The first steps of metallurgy
Information about the first metallurgists is available to humanity thanks to archaeologists. The prehistoric era gave rise to attempts to obtain and process metal.
At that time, there were remains of meteorites on Earth that gave the first iron into the hands of man. Gradually, the mining and processing of gold and copper began.
The first processing method was cold forging. It was used to give iron shape. The first product was weapon parts - spear points, arrowheads.
They also tried to use the valuable metal to create dishes and simple tools.
The first breakthrough in metallurgy was steel smelting. Early evidence of this approach dates back to the 12th century BC. At that time, steel was melted in India and cheese-blowing furnaces were used for this. Similar means were also used in Anatolia and the Caucasus. The methods were remarkably similar.
In Africa they also tried to melt iron and forge it to create weapons. Due to the inability of ancient people to protect steel from corrosion, artifacts from that era have reached us in poor condition, but the evidence is still there.
Cattle breeding development
Which animal was the first to be domesticated? The first animal that man tamed was the dog (wolf). Dogs protected the homes of ancient people from predators and enemies, and while hunting they tracked down and drove away wild animals.
If the hunt was successful, primitive people returned home not only with prey, but also with the cubs of the killed animals. They fed the animals, and they quickly got used to humans.
Over time, people managed to domesticate sheep, goats, horses and cows. As a result, from hunting came pastoralism - the raising of herd animals. Thanks to the development of cattle breeding, the need for frequent hunting disappeared.
Which metals were the first to be processed?
It all started with copper. Man discovered the first deposits by accident - then they were close to the surface.
Even 8 thousand years BC, people tried to process copper ingots, but did not use professional methods for this.
It was rough, but it was a better alternative to bone or sharpened wood.
The next metal that humanity added to its treasury was bronze. This is a product of the beginning of metal processing, when they learned to melt and mix them. This is how the combination of tin and copper came into being, often used in jewelry making.
Only the richest members of society could afford such items, but even today relics often surprise jewelers with their non-standard approach to processing and elegance of form.
It is believed that man did not conduct any directed experiments to obtain bronze. It was found by accident during mixing.
The resulting alloy surprised us with its hardness and ease of processing - due to the addition of tin, it was much more ductile than the materials used at that time. The recipe was fixed, and blacksmiths began to use it to create tools.
The products did not fail as quickly as stone or copper ones and weighed little.
The first millennium BC was marked by the advent of the Iron Age. Already from the name it is clear that at that time people discovered meteorite iron and began to try to process it. But only in the third century BC this material began to be used en masse.
It came to the point that instead of searching for meteorites rich in iron, they began to extract it from the depths. The metal became widespread and most of its analogues faded into the background.
METAL DRAWING TECHNIQUE
The formation and development of metal drawing technology occurred under the influence of the ever-increasing consumption of wire and wire products, which were widely used in the manufacture of various jewelry and household items. The production of jewelry and gold-embroidered clothing became widespread, especially during the slave period. Jewelry crafts consumed a huge amount of precious metals and their alloys. Gold and silver wire were also used as an equivalent of value in trade. The demand for wire contributed to the improvement of drawing technology.
What were the first metalworking methods?
The first processing tools were primitive. So the first lathe was created 500 years BC. Two people worked on it.
One quickly rotated the shaft on which a vice with a clamped part was installed. The second one did the carving. It’s interesting that they didn’t come to metal processing in this way right away.
Initially, turners sharpened bone and wood.
Similar funds are also found in Egypt, Greece and some other countries.
Outwardly, it was very similar to old pedal-driven sewing machines. When the master pressed the pedals with his foot, the workpiece began to rotate. All that remained was to use the chisel for turning. This is how the first rods were made, used in carts, as well as in the creation of other working tools.
The origins of agriculture
People have noticed that seeds that fall into the soil begin to germinate and bear fruit. It became clear to them that they could grow their own food if they planted grains of wild plants in the ground. This is how ancient people switched from gathering to agriculture.
Primitive people realized that crops could be collected in one place, so they switched from a nomadic lifestyle to a sedentary one .
The first crops were wheat, barley and millet. They appeared on the Asia Minor peninsula, from where agriculture spread throughout the world.
For sowing, it was necessary to prepare a plot of land - clear it of bushes and trees. To loosen the soil, ancient people created a new tool - a hoe . It was a stick with a knot. This type of farming was called hoe farming .
Women were engaged in loosening the soil. The harvest was harvested with another tool - a sickle . It consisted of stone teeth on a wooden or bone base. With the invention of the wooden plow, the process of cultivating the land became much faster and more efficient.
Hoe
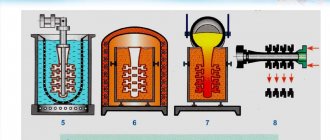
Important steps in metal processing
The man thought a lot about how to simplify the operation of the machine. Gradually, manual rotation or pressing the foot pedal was abandoned in favor of using water.
The water ensured the rotation of the workpiece at the required speed. This allowed an increase in the number of steel products that were used in everyday life.
At the end of the 18th century, metal processing became most widespread thanks to the industrial revolution. John Wilkinson introduced the world to a cylinder turning technology that produces high-quality results.
Types of processing
The metal processed by pressure, depending on the technology used, is subjected to:
- rolling;
- forging;
- pressing;
- drawing;
- volumetric stamping;
- sheet stamping;
- processing performed by combined methods.
Main types of metal forming
Rolling
Rolling is a pressure treatment of metal blanks, during which they are exposed to rolling rolls. The purpose of such an operation, which requires the use of specialized equipment, is not only to reduce the geometric parameters of the cross-section of a metal part, but also to give it the required configuration.
Types of rolling rolls
Today, metal rolling is carried out using three technologies, the practical implementation of which requires appropriate equipment.
Longitudinal
This is rolling, which is one of the most popular processing methods using this technology. The essence of this method of metal forming is that the workpiece, passing between two rolls rotating in opposite directions, is compressed to a thickness corresponding to the gap between these working elements.
Transverse
Using this technology, metal bodies of rotation are processed by pressure: balls, cylinders, etc. Performing processing of this type does not imply that the workpiece undergoes translational motion.
Cross-helical
This is a technology that is something intermediate between longitudinal and transverse rolling. It is mainly used to process hollow metal workpieces.
Types of metal rolling
Forging
A technological operation such as forging belongs to high-temperature forming methods. Before forging, the metal part is subjected to heating, the magnitude of which depends on the grade of metal from which it is made.
Metal can be processed by forging using several methods, which include:
- forging performed using pneumatic, hydraulic and steam-air equipment;
- stamping;
- forging done by hand.
In machine and hand forging, which is often called free forging, the part, while in the processing zone, is not limited by anything and can take on any spatial position.
Hand forging is used in blacksmith shops to produce a small number of products
Machines and technology for metal forming using the stamping method assume that the workpiece is previously placed in a die matrix, which prevents its free movement. As a result, the part takes exactly the shape that the cavity of the die matrix has.
Forging, which is one of the main types of metal forming, is used mainly in single and small-scale production. When performing such an operation, the heated part is placed between the striking parts of the hammer, which are called strikers. In this case, the role of supporting tools can be played by:
- regular ax:
- crimps of various types;
- rolling out.
Pressing
When performing a technological operation such as pressing, the metal is forced out of the matrix cavity through a special hole in it. In this case, the force necessary to carry out such extrusion is created by a powerful press. Parts that are made of metals that are highly brittle are mainly subjected to pressing. The pressing method produces products with a hollow or solid profile from alloys based on titanium, copper, aluminum and magnesium.
Depending on the material of the processed product, pressing can be performed in a cold or hot state. Parts that are made of ductile metals, such as pure aluminum, tin, copper, etc., are not subjected to preheating before pressing. Accordingly, more brittle metals, the chemical composition of which contains nickel, titanium, etc., are subjected to pressing only after preheating as the workpiece itself and the tool used.
Cold pressing plant for sheet metal products
Pressing, which can be performed on equipment with a replaceable matrix, allows the production of metal parts of various shapes and sizes. These can be products with external or internal stiffeners, with a constant or different profile in different parts of the part.
Drawing
The main tool with which such a technological operation as drawing is performed is a die, also called a die. During the drawing process, a round or shaped metal blank is pulled through a hole in the die, resulting in a product with the required cross-sectional profile being formed. The most striking example of the use of such technology is the wire production process, which involves a large-diameter workpiece being sequentially pulled through a series of dies, ultimately turning into wire of the required diameter.
Technological processes for producing wire by drawing
Drawing is classified according to a number of parameters. So, it could be:
- dry (if done using soap shavings);
- wet (if a soap emulsion is used to perform it).
According to the degree of cleanliness of the surface being formed, drawing can be:
- rough;
- finishing
Copper Wire Drawing Line
Depending on the frequency of transitions, dragging occurs:
- one-time, performed in one pass;
- multiple, performed in several passes, as a result of which the cross-sectional dimensions of the workpiece being processed are gradually reduced.
According to the temperature regime, this type of metal forming can be:
- cold;
- hot.
Volume stamping
The essence of this method of metal forming, such as die stamping, is that the production of a product of the required configuration is carried out using a stamp. The internal cavity, which is formed by the structural elements of the die, limits the flow of metal in an unnecessary direction.
Depending on the design, dies can be open or closed. In open dies, the use of which makes it possible not to adhere to the exact weight of the workpiece being processed, a special gap is provided between their moving parts, into which excess metal can be squeezed out. Meanwhile, the use of open-type stamps forces specialists to remove flash that forms along the contour of the finished product during its formation.
A feature of hot metal stamping is the effect of high temperature, as a result of which the workpiece is deformed, taking the shape of the stamp
There is no such gap between the structural elements of closed-type dies, and the formation of the finished product occurs in a confined space. In order to process a metal workpiece using such a stamp, its weight and volume must be accurately calculated.
Order galvanized pipes from Tochinvest Zinc
offers customers the technology of hot-dip galvanizing of pipes. We use modern means to increase the duration of use of the products obtained in this way.
- We have accumulated experience in galvanizing – we have been working since 2007.
- 3 own hot-dip galvanizing workshops and an annual production capacity of 120 thousand tons per year.
- Exact compliance with the requirements of GOST 9.307-89.
We use equipment from brands such as EKOMOR and KVK KOERNER.
Return to articles Share article
The emergence of craft
A sedentary lifestyle contributed to the improvement of tools and the creation of new inventions. Pottery was one of the first types of handicraft production.
What observations led to the invention of a method for making clay pots? Ancient people discovered that river clay became hard when held over a fire. This discovery allowed primitive people to make dishes from clay. It was possible to cook and store food in it.
Then people learned to spin threads from wool and flax, from which, using primitive looms, they made scraps of fabric. They began to make new, comfortable clothes from the scraps, which replaced the old ones made from animal skins. This is how ancient people invented weaving.
Gradually, people who were exclusively engaged in the production of pottery, textiles or tools began to stand out from the circles of pastoralists and farmers. They began to be called artisans .
Craft is the production of various products using tools.
Over time, crafts became more and more complex. A person had to spend a lot of effort and time to become a master of his craft.
The emergence of craft
Innovative metalworking technologies
The development of the economy of each country largely depends on the level of development of metallurgy. It is this industry that has a great influence on the entire state industry, so often both control and support for metallurgy are provided at the highest level. Much attention is paid to the modernization of metallurgical enterprises and the timely introduction of innovations in production.
- Bimetal technology.
Ultra-modern technology for processing bimetals is based on the connection of two components by diffusion bonding. The result is a material that has the characteristics of both elements.
Thus, high-voltage wires are made of steel and aluminum. These two materials together meet all the necessary requirements: high strength and maximum electrical conductivity. Aluminum is an excellent conductor, and steel is very strong. In thermometric technology, bimetals with different coefficients of thermal expansion are used.
- Laser welding.
The invention of the focused laser significantly expanded the range of metalworking capabilities. Now you can carry out welding work on the smallest parts. This was a huge plus for the development of radio electronics. In addition, this technology helps to apply carbide cutting elements to cutters.
Until quite recently, this metalworking technology was one of the most expensive, but now, when they began to use a gas laser instead of a pulsed laser, there has been a significant reduction in the cost of the technique. Laser welding technology allows you to work in an inert environment and in a vacuum. At the same time, the equipment has high accuracy, which is explained by the presence of software control.
- Plasma cutting.
Plasma cutting technology is more economical than laser cutting, but the cut thickness is larger.
Today this is the most popular metalworking method, providing high repeat accuracy. The effectiveness of the method is ensured by a high-speed gas jet that blows an electric arc. The popularity of the method is so high that even hand-held plasma cutters have been created.
- Electrical discharge machining.
Probably everyone knows that ordinary lightning can cause great destruction. Her power is enormous. At the same time, even a small electric discharge can be used with considerable benefit for the benefit of metalworking. Thus, industry has long used weak electric discharges to create metal parts of complex configurations.
Electroerosive metalworking is performed using a special tool made of heat-conducting or refractory material. It and the workpiece are connected to an energy source and the electrical voltage is systematically turned on and off, creating short-term discharges of current. Another option for electrical discharge metalworking would be to quickly move the tool relative to the workpiece.
The treated metal is cooled with oil or kerosene. This processing method is used when it is not possible to use a metal-cutting machine.
- Ultrasonic treatment.
The use of ultrasound has become very popular in recent years. It is used to drill glass, tan leather, measure sea depths, and even weld metal. Sound waves are inherently alternating compression and rarefaction of particles of air, water or other environmental elements.
The more compression and rarefaction occurs, the higher the frequency of the sound. One oscillation represents one compression and rarefaction.
Using an ultrasonic machine, you can make a hole of any complexity in the most fragile material. That is why such equipment is suitable for creating carbide die matrices, ferrite cells of computers, etc.
- Nanotechnology.
Nanotechnologies make it possible to create ever new metalworking methods that are more efficient than those previously used. Femtosecond laser ablation is mainly used to produce nanoholes. Another option is the ion etching method, when it is possible to obtain the thinnest nanomembranes with holes with a diameter of 28.98 nm and a density of 23.6x106 per mm2.
American scientists are working on creating a new technology for producing nanoholes by evaporating metal using a silicon template. This option is especially relevant in light of the fact that these membranes can be used in solar panels.
- Nano-coatings with high wear resistance.
Since the 70s of the last century, metalworking technologies began to be developed that involve strengthening the thin surface layer of the product. Such nanocoatings can be obtained in different ways. The most popular are: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Diamond Like Coatings (DLC), etc.
Chemical Vapor Deposition is a process for producing nanocoatings using chemical vapor deposition. All this happens at a very high temperature (about +1000 °C). This results in a coating with high wear resistance.
CVD technology produces particularly durable cutting tools. Moreover, the coating itself consists of several layers, which significantly improves adhesion while maintaining the strength of the base material of the product. Usually in such a coating the following order of layers is:
- Titanium carbide.
- Aluminium oxide.
- Titanium nitride.
In this case, aluminum oxide is used to reduce the effect of high temperatures on the base of the product.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), the essence of which is condensation with ion bombardment, appeared later than chemical condensation. In this case, the coating is formed from titanium nitride (TiN).
PVD metalworking technology has many advantages. This increases the level of adhesion of the material and the possibility of applying a coating to the cutting edges of the product.
In addition, coating requires a lower temperature than for CVD processing (+500 °C is sufficient). Also, the thickness of titanium carbide coatings can be greater; accordingly, they can be used for different types of steel. TiNAl coating is considered the most promising today.
Carbon is used to create Diamond Like Coatings. This coating also belongs to the PVD variety. Its structure resembles diamond and is characterized by very high wear resistance. However, it is not widely used because it is prone to oxidation and is unstable at temperatures above +300 °C. Its scope of application remains exclusively cutting silumin and aluminum. Perhaps, with the development of modern metalworking technologies, these coating disadvantages will be overcome.
- Fiber laser.
When plasma processing appeared, it seemed to be a very promising metalworking technology, but then laser devices were created, and on their basis, a fiber laser. This opened up new horizons in the field of metal processing. A fiber laser consists of a light guide, a resonator and a pump module. In a conventional laser system there is no light guide, so the radiation power can be lost as the laser beam travels. In a fiber laser, radiation is generated directly in the fibers, so complex beam injection schemes are not needed.
The undoubted advantage of a fiber laser is its resistance to vibration, small installation dimensions, high-quality cooling and high thermal stability. All this is ensured by the ratio of the resonator volume to its area.
The main applications of fiber lasers are welding, cutting and engraving. It is indispensable when it is necessary to change the optical properties of the surface of a material without disturbing its internal structure. For example, welding steel parts of medical equipment or electronic devices, where the size of the processed surface does not exceed a few millimeters.
Perhaps soon new metal processing technologies using fiber lasers will take a leading position. This is due to the many advantages of this method:
- requires less energy;
- no gas environment required;
- easy to adjust;
- air is not an obstacle to high quality processing;
- there is no thermal damage to the material in the area outside the action of the fiber laser;
- no special operating conditions are required (a certain level of pollution, vibration, humidity, gas quality, etc. is allowed);
- service life without maintenance can reach 100,000 hours;
- low operating costs;
- thinner cut compared to CO2 gas lasers, respectively, low emissions of working gases, and metal savings due to more efficient layout;
- there is no beam defocusing effect due to the absence of losses in the light guide;
- low operating costs - due to high efficiency, low cost and rare replacement of consumables, and the use of inexpensive gases;
- wide range of uses - cutting, welding, surfacing, spraying, engraving, marking, color marking, hardening;
- the ability to scale the power of the laser source by increasing the number of LED clusters.
If we talk about the disadvantages of this technology, it can be noted that the fiber laser does not provide high polarization stability where it is difficult to use fibers that maintain polarization. In addition, in the spectral range from 0.7 to 1 micron, solid-state lasers show greater efficiency.
However, if it is necessary to use a wavelength for which there is no acceptable active medium, then fiber lasers are used. Such metalworking is carried out in the absence of mirrors, which makes the design simpler and reduces the error of the operation.
Based on the above, it should be understood that this metalworking technology will in the near future develop in the field of two- and three-dimensional welding, various deposition techniques and increasing strength, etc.
The struggle of people with sands, swamps and thickets.
With the advent of copper tools in Egypt, the Egyptians fought the sands, swamps and thickets more successfully than before.
The Egyptians fenced off areas of land with dams made of clay mixed with reeds. Gates were installed in the dams; Through them, water flooded the area when it spilled. Then the gate was closed and the water was not released until it had thoroughly saturated the soil. To areas where the flood did not reach, the Egyptians laid canals from the river.
Map of the Kingdom of Egypt:
Canals were dug in swampy areas to drain excess water into the river. Bushes and reeds were cut down with copper axes.
The wind blew sand into the canals. The Nile floods washed away the dams. Every year the population cleared and repaired them.
Thousands of people living next door to each other worked together to build and repair canals and dams.
Thanks to the labor of people, much land in the valley and the Nile Delta became suitable for agriculture.