12/14/2021 Author: VT-METALL
From this material you will learn:
- What is a weld seam?
- Methods for welding seams along the inclination and trajectory of the electrode
- Classification of welds according to welding method
- Shape and length of the weld
- Layers and location of welds in space
- Weld defects
There are various methods for welding seams. They are classified according to various parameters: according to the method of connecting parts, the angle of inclination and trajectory of the electrode, according to the welding mode, etc. Each method is suitable for a certain type of metalworking.
For example, butt welds are the most common. Used for welding sheet metal and pipes. You will learn about in what cases to use other methods of welding seams and how they are affected by welding parameters from our material.
What is a weld seam?
Quite often, the assembly of structures is carried out according to drawings, which indicate the locations of the planned welded joints. Correct assembly cannot be performed without certain skills in welding in the required spatial position, as well as without knowledge of the classification and types of welded joints.
A permanent welding joint is formed as a result of melting of the edge surfaces of two joined parts. To fill the gap between them and strengthen the bond, a filler metal is used, which is mixed with the base metal during the welding process.
VT-metall offers services:
The melting process is carried out using:
- coated consumable electrodes (for the MMA method);
- tungsten electrodes (for TIG welding);
- wire from the torch (for MIG technology).
After manual arc welding (MAW), a slag layer remains on the surface of the seam, which is beaten off using special hammers. The same crust occurs during electric welding with flux. With other methods of welding seams, the output immediately results in a clean surface, the quality of which can be determined visually.
One cable coming from the current source is connected to the workpiece and serves as a ground, and the second is connected to the torch or holder, which the welder holds in his hand as a working tool. The arc temperature can reach +5,000 °C, thanks to which the edges of the metal melt and form a joint. The speed of execution and strength of welding joints allows them to be actively used in the construction, automotive and shipbuilding sectors.
SUTURES FOR METAL THICKNESS MORE THAN 15 MM
WITH THE CASCADE METHOD, the seam is divided into sections of 200 mm. After welding the first layer of the first section, without stopping, continue to lay the first layer on the adjacent section. Then each subsequent layer is applied to the metal of the previous layer that has not had time to cool
WELDING “HILL” is a type of cascade method. Conducted by two welders simultaneously from the middle to the edges
Both methods are reverse-stage welding not only along the length, but also along the cross-section of the seam, and the welding zone always remains hot
WHEN WELDING WITH BLOCKS, the seam is filled in separate steps along the entire height of the seam section. Used when connecting parts made of steels that are hardened during welding
Source
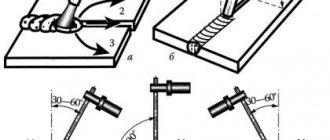
Methods for welding seams along the inclination and trajectory of the electrode
Classification of welds is carried out according to several criteria. The types and varieties of welded joints must be considered step by step, while delving into the technological subtleties. The quality of the weld can be affected by the trajectory, location and direction of the electrode.
Electrode tilt
After fixing the electrode in the holder, setting the current, selecting the required polarity, you can proceed directly to the welding process.
Each master prefers to hold the electrode at his own angle. For most welders, the optimal value from the horizontal plane is an angle of 70°.
In this case, an angle of 20° remains from the vertical. For some specialists, it is convenient to work at a maximum angle of 60°. Almost any literature on the welding topic recommends holding the electrode between 30 and 60 degrees relative to the vertical axis during operation.
There are situations when welding in hard-to-reach places can only be performed with a strictly perpendicular position of the electrode relative to the surface of the material being welded.
The direction of movement of the electrode can also be different: both away from you and towards you.
If you want the material to be heated more deeply, then the electrode should be moved towards you. When moving behind it, a working zone is formed, on which a layer of slag appears, covering the molten area.
If strong heating is not provided, then the electrode should be moved away from you. A trace of the welding zone remains behind it. With this method of seam welding, the heating depth is minimal.
Trajectory of electrode movement.
In any case, the trajectory of the electrode is zigzag in nature, since otherwise the connection of the two surfaces will not occur. It is this property that is particularly reflected in the formation of the seam.
Oscillations can resemble zigzags in shape, having different steps between the sharp corners of the trajectory. The latter can be performed with smooth movements depicting an offset figure eight. It can be in the form of a capital letter Z with curls both at the bottom and at the top, or in the shape of a herringbone.
A high-quality seam is characterized by uniform width and height, a smooth surface without any undercuts, pores, uncooked areas and craters. Just by the name of the defect you can determine what type of deviation it belongs to. Having accumulated enough experience, you can successfully use any method of welding seams and connecting various metal structures.
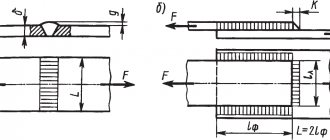
Methods for making welding seams of various lengths
The size of each grip is determined so that a whole number of electrodes are removed. This is done so that the weld pool is heated evenly. If the metal is thin, the seams are shorter, if the metal is thick, the seams are longer. Types of reverse-stage welding:
To avoid deformation, electrodes of larger diameter and higher current are used. Vertical lap and circular T-seams are made on both sides using a reverse-step method.
Workpieces with a thickness greater than average are connected with multi-layer seams. In this case, the first one is continuous, the subsequent ones are reverse-staged, in sections. The ends of sections in adjacent layers should not coincide; they are shifted by 15-20 mm due to the fact that slag inclusions and lack of penetration are likely at the end points.
Shape and length of the weld
The shape of the seams can be either even (flat) or convex. In some cases, the task is to make a concave-shaped connection. Convex seams are used in structures and assemblies with increased loads.
When welding concave seams, the joints withstand dynamic loads well. And the flat type of seams is characterized by its versatility.
The length of welded joints can be continuous (solid), which do not have breaks in the fused line. In some cases, it will be sufficient to make an intermittent type of seam.
Modern industrial enterprises widely use contact seam welding, which is one of the types of intermittent metal joints. To perform it, you need special equipment equipped with rotating disk electrodes.
They are usually called rollers, and this method of welding seams is called roller welding. In addition to intermittent connections, such equipment allows you to make continuous seams. The seam obtained by this method is absolutely sealed and has quite high strength. This technology is widely used on an industrial scale in the production of sealed modules, containers and pipes.
MULTILAYER MULTIPASS DOUBLE SIDED
more often - for corner and tee
I - III - order of application of layers; 1 - 8 - sequence of suturing
To heat the metal evenly along its entire length, seams are applied:
With the double layer method, the second layer is applied over the uncooled first layer after removing the welding slag in the opposite direction at a length of 200-400 mm
Layers and location of welds in space
The weld can be a bead made in one pass. This type is called single-layer. If it is necessary to connect parts of large thickness, seams are applied in several passes, resulting in a sequential overlap of rollers one on top of the other. This method of welding seams is called multilayer.
With all the variety of production operations in which welding is used, it is quite clear that the seams are oriented differently in each individual case. There are seams of lower, upper (ceiling), vertical and horizontal types.
Welding of vertical seams is usually done from the bottom up. In this case, the trajectory of the electrode is in the form of a zigzag, herringbone or crescent. Beginner welders prefer to use the crescent motion.
The horizontal method of welding seams is performed in several passes, the movement of which is directed from the bottom to the top edge of the workpieces being welded.
In the lower position, the butt welding method or any corner method is used. Good results are achieved by welding the seam at an angle of 45°. Welders call it “in a boat”. With this method, connections can be either symmetrical or asymmetrical. If it is necessary to weld in hard-to-reach places, the asymmetrical “boat” method will be more convenient.
When connecting metal workpieces with a thickness in the joint area above 8 mm, welding is performed in several passes. The first pass should have a diameter of 4 mm, and all subsequent passes should have a diameter of 5 mm.
The selection of the appropriate electrode position depends on the orientation of the seam. When connecting non-rotating pipe joints, using ceiling, vertical and horizontal seam welding methods, the electrode must be directed at an angle forward.
Methods for making welding seams of various lengths
The size of each grip is determined so that a whole number of electrodes are removed. This is done so that the weld pool is heated evenly. If the metal is thin, the seams are shorter, if the metal is thick, the seams are longer. Types of reverse-stage welding:
To avoid deformation, electrodes of larger diameter and higher current are used. Vertical lap and circular T-seams are made on both sides using a reverse-step method.
Workpieces with a thickness greater than average are connected with multi-layer seams. In this case, the first one is continuous, the subsequent ones are reverse-staged, in sections. The ends of sections in adjacent layers should not coincide; they are shifted by 15-20 mm due to the fact that slag inclusions and lack of penetration are likely at the end points.
Source
Weld defects
All types of welding defects are divided into three main groups: those located inside the joint, outside it and through. Defects in resistance welding of an external nature are easily detected during visual inspection, which must be performed when monitoring the quality of any welded joints, regardless of the requirements placed on them.
The most characteristic signs of external defects are different widths of the legs in corner joints, as well as individual sections of longitudinal seams. The presence of deposits on the main seam is quite easily determined. The external type of weld defects includes any fistulas, sagging, undercuts, craters, cracks, bulges and depressions.
Internal weld defects are not detected by visual inspection. Basically, the reason for their appearance is the use of low-quality material and deviation from welding technology. In addition, invisible cracks can also appear in the internal structure of the metal. Untimely detection of such defects can lead to an increase in the stress of the structure during operation and its premature destruction.
Cracks may appear due to the weld cooling too quickly. Hidden defects occur when harmful impurities are formed in the weld structure during welding.
Insufficient fusion of edge surfaces leads to the formation of lack of penetration. The main reason is improper preparation of the edges of parts, which leads to the appearance of scale and rust on the surfaces. In addition, lack of penetration can occur if, during setup, the current is set to insufficient strength, and also when the axis of melting and the electrode does not coincide. If such a defect is of a large extent, re-welding of the seam is required.
Recommended articles
- Welding wire: classification, marking
- Production of metal products: technologies, advantages, step-by-step control
- Fusion welding: where it is used and how it is produced
Hidden types of welding defects include pores containing gas. The main reason for their appearance is high humidity and the presence of foreign impurities in the materials being welded. If the permissible concentration of porosity is exceeded, the seam should be redone. Violation of the manufacturability of the process can lead to the appearance of various inclusions inside the weld: oxide, tungsten or slag.
A through defect is a porosity that is not located inside the weld structure, but passes through the entire welded joint. This type of defect is easy to determine by visual inspection. Another type of welding defect is burn-through, which occurs when the electrode moves at a low speed and the current is too high.
With the development of the technical process in welding, updates also appear that apply to all seam welding methods. Not only new technologies for processing and welding metals, but also materials are emerging. This means that in order for your professional level to constantly improve, you should constantly work to expand your horizons in this area and not ignore emerging changes.
Electric arc in manual arc welding
Excitation of the welding arc
Excitation of the arc can occur in two ways. You can touch the metal being welded with the electrode, and then withdraw the electrode to a distance of 3-4 mm, maintaining the burning of the resulting arc.
You can light an arc by touching the metal being welded with a quick lateral movement and then withdrawing the electrode to a distance of 3-4 mm (this movement is similar to how a match is lit). The contact of the electrode with the metal must be short-term, otherwise the electrode will be welded to the metal. The welded electrode should be torn off by turning it to the sides with sharp movements.
Arc length
In the process of welding metal, it is necessary to maintain a welding arc of a certain length, depending on the brand of the electrode and its diameter. The length of the arc largely determines the quality of welding and the shape of the weld.
The recommended welding arc length is 0.5-1.1 times the electrode diameter. If the arc is short, this can cause welding of the electrode to the metal, interruption of the arc and disruption of the welding process.
With a large arc length, its combustion becomes unstable, the penetration depth decreases, the molten electrode metal splashes and the weld metal is saturated with nitrogen and oxygen. In this case, it is difficult to obtain a weld with the required shape. For electrodes with a thick coating, the manufacturer indicates the recommended arc length in the data sheet. The ability to maintain a constant arc length throughout the entire welding process determines the professional level of the welder.
Why should you contact us?
We treat all clients with respect and carry out tasks of any size equally scrupulously.
Our production facilities allow us to process various materials:
- non-ferrous metals;
- cast iron;
- stainless steel.
When completing an order, our specialists use all known methods of metal machining. Modern equipment of the latest generation makes it possible to achieve maximum compliance with the original drawings.
In order to bring the workpiece closer to the sketch submitted by the customer, our specialists use universal equipment designed for jewelry sharpening of tools for particularly complex operations. In our production workshops, metal becomes a plastic material from which any workpiece can be made.
The advantage of contacting our specialists is their compliance with GOST and all technological standards. Strict quality control is carried out at every stage of work, so we guarantee our customers a conscientiously completed product.
Thanks to the experience of our craftsmen, the output is an exemplary product that meets the most demanding requirements. At the same time, we start from a strong material base and focus on innovative technological developments.
We work with customers from all regions of Russia. If you want to place an order for metalworking, our managers are ready to listen to all the conditions. If necessary, the client is provided with free specialized consultation.