CIS countries, the diagnostic process is a little different: at a temperature of 20 degrees and for 10 minutes. In Belarus, we most often encounter equipment tested according to CIS standards, however, the famous Russian brand Svarog indicates in the technical characteristics of its products that the load factor is assessed at an ambient temperature of 40 degrees.
Why is this indicator important and at the same time not important?
On the one hand, you should not completely ignore PV. Just imagine a situation in which you are the happy owner of a device with an on-time of as much as 20%. And it's hot outside - +30. And as a result, you only have less than 2 minutes to operate at maximum current, and then a long and painful “break” while waiting for the inverter to cool down. Agree, not the most pleasant situation. Or another situation: you choose a welder and cannot decide between 2 models. Their maximum current is the same, but the PV is different. Therefore, the one with a longer duty cycle is likely to have better cooling mechanisms. This means it has a more impressive safety margin and a longer service life. All these arguments are extremely revealing. But there is one extremely unpleasant nuance. Many manufacturers lately, fighting for the client, resort to very ugly tricks. So, for example, many unscrupulous developers prescribe a duty cycle of 90% or even 100%, but they forget to note that this is not at maximum currents, but at 100 A, for example. It’s sad, but true, today you can only trust proven brands, such as Svarog, EWM or ITS.
How does the device work?
Welding transformers are already fading into the background. With the advent of inverters, welding metal structures has become much easier. Their design is simple and lightweight. The equipment itself can be easily placed in a small bag or car for transportation, for example, to the country. At the same time, learning the welding process using an inverter is much easier than using a transformer. This device does not require such effort and special training.
Before starting work, it is recommended to understand the basic principles of operation of this equipment. The operating principle consists of several stages of converting electric current using an inverter type. The basic process is as follows:
- Electrical alternating current from the main network is converted into direct current while passing through the spiral, which allows the arc to be stabilized.
- Direct current is again converted to alternating current. At the same time, its frequency increases several times.
- After this, the voltage level of the electric current is reduced to the most optimal value. As a result, it is possible to achieve the maximum current value.
- After this, the voltage level in the network is rectified.
This principle of operation allows the conversion units to be significantly smaller than those of transformers, which is convenient for a novice welder. Due to this design, the dimensions of all equipment are quite small, which makes it easy to buy such a device for a summer residence and use it at home.
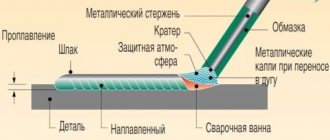
In order to start welding work, it is necessary to connect the electrode holder to the electrode, and the ground clamp to the structure to be welded. Then touch the electrode to the part, which will lead to an electrical short circuit and the formation of an arc for welding. When the electrode melts, the coating on its surface burns and protects the weld pool from oxygen. This discharge will generate enough heat to melt any metals, and the thickness will depend on the strength of the welding current.
The electrode must be held at a distance of several millimeters from the surface to be treated. As a result of high temperatures, the welded part and the rod begin to melt at the point where the electric arc passes and are combined into a monolithic structure. The joint can be easily identified by the weld seam, from which the slag will need to be removed after work. If you want to get an aesthetically beautiful part, the seam itself should be processed with a grinder.
If you follow all the rules of welding, the weld should not differ significantly from the original structure of the metal. In some cases, it is possible to achieve a more effective result. Let's consider which welding machine is better to choose. To do this, it is recommended to study the pros and cons of the device.
Additional functions of inverter welding machines
The presence or absence of service functions is not critical, but it makes life a lot easier, especially for a beginner. Their set is usually standard:
- “Hot start” HOT START - affects the ignition of the arc. When igniting, an additional impulse is given, which makes it easy to start welding.
- “Arc Force” - ARC FORCE - when the electrode suddenly approaches the metal, the welding current automatically increases. This prevents the electrode from sticking.
- “Anti-stick” - ANTI STICK - turns off the power when the electrode gets stuck, turns it on after it comes off. A convenient function, especially relevant for novice welders.
There are some other useful features. For example, indication and automatic shutdown when overheating. This is a useful addition - it is not always possible to keep track of the time or the overheating indicator. Automatic shutdown saves you from burnout and expensive repairs.
A welding machine for manual electric arc welding allows you to weld almost all metals, except non-ferrous ones
Pay attention to the package: in addition to the welding machine, there is usually a power cable (sometimes it is removable, sometimes it is stationary), two welding cables - one with a clamp for attaching to the part, the second with an electrode holder. It is better if the cables are light, flexible and long. But such luxury is not always available. More often, working cables are about 2 meters long, which is not always convenient. When looking at the cables, pay attention to how they are terminated, soldered (preferably) or clamped/rolled.
Pay attention to the warranty period, as well as how close the nearest service center is to your home/dacha. The lack of a service network is an alarming sign. This means that even if there is a warranty breakdown, you will have to repair it yourself, for money. You won’t send your device for repairs across half of our rather large country...
Load duration (LOD) of the welding inverter. What is it and why should you know it?
The PN/PV parameter is always indicated as a percentage and shows the operating time of the inverter in a ten-minute cycle. For example, if MF/MF is 40%, this means that after 4 minutes of operation the device will need to take a break and cool down for 6 minutes before restarting. Thus, the figure allows you to approximately estimate how many times the inverter will turn off due to overheating during uninterrupted operation for a long time.
The load of the power source (hereinafter referred to as IP) for arc welding is, as a rule, variable. The welding process consists of repeating cycles in which the working period alternates with pauses necessary for replacing electrodes, preparing for the next weld, adjusting parts, etc. According to the standards, three typical operating modes are distinguished:
- Long lasting with constant load;
This is how IP for automatic welding and multi-station sources work.
- Alternate;
Working periods are interrupted by operating modes at XX. In this case, the concept of load duration (LOD) is used.
- Intermittent
Working periods alternate with periods of complete disconnection of the power circuits of the power supply from the network.
In this case, the operating mode should be referred to as on-duration (ON)
PN/PT is equal to the ratio of the operating time of the device to the time of the entire cycle. The cycle duration is assumed to be 10 minutes. The formula looks like this:
Difference between PN and PV
- Log in to reply to this topic
#1 Deputattt
This is the first time I’ve seen a device with 100% PV, it’s like that.
- Top
- Insert nickname
#2 blazen79
The duty cycle (on duration) is 100% for all devices, but the duty cycle (load duration) is different.
- Top
- Insert nickname
#3 AMBIVERT42
The duty cycle (on duration) is 100% for all devices, but the duty cycle (load duration) is different.
Exactly! PV is valid for semi-automatic machines. For REDS/RADS devices, the PN indicator is used.
It is better to be a sheep among wise men than a wise man among sheep.
- Top
- Insert nickname
#4 ARGONIUS
- Participant
- Messages: 2,578
- City: N. Novgorod
- Top
- Insert nickname
#5 morgmail
ARGONIUS , we also need to invite welding engineers here.
P.S. Self-propellers, pass by. Otherwise, they will start making their own numbers in order to embellish the capabilities of their self-propelled guns.
Post edited by morgmail: March 15, 2014 09:43
- Top
- Insert nickname
#6 ARGONIUS
- City: N. Novgorod
- Top
- Insert nickname
#7 morgmail
I have stolen two opinions on this matter.
The components of the characteristic element - PV (PN) - are subject to separate consideration
On-time (ON) or load duration (LO) as a percentage is the ratio of the operating time under load or cooling over a certain period of time, at a certain ambient temperature. (the ratio of the time of work under load and rest from overheating). The accepted value of the total time according to the European standard is 5 minutes at 40 degrees Celsius, in other countries and Russia 10 minutes at 20 degrees Celsius. The optimal PV value is about 60%, i.e. 6 minutes of work and 4 minutes of break. Increasing the operating time under load will trigger the thermal protection of the control unit.
In other words, if you turn on the device at maximum load and detect the time after which it turns off due to overheating, this will be its duty cycle. And since PV is measured in %, this is the ratio of the “work” and “rest” time of the welding machine.
We give an example if we take a welding cycle of 10 minutes (and not 5 minutes - European standard), the ambient temperature is 20 degrees (and not 40 degrees - European standard) and the machine turns off after 5 minutes, which means the duty cycle is 50% (we work for 5 minutes, rest for 5 minutes), if it turns off after 3 minutes, then the duty cycle is 30% (work for 3 minutes, rest for 7 minutes), if the device turns off after 6 minutes, then the duty cycle is 60% (work for 6 minutes, rest for 4 minutes). What does this mean for us in a practical sense? PV 50-60% (welding cycle 10 minutes and ambient temperature 20 degrees) is more than enough for any MMA welding work at currents up to 200A.
What is “PV” and what does this indicator affect?
- this is the duration of switching on of the welding machine
, i.e. the time of its continuous operation.
This indicator is one of the main characteristics of a welding inverter
. The duty cycle is always indicated in % based on a 10-minute welding cycle. Indicated on the nameplate on the rear panel of the device. For all welding inverters (SAI), the PV at maximum current is 70% (for example, for SAI 220, the PV is 70% at a current of 220A), i.e. the device works for 7 minutes, after which, in theory, it requires 3 minutes of rest.
The average person may misunderstand this indicator. They say: “What can I cook in 7 minutes? And then he constantly needs to rest for 3 minutes?” NO! PV
shows the duration of continuous cooking. It is impossible to cook continuously for seven minutes! Firstly, because the electrode will burn out much faster and while the person is changing the electrode, the device cools down. Secondly, after 3–5 minutes of the welding process, there is usually a need to prepare parts for further work and check the welding seam - this time is enough for the AIS to cool down. That is why, when working in domestic conditions, almost 100% PV is usually achieved - work is carried out continuously and with high quality throughout the day!
If, nevertheless, the buyer wants to purchase a welding machine with a high duty cycle
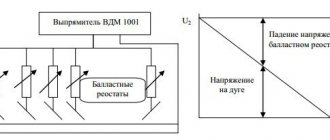
, than 70% (usually professional welders or older people who heard “somewhere, something” from a neighbor), he should simply be recommended to purchase a device of a higher rating than he chose. Because 70% is at the maximum welding current; when the value on the regulator decreases, this figure immediately increases. That is, for example, for SAI 160 PF3 at 160A is 70%, and for SAI 250 at the same 160A it will already be 100%, i.e. continuous operation (see Fig. 2).
Always pay attention to the PV
! It can help you a lot in positioning the AIS. So, for example, what we can see when considering the Telwin SAI 165. The duty cycle at the maximum current (150A) is not indicated at all, there is data only for 140A and the duty cycle at this current is only 7% (42 seconds.). This is just that time out of a 10-minute lfiacria that the welder at this current is in operating mode. Not a bad argument in our favor, right? Yes, here one person out of a thousand can argue about the temperature conditions for which PV is considered (you can read about this in any source on the Internet). But still, an attempt at justification will sound sluggish!
Also, for example, for devices (Weld hWD-200) and “DON” (DON-230), the actual PV indicator is almost 3 times lower than the declared one: 13% and 12%, respectively, with a declared 35% at maximum current.
Important: Remember that the PV indicator is calculated for an ambient temperature of +25°C, therefore, if a person works with the machine in the summer in the heat at a higher temperature, the body of the device will additionally heat up (accordingly, the PV indicator will drop slightly) and the likelihood of the welder turning off due to thermal protection increases. If suddenly the temperature approaches the limit value, the overheating indicator on the front panel of the AIS will light up and the device will turn off and turn on only after cooling.
Choosing a welding inverter for home and garden
Depending on the class, welding inverters are household, semi-professional and professional. The former are affordable and suitable for simple work and occasional use. Professional (universal) inverters are designed for many hours of daily use. The golden mean can be called semi-professional units. Today I will tell you what technical parameters deserve attention when choosing.
How to choose an inverter current welding machine for home
First of all, I advise you to select the maximum welding current (unit of measurement - Amperes, designation - Imax). The fact is that the thickness of the metal with which you can work depends on the current. Let's say, for welding a channel, angle and other ferrous metal up to 1 cm, an inverter of 160-180 A is enough.
If you have to work with a greater thickness, you need all 200 A. In everyday life, sheets thicker than 2 cm are practically not used, so a current of 250 A is clearly overkill for a summer house and at home. You shouldn’t overpay for extra power; it’s better to give this money for higher-class equipment.
The minimum current is needed when working with stainless steel and steel up to 2 mm. Usually the lower limit is 10 A, but there are examples whose minimum is rated at 30-40 A. Such units are good when there is a separate semi-automatic welding machine for thin metals.
Check the current setting. Optimal mode settings for a specific metal and electrode are provided by smooth adjustment.
Yandex.RTB RA-1479455-2 How to choose a welding inverter for your home or cottage, if there are dozens of brands?
Important parameters
Before starting work, you need to understand what quantities you have to deal with. Main parameters influencing the welding mode:
- strength, type and polarity in the case of direct current;
- electric arc voltage;
- welding wire thickness;
- number of passes;
- welding speed.
Secondary factors influencing the characteristics of the connection include the condition of the parts being welded, the shape of the edges, the brand, type and thickness of the electrode coating. The choice of welding seam type has a certain influence.
The most important thing is to calculate the modes for automatic welding. Some characteristics are set using ready-made tables, while others have to be determined using formulas contained in the instructions for the equipment. Each equipment has its own tables, worked out empirically.
What is PV?
The abbreviation PV stands for duration of switching on, and PN, respectively, for duration of load. Measurements are made according to different standards, which significantly affects the results. In Europe, welders are evaluated at a temperature of 40 degrees and for a 5-minute interval. But in the CIS countries, the diagnostic process is a little different: at a temperature of 20 degrees and for 10 minutes. In Belarus, we most often encounter equipment tested according to CIS standards, however, the famous Russian brand Svarog indicates in the technical characteristics of its products that the load factor is assessed at an ambient temperature of 40 degrees.
Duration of continuous operation of a welding machine: what is the point?
Let's move directly to the essence and meaning of the indicator. Let’s say that the purchased inverter from a Russian manufacturer has a standard duty cycle of 60%. This means that at maximum amperage it can be used for 6 minutes out of a 10 minute cycle. The equipment then needs 4 minutes to cool down.
Let us remind you that these are the manufacturer’s recommendations at an ambient temperature of +20 °C. What does this mean practically? If work is carried out in the hot summer season, when the temperature on the thermometer is +30 °C or more, then the time of continuous operation of the inverter is reduced. If the temperature is below the set measurement value (+20 °C), then you can operate the device at maximum values a little longer.
For products of European brands (for example, EWM, Esab, Foxweld, Telwin and others) the approach to assessing the efficiency and continuous operation time of the inverter will be different. They are tested at temperatures that are almost unattainable in the conditions of central Russia and especially in the northern and continental regions of the country. Therefore, the actual operating time of the device at maximum current can be increased through a certain coefficient. It can be defined as the ratio of the theoretical design temperature (+40 °C) to the real one (for example, +25 °C). Thus, the duration of operation without the need for cooling in practice under such conditions increases.
Electrode angle
The concept of welding mode refers to the angle of inclination of the electrode.
During operation, the electrode relative to the seam is positioned with a deviation from the normal by about 10 degrees in any direction. The depth and width of the seam depends on the position of the welding wire relative to the joint of the workpieces. If welding is done at an angle forward, the depth decreases and the seam becomes wider. This is due to the fact that the arc, as it were, drives a wave of melt in front of itself, through which the metal of the product has to be melted.
If the backward angle welding mode is selected, the melt is expelled to the end of the pool. The electric arc acts directly on the products being welded. This mode of electric arc welding makes deeper penetration of the joint and at the same time reduces the width of the joint.
The length of the working part of the electrode also matters. The longer it is, the more it heats up and melts, which reduces the current, and the depth of the bath decreases accordingly. This is especially true when using thin welding wire.
Welding parameters
Before choosing the desired welding mode, it is necessary to accurately determine the composition of the metals, thickness and type of structure. After receiving the data, the appropriate mode is set. There are many factors on which the quality of welding depends, so they are divided into two groups: primary and secondary.
Basic
The amount of energy, as well as the method of its transfer to the metal surface, depends on these parameters. The main parameters of the welding mode include:
- current magnitude, polarity and type;
- electrode diameter;
- welding arc length and voltage;
- speed of movement along the seam;
- number of passes.
The formation of the seam depends on each of the parameters. By changing one or another indicator, you can get a more reliable connection. Let's briefly look at some points.
- The intensity of the current determines how intensively the material melts. The higher the indicator, the more productive the welding. If you set too much current without using a sufficient electrode diameter, then the quality will decrease. And vice versa: at low current levels, the welded arc may break, causing lack of penetration.
- Current polarity refers to the direction of energy movement - from the cathode to the anode or vice versa. Along with the direction, the type of current is chosen - either direct or alternating. Thus, when welding parts with direct current with reverse polarity, the seam will be 40% deeper.
- It is important that the melted material has time to fill the seam and does so evenly. Otherwise, the strength will decrease.
Additional
Secondary parameters include:
- electrode protrusion;
- material and thickness of electrode coating;
- temperature of the parts being welded;
- position of workpieces;
- edge shape;
- quality of surface preparation.
Electrode characteristics
The dimensions of the electrode are interrelated with the dimensions of the products and the type of edges.
If the thickness of the alloy being welded is 3-5 mm, then the welding wire should be 3-4 mm. When welding thick-walled workpieces, many passes are required. For the first time they pass with an electrode with a diameter of no more than 4 mm. When making ceiling seams, it is also recommended to use wire no thicker than 4 mm.
Usually there is a table on the packaging of the electrodes, which indicates the most preferred modes. With a diameter of 1.5-2 mm, the recommended welding current is 30...45 A, 3 mm - 65...100 A, for 3-4 mm - 100...160 A, and so on. The variation is related to the type of welding and the thickness of the alloy.
With a thickness of the alloy being welded of 1-2 mm, it is recommended to use a welding wire with a diameter of 2-3 mm, with a thickness of 3-5 mm - 3-4 mm, a thickness of 4-10 mm - diameter 4-5 mm, if the thickness is 12-24 mm, then use a 5-6 mm electrode. When choosing a mode, it is necessary to take into account the position of the part or seam in space; the number of passes also influences the choice.
Mon/sw =twork/tcycle *100%
For most professional welders, not to mention amateurs, the concept of the operating mode of a welding machine is not very clear. This characteristic should show how the welding machine will behave when operating at maximum current and temperature of +40 degrees. Professional welders, when choosing a device for work, look at the continuous load current, which is indicated on the nameplate of the device in the PN 100% column. Based on the numbers in this column, a welding expert can imagine whether the current declared by the manufacturer will be sufficient to solve the problems facing the welder. If the current modes indicated in the 100% column coincide or exceed the estimated currents required to perform specific tasks, then the device will not overheat during operation and go into protection.
For domestic use, high PN values are not so important, since for housework the device is rarely used to the limit of its capabilities, and the loads are rather short-term in nature. The declared data on the operating mode of the inverter are the results of research by equipment developers. The required PN or PV is included in the design calculations. In accordance with the task for the duration of the load, engineers select the components of the welding machine. Many nuances are taken into account. For example, the heat resistance of wire insulation, the size and number of cooling radiators, the ratings of temperature sensors, and their installation locations. Engineers calculate the most heat-loaded components and check how they will affect the operating mode of the inverter during long-term operation.
Selecting the appropriate mode
Having seen what mode parameters there are in general, let’s move on to the settings of each individually.
Ratio of current to electrode thickness
The diameter of the electrode is selected based on the thickness of the seam being welded and the welding method. So, for metal 3-4 mm thick, a 3 mm electrode is suitable. Multi-profile parts are welded in several passes, first using a 4 mm electrode.
Important! If you take an electrode with a smaller diameter, then the seam will not be filled properly, which will reduce the strength of the connection.
Having selected an electrode, refer to the tables to determine the required current strength. For the same diameter of 3 mm, the working indicator is 65-100 A. In addition, if you have to carry out vertical welding or a seam overhead, the diameter of the electrode should not be less than 4 mm. When horizontal welding, the current strength is reduced by 15-20%.
Arc length
This parameter means the distance from the end of the electrode to the object. The indicator depends on the size of the selected electrode and is given in the tables. For high-quality penetration, it is necessary to achieve a uniform value along the entire length of the seam. It is difficult for a person to monitor the uniformity of the indicator; experience is needed. So, for a 4 mm electrode, the arc length is 4.5 mm, and it is difficult to maintain this distance. To automate the process, welding carriages are used.
Penetration rate
When carrying out welding work, it is important that the molten metal fills the bath. There should be a uniform transition, edge coverage, and a seam without undercuts or sagging. In this case, the recommended seam width is 1.5-2 times larger than the diameter of the electrode used. If the welding speed is too high, the metal will not heat up sufficiently and strength will be lost.
Polarity and type of current
Many models of welding machines convert household alternating current into direct current. It is important not to make a mistake with the polarity, the direction of flow of electricity. Basic polarity involves connecting the part to “+” and the electrode to “-”. Depending on the properties, the selected mode parameter is applied.
- Straight polarity is suitable for welding cast iron, low and medium carbon steel with a thickness of more than 5 mm.
- Reverse polarity is selected when joining mild steel and thin sheet structures.
Electrode inclination and length
The position of the electrode affects the quality of weld welding. In most cases, the electrode is held perpendicular to the workpiece and moved at an angle forward. This method makes it possible to increase the width of the seam. If the angle is more than 90°, then the direction is changed. This position helps to completely fill the deep bathtub.
The stick out of the electrode depends on its diameter and the strength of the supplied current. The longer the length, the slower the heating occurs.
Tilt of workpieces
For normal filling of the seam, it is recommended to tilt the parts at an angle of 8-10°. Otherwise, either lack of penetration may result, or the molten metal will drain. When connecting pipes, it is impossible to change the angle of the seam, so welding is done from top to bottom.
Before starting work, it is necessary to obtain all the data on the parts to be welded. After this, you can make the correct choice of welding mode. We recommend setting up the machine correctly, choosing electrodes and welding at the required speed. If you apply the tips from the article, the connections will be strong and reliable.
How are PN/PT checked?
Only engineers can calculate the inverter voltage at the source design stage. In a laboratory setting, you can only confirm the original data stated by the manufacturer or refute them. It is only possible to calculate the PN of a particular device based on the data obtained during testing only conditionally and very approximately. There is a method for checking the operation of the IP. It is designated in GOST R IEC 60974-1-2012 and implies loading the source with the maximum current declared by the manufacturer. This method allows you to confirm or refute the declared values of the operating mode quite quickly. However, it is associated with the use of additional calibrated devices to simulate the operation of the device under load, temperature control devices at certain points, etc. Among the important parameters of this test, it is worth noting the test time, which according to the standard should be 10 minutes, as well as the temperature inside the heat chamber of 40 o C. These two parameters allow us to obtain data with uniform initial conditions.
It is worth saying a few words about why a single standard of time and temperature is so important. Some manufacturers, for marketing purposes, strive to increase the PN/PT value and indicate data for a five-minute cycle. For example, a device with a test cycle of 5 minutes is declared as an inverter with a duty cycle of 40%. In fact, if we translate this value into the coordinate system regulated by GOST R IEC 60974-1-2012, the PN will be 20% (with a cycle of 10 minutes). The same story with temperature. In GOST, the value of this test parameter is indicated at 40 o C. If the temperature in the heat chamber is lowered to (20 -25) o C, then the PN will increase by 2 times and amount to 80%. That is, an inverter with a real PN of 40% at a temperature of 20 o C can stand under load for more than 8 minutes. And at the same time do not overheat. This “trick,” by the way, is often used by unscrupulous manufacturers of welding equipment. By indicating PN at 20 o C or for a 5-minute test cycle, you can get much more beautiful numbers without changing the actual operating mode of the inverter. Therefore, when purchasing a device, you need to clarify how much the data indicated on the inverter corresponds to GOST requirements.
Effect of current
When setting the mode, the current strength is selected according to the tables.
The current depends on the thickness of the products being welded and the welding wire. Precise adjustment is made according to the type of arc and seam. It is necessary to understand that the stronger the current, the higher the temperature under the base of the arc will be and this will affect the speed of welding. Welding mode with high current and an excessively thin welding wire will cause overheating and spattering of the metal. If the workpieces are thin, then they are often burned out in this mode.
With a weak current, the arc becomes unstable or breaks off completely. The seam is of poor quality, uncooked areas appear. This mode should not be chosen.
It must be taken into account that the depth of the weld pool depends on the type of current. If a device is used on direct current, then its penetration depth will be 15% greater than that of alternating current.
Welding in DC mode also has its own characteristics. Thus, with direct polarity, the crater depth is 40% less than when using reverse polarity.
Direct polarity is when the electrode is connected to the inverter terminal with the “-” sign, and the connected products are connected to the terminal with the “+” sign. With reverse polarity, everything is connected in reverse.
With direct polarity, an electrode with calcium-fluorine coating can be used; it allows you to weld low and medium carbon steel and cast iron.
Inverter mode (reverse polarity) is used when it is necessary to weld low-carbon and low-alloy steels and thin-sheet parts.
The current also changes depending on the position of the welded joint in space. So, with a horizontal seam, it is recommended to reduce the table values by 15-20%.
Duration of inclusion (DT) as a means of manipulating the buyer
As we can see, the duration of switching on at maximum current for an inverter is, on the one hand, a rather important indicator. Imagine a situation in which you choose two similar models of welding machine. A number of characteristics, including the maximum current, are almost similar, but the duty cycle differs. It is reasonable to assume that the cooling system of the model with a higher PV is more advanced and efficient. This has a positive effect on the efficiency of the welding task, reliability and overall service life of the equipment.
BUT! It is not always worth focusing on this indicator in such cases. And there are a number of reasons for this that definitely deserve to be taken into account. These reasons include:
- Manipulation of measurements by manufacturers. Especially little-known equipment manufacturers often make mistakes with this indicator. In the passport for a household inverter with a duty cycle of 80-90%, it may be written in small font “measurements were made at 100 A). That is, not at the maximum output current, but at a different amperage value, loading the device noticeably less intensively.
- Rare work of a welder at maximum current. This circumstance can significantly increase the continuous operation time of the inverter without the need for a break to cool it.
- A significant PV indicator is not needed for all types of welding. As a rule, a standard electrode lasts no more than a minute or so of continuous burning. Thus, the welder will probably have to stop to replace it, check the quality of the weld, or clean its surface. Meanwhile, the inverter will cool down. Therefore, the duration of switching on at a maximum current of even 50% is quite enough to perform most household welding tasks.
As you can see for yourself, the duty cycle indicator is not a priority for choosing household welding machines. When selecting professional welding equipment for a particular production, completely different criteria come to the fore.
Buyers of welding equipment can draw the appropriate conclusions on their own. And if you are looking for appropriate high-tech products for your needs, we recommend looking for them in our online store.
Arc length and seam quality
The length of the arc affects the quality of the connection.
It is important that it be the same throughout the entire seam; the distance between the end of the welding wire and the edge of the part should be equal to its thickness. Welding mode with too short an arc leads to burning or sticking of the electrode. The mode with a long arc causes its extinguishing and lack of penetration. The length of the arc can be controlled by the sound it makes.
The optimal weld width is considered to be 1.5-2 wire diameters. In this case, a small bead should form along the connection line without sagging from the molten electrode. The optimal seam depends on the welding speed, the thickness of the product and the width of the seam.
The welding mode, in which the holder with the electrode moves very slowly, leads to excessive accumulation of liquid metal in the weld pool, which will splash and prevent normal penetration of the joint.
Moving the holder too quickly along the seam will lead to lack of penetration, and it may crack or become deformed after cooling.
If a pool is formed with a width of 1.5-2 wire diameters, a depth of up to 6 mm and a length of 10-30 mm, then this indicates the optimal welding speed for this particular material and type of connection.