Mechanical properties of bolts, screws, studs, nuts according to GOST 17594 (ISO 898/1)
The grades and mechanical properties of carbon and alloy steels used for the manufacture of screws, bolts and studs are given in Table. 1.
Table 1
| Mechanical properties | Strength class | ||||||||||||
| 3.6 | 4.6 | 4.8 | 5.6 | 5.8 | 6.6 | 6.8 | 8.8 | 9.8 | 10.9 | 12.9 | |||
| ≤M16 | >M16 | ||||||||||||
| Tensile strength σ, N/mm2 | Nom. | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 800 | 800 | 900 | 1000 | 1200 | |||
| Name | 330 | 400 | 420 | 500 | 520 | 600 | 800 | 830 | 900 | 1040 | 1220 | ||
| Yield strength σt, N/mm2 | Nom. | 180 | 240 | 320 | 300 | 400 | 360 | 480 | — | — | — | — | — |
| Name | 190 | 240 | 340 | 300 | 420 | 360 | 480 | — | — | — | — | — | |
| Conditional yield strength σ0.2, N/mm2 | Nom. | — | — | — | — | — | — | 640 | 640 | 720 | 900 | 1088 | |
| Name | — | — | — | — | — | — | 640 | 660 | 720 | 940 | 1100 | ||
Depending on the mechanical properties, strength classes of materials are established, which are included in the symbols of threaded parts. The strength class is indicated by two numbers. The first number, multiplied by 100, determines the value of the minimum tensile strength σв in MPa, the second number, multiplied by 10, determines the ratio of the yield strength σт to the tensile strength σв in percent; the product of numbers determines the value of the yield strength in MPa; for strength class 3.6, the mechanical properties are approximate.
For example, strength class 5.8 is deciphered as follows:
σв = 5 100 = 500 MPa,
σт/σв=8·10=80% or σт=5·8·10=400 MPa.
Aluminum fasteners
One of the main advantages of aluminum fasteners is their low weight, which allows them to be used to reduce the specific weight of structures for various purposes. Thanks to this feature, aluminum hardware is used to create aircraft, space satellites, and lightweight automobile engines.
Another important factor determining the use of aluminum fasteners is its high conductivity. Therefore, aluminum hardware is, among other things, used in the wiring of power lines, as well as in the production of electrical equipment components.
Aluminum is divided into forged and cast. For the manufacture of hardware, forged aluminum is used, which, in turn, is marked in a certain way. The digital designation indicates the properties of the alloy - the more aluminum in the alloy, the lower the digital value (1 - pure aluminum without impurities).
The letter values indicate the following:
- N – increased strength under deformation load.
- O – the material was fired.
- T – heat treatment.
- F – aluminum has not undergone factory processing.
- W – hardened metal.
The degree of heat treatment is indicated by markers T4 or T6. For example, T6 means that the metal, after heating, was placed in a special furnace, where it cooled slowly at a controlled temperature. When choosing aluminum fasteners, you need to take into account all the parameters of the metal, otherwise the products will not meet the tasks assigned to them.
Strength classes of nuts and bolts with metric threads from 1 to 48 mm according to GOST 1759.5
In table 4 shows the recommended combinations of strength classes of mating parts for various thread diameters. In special cases, fasteners can be made from corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant, heat-resistant steels, as well as non-ferrous alloys. The strength class of the nuts is indicated by a number which, when multiplied by 100, gives the value of the stress from the test load in MPa.
As a rule, nuts of high strength classes can replace nuts of low strength classes. This replacement is recommended for bolt-nut connections, the stress in which will be higher than the yield strength, or the stress from the test load of the bolt.
Related Pages
- Cylindrical threads
- Tapered threads
- Metric thread
- Runs, undercuts, grooves and chamfers according to GOST 10549
- Thread persistent
- Trapezoidal thread
- Symbols of fasteners according to GOST 1759.0 (ST SEV 4203)
- General Purpose Hex Head Bolts
- General purpose screws
- Captive screws
- Set screws
- Special purpose bolts and screws
- Self-tapping screws for metal and plastics
- Locking the nut against the bolt with additional elements
- Locking the nuts relative to the body
- Locking the nut relative to the bolt due to additional friction, welding and plastic deformation
- Locking bolts. Preventing screws and nuts from being lost
- Locking screws
- Flange connection parts
- Flange connections for pipes and cylinder heads
- Flange connections for metal structure pipes
- Application examples for set screws
- Terminal connections
- Friction screw clamps
- Ties and stops
- Fastening machines to bases
Production process
You can learn how nuts are made in Russia from the patents of various factories. There is a well-proven method according to RF patent No. 2361695. It uses the cold stamping method.
Stamping process according to GOST
The first step is to obtain a workpiece using drawing or calibration. Next, the product is formed on presses in five stages (the method is similar to the production of bolts):
- At the first or third stage, upsetting is carried out, formed into a cylinder and a preliminary hole is marked.
- On the fourth, a jumper is formed for the final hole and gives an almost finished look.
- Fifth, punch a hole in the middle.
After going through the stamping stage, the nut is threaded or rolled. The product is ready, all that remains is to test it. The main parameter is the load that the product can withstand before the thread breaks. Various tests are also carried out for horizontal rupture, artificial aging and deformation under various loads.
The hot forging method is very common. The cut pieces are heated to 1200 degrees. Next, a hydraulic hammer stamps hexagons with holes inside. The next step is cooling and threading using oil. Sometimes hardening is used. To do this, the product is placed in an oven at a temperature of 800 degrees, quickly cooled and immersed in oil for 5 minutes. The second heating is carried out for an hour to minimize brittleness and maintain strength.
The detailed production process is shown in the video.
Types of bolts by size
The size range of these products is very wide.
To illustrate the breadth of this range, we can compare bolts for assembling mechanical watches and cameras with bridge bolts with their counterparts used for the construction of railway overpasses across rivers and straits. It is believed that the diameters of commercially produced bolts do not go beyond the values from M5 to M160, however, for special products this series has a wider range - there are bolts measuring 1 mm and more than 160 mm in diameter. The most applicable sizes in fastening technologies are from M5 to M16.
The lengths of bolts, with rare exceptions, are determined by their diameter. Products that are not included in the restrictions of regulatory documents (large diameters, lengths, especially strong steels) are manufactured as non-standard parts.
High strength bolt technology
One of the important components in fastening technology is the clear recording of the time period after preparation and lubrication of the thread before the direct use of the fastener. This period should not exceed 10 days, which should be indicated in a special journal for installing high-strength bolts after their delivery from the manufacturer. If the preparation was carried out independently, then the data is also recorded by filling out a log. An example of the order of fastening a bolted connection:
- Prepare the entire structure for docking and installation.
- Prepare the necessary fasteners according to standards.
- Carry out installation and installation of the structure.
- Tighten the bolts.
- The joints of all fasteners are sealed.
- Carry out quality control of the assembly of the object.
Preparing High Strength Bolts, Nuts and Washers
Before installation into the structure, high-strength bolts, nuts and washers must be prepared. It includes:
- Technological cleaning of preservative factory lubricants, as well as dust and dirt. It is performed in a heated alkaline solution at a temperature of 80-100 ° C, which includes water, detergents, soda ash and caustic soda, liquid glass and trisodium phosphate. The ratio is strictly observed according to GOST. The fasteners in a special container are dipped into the solution for 20 minutes, after which they are washed 3-5 times in a washing solution.
- Drying is carried out hot for several minutes, blowing with compressed air.
- Perform running on a lathe or wrenches, checking and lubricating the threads.
- Mandatory lubrication of fastener threads is carried out by immersing it in a solution of special gasoline GOST 2084 and mineral oil GOST 0799 in a ratio of 9 to 1.
- Purified hardware is collected and stored in closed containers. When assembled, each bolt is equipped with a nut and two washers.
- Carry out quality control.
Features of the production of high-strength bolts
The class is determined not only by the grade of steel, but also by the method used for their production. Thus, high-class bolts are produced on automatic heading machines (cold or hot). The thread is rolled using special technological equipment. Then they are sent for heat treatment. After applying a coating that protects the bolts from corrosion and aging, they are ready for shipment to consumers.
Fasteners are sent to the consumer in boxes of a certain weight. In some cases, a layer of oil is applied to their surface, which ensures long-term storage of hardware products.
Equipment used for the production of high-class bolts can produce from 100 to 200 products per minute. For manufacturing, rolled wire made from low-carbon or alloy steel is used.
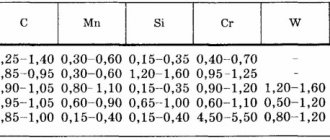
Steels for making bolts
Several grades of steel are used for production. The most common ones are 10KP, 20KP, 10, 20, 35, 20G2R, 65G, 40X. After heat treatment, the bolts receive the specified parameters defined in the relevant regulations. Heat treatment is carried out in electric furnaces using a protective environment. It prevents carbon from leaving the steel.
High strength bolts can be produced from different grades and products will be obtained that will belong to different strength groups. By varying various heat treatment modes, it is possible to obtain products with different strength parameters.
As an example, we can consider the use of steel 35 for the production of bolts belonging to different strength groups:
- 6 — bolts are made on machines of the turning and milling group;
- 6 and 6.8 - fastening is carried out on upsetting press equipment;
- 8 - this class will be obtained after undergoing heat treatment.
High-strength bolts also include specialized hardware that are used strictly in certain areas. Product requirements are determined in industry documents.
Fasteners used in the aircraft industry are produced on the basis of so-called normals (industry standards). These hardware are distinguished by increased strength, light weight and accuracy. The use of these bolts and nuts ensures safe operation of the equipment. For their production, carbon or alloy steels are used. Finished products are coated with a reinforced layer of anti-corrosion coating.
Products used in the construction of bridge structures and their structural elements are standardized by GOST R 52644-2006.
Bolts of special strength are produced in different designs. There are several options. Bolts of category “U” are allowed to operate at – 40 ºC. Products of the “HL” type are operated in the range from – 40 to – 65ºC.
Read also: Minimum diameter of V-belt pulley
For the manufacture of high-strength hardware, the following grades of alloys are used: 30Kh3MF, 30Kh2AF, 30Kh2NMFA.
Types of tests performed
To confirm the quality of products, manufacturing plants conduct a series of tests. The list and test methods are defined in GOST R 52627-2006. Tests can be carried out in the factory or any other laboratory that has passed the appropriate certification at the Rosstandart center. Below is a short list of tests:
Based on the results of the tests, the properties of the product will be determined, in particular - tensile strength, yield strength and a number of others.
Features of connection using threads
- Reliability due to the use of special metric threads and profile versatility. Numerous studies confirm that with the correctly selected bolt strength class and tightening torque, such a connection can withstand heavy loads and is also reliably protected from self-unscrewing.
- Withstands transverse and axial loads. Made from special grades of steel, the bolts resist loads well in any direction.
- Easy installation and dismantling of structures. Despite the fact that after some time it can be difficult to unscrew a threaded connection (due to metal corrosion), it is quite possible to do this with the help of special solvents.
- Low cost of work, which is significantly lower than the cost of welding. Many structures are built today using bolts because it requires less time and effort.
Read also: Paste for cleaning copper and brass
It should be noted that a small drawback of a threaded connection can be considered a strong concentration of stress at the valley of the profile of the thread itself. For this reason, the bolt marking must be selected correctly, in exact accordance with the load experienced by the part. This will reduce the risk of both self-loosening due to loose tightening and nut breakage/thread cutting due to extreme stress.
Ploughshare bolt with countersunk head
We must not forget that today all kinds of locking means are also actively used, including locknuts and spring washers.
What is a high strength bolt
This type of fastening has several classifications, but the most significant characteristic is increased resistance to heavy loads. Thanks to this, the structures connected by bolted fasteners become highly strong and durable. High-strength bolts, nuts and washers are widely used for metal structures, construction work and in heavy industry and mechanical engineering.
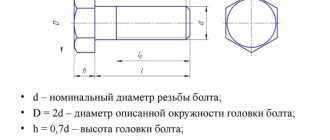
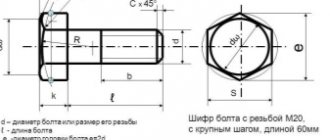
A bolt is a rod made of a metal alloy with an external thread applied to it and a head, usually in the form of a hexagon, for a wrench. Fastening is done by screwing on a nut of the required size. To distribute the load evenly, washers are used.
Copper fasteners
Copper has even greater conductivity than aluminum, and therefore copper fasteners are also used in connecting power lines and in the production of equipment powered by electricity. The disadvantage of copper is its high cost, which is why it is used less often than cheaper aluminum.
Another disadvantage of copper is that when exposed to moisture, it quickly oxidizes, becoming covered with a dense coating. To prevent copper from oxidizing, other metals are added to its composition - nickel, zinc, etc. The alloys obtained by adding other metals do not oxidize, due to which they can be used in the production of structures whose operation involves constant contact with water.
Types of bolts by shape
The shape of these products is determined by the diameter and length of the rod, the type of thread, the design of the head, the technology and tightening tool, and locking elements.
The most varied types of heads are:
- hexagonal;
- square;
- round;
- secret;
- semicircular;
- wide semicircular;
- hexagonal with flange.
Round heads, in turn, are divided into separate types according to internal spline options. These elements can be hexagonal, square, flat, cross-shaped, octagonal, twelve-sided, various modifications of the Torx system and many others.
Types of bolts by purpose
According to their intended use, bolts are divided into machine-building, construction, road, furniture, plowshare and others.
Engineering bolts are the most widely used and therefore are typical representatives of the very concept of “bolt”. In our country, they are produced according to several Russian standards, as well as according to German standards (DIN).
Construction bolts are designed to connect house elements to each other - walls, beams, metal and other structures. They are also used for fastening window and door frames in openings. The main types of construction bolts include anchor, foundation, bridge and stud bolts. There are also high-strength products of large diameters with large thread pitches and strength classes from 5.6 to 12.9.
Furniture bolts are distinguished by a long shaft and a wide, aesthetic head with a flat or cross slot, which remains visible when assembled. They are used in conjunction with nuts, washers and other parts. Some products are made with a square head - a square-section protrusion under the head that serves to prevent the bolt from rotating around its axis when the nut is tightened.
A similar design - with a square head and an enlarged semicircular head - are road bolts . They are designed for screwing steel barrier beams to vertical supports on highways. These bolts are shorter than furniture bolts, but much more powerful.
Ploughshare bolts also have square heads, but, unlike furniture and road bolts, they are larger in diameter, and their heads are countersunk. Such products are used to secure the executive elements of agricultural and road equipment - plows, bulldozer and excavator buckets. Recessed heads increase bolt life, and square head supports center bolt installation and make nut tightening easier.
In addition to the widely used options described, there are many products of the same name for special applications. They differ from each other in the type of thread, head shape, locking technology and tightening method.
How to choose a threaded rod?
All studs are designed to handle a specific load. And their load-bearing capacity directly depends on their design, material, size, etc.
The load-bearing capacity of a threaded rod that can withstand a load in a plane depends on the depth of its screwing. The load capacity is also affected by the thread pitch.
With a perpendicularly directed load, the load-bearing capacity of the studs is determined by the resistance of the material to bending and shearing. This parameter is influenced by the material and diameter of the rod, while the length of the threaded part does not matter much.
When selecting a material for a stud, environmental parameters and the impact on the stud should be taken into account. It is also worth remembering that contact of dissimilar materials leads to electrochemical corrosion.
Rules for tightening BVP
Tensioning of high-strength bolts is carried out in two stages:
- Align the holes of the parts for high-strength bolts and fix the position of the structural parts using mounting plugs.
- At the first stage, bolt fasteners are inserted and plugs are removed. Next, using wrenches, the bolt fasteners are tightened only to 50-90%. At the beginning of tensioning, the fastener head must be held from turning. If it is impossible to eliminate the scrolling, the element is replaced.
- At the second stage, fastening is carried out completely, using torque wrenches. The tension of the bolts is carried out after checking the compliance of the geometry of the entire structure with respect to standards and rules, and checking the tightness of the structure's screed.
Excellent technical characteristics of connections made with high-strength bolts ensure the strength of the entire structure. If all instructions are followed, the structure will last for many decades.
Did you manage to solve your problem using the recommendations from the article?
Yes!
46.39%
No. More answers required. I'll ask in the comments now.
38.56%
Partially. There are still questions. I'll write in the comments now.
15.05%
Voted: 804
How to properly tighten and loosen a bolt
Most often, when tightening bolted connections on various structures in the household, ordinary wrenches are used - socket, open-end and box-end wrenches. However, in this case, it is difficult to accurately determine the tightening torque, so in industrial production and repair shops, experienced mechanics use special torque wrenches or pneumatic impact wrenches, the main advantage of which is the ability to set the required tightening level, depending on the type of mechanism.
To unscrew the bolt, the same keys are used, however, in old designs, most often the bolts “stick” strongly to the nut due to corrosion. For safe unscrewing, several simple methods are used:
- use of aerosol-type penetrating lubricant WD-40;
- lightly tapping the rusty bolt with a hammer to destroy the rust in the profile of the threaded connection;
- Turn the nut slightly in the direction of tightening (just a few degrees).
Threaded connections are used in many structures and mechanisms, since in practice they have proven their high reliability and efficiency. The correct type of bolt, tightened to the required tightening torque, is able to cope with the load throughout the entire life of the mechanism.
Types of threaded fastening
To make a threaded connection, you need at least two parts, one of which has an external thread and the other has an internal thread. There are several structural types of threads.
Through holes are drilled in the parts to be connected, after which a bolt is inserted inside, which is tightened on the other side with a nut.
In this type of connection, the role of the nut is played by the part itself, in which a hole is first drilled, then a thread is applied, after which another part is fastened using a bolt or screw. If you use self-tapping screws, then it is not necessary to drill a preliminary hole, since the part itself automatically makes a thread when screwed.
Using studs
One end of such a pin is screwed into the component part, and a suitable nut is screwed onto the second in a special way.
Stud with screw-in end
Titanium fastener
Titanium is a durable and lightweight metal used for the manufacture of high-reliability fasteners. Plus, titanium is not afraid of moisture, and also does not oxidize when in contact with aggressive chemicals. These features make it possible to use titanium fasteners in the manufacture of structures operated in extremely difficult conditions - aircraft, satellites, military equipment, etc.
However, titanium is one of the most expensive metals, which significantly limits the possibilities of its use. Therefore, titanium fasteners are used only in cases where there are no other alternatives.
Steels for making bolts
For the manufacture of high-strength fasteners, alloy carbon steel of increased strength and durability is used. Special manufacturing technologies include hot or cold heading of blanks, which significantly increase the level of strength. Mandatory heat treatment in electric furnaces gives the product anti-corrosion properties, greatly increases strength, and extends service life.