To view the video, you need a modern browser that supports HTML5 video.
After the advent of technology such as milling, planing processing was written off by many as outdated and ineffective. And it is very premature, because for processing metal workpieces this technique is considered one of the most effective and inexpensive. Planing refers to a wide range of operations - leveling the surface, finishing grooves and protrusions, creating grooved surfaces, grooves, as well as other actions.
Device
To perform the functions assigned to it efficiently, planing machines must include the following components:
- bed;
- control unit;
- a support with one or more tool holders;
- frame (on large machines the frame has a portal configuration, on smaller ones it is made in the form of a console);
- mechanism for moving the table and/or support;
- work table with T-shaped slots for precise positioning of the product;
- electric motor;
- pumping station for supplying lubricating and cooling media to the planing zone;
- a cross member that connects the elements of the frame and gives it the necessary rigidity;
The general classification index for such equipment includes an alphanumeric designation of the type XXXX. The first digit indicates the group number according to the classification tables. For planing machines, this is number 7. The second number indicates the type of machine (1 - single-column longitudinal planing; 2 - two-column longitudinal planing; 3 - cross-planing; 4 - slotting; 5 - broaching horizontal; etc.) . The third and fourth digits indicate the largest size of the workpiece.
Schemes of metal processing by planing
The last two digits of the marking indicate the main technological parameter of the equipment. As a rule, this is the largest dimension of the processed product in decimeters. For example, brand 7310 will indicate that this unit is a cross-planing unit and is intended for processing metal with a maximum plane length of up to 1000 mm. The letter in the designation (for example, 7A110) indicates a modification of the base model (for example, the presence of a hydraulic drive, an additional clamping unit, etc.). The presence of the letter F in the designation indicates that this equipment is equipped with a CNC system.
Planing equipment should be used in technological campaigns for the processing and production of various types of parts. The initial types of workpieces undergo a multi-stage processing process on machines of a certain type. The equipment produced at a machine-building enterprise uses parts of different configurations and dimensions.
Planing the ends of the column support tables. Why do they do it? Methods of execution
For the strength and integrity of buildings, building supports are used, which are a load-bearing structure onto which the load of ceilings and floors is evenly distributed when delimiting the space. The safety of operation of building structures depends on the quality and strength of metal columns.
Support tables are installed at the base of metal columns for structural strength. Columns are designed based on the weight and dimensions of the entire structure, so that there is a margin of safety. For ease of installation of the column, support tables are used, since without them it is problematic to attach the beam to the column without support.
First, you need to calculate the dimensions and thickness of the metal from which you need to prepare plates for making a support table of a specific design. Then blanks are made, metal plates are cut, in order to bring the plate blanks to design accuracy, and the ends of the sheets are processed.
For processing, the planing method is used, since blank sheets are always produced with an allowance and accuracy is achieved already during the manufacture of the product.
The support tables are welded to the column flange with three seams; for light loads, the tables can be made from corners; if the support reaction is in the range of 300-4000 kN, then thick sheet steel is used as the material.
Section of a column and designation of the place of planing on it
For such a product, the horizontal plate is made of a metal sheet, which, depending on the weight of the structure and design data, can be in the range of 20-40mm. Vertical racks are made of thinner metal, only precisely calculated parts for the existing load, and made according to the design in compliance with all dimensions and GOSTs will ensure reliability and strength during the operation of the building structure.
Cutouts are made in the support tables to enlarge the weld seams, which increases the strength of the weld. All work on planing ends and cutouts is carried out on special equipment, machines designed for metal processing.
Metal planing
The method of planing metal processing is a universal method; with its help, maximum design accuracy is achieved, which is necessary for further installation of the structure. The process occurs through reciprocating movements of the workpiece on the machine, or machine parts, depending on the size of the workpiece.
According to this principle, equipment is divided into machine categories:
Cross-planing;
Longitudinal planing;
Planing and slotting;
Edge planers.
Supporting unit for beams on top of columns
There are several types of cutters that are installed on machines, depending on the task that needs to be performed: according to the configuration of the rod, according to the direction of the head, straight or curved. The use of curved cutters makes it possible to produce a more precise edge, without jagged edges, since such cutters have practically no spring.
Currently, universal combined cutters, which are made from high-speed high-quality steel or hard alloys, are widely used.
19.10.2020
Types of metal planing machines
A classic metal planer carries out controlled removal of material of a certain thickness from the surface of the workpiece. It is distinguished by both the accuracy of the process and the technological schemes.
The main difference between planing machines and milling or turning machines is the configuration of the workpiece and the principle of operation. It does not have a rotation shape - its sides are often flat. The cutter processes one or more sides of the part, which is rigidly fixed on the work table.
Depending on the manufacturing technology, the following types of equipment are distinguished:
- Longitudinal planing machines (“1” – single column, “2” – with two columns). They can be used to give a certain shape to large samples. As an option, several medium-sized workpieces can be processed simultaneously. The cutter (there may be several of them) is fixed, and the blank, fixed on a special platform (table), moves with it.
- cross-planing (“3”). The cutting part moves, but the workpiece remains motionless. Used for the manufacture of large-sized parts. In addition, several types of operations can be carried out simultaneously to increase production speed. This depends on the number of cutters installed in the spindle slots of the cutter - from one to four. As a result of processing, recesses, grooves and recesses of a given shape are formed.
In addition, there are special-purpose machines. They perform similar operations, but differ in the form of influence on the workpiece:
- slotting (“4”). They make holes, select metal for grooves, protrusions, recesses, splines, grooves, that is, they are used for specific operations. Their working tool is called a “cutter”, the teeth of which perform the function of traditional cutters. The head can be rotatable, which allows processing in several planes, at an angle.
- Lengthy (“5” – horizontal; “7” – vertical). Mainly for removing chips from long workpieces.
- Shaped-planing machines (“9”). For processing curved surfaces (punches, bays of railway cars, etc.) or with ledges, when individual surface segments are located in different planes.
Elements that have the shape of a body of revolution are processed on some machines, and body objects are processed on others. The longitudinal combustion method is used when processing shaped and flat products. To achieve the highest level of cleanliness and surface quality of the product, it is worth using separate tools and technological processes.
Inferior to milling and turning models in productivity and price, this equipment wins in the low cost of the attached working tool and in the ease of sharpening it. For this reason, such machines are recommended to be purchased if you need to remove scale or form precise grooves and grooves in flat and shaped workpieces in a minimum number of passes
Metal processing on planing and slotting machines
Topic 13 “Group of planing, slotting, broaching machines”
Planing and slotting machines process planes, straight grooves, grooves, recesses of various profiles, shaped linear surfaces, etc.
The peculiarity of planing and slotting machines in comparison with lathes, drilling and milling machines is that their cutting movement (the main movement) is rectilinear (reciprocating), and the feed movement occurs periodically, only at the time of the next working stroke of the slider or table.
The disadvantage of the machines is that they spend a significant amount of time on idling and obtaining high speeds on working and reverse idling is very difficult due to inertial forces and vibrations at the moment of reciprocating movement of the slide or table.
These machines are divided into cross-planing (single-support and double-support), longitudinal planing (single-column, double-column and edge planing) and slotting (universal).
These types of machines are used in single and small-scale production.
® Concept of the planing process
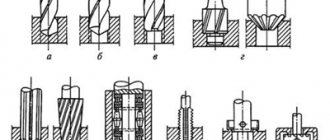
. When working on cross-planing and slotting machines, the cutter performs a rectilinear reciprocating motion, and the part receives an intermittent feed. When working on planing machines, straight and curved cutters are used (Fig. 10.1), which come in different types: through (Fig. 10.1, a), finishing (Fig. 10.1, b), wide finishing (Fig. 10.1, c) , scoring (Fig. 10.1, d), cutting (Fig. 10.1, e), etc. In Fig. 10.1, e shows a double-sided slotting cutter, in Fig. 10. 1, g - slotting cutter. Curved cutters, allowing squeezing around point O during planing (Fig. 10.1, h), capture a smaller depth of cut t, while a straight cutter during squeezing (Fig. 10.1, i) captures a greater depth of cut when planing, which reduces the processing accuracy details. Therefore, when planing you need to use curved cutters. Securing the cutters in the folding tool holder 6 reduces their wear, since during the reverse stroke when the tool holder is folded, the cutter slides freely over the surface of the part. Feed Smm/d. x is the movement of a part or cutter in the transverse direction during one double stroke, i.e. during the working and return stroke. Feeding is always carried out at the end of the return stroke, when the cutter is not loaded with the layer of metal being removed. As with turning, the area of the cut metal layer / mm2 is equal to the product of the cutting depth t and the feed s.
Rice. 10.1 Planing and slotting tools:
a—e—planing cutters, e—g—slotting cutters, h—squeezing a curved cutter, i—squeezing a straight cutter
Work performed on planing and slotting machines
.
Examples of some types of work performed on planing machines are shown in Fig. 10.2. Horizontal, vertical and inclined planes (Fig. 10. 2, a) are planed with passing or scoring cutters with the appropriate feed direction. Cutting and slotting work (Fig. 10.2, b) is performed with cutting tools. With a large groove depth, in order to avoid breakage of the cutter, its width b is made less than the width of the groove B , and cutting is carried out in steps. Planing of T-grooves (Fig. 10.2, c) and dovetail grooves (Fig. 10.2, d) is carried out with groove cutters of the appropriate configuration. When planing closed grooves, the cutter does not tilt back during the reverse idle stroke. Planing of shaped surfaces is carried out either with shaped cutters or with a fillet cutter according to the markings (Fig. 10.2, e). In the latter case, the cutter receives two feed movements, which are performed manually by moving the table and support.
Fig. 10.2 Planing work
Chiseling process
, in essence, is no different from the planing process, but the nature of slotting work is completely different from planing.
By chiselling you can process blind and through shaped holes: polyhedra (Fig. 10.3, a), internal guides (Fig. 10.3, b and h), internal keyways (Fig. 10.3, c), multi-keyed (splined) holes (Fig. 10.3 , d), matrices of complex configuration (Fig. 10.3, e), etc.
Rice. 10.3. Slotting work
Some types of external surfaces (Fig. 10.3, f and g) are also more convenient to process on slotting machines, although they can be made on planing and milling machines. Due to low productivity, the chiselling operation is used mainly in single and small-scale production. In large-scale and mass production, broaching is used in similar cases. Planing accuracy on planing and slotting machines reaches 3-4 classes; surface cleanliness of 6-7 classes.
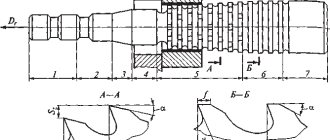
Cross-planing machines 7305TD and 7307TD (Fig. 10.4) Designed for processing horizontal, vertical and inclined, flat and shaped surfaces with a cutter, as well as for cutting grooves and grooves.
Rice. 10.4 Cross-planing machines model 7307GT and model 7307TD
(with additional slotting head) with ram stroke 710 mm
| Specifications | 7307GT, 7307TD |
| Slider stroke, mm: - largest for planing - largest for chiselling | 710 250 |
| Dimensions of the upper working surface of the table, mm | 710×450 |
| Slider stroke frequency, motor. stroke/min | 10,6 — 118 |
| Table feed, mm/double stroke: - horizontal - vertical | 0,2 — 5,0 0,04 — 1,0 |
| Main drive power, kW | 5,5 |
| Machine weight (without accessories), kg, max | |
| Overall dimensions of the machine, mm | 2790×1375×1665 |
| Overall dimensions of packaging, mm | 2800×1400×1740 |
Cross-planing machines OD 61-5 and OD 61-7 (Fig. 10.5) Designed for processing parts by planing flat and shaped (horizontal, vertical and inclined) surfaces, cutting grooves and grooves, as well as for processing surfaces by chiselling during installation replaceable slotting head instead of planing head.
Rice. 10. 5 Cross- planing machines OD 61-5 and OD 61-7
Indexes of cross-planing machines: 7M36, V5020, V5032, 7D36.
Topic 13 “Group of planing, slotting, broaching machines”
Planing and slotting machines process planes, straight grooves, grooves, recesses of various profiles, shaped linear surfaces, etc.
The peculiarity of planing and slotting machines in comparison with lathes, drilling and milling machines is that their cutting movement (the main movement) is rectilinear (reciprocating), and the feed movement occurs periodically, only at the time of the next working stroke of the slider or table.
The disadvantage of the machines is that they spend a significant amount of time on idling and obtaining high speeds on working and reverse idling is very difficult due to inertial forces and vibrations at the moment of reciprocating movement of the slide or table.
These machines are divided into cross-planing (single-support and double-support), longitudinal planing (single-column, double-column and edge planing) and slotting (universal).
These types of machines are used in single and small-scale production.
® Concept of the planing process
. When working on cross-planing and slotting machines, the cutter performs a rectilinear reciprocating motion, and the part receives an intermittent feed. When working on planing machines, straight and curved cutters are used (Fig. 10.1), which come in different types: through (Fig. 10.1, a), finishing (Fig. 10.1, b), wide finishing (Fig. 10.1, c) , scoring (Fig. 10.1, d), cutting (Fig. 10.1, e), etc. In Fig. 10.1, e shows a double-sided slotting cutter, in Fig. 10. 1, g - slotting cutter. Curved cutters, allowing squeezing around point O during planing (Fig. 10.1, h), capture a smaller depth of cut t, while a straight cutter during squeezing (Fig. 10.1, i) captures a greater depth of cut when planing, which reduces the processing accuracy details. Therefore, when planing you need to use curved cutters. Securing the cutters in the folding tool holder 6 reduces their wear, since during the reverse stroke when the tool holder is folded, the cutter slides freely over the surface of the part. Feed Smm/d. x is the movement of a part or cutter in the transverse direction during one double stroke, i.e. during the working and return stroke. Feeding is always carried out at the end of the return stroke, when the cutter is not loaded with the layer of metal being removed. As with turning, the area of the cut metal layer / mm2 is equal to the product of the cutting depth t and the feed s.
Rice. 10.1 Planing and slotting tools:
a—e—planing cutters, e—g—slotting cutters, h—squeezing a curved cutter, i—squeezing a straight cutter
Work performed on planing and slotting machines
.
Examples of some types of work performed on planing machines are shown in Fig. 10.2. Horizontal, vertical and inclined planes (Fig. 10. 2, a) are planed with passing or scoring cutters with the appropriate feed direction. Cutting and slotting work (Fig. 10.2, b) is performed with cutting tools. With a large groove depth, in order to avoid breakage of the cutter, its width b is made less than the width of the groove B , and cutting is carried out in steps. Planing of T-grooves (Fig. 10.2, c) and dovetail grooves (Fig. 10.2, d) is carried out with groove cutters of the appropriate configuration. When planing closed grooves, the cutter does not tilt back during the reverse idle stroke. Planing of shaped surfaces is carried out either with shaped cutters or with a fillet cutter according to the markings (Fig. 10.2, e). In the latter case, the cutter receives two feed movements, which are performed manually by moving the table and support.
Fig. 10.2 Planing work
Chiseling process
, in essence, is no different from the planing process, but the nature of slotting work is completely different from planing.
By chiselling you can process blind and through shaped holes: polyhedra (Fig. 10.3, a), internal guides (Fig. 10.3, b and h), internal keyways (Fig. 10.3, c), multi-keyed (splined) holes (Fig. 10.3 , d), matrices of complex configuration (Fig. 10.3, e), etc.
Rice. 10.3. Slotting work
Some types of external surfaces (Fig. 10.3, f and g) are also more convenient to process on slotting machines, although they can be made on planing and milling machines. Due to low productivity, the chiselling operation is used mainly in single and small-scale production. In large-scale and mass production, broaching is used in similar cases. Planing accuracy on planing and slotting machines reaches 3-4 classes; surface cleanliness of 6-7 classes.
Cross-planing machines 7305TD and 7307TD (Fig. 10.4) Designed for processing horizontal, vertical and inclined, flat and shaped surfaces with a cutter, as well as for cutting grooves and grooves.
Rice. 10.4 Cross-planing machines model 7307GT and model 7307TD
(with additional slotting head) with ram stroke 710 mm
| Specifications | 7307GT, 7307TD |
| Slider stroke, mm: - largest for planing - largest for chiselling | 710 250 |
| Dimensions of the upper working surface of the table, mm | 710×450 |
| Slider stroke frequency, motor. stroke/min | 10,6 — 118 |
| Table feed, mm/double stroke: - horizontal - vertical | 0,2 — 5,0 0,04 — 1,0 |
| Main drive power, kW | 5,5 |
| Machine weight (without accessories), kg, max | |
| Overall dimensions of the machine, mm | 2790×1375×1665 |
| Overall dimensions of packaging, mm | 2800×1400×1740 |
Cross-planing machines OD 61-5 and OD 61-7 (Fig. 10.5) Designed for processing parts by planing flat and shaped (horizontal, vertical and inclined) surfaces, cutting grooves and grooves, as well as for processing surfaces by chiselling during installation replaceable slotting head instead of planing head.
Rice. 10. 5 Cross- planing machines OD 61-5 and OD 61-7
Indexes of cross-planing machines: 7M36, V5020, V5032, 7D36.
Cutters for metal planing machines
Manual planer
Planing machines for metal processing are used to complete technological lines with high productivity and repair shops. Their advantage is relatively simple setup and maintenance.
The main factor in the correct processing of the workpiece is the choice of the appropriate cutter. It must be designed to perform a specific operation or have a universal application. To do this, in the production process of cutters, high-speed steel blanks are used or carbide brazing is made.
Advantages and disadvantages of metal planing
Modern planing machines, in which most processes are automated, make working on them simple and convenient. The advantages of this equipment include:
- high speed, ability to regulate the rate of processing of the workpiece;
- work with various types of metals and alloys;
- variety and versatility of operations,
- selection of tools for solving a specific task, wide selection of cutters;
- performing not one, but a whole series of operations: from processing flat surfaces on planing machines to forming relief ones.
However, this equipment also has a lot of disadvantages.
When machine systems interact, it is impossible to avoid such an effect as inertia. Planing machines are quite noisy neighbors compared to other mechanical machines, and vibration is added to their characteristic hum. In general, the high speed of work is reduced by the forced pauses required to move the cutter. Yes, there are a lot of disadvantages, but still they do not cover the advantages and are not considered critical. Therefore, gouging equipment is in consistently high demand.
Types of cutters for planing equipment
Cutters used for processing parts on a metal planing machine are divided according to a number of characteristics:
- In the direction of delivery; (left and right)
- According to the shape of the head; (straight, bent, with a retracted head)
- By manufacturing method; (solid and composite)
- By type of work performed (through roughing and finishing, shaped, cutting, grooving, etc.)
The process of planing metal occurs only with a working cutter, or on tables with a firmly fixed workpiece.
At the moment when the cutting tool is tightly fixed in the folding holder, its process of wear and exhaustion will take much longer, since during the return stroke it begins to fold back and move freely over the entire surface.
Main criteria for choosing a cutter model:
- type of equipment - for longitudinal or transverse operations;
- cutting edge material. Affects the speed and accuracy of work;
- cutter shape. Depending on this parameter, grooves, holes or grooves will be formed on the surface of the part.
There are several types of operations carried out on a longitudinal planing machine. They can be pass-through, finishing, shaped, trimmed or cut-off. To increase the service life of cutters, it is recommended to use equipment with a folding locking head. After initial processing, the cutter returns to its original position. During the return stroke, it should not come into contact with the surface of the workpiece.
The most common are longitudinal planing machines. They are characterized by relatively small dimensions and ease of operation. Particular attention should be paid to the quality of cutting tools. To ensure an uninterrupted technological process, it is necessary to have a small supply.
The essence of planing processing
According to the characteristics of the process, this technology refers to cutting operations.
During the work, the shape of the workpiece does not lose its integrity and does not undergo significant changes: chips are removed from it, as when planing wood. But if you can achieve a smooth surface of a wooden product using a simple plane, special equipment is used for planing metal. Processing on a planing machine can be both roughing and finishing. This technology is often used to correct shortcomings that arose during other operations: for example, to straighten sloppy welds.
Review of the best models of cross-planing machines
Planing equipment with a reciprocating movement of the cutter and a stationary workpiece mounted on the feed table has a limited scope of application and is used primarily in small-scale and one-time production. Nevertheless, it has its advantages and is considered worthwhile when it is necessary to perform roughing and finishing operations for planing and preparing grooves in relatively small metal workpieces with a flat and shaped shape.
The model range of these machines is limited, but all offered devices are valued for their simplicity of layout, high processing accuracy, reliability and unpretentiousness.
Scope of application
This equipment is not highly productive; due to the idle reverse motion and the inadmissibility of high cutting speeds due to inertia, the dimensions of the workpieces processed are limited; longitudinal planing machines are practically not used for mass production of metal products. But they are the best when it is necessary to form complex grooves and profiles using cutters or the use of rotating cutters is inadmissible.
A wide variety of working tools are fixed in the support assembly of such machines, including passing, trimming, slotting and shaped cutters, which allow roughing and finishing planing operations to be performed with their inherent accuracy (average deviations do not exceed 0.03 mm per 300 mm length of the metal workpiece).
In particular, the cross-planing machine is successfully used:
- When planing horizontal planes with the help of universal cutters, vertical ones with scoring cutters complete with stops.
- Processing of parallel planes with division of the process into two stages and sequential execution of work
- When planing inclined planes by installing the support at an angle and ensuring its feed in a parallel direction. The maximum effect is achieved when it is necessary to process a narrow strip (10-30 mm); with such parameters, all the advantages of fixing a wide and non-rotating cutter are manifested.
- When making grooves and grooves, including keyways.
- When planing chamfers using concave, convex and similar cutters. In the manufacture of gears, couplings and cams (subject to the use of additional specialized and dividing devices).
Inferior to milling and turning models in productivity and price, this equipment wins in the low cost of the attached working tool and in the ease of sharpening it. For this reason, such machines are recommended to be purchased if you need to remove scale or form precise grooves and grooves in flat and shaped workpieces in a minimum number of passes.
Machine units of the planing group
The most common modifications are:
- cross-planing,
- longitudinal planing.
The equipment of the first group is used for the serial production process. It is ideal for working with metal products whose length is no more than one meter. The machines of the second group are designed to work with heavy and large parts. The maximum planing width of this equipment reaches four meters. If we consider the travel of the aggregates table, then the maximum parameter is 12 m.
In order to process a workpiece on such units, it is necessary to check the design parameters of the parts. They are subject to a number of specific technological requirements. Not all metal elements can be processed on planing and slotting machines. List of basic requirements:
- workpieces are produced so that the surfaces are represented by a plane or a combination of planes;
- complex shaped surfaces are not suitable;
- the surfaces intended for processing are concentrated in one plane, which simplifies the operation;
- in those areas where the working tool enters and exits, chamfers are pre-prepared. This approach will prevent such a negative moment as chipping the edge of the surface when the cutter comes out. The working tool will cut smoothly into the part;
- the surfaces of the workpiece should not obstruct the exit of the cutting tool when the working stroke is completed;
- Only the longitudinal direction is chosen for processing metal products with a narrow and elongated surface.
It is also noted that it is inappropriate to use the technology to work with discontinuous, ribbed surfaces.
Otherwise, strong vibration vibrations will occur in the technological system. Surfaces concentrated in recesses and recesses are not suitable for processing. As for chiselling, it is not designed for processing parts with elongated surfaces. To do this, you need a working tool with a large reach, which contributes to its deformation, and then to its final breakage. Go to list of articles >>
Design and principle of operation of the equipment
The layout of the units is simple and includes several large elements:
1. A foundation slab with a stable frame secured with bolts. The metal planing machine is a fairly massive structure and weighs at least 1800 kg.
2. A slider with a built-in support that holds and regulates the position of the planing cutter and its feed mechanism.
3. Cabinet or casing with a motor (mostly asynchronous) and electrical equipment and drive. Planing types of machines are equipped with rocker, crank, gear, portable or hydraulic transmission mechanisms, the first group is the most common, but has a relatively limited stroke length of the slide (up to 700 mm), varieties with movement within 700-1000 mm are usually hydraulically powered and have a separate drive for accelerated return of the caliper.
4. Work table with stands for additional fastening and increased rigidity and guides for horizontal movement. In improved modifications it is inclined.
Transverse planing in these machines is carried out using a reciprocating slider with a fixed cutter with different sections and shapes; during contact with the tool, the workpiece itself remains motionless.
The removal of metal or the formation of a groove is carried out during the working stroke of the caliper assembly, followed by its idling (usually accelerated several times) with a return to its original position. Upon completion of each return operation, the machine moves the table feed in a transverse direction relative to the main stroke.
The main dimensional characteristic is the stroke length of the slider, varying from 200 to 2400 mm, with an average range of 500-700. The support with the cutter is capable of moving in the longitudinal and vertical direction and rotating around a horizontal axis. The speed of its movement, along with the dimensions and feed parameters of the table, have a direct impact on the functionality and dimensions of the workpiece being processed. The devices are powered by a three-phase network and have simple controls.
Overview of the machine range
The main developer and manufacturer of planing equipment of this group is the Orenburg SZ; many domestic companies offer to purchase ready-made, repaired or modernized devices, Pressmash, Stanochny Mir); among used machines, the products of the Gomel SZ have good reviews. The models have a generally similar design, the differences are manifested in the dimensions, power and parameters of the workpiece being processed. The main indicators of the most common of them are presented below:
7305T
The basic model of a cross-planing machine, supplied without a slotting head at a price of 680,000 rubles and used for processing flat and shaped metal products in all planes, including inclined.
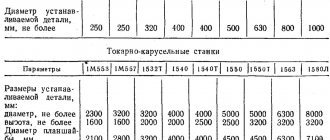
| Characteristic | 7305T | 7307GT |
| Slider stroke, mm: | ||
| largest for planing | ||
| largest for chiselling | ||
| Dimensions of the upper working surface of the table, mm | 500x400 | 710x450 |
| Slider stroke frequency, stroke/min | 13,2-150 | 10,6-118 |
| Table feed, mm/double stroke: | ||
| Horizontal | 0,2-5,0 | |
| Vertical | 0,04-1,0 | |
| Main drive power, kW | 5,5 | |
| Weight 7305T machine (without accessories) kg, max | ||
| Overall dimensions of the machine, mm | 2380x1085x1560 | 2790x1375x1665 |
| Overall dimensions of packaging, mm | 2400x1306x1620 | 2800x1400x1740 |
This equipment is distinguished by its increased rigidity of the frame and guide and has a good power resource (up to 5500 W), facilitating the precise performance of finishing, roughing and fine planing.
The machine is equipped with a 500×400 rotary table with 25 feeds and three T-shaped slots for gripping workpieces with a slide stroke of up to 510 mm and an outreach of up to 560; the maximum distance between the horizontal plane and the guides is 40 cm.
7307TD
Expanded modification 7305T with a slotting head and a slider stroke increased to 710. By analogy with the previous one, this cross-planing machine is recommended to be purchased when processing flat and shaped workpieces made of hard materials (the permissible cutting force reaches 19.6 kN); with equal power and table movement speed, it wins in functionality and increased working space.
This affects the price; in new condition, this model can be purchased from 800,000 rubles and above. At the same time, its optimal scope of application is enterprises with single and small-scale production conditions.
7B35
Planing equipment for processing with a cutter workpieces with a length of up to 500 mm inclusive and forming grooves and grooves in them with different shapes and depths within the cross-section of the working tool 20×32 mm. The model was developed for installation in repair, mechanical and tool shops of mechanical and instrument manufacturing enterprises with relatively small production volumes (single and small-scale production of metal parts).
In the basic version, 7B35 has a fixed table with 20 feeds and manual, mechanical and root movement; models with universal rotary structures are made to order. The machine is equipped with a centralized lubrication unit and a chip collector; the estimated costs for purchasing it in basic configuration and in good condition are 600,000 rubles.
7M36 and 7M37
The cross-planing machine of the Gomel SZ is the base for models with a universal rotary table and copying devices, used for processing their metal surfaces with a slide length of up to 700 mm inclusive. At the moment, the model has been discontinued from main production and replaced with improved slotting analogues, but thanks to the reliability of the components and hydraulic drive, it is still used in machine shops of machine-building enterprises and is sold in used condition at a price of 140,000 rubles and above.
The machine has 2 electric motors (the main one ensures the start of all components, the auxiliary one ensures rapid movement of the worktable with dimensions of 450×700 and 560×1000 mm, respectively), the lubrication of its frame and slider guides is carried out automatically, the same applies to the feed of the support and cutter.
Transverse and longitudinal planing
Metal gouging is also performed by two other types of machines - longitudinal and transverse.
Machines for longitudinal planing processing are designed in such a way that the fixed part in them is the cutter. The workpiece, on the contrary, moves along a reciprocating trajectory. In more complex machines there may be two static cutters. This is very productive equipment, capable of simultaneously processing not one, but two edges. However, for efficient work you have to “pay” with space: the machine is quite massive, and an entire industrial area has to be allocated for it.
Cross-planing is considered a more universal operation than the two already described. This method can be used to process not only horizontal and vertical planes, but also inclined planes. The shape of processed rolled products can also be different: these are not only leaves and strips, but also profile products. The main limitation is that the workpieces must be small.
Factory quality planing work
Are you looking for cross-planing machines with the best price/quality ratio? You've already found it! We work only with impeccable domestic raw materials and are responsible for every part we produce. Our advantages:
- transparent and strictly fixed prices at the time of signing the contract,
- product warranty,
- work on projects of any complexity and urgency,
- progressive discount system.
We are open to long-term cooperation and will be glad to see you among our regular customers. Contact us!