HILTI anchor fasteners are certified in accordance with international and domestic standards and have a high safety factor and are particularly reliable fasteners.
Each anchor has its own load safety factor, but not less than 2. All fasteners are galvanized or stainless steel, which increases their durability.
You can order a free visit from a HILTI specialist for consultation to the site or office, and specialists can also test the load-bearing capacity of the anchor for pull-out directly at the construction site. If necessary, specialists will calculate anchor connections and also analyze the reliability of fasteners for dynamically loaded elements. Find out detailed information from your local HILTI representatives.
When designing projects, I often use the HILTI AutoCAD catalog and blocks.
The catalog provides detailed information on which HILTI anchor should be used in a particular material, and also indicates the technical characteristics of the fastener.
The table below provides a short list of fasteners that must be used when installing in various materials:
Design features
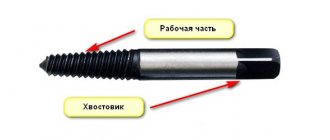
The anchor bolt can have different sizes, but structurally consists of the following main elements:
- threaded rod (has a cone-shaped head at the end);
- outer sleeve;
- lock nut;
- washer.
The inner rod is threaded to established standards and looks like a regular bolt. The main difference is its head. It is made under a cone, which makes it easier to expand the lower part of the sleeve. Its dimensions are determined by the requirements for the reliability of fastening of specific products (their dimensions and weight).
The bushing is made in the form of a cast rod. It has longitudinal slits that resemble petals. Thanks to them, during the fastening process, this part of the sleeve expands, which significantly increases the effect of adhesion of the anchor to the hole. The sleeve is made of metal. Like the entire anchor, it is covered with an anti-corrosion layer. It ensures its durability.
The lock nut has a hexagonal design. Some designs use a nut with a pressed washer.
The operating principle of such a device is to create the effect of reliable fastening in a pre-prepared hole. This can be achieved due to the fact that during the process of tightening the nut of the inserted anchor, the petals of the stud expand. It fits tightly to the walls of the hole, which significantly increases the friction force. The permissible load on the entire structure increases many times over. To prevent excessive deepening of the nut, a special lock washer is used.
To more accurately select the dimensions of the required anchor bolt, a special table has been developed. It shows the dimensions of the products and their main technical characteristics. Before installing the anchor, it is necessary to develop a drawing of the future fastening. With its help, the type, its diameter and length of the anchor bolt are selected.
Anchor blocks or anchor groups are very widespread. The wide range of applications of these fasteners is created by their simple and stable design, as well as a large selection of models. This type of metal products is used today as a reliable fastener to the base of foundations of various large equipment, structures used in construction and for other industrial purposes. of anchor blocks produced by the Nedwals Company provides one of the most reliable fixations of building structures, which ensures the speed of installation of construction projects. Why anchor blocks provide such reliable fastening between the dimensional elements of buildings? The secret is actually simple, these are anchor bolts, welded together using high-quality rolled metal with precise adherence to the center distances. Thanks to this system, the structure can withstand enormous loads and hold rigid ligaments.
Where are anchor groups used? Anchor blocks in Novosibirsk are most often used in the field of concreting and monolithic construction. They are also used in connecting dimensional structural elements made of metal or reinforced concrete, strengthening parts of buildings on the base, and for attaching heavy structures to the foundation. Often, using manufactured anchor blocks in accordance with GOST, diesel generators, heating boilers, fireplaces, gas installations and other equipment are attached to a reinforced concrete base.
The price of anchor blocks depends on the number of studs and the design of the fastening reinforcement. Welded structures can consist of 4 studs or bolts, fastened with metal flanges or plates. The design of each type differs in the shape of the component parts, degree of reliability and price.
What are the benefits of anchor groups? Durability. Several types of steel are used in the manufacture of anchor blocks This technology makes anchor blocks in Novosibirsk almost wear-free; their service life lasts several decades. The design is resistant to the influence of adverse external factors thanks to a special special coating, which helps protect against corrosion.
Manufacturability . The production process of anchor blocks in accordance with GOST is carried out under strict control. When creating them, all accepted standards are observed, so after production, high-quality blocks with high performance and characteristics are obtained. To improve the performance properties of the product, profile materials made of high-strength steel are used. The process itself is fully automated, which eliminates the human factor and allows you to maintain a favorable price for anchor blocks .
Design feature . Anchor blocks have very precise geometric characteristics. A clear calculation of their design makes it possible to maintain the correct distance between the ends of the studs. It is thanks to these calculations that the supporting structures and foundation have strong adhesion. of anchor blocks in Novosibirsk is calculated in advance. The design of anchor blocks is tested using an anchor-loading mechanism. This process is called “load-locking” and is a visual test of the load-bearing capacity of each anchor.
Large selection of shapes. Thanks to their prefabricated design, anchor blocks Typically, to create the shape of an anchor block in Novosibirsk, a welded frame structure made of various profile materials, such as a channel, angle, circle, strip, reinforcement, etc. is used. or in arbitrary combinations of these profiles with each other.
According to the customer's individual project. The Nedwals company produces anchor blocks in accordance with GOST , as well as according to customer drawings. At the same time the price of anchor blocks is also calculated according to an individual scheme according to the design documentation. Bolts in anchor blocks can be fastened to each other in a variety of ways, according to your order.
Main types of anchor blocks.
Angle anchor block. It has a simple design, which includes a welded frame made of metal angle and 4 studs. The block is welded from a metal corner in the form of a rectangular frame, the studs are located in its corners and come out after concreting.
Anchor block on flanges. It consists of 6 studs welded into two steel flanges, this increases the reliability of the structure. Flanges create and guarantee reliable fixation of studs in the structure.
Anchor block with plate. It differs in a much more durable design from a product with flanges, as solid steel plates are used.
The Nedwals plant produces anchor blocks in Novosibirsk for various industrial and construction purposes. During the manufacture of such products, only modern technologies are used. All anchor blocks are produced only in accordance with GOST, so they are characterized by high strength, reliability and durability.
We remember our customers and try to maintain reasonable prices for anchor blocks . You can place an order for anchor groups on our website or by contacting our managers. Our employees know the production features and the smallest design details inside and out.
Types of anchor bolts
The classification of anchor bolts offered by modern manufacturers is based on many parameters. They all fall into two categories:
- with mechanical fixation;
- the use of chemical adhesive fillers;
- on vibrocaulking.
In the first case, the reliability of the fastening is ensured by creating conditions that significantly increase the friction force. In the second, fastening is added to the initial effect (mechanical fastening) through the use of reliable adhesive joints. In this case, the effect of adhesiveness is used - the ability of the adhesive to penetrate into the pores of the material where the sleeve is placed. To implement the fastening, you need a tube of adhesive and a special gun. First, glue is squeezed into the hole. Then the anchor bolt is driven in. Such anchors are used for fastening structures in some brands of cellular concrete or in walls made of material with a porous structure.
In more detail, the types of anchor bolts are classified according to the following parameters:
- purpose and scope of application;
- form of design;
- geometric dimensions;
- type of fastening;
- head shape;
- bushing material.
The purpose and scope of application is given in more detail below.
According to the design form, the following types of anchor bolts are distinguished:
- design with hook-shaped tips;
- with a ring attached to the tip;
- with a fixed nut;
- stud anchor.
The installed hooks are used for subsequent installation of suspended structures. Products that have a hanging system on ropes or cables are attached to the finished rings. There are anchor bolts with a fixed nut. This allows you to set the depth of screwing in the anchor. The latest design has fastenings on both sides. They are tightened with a nut. Most often, such bolts are equipped with a cone-shaped working part of the sleeve. The use of this design allows you to select the most optimal pressure on the walls of the hole, that is, the adhesion force of the anchor and the wall.
Stud anchors are divided into HAS and HST designs. They allow you to work in concrete prone to cracking. They are used for through fastening.
Based on the type of fastening in the wall or ceiling, anchors are divided into two categories: expansion and wedge. The first type is most widespread. In practice, one and two spacer structures are used. The second type of product is equipped with two sleeves, which increases resistance and improves the reliability of fastening.
The shape of the anchor bolt heads is either a turnkey or a screwdriver. In the second case, the most common are threads for a Phillips screwdriver.
Depending on the type of fastening, it is divided into:
- ordinary anchor bolt;
- bolt with sleeve and nut;
- expansion type collet bolt;
- driven anchor bolt.
All these structures work on the principle of expanding the bushing at the moment the bolt shaft is tightened. The most complex design of the bushing is the collet bolt. Four cuts are made on its surface. Therefore, at the moment of screwing in, its end takes the shape of four petals, which increases the reliability of the installation. The drive-in anchor has a cone-shaped sleeve with internal slots. As the anchor is driven into the hole, the sleeve compresses and the central notched parts expand.
Anchor bolts are made of steel or brass. In accordance with standards and building codes, steel is selected depending on the application and operating conditions of the fasteners. In some cases, certain grades of carbon steel are used, for example VSt3kp2; for low-temperature conditions, low-alloy steel grade 09G2S-8 or their analogs are used.
Designation of anchor bolts in the drawings
Fasteners are used to connect various parts of structures. Fasteners (and this is what fasteners are often called in everyday life) include screws, bolts, nuts, self-tapping screws, screws, rivets, studs, pins, washers, dowels, etc.
In technology, one of the most important and widespread detachable connections is the bolted one. Its main advantage is that when using it, it is not necessary to cut threads on the parts that are fastened together. This feature of a bolted connection is especially important when the material from which the parts being connected are made is not able to provide the required thread strength and durability.
Bolted connections also have their disadvantages. These include, for example, that to implement it, there must be enough space on the parts being connected to accommodate the head of a screw or nut. In addition, during the process of screwing or unscrewing nuts, you need to hold the screw head to prevent rotation. It should also be noted that compared to, say, a screw connection, a bolted connection leads to a greater increase in the mass of the finished product.
If for some reason it is impossible to install a bolted connection or it turns out to be irrational, then screws and studs are used. This, for example, is usually done when there is no way to provide access to the head (nut) or there is simply no space to place it. Another common case is the significant thickness of the parts, which results in the need for deep drilling and the use of long bolts.
Washers are used as backing elements. They are installed under the heads of screws or nuts in order to reduce the degree of deformation of parts by clamping elements when they are made of not very durable material (for example, wood, aluminum, plastic, etc.). In addition, with the help of washers, it is possible to prevent parts from being scratched when screwing a screw or nut, and also to compensate for significant hole clearance. As practice shows, using washers in other cases does not make much sense. If it is necessary to protect the connection from self-unscrewing, then safety or lock washers are also used.
Simplified and conventional images in general view drawings and assembly drawings of images of fasteners for all industries and construction are established by a document such as GOST 2.315 - 68.
The choice of a conventional or simplified image of fasteners in general view drawings and assembly drawings is made depending on the exact scale and purpose of each specific technical document. Conventional images are used for those fasteners whose rod diameters, when depicted in the drawings, are 2 millimeters or less. In this case, the rule that a complete picture of the nature of the connection must be given should be fully observed.
The use of conventional and simplified images of fasteners should be carried out in accordance with the tables below.
| Simplified and conventional images of fasteners | ||
| Simplified image | Conditional image | Name |
| Hex Bolts | ||
| Square Head Bolts | ||
| Hammer Head Bolts | ||
| Button head bolts | ||
| Round Head Hinge Bolts | ||
| Swivel bolts with fork | ||
| Foundation bolts | ||
| Button head screws | ||
| Pan head screws | ||
| Pan Head and Sphere Screws | ||
| Phillips Button Head Screws | ||
| Phillips Pan Head Screws | ||
| Allen screws | ||
| Countersunk head screws | ||
| Countersunk screws | ||
| Countersunk Phillips Screws | ||
| Self-tapping screws with cylindrical head | ||
| Self-tapping screws with a countersunk cross head | ||
| Round nuts | ||
| Hex nuts | ||
| Hexagon slotted and castle nuts | ||
| Wing nuts | ||
| Round head screws | ||
| Countersunk screws | ||
| Countersunk head screws | ||
| Hairpins | ||
| Plain washers, lock washers, etc. | ||
| Lock washers with tongue | ||
| Spring washers | ||
| Cylindrical pins | ||
| Conical pins | ||
| Nails | ||
| Cotter pins | ||
| Threaded inserts | ||
| Examples of simplified and conventional images of fasteners in connections | |
| Simplified image | Conditional image |
If objects on assembly drawings have several similar connections in their design, then the fasteners included in them in one or two places of each of them should be depicted in a simplified or conditional manner, and in other places it is enough to simply use axial or center lines.
Designation of fasteners in the drawing
In cases where the drawing contains a number of fastening groups that differ in size and type, it is better to apply them using symbols, indicating the position number only once.
If there are identical fastening groups on the construction drawings, then it is permissible to outline them with a thin solid line, and make an explanatory inscription on the leader shelf. As for the predominant fasteners, they are not outlined and are not specified in the general instructions for the drawing.
Read also: Selecting cutting modes when milling
Same fasteners
To depict the slots on the fastener heads, one solid line is used.
Designation of splines in the drawing
In cases where the slot line drawn at an angle of 45° to the drawing frame coincides with the center line or is close to it, then it is drawn at an angle of 45° to the center line.
Fasteners
— parts for fixed connection of machine parts and structures.
These usually include parts of threaded connections: bolts
,
screws
,
studs
,
nuts
,
screws
,
washers
, cotter pins, and
pins
.
The main parameter of threaded fasteners is the thread, the shape and dimensions of which comply with the standards.
Designation system for fasteners according to GOST R ISO 8991-2011 (Fastening products. Designation system)
The symbol does not indicate: version 1, large thread pitch, right-hand thread, lack of coating, as well as parameters that are clearly defined by product standards.
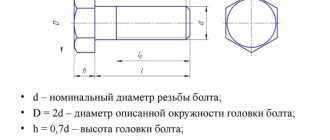
Hex head bolt (GOST 7805-70)
Bolt
- a fastening threaded part in the form of a cylindrical rod with a head, part of which is threaded. The designs of bolts are very diverse and depend on the purpose of the bolted connection. Bolts can have either a special design or meet the requirements specified by the standard. In the latter case, they are considered standard products.
The use of standard products helps optimize production. Depending on the purpose of the bolt and its design features, a series of standards have been developed.
The standards provide for the following bolt designs:
Conical bolt (GOST 15163-78).
Hinged bolt (GOST 3033-79).
Round head bolts (GOST 17673-81, 7783-81, 7785-81, 7786-81, 7801-81, 7802-81).
Hex head bolts (GOST 7805-70, 7808-70, 7811-70, 7817-80, etc.).
Foundation bolts (GOST 24379.1-80).
Eye bolt (GOST 4751-73).
For general technical needs, hex head bolts are most often chosen.
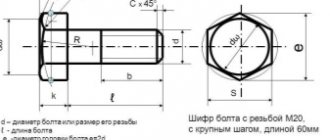
GOST 7805-70 “Hex head bolts”
The standard establishes the following requirements: a bolt with a nominal thread diameter from 1.6 to 48 mm, made of steel grades: 10 kp, 20 kp, 10, 20, 35, 40Х, ЗОХР, two accuracy classes are provided (A, B) and four classes strength (4.8; 5.8; 8.8; 10.9) with thread tolerance: 6g, 8g. All design dimensions are determined by the standard and depend on the type of design, of which there are four.
Hex head bolt (GOST 7805-70)
Bolt M12- 6g.60.58 (S18) GOST 7805-70
— bolt version 1 with thread diameter
d
= 12 mm, wrench size
S
= 18 mm, length
l
= 60 mm, with large thread pitch, with tolerance range 6g, accuracy class 5.8, uncoated.
Bolt 2M12x1.25- 6g.60. 109.40Х.016 (S18) GOST 7805-70
— bolt version 2 with thread diameter
d
= 12 mm, wrench size
S
= 1 8 mm, length
l
= 60 mm, with fine thread pitch, with a tolerance range of 6g, accuracy class 10.9, made of steel grade 40X, with coating 01 with a thickness of 6 microns.
Examples of symbols according to GOST R ISO 8991-2011:
Hex bolt ISO 4014 -M12
x
80 - 8.8
- a hex head bolt with a diameter of ISO 4014, thread size
d
= M 12, nominal length
l
= 8 0 mm, and strength class 8.8.
Hex bolt ISO 4014 -M12
x
80 - 8.8 - A2P
- a hex head bolt with a diameter of ISO 4014, thread size
d
= M 12, nominal length
l
= 8 0 mm, and strength class 8.8, electrolytic coating in accordance with ISO 4042, designation A2P.
When designing a threaded connection, the length of the bolt is calculated based on the dimensions of the parts being connected and rounded to the nearest larger value provided for by the standard.
Round head screw ( GOST 17473-80)
Screw
- a fastening threaded part in the form of a cylindrical or conical rod with or without a head.
The difference between a bolt and a screw is in the application and lies in the fact that a nut is screwed onto the bolt, and the screw is screwed directly into the part.
The standards provide for the following screw designs:
Normal screws (fastening) (GOST 1491-80, 11664-85, 11738-84, 17473-80, etc.).
Captive screws (GOST 10336-80, 10337-80, 10338-80, etc.).
Thumb screws (GOST 21331-75, 21332-75, 21333-75, etc.).
Self-tapping screws (GOST 10619-80, 10620-80, 10621-80, etc.).
Set screws (GOST 11074-93, 11075-93, 1476-93, etc.).
Mounting screw
most common in technology. The screw head is used to press the parts being connected and to grip the screw with a screwdriver, wrench or other tool. Mounting screws with countersunk, semi-countersunk, semicircular, hexagonal, cylindrical, etc. have become widespread. heads.
Read also: Diamond pencil holder
For general technical needs, fastening screws with cylindrical (GOST 1491-80), semicircular (GOST 17473-80), semi-countersunk (GOST 17474-80) and countersunk (GOST 17475-80) heads are most often used.
GOST 1491-80 “Cylindrical head screws”
The standard applies to cylindrical head screws of accuracy classes A and B with a nominal thread diameter from 1 to 20 mm, steel grade 10kp, accuracy class B, thread tolerance range 6g.
Screw with cylindrical head (GOST 1491-80)
Screw A.M8-6gx50.48 GOST 1491-80
— a cylindrical head screw of accuracy class A, version 1, thread diameter
d
= 8 mm, with a large thread pitch, with a thread tolerance field of 6g, length
l
= 50 mm, normal thread length
b
= 22 mm, strength class 4.8, uncoated .
Screw V2.M8x1-6gx50-34.48.016 GOST 1491-80
— a cylindrical head screw of accuracy class B, version 2, thread diameter
d
= 8 mm, with a fine thread pitch, extended thread length
b
= 34 mm, with a zinc coating 6 microns thick, chromated.
Examples of symbols
according to GOST R ISO 8991-2011 :
Hex head screw ISO 8676 – M12
x
1.5
x
100 -10.9
- screw with hex head ISO 8676, thread size
d
= M 12 and pitch 1.5, nominal length
l
= 10 0 mm, and strength class 10.9.
Self-tapping screw ISO 7049 – ST3.5
x
16 - C - Z
- self-tapping screw with a rounded head and a Phillips slot ISO 7049, CT3.5 thread, nominal length
l
= 16 mm, with a conical end of a type C and a slot type Z.
High-strength nuts (GOST 22354-77)
screw
- a part of a threaded connection or screw drive having a threaded hole.
The standards provide for the following nut designs:
Cap nuts (GOST 11860-85).
Round nuts (GOST 10657-80, 11871-88, 6393-73, 8183-73).
Slotted, castle nuts (GOST 10606-82, 10609-82, 2528-73, 5918-73, etc.).
Hex nuts (GOST 10605-94, 10607-94, 10605-94, 10608-72, 5915-70, etc.).
Wing nuts (GOST 3032-76).
A fastening nut in a threaded connection is screwed onto the end of a bolt or stud or onto a threaded section of a shaft or axle to secure the parts sitting on them - rolling bearings, pulleys, etc. - from axial movement.
GOST 5915-70 “Hex nuts, accuracy class B. Design and dimensions”
The standard applies to hex nuts of accuracy class B with a thread diameter from 1.6 to 48 mm; three versions are provided.
Hex nut version 1 (GOST 5915-70)
Nut М12-6Н.5 (S18) GOST 5915-70
— nut version 1, thread diameter
d
= 12 mm, wrench size
S
= 18 mm, large thread pitch, thread tolerance 6 H, strength class 5, uncoated.
Nut
2M12x1.25-6N.12.40X.016 GOST 5915-70
- nut version 2, thread diameter
d
= 12 mm, wrench size
S
= 1 9 mm, with fine thread pitch, made of steel grade 40X, coated 01 6 microns thick.
Examples of symbols according to GOST R ISO 8991-2011:
Hex nut ISO 4032 – M12 – 8
— hex nut ISO 4032, thread diameter
d
= M12 and strength class 8.
Hex nut ISO 4036 – M6 – St
— low hex nut ISO 4036, thread diameter
d
= M6? made of steel with hardness 110 HV min (St).
Threaded rod
- a fastener, which is a metal rod with threads at both ends. The end of the stud is screwed into one of the parts to be joined, and the other part is pressed against the first when screwing the nut onto the other end of the stud.
The designs of studs are regulated by standards depending on the accuracy class, design and length of the screwed end. Thus, the following standards apply to threaded studs of accuracy class A and B (version 1), depending on the length of the screwed end:
GOST 22034-76 “Studs with a screw-in end, length 1.25d. Accuracy class B. Design and dimensions"
This standard applies to studs with thread diameters from 3 to 48 mm, screwed into threaded holes in ductile and gray cast iron parts. These pins can be used for screwing into threaded holes in steel and bronze parts.
Threaded rod (GOST 22034-74)
Hairpin M16- 6g x 120.58 GOST 22034-76
— a pin with a thread diameter
d
= 16 mm, with a large pitch
P
= 2 mm, with a tolerance range of 6g, length
l
= 120 mm, strength class 5.8, without coating.
Hairpin 2М16х1.5- 6g x 120.109.40Х.026 GOST 22034-76
— a pin with a thread diameter
d
= 16 mm, with a fine pitch
P
= 1.5 mm, with a tolerance field of 6 g, length
l
= 120 mm, strength class 10.9, made of steel 40X with a coating 02 6 microns thick.
Read also: Gearbox designation on the diagram
Spring washer (GOST 6402-70)
Washer
- a part placed under a nut or bolt head to prevent crushing of the surfaces of the parts being connected, to protect them from scratches when screwing in nuts, screws, and to bridge the gap between the bolt shaft and the hole in the parts.
According to the purpose of the washers there are:
Round washers (general purpose)
- to increase the support area if the supporting surface is made of soft material or uneven, as well as if the hole for the screw is oblong or of increased diameter (GOST 11371-78, 6958-78, 10450-78, 9649-78).
Oblique washers
— to eliminate distortion of the nut or screw head when tightening (GOST 10906-78).
Spherical and conical washers
— to eliminate distortion of the nut or screw head when tightening (GOST 13438-68, 13439-68).
Quick release washers
- used in devices to save time on removing a machined part and installing a new one.
Spring washers
— reduce the risk of self-unscrewing of screws or nuts due to the elastic forces of the compressed washer (GOST 6402-70).
Locking washers
— by bending their parts, the possibility of rotating the nut or screw relative to the supporting part is eliminated (GOST 466-77, 11872-89).
End washers
— prevent axial movement along the shaft of parts fixed or rotating on it (GOST 14734-69).
In assembly drawings and general view drawings, the image of fasteners (simplified or conditional) is chosen depending on the purpose and scale of the drawing. Fasteners whose rod diameters in the drawing are 2 mm or less are depicted conventionally. The size of the image should give a complete picture of the nature of the connection.
If the object shown in the assembly drawing has a number of similar connections, then the fasteners included in these connections should be shown conventionally or simplified in one or two places of each connection, and in the rest - with center or axial lines (Fig. 1).
Figure 1. Assembly drawing depicting a number of similar connections
If there are several groups of fasteners in the drawing, different in type and size, then instead of applying repeating item numbers, it is recommended to designate identical fasteners with symbols, and apply the item number only once (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. Image on the assembly drawing of groups of fasteners
In construction drawings, it is allowed to outline identical groups of fasteners with a solid thin line with an explanatory inscription on the shelf of the leader line; however, the predominant fasteners are not outlined or specified in the general instructions for the drawing.
The slots on the heads of fasteners should be depicted as one continuous line, as shown in Fig. 3: in one view - along the axis of the fastener, in the other - at an angle of 45° to the drawing frame.
Figure 3. Image of the slots on the heads of fasteners at an angle of 45 0 to the drawing frame
If the slot line drawn at an angle of 45° to the drawing frame coincides with the center line or is close to it, then the slot line is drawn at an angle of 45° to the center line (Fig. 4).
Figure 4. Image of the slots on the heads of fasteners at an angle of 45 0 to the center line
Table 1. Simplified and conventional images of fasteners
Name
Image
Simplified
Conditional
Table 2 Examples of simplified and conventional images of fasteners in connections
| 1. Bolts and screws |
| – with hex head |
| – with square head |
| – with hammer head |
| 2. Bolts |
| – with a semicircular head and mustache |
| – folding with round head |
| – folding with fork |
| – fundamental |
| 3. Screws |
| – with a semicircular head |
| – with cylindrical head |
| – with cylindrical head and sphere |
| – with a semicircular head and a cross-shaped slot |
| – with cylindrical head, sphere and Phillips slot |
| – with a cylindrical head and a hexagonal socket |
| – with a semi-concealed head |
| - with countersunk head |
| – with a countersunk head and a cross-shaped slot |
| – with a cylindrical head, self-tapping |
| – with a countersunk head and a cross-shaped slot, self-tapping |
| 4. Nuts |
| – round |
| – hexagonal |
| – hexagonal slotted and crowned |
| – wing nuts |
| 5. Screws |
| – with a semicircular head |
| - with countersunk head |
| – with a semi-concealed head |
| 6. Hairpins |
| 7. Washers |
| – simple, locking, etc. |
| – locking with tongue |
| – spring |
| 8. Pins |
| – cylindrical |
| – conical |
| 9. Nails |
| 10. Cotter pins |
Application
Each type of anchor developed is used to solve specific problems. Therefore, before starting work, it is necessary to determine what a specific sample is used for. According to the approved standard, the use of anchor bolts is carried out as follows:
- the mortgage is used at the stage of pouring concrete or producing brickwork;
- spacer allows you to attach massive structures to a concrete or brick base;
- wedges are used in connections where heavy loads are expected;
- bolts with a ring or hook are necessary for mounting suspended elements, fastening hinge joints, cables, chains or other tension structures;
- frame is used for installing doorways and window frames;
- using a façade anchor, various elements of building facades are secured;
- a ceiling anchor allows you to securely attach various elements of suspended structures to the ceiling (it must withstand the weight of any selected product);
- spring fasteners are used for mounting elements to thin-walled structures.
Before you begin choosing the necessary anchorage, you should consult with professionals. This will help avoid serious mistakes. The result of incorrect application will be difficult to correct.
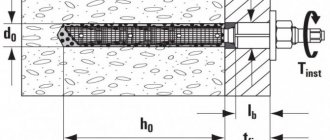
Anchor design with bolt
An anchor bolt is an independent product consisting of several elements. It is enough to have a fastener with a size corresponding to the calculations, an attached element, a working surface and an appropriate hand tool.
No additional fasteners are required for the unit. This is an excellent advantage over prefabricated fastenings, where you still need to select the size of one element to another.
The design of the anchor bolt is simple and consists of:
- bolt , a fastener with a metric thread due to which the anchor is screwed into the prepared hole;
- flat washers , which allows you to distribute the load over a large surface when tightening the bolt;
- conical part , which, when the bolt is screwed in, rises up the thread and contributes to the expansion of the three wings of the bushing;
- spacer sleeve - a cylindrical element that, when expanded, fits into the base material.
Marking of anchor bolts
Since 2012, all anchor bolts have been marked in accordance with the interstate standard. Its requirements apply to the territory of the countries that have signed it. In this standard, the anchor bolt has the following designations:
- the first letter together with the number indicates the thread diameter, for example M8;
- the next number indicates the diameter of the drill that must be used to prepare the hole, for example 10;
- the number located after the slash means the thickness of the attached structure or product;
- the last digit located after the “x” sign indicates the minimum permissible depth of the prepared hole in millimeters, for example 90.
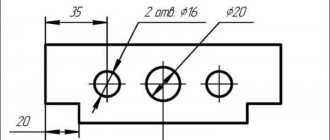
Combining all the designations, we get the following abbreviation - M10/35x100. On construction drawings and plans, the markings, in addition to digital symbols, have special signs. They are placed in a circle and indicate the type of anchorage used.
Anchor products manufactured in other countries have their own markings. For example, on anchors from the German company Fisher, the marking is as follows - FBN 12/100[+120][GS]. The first letters indicate the name of the product. The number 12 indicates the diameter of the anchor taking into account the thread. The second digit determines the useful length. The number in the first square brackets corresponds to the useful length. The last two letters indicate that the anchor is equipped with a wide washer.
Therefore, to correctly select the type of anchor bolts, it is necessary to understand in detail the marking system and clarify the necessary characteristics.
Advantages and disadvantages of anchor connections
The advantages of such connections are:
- have the best load capacity;
- supplied with a wide range of fixing elements;
- possibility of use in various environmental conditions;
- ease of use (there is no need to use specific equipment for installation);
- Possibility of application for static and dynamic structures.
The disadvantages of professionals include:
- the need for careful preparation of holes in durable structures;
- careful selection of anchor type;
- higher cost.
Correctly selected anchor fasteners will allow you to securely attach the structure to the wall, ceiling or floor. It will allow you to obtain a durable and reliable connection.